Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2
The main difference between type 1 and type 2 bipolar is full manic episodes. Bipolar II patients dont go beyond hypomania. Second, bipolar II disorder has more frequent cycling than bipolar I disorder. It also has a more chronic course than type 1.
When it comes to diagnosis, it is much easier to confirm bipolar 1 than bipolar 2. This is because type 1 looks for evidence of a manic episode. Type 2 depends on identifying hypomania after emerging from a depressive state.
Bipolar II patients are more likely to commit suicide than those with bipolar I disorder.
Symptoms That Lead To A Diagnosis
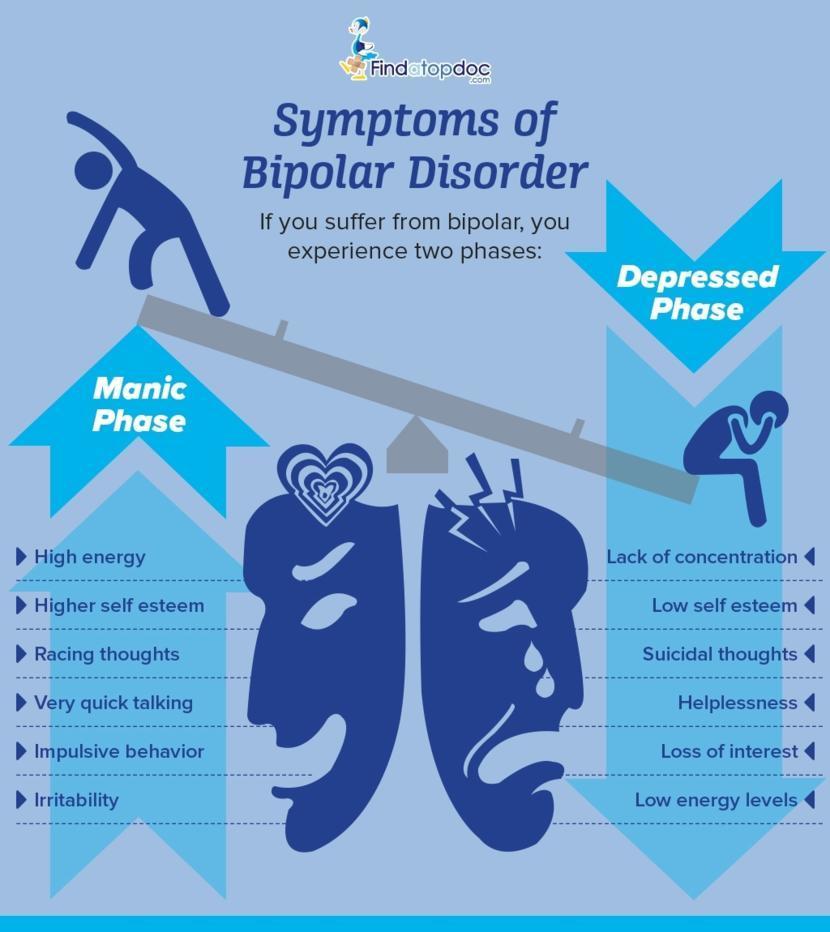
If youre suffering from any kind of mental health disorder, its important that you identify and understand your symptoms in order for our doctors to correctly diagnose you. Bipolar disorder consists of both manic and depressive episodes that create an unstable mood.;
Mania can be extreme changes in mood, or you can have hypomania which is typically less severe. Symptoms of mania include:
Difficulty sleeping Extreme energy Increased self-esteem Difficulty concentrating Racing thoughts
On the opposite end of the spectrum, depression can change your emotional highs to hopeless lows. If you have bipolar disorder with depression, symptoms you may experience include:
Fatigue Sadness Decreased energy Overeating or loss of appetite Suicidal thoughts
Our team at Boston MindCare take a detailed history to decipher your symptoms and give you a definitive diagnosis. With that, we can also form a customized treatment plan for you.
What Causes Bipolar Disorder
Scientists dont know what causes bipolar disorder. Abnormal physical characteristics of the brain or an imbalance in certain brain chemicals may be among the main causes.
As with many medical conditions, bipolar disorder tends to run in families. If you have a parent or sibling with bipolar disorder, your risk of developing it is higher. The search continues for the genes which may be responsible for bipolar disorder.
Researchers also believe that severe stress, drug or alcohol abuse, or severely upsetting experiences may trigger bipolar disorder. These experiences can include childhood abuse or the death of a loved one.
You May Like: Does My Puppy Have Separation Anxiety
Whats The Difference Between Bipolar I And Ii
On first impression bipolar disorder is easy to understand. Its a disorder where a person experiences extreme mood changes, highs and lows, with periods of normality in between.
But, when we look further into the disorder, or we hear people talk about their experiences, it starts to get a little more complex, and the terms bipolar I and bipolar II emerge.
So, whats the difference? And how do these symptoms affect people living with the disorder?
Bipolar I Disorder: Definition Causes Symptoms And Treatment
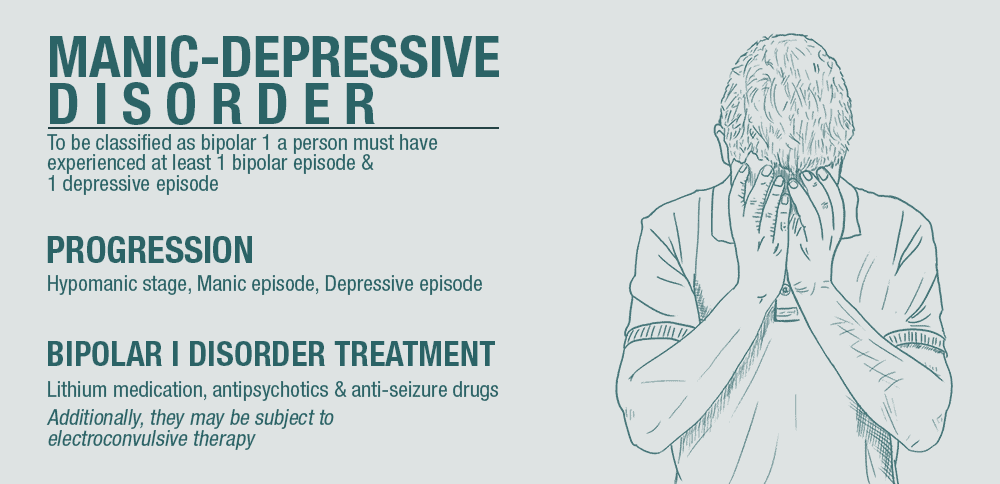
Bipolar 1 disorder goes by the name manic-depressive disorder. The pronunciation is bipolar one.
A person must experience at least one manic episode to have the bipolar 1 classification. They must also have a depressive episode at some stage. The depressive episodes last longer than the manic ones.
Manic episodes progress from the hypomanic stage to full-blown mania. Thus, the patient has the atypical elevated mood and energy. Experiencing one manic episode is the key to making an accurate diagnosis.
Later, the individual may cycle through the manic and depressive phases. This causes a disruption in their lives. Their mood may go from feeling euphoric to being irritable. Add the reckless behavior and this disorder can have serious repercussions.
For example, people in the manic phase might feel overconfident. They might carry themselves in a grandiose manner. As such, this might lead them to spend all their money to match their perceived status.
Untreated manic episodes last for weeks or months. Thereafter, the depressive phase takes over. These depressive episodes have the same symptoms as clinical depression.
Psychosis: Symptoms, and Causes
In dire circumstances, the manic episodes may trigger psychosis. In this state, the individual is no longer in touch with reality. It ranges from engaging in abnormal behavior to being in a disturbed mental state.
Diagnosing and Treating Bipolar I Disorder
You May Like: What Can Anxiety Do To You
Bipolar Relationships: What To Expect
Ups and downs are natural in any romantic relationship, but when your partner has bipolar disorder it can feel like youre on an emotional rollercoaster. Not knowing what to expect each day is stressful and tiring. Over time, it wears on the relationship.
Understanding why your partner acts out sometimes or becomes withdrawn is the first supportive step you can take in strengthening your relationship. Learn exactly what a bipolar diagnosis means, how it could affect your partners behavior and what you can do to foster a healthy, stable relationship.
Bipolar Disorder Causes And Risks
While the exact causes of bipolar disorder are unknown, there are a few factors that play a role, including:
- Genetics Bipolar disorder is more common in people who have a first-degree relative with the condition, such as a parent or sibling, and researchers continue to search for the genes that are involved in causing bipolar disorder. But just because you have family members with a history of bipolar disorder, does not mean that you will develop it. Most people who have bipolar disorder in their family history will never actually develop this mental health disorder.
- Brain structure There are biological differences for those that have the disorder, including physical changes to their brains. Any abnormalities in the structure or functions of your brain may increase the risk for bipolar disorder.
- Environmental factors Beyond your own biology and family history, environmental can contribute too.;
- Other Extreme stress, traumatic experiences, and physical illnesses can also influence who develops bipolar disorder.;
Recommended Reading: Is Ptsd Covered By Ada
Both Types Should Be Properly Treated
Since hypomania is less severe than the mania that occurs in bipolar I disorder,;bipolar II;is often described as “milder” than bipolar Ibut this is not completely accurate.;Certainly, people with bipolar I can have more serious symptoms during mania, but hypomania is still a serious condition that can have life-changing consequences and so should be properly addressed.
In addition, research suggests that bipolar II disorder is dominated by longer and more severe episodes of depression. In fact, over time, people with bipolar II become less likely to return to fully normal functioning between episodes.
One;study;specifically concluded that bipolar type II was linked to a poorer health-related quality of life compared to type I. This remained true even during long periods of euthymia.
Thus, experts tend to believe that bipolar II disorder is equally ;disabling than bipolar I disorder because it can lead to more lifetime days spent depressed and not doing as well overall between episodes. Proper treatment should be pursued for all types of bipolar disorders, and you should work closely with your healthcare team to figure out the best treatment for you.
Unspecified Bipolar Disorder: Definition Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Some bipolar disorders dont have a specific pattern. They also dont match the other three disorders. Yet, they still have to meet the criteria for abnormal mood changes.
The subtypes of bipolar disorder are bipolar 4 and 5. They are subthreshold types of disorder. This means their symptoms are not as pronounced.
Bipolar IV Disorder
In this subtype, hypomanic and manic episodes come from taking antidepressant drugs. Doctors prescribe antidepressant medication to treat other types of mental illness. Unfortunately, this can trigger bipolar disorder.
Patients must then learn to cope with the manic and depressive feelings. They must learn to avoid substances like alcohol as well.
Bipolar V Disorder
This subtype involves people who have genetic bipolar disorder. The patient only suffers from major depression despite a family history of bipolar disorder.
Don’t Miss: Why Do Eating Disorders Happen
Depression And Bad Decision
Between high school and college, I took a gap year to backpack around Asia and Europe. My highs and lows continued. At times I went days without sleeping, traveling on overnight buses and talking with new friends. I took impulsive risks: I went on road trips with people I didnt know, slept on beaches illegally, and continued to travel even after I became sick with the plaguebut thats a whole other story.
Then my mood and behavior would change. I isolated myself and stayed in my room for days, feeling hopeless, exhausted, and disinterested in exploring the fascinating places I was visiting.
After I returned from my trip, I finally reached out to a psychiatrist. She had me try all kinds of antidepressants, but low doses of each resulted in extreme reactions, such as euphoria and psychotic breaks. My psychiatrist explained that my reactions were nearly impossibleunless I had a mood disorder. After asking me a series of questions, she confirmed her theory: I had bipolar II disorder.
RELATED:10 Helpful Books About Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder Type Ii Prognosis
Those with bipolar disorder can have repeated relapses throughout the lifespan. This can even happen when on medication as for many, medications do stop working and have to be evaluated at one or more points. Nonetheless, those who stay on medication do have the brightest prognosis. Psychotherapy and social support also improve the prognosis of those with bipolar disorder.
While the initial diagnosis of bipolar disorder type II can be very scary, learning about bipolar disorder, working with qualified mental health professionals and staying adherent to treatment can make managing the illness quite possible.
Also Check: How To Help Your Significant Other With Depression
Treatments For Bipolar Disorder
The high and low phases of bipolar disorder are often so extreme that they interfere with everyday life.
But there are several options for;treating bipolar disorder that can make a difference.
They aim to control the effects of an episode and help someone with bipolar disorder live life as normally as possible.
The following treatment options are available:
- medicine to prevent episodes of mania and depression;;these are known as mood stabilisers, and you take them every day on a long-term basis
- medicine to treat the main symptoms of depression and mania when they happen
- learning to recognise the triggers and signs of an episode of depression or mania
- psychological treatment;;such as talking therapy, which can help you deal with depression, and provides advice about how to improve your relationships
- lifestyle advice;;such as doing regular exercise, planning activities you enjoy that give you a sense of achievement, as well as advice on;improving your diet and getting more sleep
It’s thought using a combination of different treatment methods is the best way to control bipolar disorder.
Help and advice for people with a long-term condition or their carers;is also available;from charities, support groups and associations.
This includes self-help and learning to;deal with the practical aspects of a long-term condition.
The Use Of Diagnostic Categories And Systems
A key question that governs the dimensional/categorical distinction in difficult contexts is: for whom are diagnostic categories composed? In other words, who needs or uses them? It would seem that four groups have a stake in this: patients and their families; clinicians; scientists/clinical researchers; and governmental agencies, insurance companies and the legal professionall have differing needs, make different uses of the diagnoses and require different applications from a diagnostic system.
The first group that has an interest in this issue are patients and their families. As Porter reminded us, among the central roles that physicians have been tasked with for millennia is giving semantic shapea label, a diagnosisto patients suffering due to illness. For this purpose, describing a disorder in dimensional terms simply does not suffice for most patients and their families. A term, a categorical diagnosis: You have a disorder called X is what is specifically asked for and needed. Does it help patients and their families to distinguish between bipolar I and II disorders vs. combining them within the term bipolar disorder? The recent controversy over the decision for DSM-5 to eliminate Aspergers syndrome as a separate disorder from autism and subsume it under autism spectrum disorders is another example of that controversy .
Also Check: What Are The Causes And Symptoms Of Ptsd
What Is Bipolar Disorder
Before delving into the question of “What is bipolar 1 vs. bipolar 2,” you first need to understand the larger spectrum of the disorder. Bipolar is a psychiatric disorder that affects millions of people in the U.S. every year, although experts disagree on the precise percentage. It is a spectrum disorder with a range of subtypes, each with its diagnostic criteria. The condition in each of the types of bipolar is marked by periods of mania and hypomania and periods of depression. The following definitions can help you understand these specific phases of bipolar disorder and lay the foundation for learning about bipolar type 2.
Mania Definition
Mania is the part of bipolar disorder in which your mood is elevated. You may be either euphoric or irritable, but in either case, you have increased energy. You feel little need to sleep and may go days without it. You may have psychotic symptoms, such as delusions of grandeur and hallucinations. To be considered a manic episode, the state must last at least a week or require hospitalization.
Hypomania Definition
Hypomania is similar to mania in that energy is increased, and the mood is typically elevated to some degree. However, when you have a hypomanic episode, people may still view your behavior as “normal.” People who are hypomanic tend to be more productive and still able to function well in their everyday lives. They need less sleep, but still get enough to remain healthy.
Depression Definition
Symptoms Specific To Bipolar I
Where bipolar I and II differ is the length and intensity of the high and the presence of major depression. Bipolar I requires one experience of mania, but does not require an episode of major depression .
The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders classifies mania to be a period of abnormality, featuring an elevated, persistent or irritable mood, severe enough to impair functioning, with three or more symptoms of:
- Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
- Increased goal-directed activity
- Excessive involvement in activities that have high potential for painful consequences.
For an episode to be defined as manic it must last at least one week. Someone experiencing mania may not know they are ill or in need of treatment, and occasionally an episode will include an experience of psychosis or delusional thoughts.
Many people who experience mania describe their actions as euphoric, a feeling of invincibility, where no idea is too big or too optimistic.
Dov is a SANE Speaker who was diagnosed with bipolar disorder while completing his medical degree. Dov describes mania as a highly traumatic roller coaster ride.
Also Check: How To Know If You Have Ptsd
What Is The Treatment For Mania Hypomania And Depression
You can check what treatment and care is recommended for bipolar disorders on the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence website.
NICE produce guidelines for how health professionals should treat certain conditions. You can download these from their website at:
The NHS doesnt have to follow these recommendations. But they should have a good reason for not following them.
What medications are recommended?
Mood stabilisers are usually used to manage mania, hypomania and depressive symptoms.
The mood stabilisers we talk about in this factsheet are:
- Lithium
- Certain benzodiazepine medication
Mania and hypomaniaYou should be offered a mood stabiliser to help manage your mania or hypomania. Your doctor may refer to your medication as antimanic medication.
If you are taking antidepressants your doctor may advise you to withdraw from taking them.
You will usually be offered an antipsychotic first. The common antipsychotics used for the treatment of bipolar disorder are:
- Haloperidol
- Quetiapine
- Risperidone
If the first antipsychotic you are given doesnt work, then you should be offered a different antipsychotic medication from the list above.
If a different antipsychotic doesnt work, then you may be offered lithium to take alongside it. If the lithium doesnt work you may be offered sodium valproate to take with an antipsychotic. Sodium valproate is an anticonvulsive medication.
Sodium Valproate shouldnt be given to girls or young women who might want to get pregnant.
Definition Of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a type of mental illness called a mood disorder because it causes unhealthy and unusual changes in mood in those who live with it. This disorder was once known as manic depression because it is characterized by shifts in mood from mania to depression and back again. Mania is a euphoric mood, which can cause high energy and activity levels, lack of sleep, irritability and anger, and risky behaviors.
The opposite of mania is depression. The depressive phase of bipolar disorder causes sad, hopeless moods that persist for a couple of weeks or longer. The depressive moods may also cause lethargy, physical aches and pains, changes in sleeping and eating habits, loss of interest in activities, withdrawal, difficulty thinking, and other symptoms.
Bipolar disorder can affect mood, thoughts, and behaviors to the extent that day-to-day life becomes challenging. It can prevent a person from functioning normally at home, at work, at school, and in relationships with other people. The average age of onset of bipolar disorder is 25, but many people begin to experience the first signs of the condition in their teens. While bipolar disorder can be very disruptive, it can also be managed with treatment, including residential therapy and support along with medications.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Phobia Of Thunder And Lightning Called
Find The Right Therapist For You
Do a search to find all therapists in your area
Please note: Our screens are for adults only. By participating you acknowledge that the screen is not a diagnostic instrument and is only to be used by you if you are 18 years or older. You are encouraged to share your results with a physician or healthcare provider. Mind Diagnostics, sponsors, partners, and advertisers disclaim any liability, loss, or risk incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, from the use and application of these screens. If you are in need of immediate assistance, please dial 911 or the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1 273-8255.