Information For Carers Friends And Relatives
It can be very distressing if you are a carer, friend or relative of someone who has psychosis. You can get support.
How can I get support for myself?
You can do the following.
- Speak to your GP about medication and talking therapies for yourself.
- Speak to your relatives care team about family intervention. For more information about family intervention please see the section above.
- Speak to your relatives care team about a carers assessment.
- Ask for a carers assessment.
- Join a carers service. They are free and available in most areas.
- Join a carers support group for emotional and practical support. Or set up your own.
What is a carers assessment?NICE guidelines state that you should be given your own assessment through the community mental health team to work out what effect your caring role is having on your health. And what support you need. Such as practical support and emergency support.
The CMHT should tell you about your right to have a carers assessment through your local authority. To get a carers assessment you need to contact your local authority.
How do I get support from my peers?You can get peer support through carer support services or carers groups. You can search for local groups in your area by using a search engine such as Google. Or you can call our advice service on 0300 5000 927. They will search for you.
How can I support the person I care for?
You can do the following.
There is no definition for what high risk means. It could include:
Schizoaffective Disorder Vs Schizophrenia
Comparing schizoaffective disorder vs schizophrenia is important. Far too often, people lump these mental disorders together. In reality, theyre completely different disorders that cause different symptoms.
For example, people who have schizophrenia have a hard time telling the difference between reality and fiction. They might see or hear voices that arent really there. To them, the voices and imagery are as real as it comes. However, others cant see nor hear these nonexistent things.
With schizoaffective disorder, people feel detached from reality. While it makes them see or hear things that arent there, it also affects their mood a great deal. In fact, two common types of schizoaffective disorder are bipolar and depressive disorders.
With that said, its important to note that these disorders share some other symptoms. However, theyre still completely different and often require different treatments.
Schizophrenia And Psychotic Disorders
For up-to-date information on COVID-19, including the vaccination, visit the Department of Health website. For up-to-date information on COVID-19, including the vaccination, visit the Department of Health website. COVID-19 support: information and resources COVID-19 support: information and resources
About
What is Head to Health?
News and announcements
Communication Materials
Give us your feedback
COVID-19 Support
- Find support that works for you link
- Impacts on everyday life link
COVID-19 Support
Find support that works for you
For people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds
Living with lockdown
Grief and trauma support for aged care
Impacts on everyday life
Staying connected
Stability and security
The impact on you and your family
Maintaining good mental health
Government’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic
Chatstarter – Helping parents and young people support each other
Head to Health Pop Up services
Meaningful life
Physical health
Physical health
Being active
Food
Sleep
Connectedness
Connectedness
Community
Culture
Environment
Pets
Spirituality
Purposeful activity
Purposeful activity
Getting involved
Hobbies
Learning and education
Volunteering
Work
Feeling safe, stable and secure
Feeling safe, stable and secure
Finances
Home and housing
Neighbourhood
Mental health difficulties
- Mental health conditions and disorders link
- Challenging situations link
What should you know about mental health conditions and disorders
Mental health conditions and disorders
Also Check: Bipolar And Bpd Comorbid
Rose Hill Center Can Help You Overcome Both Disorders
While theres clearly a difference between these two disorders, it doesnt have to change where you get help. At Rose Hill Center, we understand the differences between the two. For that reason, we offer different treatment options at one location.
At Rose Hill Center, we strive to offer a variety of treatment services for mental health problems. A few of these include:
Whats The Difference Between Psychosis And Schizophrenia

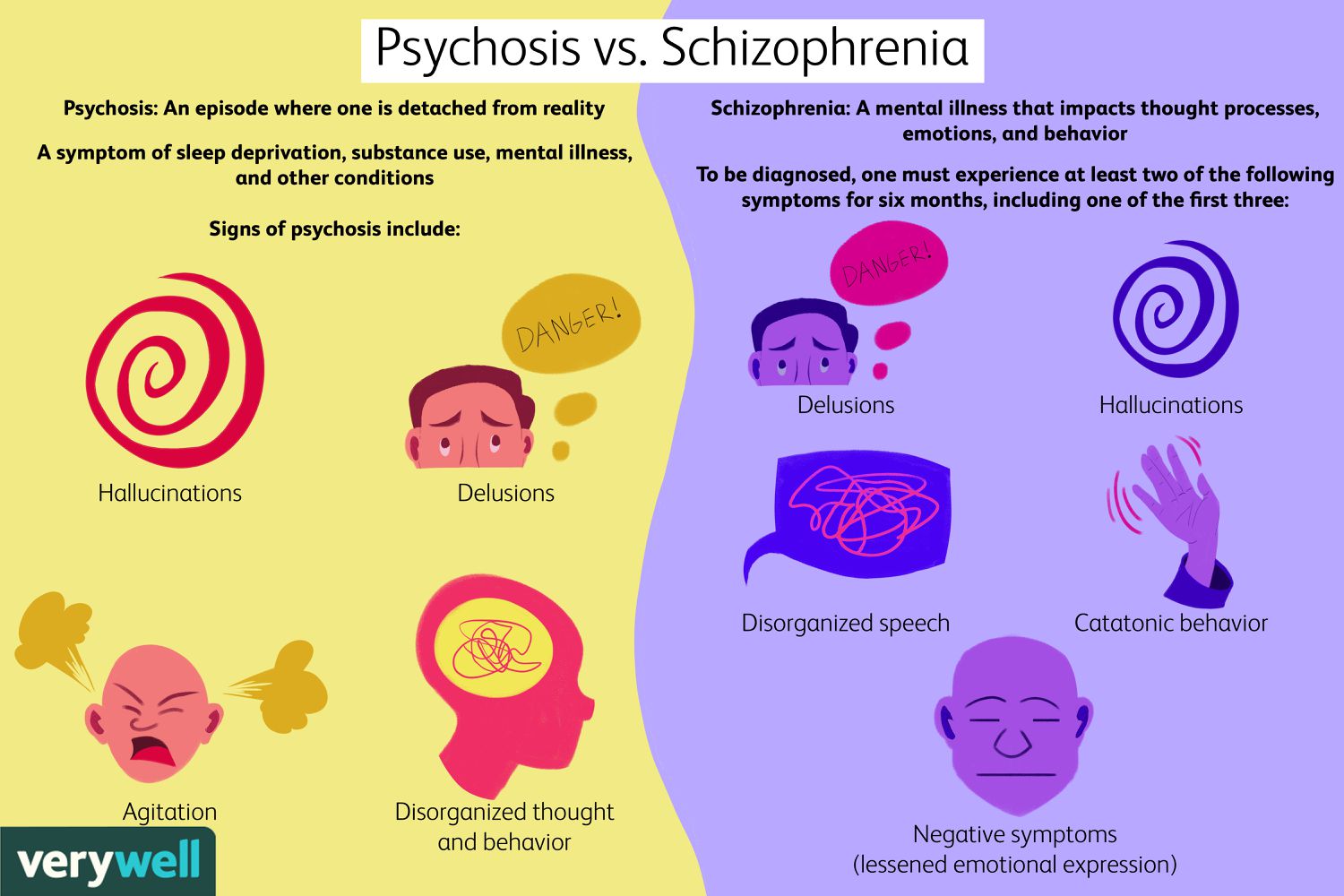
Psychosis is a syndrome or group of symptoms. Someone experiencing an episode of psychosis is having a break with reality. Major symptoms of psychosis are hallucinations and delusions. Hallucinations are sensations that are not real, such as hearing voices or sounds that arent real. Hearing voices is a common hallucination, but hallucinations can be experiences with any sensehearing, sight, smell, taste, or touch. Delusions are strong beliefs that cant possibly be true. Common delusions include the belief that someone is following or monitoring you, or the belief that you have extraordinary powers or abilities. Other symptoms of psychosis include difficulties concentrating, completing tasks, or making decisions. Thoughts may feel jumbled or confused. Some people have a hard time following conversations or speaking clearly. Psychosis can even affect the way people move or express their emotions.
Psychosis and schizophrenia are treatable. Its important to seek help as soon as possible.
Where can I learn more?
Recommended Reading: Spasmenagaliaphobia
Signs & Symptoms Of Psychotic Disorders
People with psychotic disorders can experience hallucinations they may see, hear, feel, taste or smell things that arent there. They can also experience delusions, which are unshakable beliefs in false or inaccurate ideas that conflict with reality. These experiences are very real to people with these disorders.
Signs of Schizophrenia
Symptoms of schizophrenia are considered either positive or negative and most people with the illness experience both. Negative symptoms are normal feelings and abilities that schizophrenia takes away, such as feeling motivated or being interested in activities. Positive symptoms are easier to treat than negative ones, which tend to remain longer.
People with schizophrenia have at least two of these symptoms for six months or more. One of the two symptoms must include hallucinations, delusions or confused speech. Signs and symptoms of schizophrenia include:
- Hallucinations seeing, hearing, feeling, tasting or smelling things that arent there
- Delusions false ideas that are easily proved wrong, like believing you can fly or thinking youre a different person
- Confused speech using words and sentences that don’t make sense
- Strange or repetitive behavior acting in odd ways, like walking in circles or sitting motionless for hours
- Withdrawal and lifelessness displaying no emotion, motivation or interest in regular activities
Schizophrenia Triggers
Positive And Negative Symptoms
The symptoms of schizophrenia are usually classified into:
- positive symptoms any change in behaviour or thoughts, such as hallucinations or delusions
- negative symptoms where people appear to withdraw from the world around then, take no interest in everyday social interactions, and often appear emotionless and flat
You May Like: What Is The Phobia Of Puke Called
What Are The Causes Of Psychosis Vs Schizophrenia
Even though psychosis and schizophrenia have similar symptoms, the causes set them apart. In both cases, research is still being done to pinpoint the exact causes.
Causes of psychosis
There are several things that may cause psychosis or a psychotic episode. They fall into three categories: a psychological condition, medical condition, or the misuse of drugs and/or alcohol.
Some psychological conditions that are known to cause psychotic episodes are:
- Schizophrenia
- Cannabis
Causes of schizophrenia
Its still not known exactly what causes schizophrenia, but researchers think its a combination of factors. Genetics are thought to play a part, as schizophrenia runs in families. Youre six times more likely to have schizophrenia if a close family member also has it.
Your environment may also be a cause, including complications at birth. Research shows that babies born prematurely, with low birth weight, or who were malnourished in the first two trimesters are more likely to develop schizophrenia.
People with schizophrenia have shown to have small differences in their brain structure. Certain brain chemicals, like dopamine and glutamine, may also contribute to schizophrenia.
Ological Limitations And Considerations
An overview of the methodological considerations in the examination of research that has compared symptoms between METH psychosis and schizophrenia is shown in Table . One of the biggest limitations with METH psychosis research is that little effort is made to distinguish between those with acute and chronic METH psychosis, with the majority of the findings portraying a blended representation of all types. Indeed, the majority of studies failed to report the length of time of abstinence from METH at the time of the assessment. For the purpose of this review, therefore, we considered these studies to represent acute METH psychosis studies as there was no evidence to suggest that these samples had been abstinent for long enough to be considered to be representative of chronic METH psychosis . Additionally, few studies indicate whether their samples are abstinent at the time of the assessment. Taken together, the findings presented in these papers may not be generalizable to samples of chronic METH psychosis, as it is uncertain whether these behavioral outcomes are referable to the direct effects of METH, acute METH psychosis or persistent METH psychosis.
Read Also: Does Dehydration Cause Anxiety
How Are Psychotic Disorders Diagnosed
The distorted thought processes and disorganized speech of psychotic disorders can make clinical interviews difficult for acutely psychotic individuals. Diagnosing psychosis often involves observing voluntary speech and action made outside of the context of clinical interviews and confirming the presence of hallucinations and delusions.
Unfortunately, psychotic disorders are rarely detected before the first psychotic break. Negative symptoms are subtle and can signal a range of other conditions, requiring a long process of differential diagnosis to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
The emergence of positive symptoms of psychosis for the first time is called a psychotic break and is often accompanied by dangerous or bizarre behavior and a heightened risk of harm to self or others.
People experiencing a psychotic episode might consider harming themselves and, in rarer cases, thoughts of harming others. But they typically are unable to care for themselves or to protect themselves from harm.
Many people are diagnosed with a psychotic disorder after involuntarily committing to inpatient treatment. The behavior that leads to hospitalization is often first noticed by other concerned individuals, especially loved ones.
Re: Difference Between Imagination And Psychosis
by phoenix-8ste» Fri Jan 13, 2017 2:12 am
by Infinitude» Fri Jan 13, 2017 5:38 am
phoenix-8ste wrote:My baseline off medicine is imaginative with some features of magical thinking. The difference between this and psychosis is that I’m not immersed in the experience or absolutely convinced. I don’t feel bombarded or harassed by evil. It’s more of a yearning and curiosity about other realms, conspiracy theories and it maybe makes me a bit woo woo. I’m more likely to think religiously or spiritually, make meaning from coincidences, try to connect to higher realms and imagine past lives or the form of my spirit.
It resembles the positive symptoms of schizotypal personality disorder rather than schizophrenia. You might find it helpful to research the distinction.
In contrast, I find it hard to think outside the box when I’m on medication. I use inherent logic, convergent thinking rather than divergent thinking, I’m very no-nonsense and skeptical. It is a bit boring. Considering the positive symptoms of my schizophrenia tend to show up when triggered by a stressor and I can go for long periods medication-free without them I’m tempted to seek out that more imaginative, magical, superstitious side of myself. If that’s all that it was it would probably make me feel less valid with my diagnosis but I can’t really argue with doctors anymore that it’s just my personality because I’ve had such bad times.
Recommended Reading: Schizophrenia Cycles
Is There A Cure For Drug Induced Psychosis
There is no cure for drug-induced psychosis because it is not a disease in the traditional sense. Drug-induced psychosis subsides as the body metabolizes the substance that caused it in the first place however, there are some drugs that can cause psychosis symptoms for days, months, and even years after an individual stops taking them. With heavy use, cocaine, amphetamines, and sometimes alcohol can cause psychosis symptoms that persist well into sobriety.
The Challenge of Co-occurring Disorders
According to a report originally published in JAMA Psychiatry, people who have severe mental health disorders like schizophrenia are more likely to develop a substance use disorder than those who do not. Diagnosing co-occurring disorders and devising effective treatment plans are challenging when both of the disorders present with the same symptoms.
The Australia Governments National Drug Strategy suggests that healthcare professionals can distinguish between schizophrenia coupled with substance abuse and drug-induced psychosis alone by monitoring symptoms after an individual finishes the withdrawal stage. They can also look for the existence of prodromal symptoms of schizophrenia, including subtle personality changes, angry outbursts, odd thought patterns, and reclusiveness, prior to substance use.
Understanding The Subtle Differences
The difference between schizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia is often hard to spot. The reason is that a lot of the symptoms overlap. For example, doctors typically characterize schizoaffective disorder by the mood disorders that accompany it. However, its not uncommon for people with schizophrenia to experience manic or depressive moods as well.
If both experience mood disorders, how can specialists tell the difference? The key difference between schizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia is the prominence of the mood disorder. With schizoaffective disorder, the mood disorder is front and center. With schizophrenia, its not a dominant part of the disorder.
Another difference is the psychotic symptoms that people experience. With schizophrenia, the psychotic symptoms are dominant. With schizoaffective disorder, episodes of psychosis may occur.
However, it takes trained professionals to spot the differences between the two. After all, the symptoms typically start when people reach their 20s. Also, they can cause hallucinations and delusions.
Don’t Miss: Schizophrenia By Gender
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
The goal of schizophrenia treatment is to ease the symptoms and to cut the chances of a relapse, or return of symptoms. Treatment for schizophrenia may include:
- Medications: The primary medications used to treat schizophrenia are called antipsychotics. These drugs donât cure schizophrenia but help relieve the most troubling symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, and thinking problems.
- Older antipsychotic medications used include:
Note: Clozapine is the only FDA-approved medication for treating schizophrenia that is resistant to other treatments. Itâs also used to lessen suicidal behaviors in those with schizophrenia who are at risk.
Acute Meth Psychosis Vs Schizophrenia
Early findings on METH induced psychosis reported hallucinations and delusions as a predominant presenting factor , with later findings acknowledging that the similarities between METH psychosis and schizophrenia were largely directed toward positive symptoms. McKetin et al. found that unusual thoughts, hallucinations and suspiciousness were present in one-quarter of chronic consumers of METH diagnosed with acute METH psychosis. Indeed, Bousman et al. examined the variation in positive symptoms across individuals with METH psychosis. While they found three distinct sub-profiles, delusions were common amongst all individuals with METH-induced psychosis. Additional studies have also reported that METH psychosis is associated with a high prevalence of persecutory delusions, auditory and visual hallucinations, odd speech, and delusions of reference .
Also Check: Faint From Anxiety
Mood Vs Psychotic Symptoms
In schizophrenia, mood symptoms are not expected to occur without psychotic symptoms. The psychotic symptoms are almost always present, but the mood symptoms come and go.
In schizoaffective disorder, the psychotic symptoms may or may not be present during the times when a person is experiencing depression or mania. That said, the diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder requires that the psychotic symptoms be present for a long enough time when a person is not experiencing any serious mood symptoms.
Types Of Psychotic Disorders
Psychotic disorders can be short- or long-term conditions. People can experience a single psychotic episode triggered by extreme stress or other temporary changes to the brain. They can also deal with multiple psychotic breaks.
Many types of psychotic disorders exist. Schizophrenia is the most common type of psychotic disorder and is one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. But other types of psychotic conditions can also create significant health problems.
You May Like: Webmd Anxiety Disorder
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
If symptoms of schizophrenia are present, the doctor will perform a complete medical history and sometimes a physical exam. While there are no laboratory tests to specifically diagnose schizophrenia, the doctor may use various tests, and possibly blood tests or brain imaging studies, to rule out another physical illness or intoxication as the cause of the symptoms.
If the doctor finds no other physical reason for the schizophrenia symptoms, they may refer the person to a psychiatrist or psychologist, mental health professionals trained to diagnose and treat mental illnesses. Psychiatrists and psychologists use specially designed interviews and assessment tools to evaluate a person for a psychotic disorder. The therapist bases their diagnosis on the person’s and family’s report of symptoms and their observation of the person’s attitude and behavior.
A person is diagnosed with schizophrenia if they have at least two of these symptoms for at least 6 months:
- Delusions
One of the symptoms has to be
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- Disorganized speech
During the 6 months, the person must have a month of active symptoms. Symptoms should negatively affect them socially or at work, and canât be caused by any other condition.
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The word “negative” here doesnât mean “bad.” It notes the absence of normal behaviors in people with schizophrenia. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia include:
- Lack of emotion or a limited range of emotions
- Withdrawal from family, friends, and social activities
- Less energy
- Loss of pleasure or interest in life
- Poor hygiene and grooming habits
You May Like: Fear Of Bees And Wasps Phobia