Schizophrenia: What You Should Know About This Psychological Illness
Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder. It affects about 1% of the population over the course of their lifetime. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, social withdrawal, difficulty with thinking and concentration, and inappropriate or bizarre behavior.
This complex mental health condition is characterized by a wide variety of symptoms that are often hard to diagnose. The effects can be so debilitating that they interfere with everyday life. There are treatments available for schizophrenia that can help reduce or manage symptoms. Its important to know what it is so you can share it with friends or family if someone you love has it.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
Symptoms may intensify in the run-up to an acute episode of psychosis in schizophrenia. The warning signs include:
- A worrying drop in grades or job performance
- New difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating
- Suspiciousness of or uneasiness with others
- Withdrawing socially, spending a lot more time alone than usual
- Unusual, overly intense new ideas, strange feelings, or having no feelings at all
- Difficulty telling reality from fantasy
- Confused speech or trouble communicating
While these changes might not be concerning by themselves, if you or a loved one are experiencing a number of these symptoms, you should contact a mental health professional. It can be difficult for those with schizophrenia to want to get help, especially if they are experiencing symptoms such as paranoia.
If you or your loved one is thinking of or talking about harming themselves, contact someone who can help right away. You can call the toll-free, 24-hour National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-237-8255.
If you require immediate emergency care, call 911 for emergency services or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What Are The Causes Of Schizophrenia
The exact cause of Schizophrenia remains unknown but some factors can be contributing such as follows:
- Genetics: Schizophrenia is often seen in family members and hence a genetic predisposition can be the cause. Although the exact gene responsible has not been identified, recent studies by Evolutionary Biologists claim for the possibility of the existence of Dark Genome which is basically a region of the genetic material which is not usually recognized as genes but can still code for proteins. These hidden genes that are difficult to read are known as Novel Open Reading Frames or nORFs. These may also be the reason why Schizophrenia continues to exist steadily in 1% of the human population despite affecting reproductive fitness of a suffering individual and hence escaping from elimination by natural selection.
- Brain Functioning: It can also be a symptom of unregulated neurotransmitters that act as chemicals for brain functioning. They are responsible for normal functioning and processing of the brain and its circuits.
- Environmental: Stress factors, infections and exposure to drugs can trigger the disease in individuals. This is also the reason why Schizophrenia often first presents in teenage years when a person is undergoing drastic hormonal and physical changes.
Although Schizophrenia requires medical treatment under a Psychiatrist, many Homoeopathic remedies have been known to help in management of the disease.
Don’t Miss: Is Celine Dion Anorexic
What If I Am A Carer Friend Or Relative
It can be distressing if you are a carer, friend or relative of someone who has schizophrenia. You can get support.
How can I get support for myself?
You can do the following.
- Speak to your GP about medication and talking therapies for yourself.
- Speak to your relatives care team about family intervention. For more information about family intervention see the further up this page.
- Speak to your relatives care team about a carers assessment.
- Ask for a carers assessment.
- Join a carers service. They are free and available in most areas.
- Join a carers support group for emotional and practical support. Or set up your own.
What is a carers assessment?NICE guidelines state that you should be given your own assessment through the community mental health team to work out what effect your caring role is having on your health. And what support you need. Such as practical support and emergency support.
The CMHT should tell you about your right to have a carers assessment through your local authority. To get a carers assessment you need to contact your local authority.
How do I get support from my peers?You can get peer support through carer support services or carers groups. You can search for local groups in your area by using a search engine such as Google. Or you can call our advice service on 0808 801 0525. They will search for you.
How can I support the person I care for?
You can do the following.
There is no definition for what high risk means. It could include:
The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
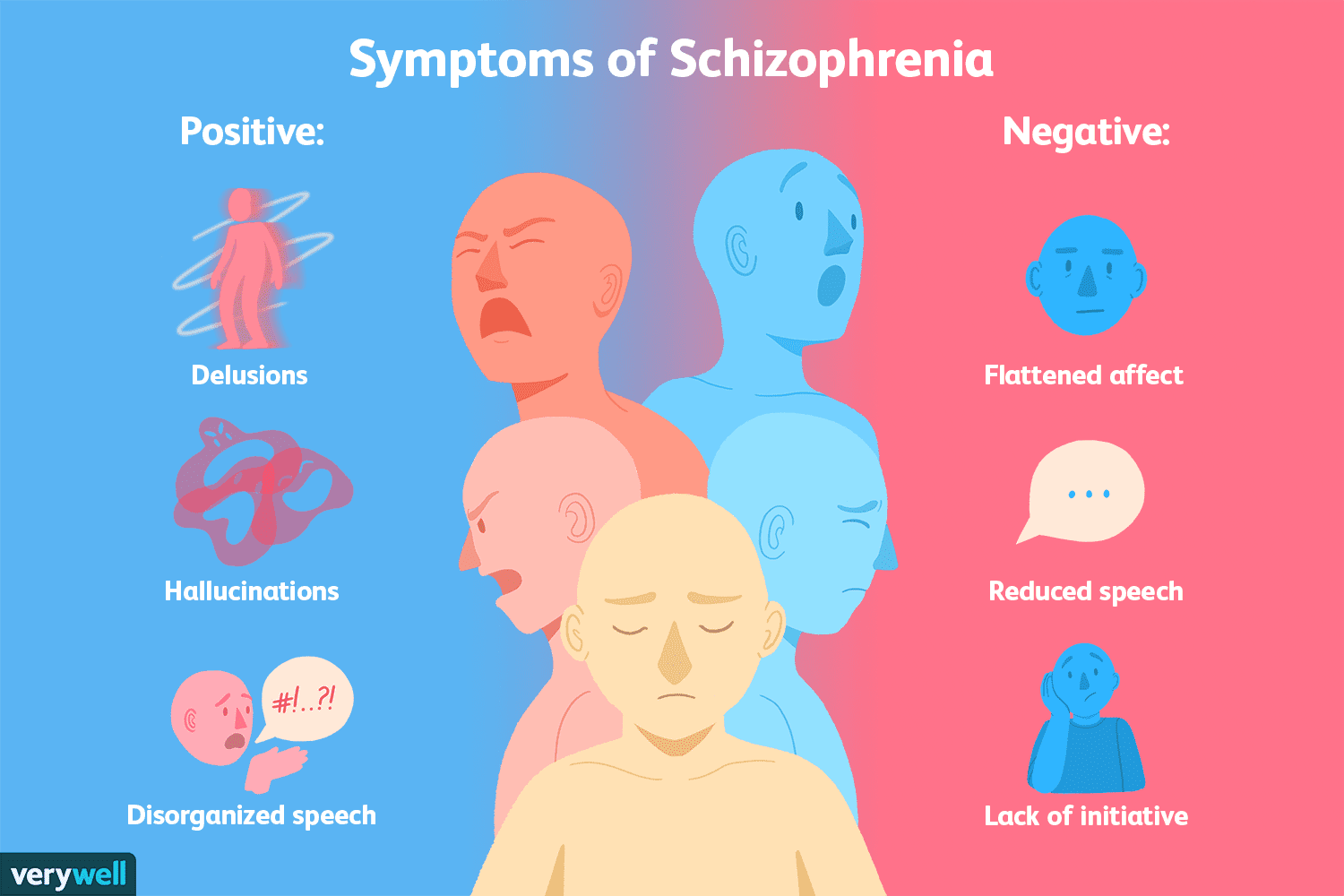
There is no single symptom that can be used to diagnose schizophrenia. Diagnosis of this disorder is based on multiple factors, such as:
- Social/occupational dysfunction
- Deficits in thinking and expression
- Abnormal motor behaviour
- Failing to recognize ones own condition
The symptoms of schizophrenia can come and go or may never go away completely. Symptoms may include: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech , grossly disorganized behavior , and negative symptoms . People with schizophrenia might not make sense when talking or respond inappropriately or abnormally when talking to others. They may have trouble staying focused on an idea when they speak and often use words in odd ways . Sometimes people with schizophrenia will withdraw from others and lose interest in the outside world .
Recommended Reading: What Assessment Findings Mark The Prodromal Stage Of Schizophrenia
When Should I See My Doctor
Some people with schizophrenia do not realise they have a problem or avoid health professionals if they have paranoid thoughts. Its important to get professional help to manage schizophrenia. If you or someone you know seems to be experiencing signs of schizophrenia, see your doctor as soon as possible.
It can be hard to recognise signs of schizophrenia at first, but over time the changes in someones thinking and behaviour may get worse.
See a doctor if you or someone you know:
- gets very preoccupied with something
- starts talking or writing very fast, or is talking much less than normal
- seems muddled, irrational or is hard to understand
- withdraws from normal activities
- is hyperactive or starts behaving recklessly
- laughs or cries inappropriately, or cannot laugh or cry or express happiness
- doesnt look after their personal hygiene
- develops depression or anxiety
Although the majority of people with schizophrenia are not violent, severe symptoms can cause some people to have thoughts of suicide or harming others. If you think someone may be at risk of suicide or violence, call triple zero .
Parkinson’s Disease And Lewy Body Dementia
is linked with for their similar hallucinatory symptoms. The symptoms strike during the evening in any part of the visual field, and are rarely polymodal. The segue into hallucination may begin with illusions where sensory perception is greatly distorted, but no novel sensory information is present. These typically last for several minutes, during which time the subject may be either conscious and normal or drowsy/inaccessible. Insight into these hallucinations is usually preserved and is usually reduced. Parkinson’s disease is usually associated with a degraded pars compacta, but recent evidence suggests that PD affects a number of sites in the brain. Some places of noted degradation include the median , the parts of the , and the neurons in the and nuclei of the .
This type of hallucination is usually experienced during the recovery from a comatose state. The migraine coma can last for up to two days, and a state of depression is sometimes . The hallucinations occur during states of full consciousness, and insight into the hallucinatory nature of the images is preserved. It has been noted that ataxic lesions accompany the migraine coma.
Read Also: Define Aerophobia
Schizophrenia: Definition And Characteristics
Schizophrenia is a type of serious mental disorder, specifically a psychotic disorder.. The overall vital prevalence of schizophrenia is 0.3-0.7% in the population however, in first-degree relatives of schizophrenic patients, it rises to 10%. This is why there is talk of an important genetic factor in its aetiology.
This disorder occurs more frequently in urban than in rural settings. On the other hand, migrants are known to have a higher risk of developing the disorder.
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
Recommended Reading: Phobia Psychology Definition
Schizophrenia: The 7 Keys To Self
Seek social support. Friends and family vital to helping you get the right treatment and keeping your symptoms under control. Regularly connecting with others face-to-face is also the most effective way to calm your nervous system and relieve stress. Stay involved with others by continuing your work or education. If thats not possible, consider volunteering, joining a schizophrenia support group, or taking a class or joining a club to spend time with people who have common interests. As well as keeping you socially connected, it can help you feel good about yourself.
Manage stress. High levels of stress are believed to trigger schizophrenic episodes by increasing the bodys production of the hormone cortisol. As well as staying socially connected, there are plenty of steps you can take to reduce your stress levels. Try adopting a regular relaxation practice such as yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
Get regular exercise. As well as all the emotional and physical benefits, exercise may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, improve your focus and energy, and help you feel calmer. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days, or if its easier, three 10-minute sessions. Try rhythmic exercise that engages both your arms and legs, such as walking, running, swimming, or dancing.
What Myths Are There About Schizophrenia
There are some myths or mistaken beliefs about schizophrenia which come from the media. For example,
- Schizophrenia means someone has a split personality
This is not the case. The mistake may come from the fact that the name ‘schizophrenia’ comes from two Greek words meaning ‘split’ and ‘mind’.
- Schizophrenia causes people to be violent
Research shows that only a small number of people with the illness may become violent. The same way as a small minority of the general public may become violent.
People with schizophrenia are far more likely to be harmed by other people than other people are to be harmed by them. But as these incidents can be shocking, the media often report them in a way which emphasises the mental health diagnosis. This can create fear and stigma in the general public.
You May Like: Feretrophobia
Clinical Presentation Diagnosis And Identification Of Negative Symptoms
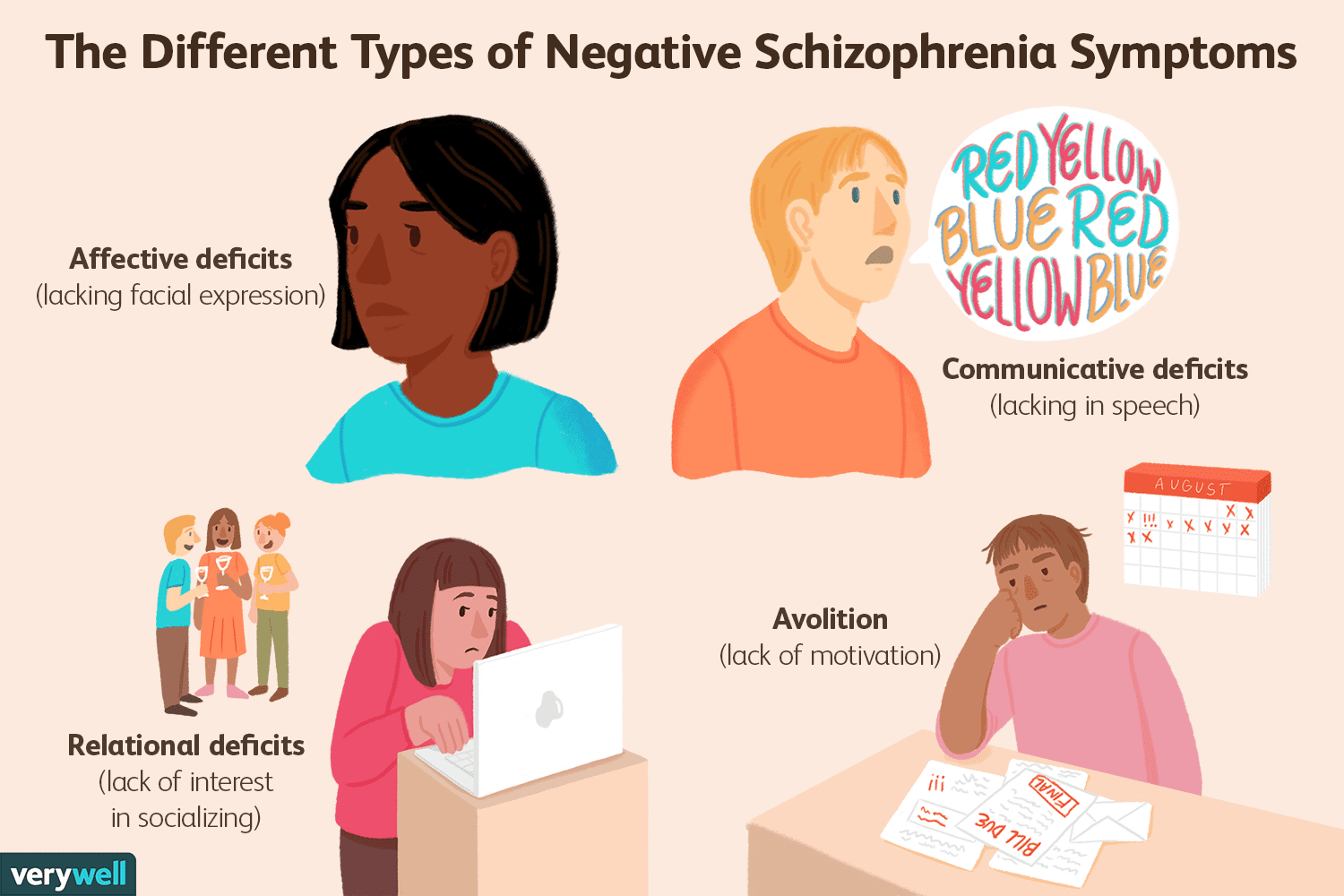
It is generally accepted that negative symptoms include 5 key constructs, which can be further categorized into 2 independent factors .,,
Key negative symptom constructs. Blunted affect=decreased expression of emotion alogia=reduction in quantity of words spoken avolition=reduced initiation and persistence of goal-directed activity due to decreased motivation asociality=reduced social interactions and initiative due to decreased interest in relationships with others anhedonia=reduced experience of pleasure during an activity or in anticipation of an activity.
Although the presence of negative symptoms is not mandatory for a diagnosis of schizophrenia, negative symptoms , are 1 of the 5 symptom criteria taken into consideration in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . Diminished expression, which includes reduction in the expression of facial emotions, eye contact, and speech intonation, and reduction in head, hands, and face movement that gives emotional emphasis to speech, is generally observable during a clinical interview. Avolition, indicating decrease in self-motivated and self-initiated purposeful activities, requires inquiry into patients behaviors outside the interview setting. A level of functioning in work, school, relationships, or self-care that is markedly below the level that has previously been achieved is also diagnostic and suggests the presence of avolition and the reduced drive to pursue goal-directed behavior.
What Causes Schizophrenia
Nobody knows exactly what causes schizophrenia, it is likely to be the result of several factors. For example:
- Stress. Some people can develop the illness as a result of a stressful event, such as the death of a loved one or the loss of a job.
- Genetics. You are more likely to develop schizophrenia if you have a close relation with the illness.
- Brain damage. This is usually damage that has stopped your brain from growing normally when your mother was pregnant. Or during birth.
- Drugs and alcohol. Research has shown that stronger forms of cannabis increase your risk of developing schizophrenia.
- A difficult childhood. If you were deprived, or abused, as a child this can increase your risk of developing a mental illness. Including schizophrenia.
There is research to suggest that may be an association between menopause and schizophrenia. This may be due to the hormonal changes during this stage of life for women.
You can find more information about:
- Does mental illness run in families? by clicking here.
- Drugs, alcohol and mental health by clicking here.
- Cannabis and mental health by clicking here.
Recommended Reading: Topographic Depression Definition
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of schizophrenia include:
- Negative symptoms. “Negative” doesn’t mean “bad.” Negative symptoms are things that are “lost” from your personality or how you experience life. You may:
- Not care about things.
- Have no interest or drive to do things.
- Not take care of yourself, such as not bathing or not eating regularly.
- Find it hard to say how you feel.
- Become angry with strangers for no reason and react to others in other harmful ways.
Symptoms usually start when you are a teen or a young adult, but they may start later in life. They may appear suddenly or may develop slowly. You may not be aware of your symptoms.
Negative symptoms usually appear first. They may be hard to recognize as schizophrenia, because they are similar to symptoms of other problems, such as depression. Positive symptoms can start days, months, or years after the negative symptoms.
These signs don’t mean you have schizophrenia. But if you notice these signs, see a doctor.
What Risks And Complications Can Schizophrenia Cause
Physical health
Research suggests that people with serious mental illness , such as schizophrenia, have a shorter life expectancy. People with mental illness may die 15 to 20 years earlier than the general population. This may because people who live with SMI are at higher risk of having a range of health issues. Such as being overweight, having heart disease, smoking and diabetes.
Because of these issues, NICE recommends that when you start taking antipsychotic medication, your doctor should do a full range of physical health checks. This should include weight, blood pressure and other blood tests. These checks should be repeated regularly.
Mental health professionals are responsible for doing these checks for the first year of treatment. Responsibility may then pass to your GP. Your doctor or mental health team should offer you a programme which combines healthy eating and physical health checks. You should be supported by a healthcare professional to help stop smoking.
Suicide
The risk of suicide is increased for people with schizophrenia. Research indicates that around 513% of people who live with with schizophrenia die by suicide.
Research has found that the increased risk is not usually because of positive symptoms. The risk of suicide is associated more to affective symptoms, such as low mood.
Key risk factors for suicide include:
- previous suicide attempts,
Also Check: Webmd Anxiety Disorder
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often appear several years before somebody experiences their first acute schizophrenic episode.
These initial negative symptoms are often referred to as the prodromal period of schizophrenia.
Symptoms during the prodromal period usually appear gradually and slowly get worse.
They include the person becoming more socially withdrawn and increasingly not caring about their appearance and personal hygiene.
It can be difficult to tell whether the symptoms are part of the development of schizophrenia or caused by something else.
Negative symptoms experienced by people living with schizophrenia include:
- losing interest and motivation in life and activities, including relationships and sex
- lack of concentration, not wanting to leave the house, and changes in sleeping patterns
- being less likely to initiate conversations and feeling uncomfortable with people, or feeling there’s nothing to say
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often lead to relationship problems with friends and family as they can sometimes be mistaken for deliberate laziness or rudeness.
What Are The Symptoms Of Psychosis
Psychotic symptoms typically include changes in thinking, mood and behavior. Symptoms vary from person to person and may change over time. Some of the more characteristic symptoms can be grouped into five categories:
- Psychosis Program, 2nd Floor Outpatient ClinicsConnecticut Mental Health Clinic, 34 Park StreetNew Haven, CT 06519
Recommended Reading: Definition Of Phobia