Effects Of Pharmacotherapy On Brain Function And Structure In Ptsd
We have begun to assess the effects of pharmacotherapy on brain structure and function in PTSD.243 We recently assessed the effects of phenytoin on brain structure and function. Studies in animals show that phenytoin, which is used in the treatment of epilepsy and is known to modulate glutamatergic function, blocks the effects of stress on the hippocampus.67 We studied nine patients with PTSD in an open-label function before and after treatment with phenytoin. Phenytoin resulted in a significant improvement in PTSD symptoms.164 Phenytoin also resulted in increases in both right hippocampal volume and right hemisphere volume.165 These findings indicate that phenytoin has an effects on PTSD symptoms as well as brain structure in PTSD patients.
We have assessed the effects of open4abel paroxetine on memory and the hippocampus in PTSD. Male and female patients with symptoms of PTSD were medication-free for at least 4 weeks before participation in the study. Twenty-eight patients were found to be eligible and started the medication phase. Of the total patient sample five patients did not finish due to noncompliance 23 patients completed the study.
Before patients started the medication phase, neuropsychological tests were administered, including the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised, WAISR , two subtests of the Wechsler Memory ScaleRevised.WMS-R, including logical memory and figural memory and the verbal and visual components of the Selective Reminding Test, SRT.
How Treatment Can Work
Understanding how PTSD alters brain chemistry is critical to understanding the symptoms of PTSD, devising treatment methods, and to providing the answers as to why some people develop PTSD from trauma, and others do not.
There is evidence that successful treatment of PTSD with therapies such as EMDR and CBT do produce measurable structural changes in brain regions associated with fear conditioning.
CBT can work by strengthening connections between the amygdala and brain regions that are involved in cognitive control, providing more control of processes that are dysregulated as a result of PTSD.
EMDR treatment has reported significantly larger hippocampal volumes and changes shown in MRI scans which show connectivity changes affecting bilateral temporal pole structures.
These studies show why its possible to reverse the effects and heal from PTSD.
Areas Of The Brain Impacted By Ptsd
Fear is a mind-killer! In the case of PTSD, the effects of trauma on the brain can result in a slow and painful process of degrading the synaptic connections in the brain.
The hippocampus and amygdala are the epicenters of emotional behavior in the brain, and together with the prefrontal cortex, are the key to mental health.
Post-traumatic stress disorder can lead to atrophy of the brain.
Don’t Miss: How Many People In The Us Are Diagnosed With Ptsd
How This Information Can Be Used
There is still much to learn about the role certain parts of the brain play in PTSD formation. Knowing how PTSD affects the brain , however, is very important to study.
Understanding which parts of the brain may impact PTSD can lead to the development of more effective medications for treating the disorder. In addition, this information may also help us better identify who is at risk for developing PTSD following a traumatic event.
Fogwe LA, Mesfin FB. Neuroanatomy, Hippocampus. National Center for Biotechnology Information. StatsPearl Publishing.
The Benefits Of Early Treatment For Post

These physical and psychological symptoms can mean long-term dangerous effects, especially the longer it takes for a person to get treatment for PTSD. The risks of developing or worsening co-occurring mental health disorders also increase when necessary treatment is delayed. If you have a loved one who is suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder, its very important to recognize that they need compassionate clinical care. This is the only way for them to safely overcome the difficult obstacles to processing their trauma and to mitigate the possible risks to their brain and body health.
Whereas life with post-traumatic stress disorder can feel volatile and out of control, treatment for PTSD can feel safe and supportive for someone who has been haunted by their trauma for a long time. Long-term treatment gives clients a chance to develop strong, trusting relationships with their therapists, who can help them to truly reshape the active relationship to stress and trauma. Only in the context of a treatment center, under the close assessment of clinicians, can a clients particular treatment needs be determined. PTSD treatment options are diverse, and individualized plans respond to each persons recovery needs. Healing begins here.
Recommended Reading: How Does Ptsd Limit Ability To Work
The Science Behind Ptsd Symptoms: How Trauma Changes The Brain
By Michele Rosenthal
After any type of trauma , the brain and body change. Every cell records memories and every embedded, trauma-related neuropathway has the opportunity to repeatedly reactivate.
Sometimes the alterations these imprints create are transitory, the small glitch of disruptive dreams and moods that subside in a few weeks. In other situations the changes evolve into readily apparent symptoms that impair function and present in ways that interfere with jobs, friendships and relationships.
One of the most difficult aspects for survivors in the aftermath of trauma is understanding the changes that occur, plus integrating what they mean, how they affect a life and what can be done to ameliorate them. Launching the recovery process begins with normalizing post-trauma symptoms by investigating how trauma affects that brain and what symptoms these effects create.
Schedule A Free Consultation
Find out More about Our Innovative Treatment Options
At Revitalizing Infusion Therapies, we combine integrative psychiatry, lifestyle medicine, and multiple modalities of ketamine administration and prescription. Our mission is to help our patients develop a solid foundation to achieve the lifestyle and breakthrough in their health they have been seeking.
Also Check: How Do You Know You Have Bipolar Disorder
How Does Ptsd Happen
During a trauma, your body responds to a threat by going into âflight or fightâ mode. It releases stress hormones, like adrenaline and norepinephrine, to give you a burst of energy. Your heart beats faster. Your brain also puts some of its normal tasks, such as filing short-term memories, on pause.
PTSD causes your brain to get stuck in danger mode. Even after youâre no longer in danger, it stays on high alert. Your body continues to send out stress signals, which lead to PTSD symptoms. Studies show that the part of the brain that handles fear and emotion is more active in people with PTSD.
Over time, PTSD changes your brain. The area that controls your memory becomes smaller. Thatâs one reason experts recommend that you seek treatment early.
How Ptsd And Trauma Affect Your Brain Functioning
John S.
We write our honest reviews but this page may contain affiliate links, with some of the partners mentioned, to support this website. Read more here
The horrors of war have disturbed the minds of many young men and gave birth to the term Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder , a mental health condition caused by a traumatic event that was either experienced or witnessed.
In recent decades, psychologists and neuroscientists have expanded their understanding of the effects of trauma on the brain and discovered that soldiers are not the only victims of the condition.
The trigger for PTSD can be any life-threatening incident, and most people suffering from the condition are undiagnosed.
Trauma affects the brain, and the consequences include difficulties adjusting to social life, in extreme cases, and the inability for self-care.
Don’t Miss: Can Babies Have Panic Attacks
How Trauma Changes The Brain
When trauma such as PTSD is inflicted, lasting changes within the key brain can be created. Traumatic stress is typically associated with an increased cortisol and norepinephrine level in response to the cause of the stress. Traumas like physical and emotional trauma often lead to PTSD which on average, affects roughly 8% of Americans. PTSD can typically be a lifelong problem for most people, resulting in severe brain damage.
What Are The Effects Of Ptsd On The Brain
The effects of PTSD on the brain seem to suggest that there is a biological basis for the symptoms of this disorder. Scientists believe that the experience of extreme psychological trauma may cause physical changes in the brain. It may be possible, however, that inherent differences in brain structure and function make some people vulnerable to PTSD. The effects of PTSD on the brain occur mostly in the amygdala, a part of the brain that helps control emotions. The hippcampus, prefrontal lobe, and prefrontal cortex may suffer damage due to traumatic experiences, and some experts believe that the effects of PTSD on the brain include changes in the way the brain uses certain neurotransmitters, like dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline.
Many sufferers of PTSD experience a numbed emotional state following the onset of symptoms. Experts believe this may be due to increased levels of the neurotransmitters responsible for the relief of pain. The effects of PTSD on the brain can also include a decreased ability to use the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is generally responsible for feelings of well-being. This could explain why depressed feelings often accompany PTSD.
You May Like: Anxiety From Dehydration
Recommended Reading: Is It Normal To Feel Depressed Before Getting Married
How To Know If You Need Help
Though theres no cure for PTSD, you should seek help from a healthcare professional if you cant socialize, function at work, concentrate or sleep at night. A PTSD diagnosis is usually made if youve had symptoms for more than one month.
Current PTSD treatments include medications, mindfulness, service animals , and individual and group therapy, Cummins says. It could be that your predominant symptoms are anxiety or depression, Dr. Saltz says. Your treatment should be aimed directly at the symptoms youre experiencing.
Having a solid relationship with your healthcare professional can be pivotal, too.
Decreased symptoms are typically seen over time when patients establish relationships with their clinicians and feel less alone in handling the challenges that come from PTSD, Cummins says. Additionally, increased support from friends and family can help reduce the feeling of social isolation that can result from PTSD.
Mri Assessment Of Brain Abnormalities In Ptsd And Trauma Spectrum Disorders
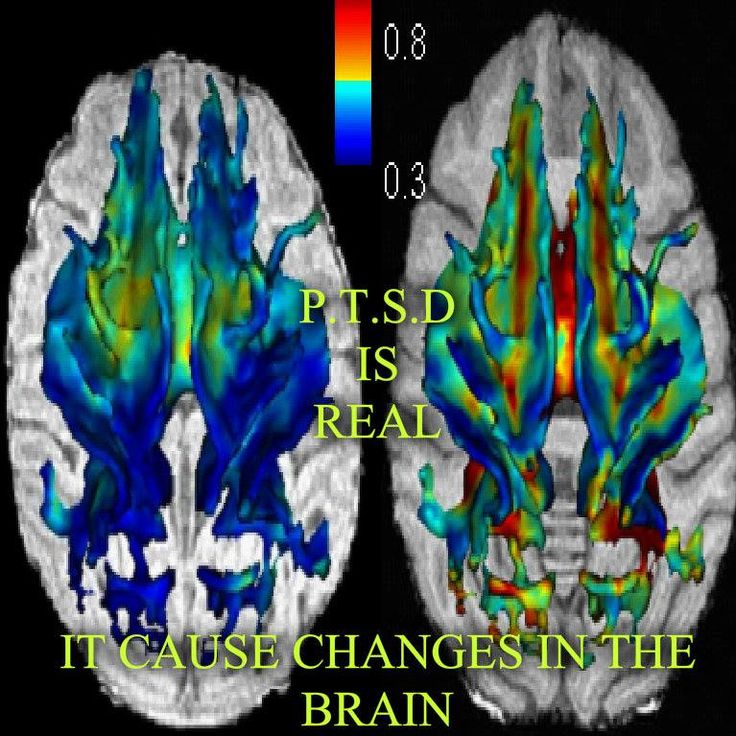
Findings of smaller hippocampal volume appear to be associated with a range of trauma related psychiatric disorders, as long as there is the presence of psychological trauma. We have used MRI to show smaller hippocampal volume in PTSD,144,145,149,196 depression,197 depression with early abuse,198 borderline personality disorder with early abuse,199 and Dissociative Identity Disorder with early abuse.200 The greatest magnitude of difference was seen in the DID patients, who had unusually severe early childhood sexual abuse histories. We did not find changes in hippocampal volume in patients with panic disorder without a history of abuse .201 We found smaller amygdala volume in BPD with early abuse199 and increased amygdala volume in depression.197,202 Patients with depression had smaller orbitofrontal cortex volume with no changes in anterior cingulate or medial prefrontal cortex .203 More recently, we found smaller anterior cingulate volume in women with abuse and PTSD relative to controls.204
Also Check: What To Do For Postpartum Depression
Emotional Trauma And The Amygdala
The amygdala is a section of nervous tissue in the brain that is responsible for emotions, survival instincts, and memory.
A major role of the amygdala is to detect fear. It recognizes and gathers information around us to determine threats. By using our senses, such as sight and sound, the amygdala will respond with the feeling of fear if it perceives a threat. This all happens unconsciously, deep in our brains.
When affected by PTSD, the amygdala becomes hyperactive.
Those who suffer from emotional trauma on the brain will often exhibit more fear of traumatic stressors than others. Often, stimuli can trigger overactivity in the amygdala if somehow connected to the traumatic event a person suffered from.
How emotional trauma affects the brain might lead to chronic stress, heightened fear, and increased irritation. This might also make it harder for those suffering to calm down or even sleep.
In English Spanish French
Brain areas implicated in the stress response include the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. Traumatic stress can be associated with lasting changes in these brain areas. Traumatic stress is associated with increased cortisol and norepinephrine responses to subsequent stressors. Antidepressants have effects on the hippocampus that counteract the effects of stress. Findings from animal studies have been extended to patients with post-traumatic stress disorder showing smaller hippocampal and anterior cingulate volumes, increased amygdala function, and decreased medial prefrontal/anterior cingulate function. In addition, patients with PTSD show increased cortisol and norepinephrine responses to stress. Treatments that are efficacious for PTSD show a promotion of neurogenesis in animal studies, as well as promotion of memory and increased hippocampal volume in PTSD.
Also Check: What Medication Is Used For Bipolar
Treatment Approaches To Trauma And Ptsd
Over the years as the scientific community has become accepting of the existence of PTSD and more open to exploring treatments a group of well-researched and increasingly-used therapies and approaches have been developed and are being implemented into treatment programs. Here we will touch on some of the most popular:
Read Also: Lindsey Stirling Anorexic
What Is The Treatment For Ptsd
While you can’t prevent every traumatic situation or how it impacts you, you can manage the symptoms of PTSD after. According to the US Department of Veterans Affairs, there are successful interventions for PTSD with cognitive behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy. There has also been success found with Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy and Stress Inoculation therapy for PTSD.
Medication treatment with SSRIs and SNRIs, in addition to these therapies, can also be beneficial for individuals with PTSD.
Therapies and medication are the first lines of defense against PTSD, especially when symptoms significantly negatively affect their life. You can do additional things in addition to these treatment options to help cope with the daily symptoms of PTSD.
Read Also: How To Come Down From A High Panic Attack
How Is The Brain Affected By Ptsd
Without giving mental health conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder a great amount of consideration, we might not consider at all the fact that PTSD affects the brain. Clearly, PTSD has to happen somewhere. Thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and the many mental symptoms of PTSD dont, just happen and disappear like clouds passing in the sky. Everything happens as a chemical impulse, taking place within the structure of the brain.
Each kind of mental illness leaves a different mark on the brain, called a biomarker. A biomarker is a measurable substance in an organism whose presence is indicative of some phenomenon such as disease, infection, or environmental exposure. The activity in different areas of the brain indicate the presence of PTSD and give us information as to how and why the symptoms of PTSD develop. The three areas of the brain most affected by are the amygdala, the hippocampus, and the prefrontal cortex.
Impulsive behaviors fueled by fear is what leads to many of the symptoms of PTSD. Nightmares, flashbacks, hypersensitivity and hypervigilance are all heightened states of mental function which are the result of how PTSD affects the brain.
Analysis Of The Hippocampi Cerebellum And Basal
The cerebellum, hippocampi, and basal ganglia were segmented in all MR images using the Multiple Automatically Generated Templates algorithm , which utilized manually segmented images as atlases. Five such atlases were used for the cerebellum and hippocampi, and one atlas was used for the basal ganglia. An arbitrary subset of the MR images, which are designated as templates, are pair-wise registered to each of the atlases to create multiple anatomical segmentations , yielding a template library consisting of 105 labeled atlases per structure. These atlases are then averaged, and the most frequently occurring segmentation label per voxel is retained, resulting in a more accurate final anatomical segmentation. This procedure is known as voxel voting . The automatically segmented cerebellar, hippocampi, and basal ganglia structures for each brain were thereafter used for calculating and comparing the average structural volumes between groups. Dividing the structural volumes by the total brain volume, as computed through the sum of the grey matter, white matter and cerebrospinal fluid volumes in CIVET, yields a measure of the relative volume occupied by each structure.
Recommended Reading: Has Anyone Died From A Panic Attack
Ending Our Time Together
Traumatic events cause many chemical reactions and initiate the fight/flight/freeze response, but for some, these chemicals never return to baseline, causing damage to some regions of the brain.
60% of men and 50% of women will experience one or more traumatic events in their lifetime. These statistics mean that more research must happen to increase our knowledge and thus treatments for PTSD.
The brain areas affected by PTSD control memory, reasoning, and thought, causing the victim to experience difficulties remembering events, thinking, and learning new information.
Epigenetics, a new kid on the block of neuro-research about PTSD, has found that a persons genes are changed by trauma and that these changes can be passed to their progeny.
The next stage of research and learning about post-traumatic stress disorder will involve those who formed PTSD due to the COVID-19 pandemic as people emerge from isolation and face a new world.
Trauma is personal. It does not disappear if it is not validated. When it is ignored or invalidated, the silent screams continue internally heard only by the one held captive. When someone enters the pain and hears the screams, healing can begin. ~ Danielle Bernock
References
Bremner JD. Alterations in brain structure and function associated with post-traumatic stress disorder. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 1999 Oct 4:249-55. DOI: 10.153/SCNP00400249. PMID: 10553030.
Epigenetics. Wikipedia. Retrieved from: