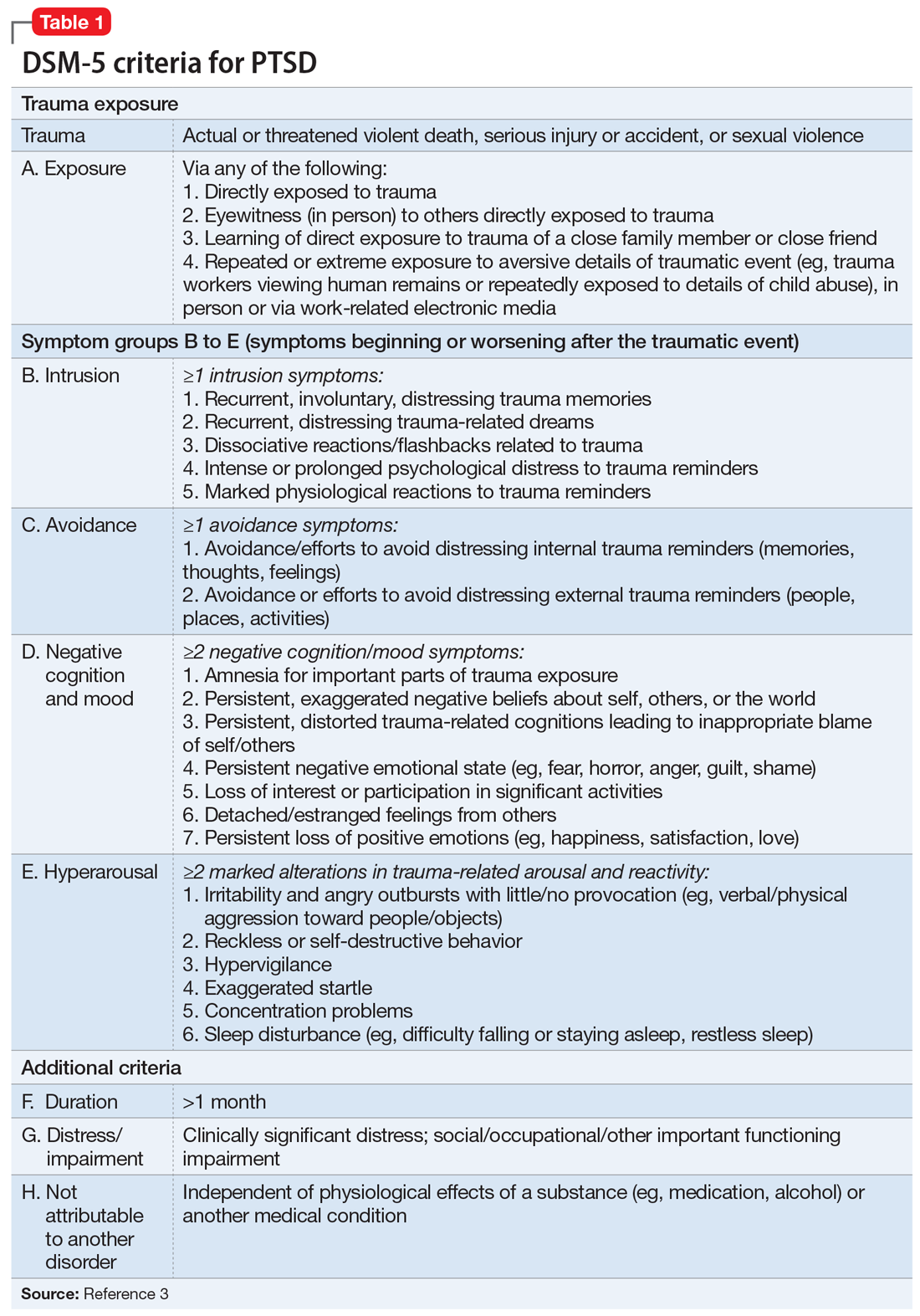
Diagnostic Classification Of Ptsd
Perhaps the most substantial conceptual change in the DSM-5 for PTSD was the removal of the disorder from the anxiety disorders category. Considerable research has demonstrated that PTSD entails multiple emotions outside of the fear/anxiety spectrum , thus providing evidence inconsistent with inclusion of PTSD with the anxiety disorders. In the DSM-5, PTSD was placed in a new diagnostic category named Trauma and Stressor-related Disorders indicating a common focus of the disorders in it as relating to adverse events. This diagnostic category is distinctive among psychiatric disorders in the requirement of exposure to a stressful event as a precondition. Other disorders included in this diagnostic category are adjustment disorder, reactive attachment disorder, disinhibited social engagement disorder, and acute stress disorder. This is the only diagnostic category in the DSM-5 that is not grouped conceptually by the types of symptoms characteristic of the disorders in it.
How Did Ptsd Change From The Dsm
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is the manual that outlines all known mental illnesses, what they are, how they are diagnosed, and in some respects, treatment. In May, the DSM released its fifth version and with it came a change in how post-traumatic stress disorder is viewed. While PTSD used to be categorized with the anxiety disorders, it now has been moved into a separate chapter called Trauma- and Stress-Related Disorders.
Criterion G: Functional Significance
The PTSD symptoms experienced by the person with the diagnosis must create distress or functional impairment in a persons life.
For example, a veteran who suffers from PTSD and currently works in an office setting may find that he has difficulty concentrating and is irritable toward his coworkers. These symptoms may harm his job performance. A college student who experienced sexual assault at a party may find that their friendships are affected by their negative affect, hypervigilance, and avoidance of other social events.
Read Also: Pristique Withdrawal
Criterion B: Intrusion Symptoms
The traumatic event is persistently re-experienced in the following way:
Correctional Psychiatry And Asylum Seekers
Several studies document increased prevalence of PTSD in jail and prison populations compared with the general population. Lifetime rates of PTSD in female jail detainees range from 33.5 to 48.2 percent,, considerably higher than the 10.4 percent rate reported in a community sample, according to DSM III-R criteria. Trestman et al. reported that 20 percent of males and 41.8 percent of females screened at jail intake met criteria for DSM-IV PTSD. In a study of convicted female prisoners, Warren et al. reported that, in addition to high rates of violence and sexual victimization, 93.5 percent of these women reported witnessing harm to others. All these studies emphasize the need to include screening for PTSD in correctional settings. Although it is unclear whether the DSM-5 criteria will alter the prevalence of PTSD among detainees and prisoners, increased training of correctional mental health staff is needed in the recognition, and more important, the treatment of PTSD. Improved recognition and treatment of PTSD with particular attention to diminishing hyperarousal symptoms may diminish assaultive behavior that is disruptive in the correctional environment.
Recommended Reading: Pristiq For Depression And Anxiety
What Is The Dsm
DSM stands for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. It’s a book that is basically like an encyclopedia of mental health conditions. The book originally was published in 1952, but has been updated multiple times resulting in the current edition of the DSM-5.
The DSM was created by over a hundred and sixty clinicians and researchers from all over the globe. The purpose of creating the DSM is to provide a handbook for mental health professionals and other healthcare workers.
The DSM includes lists of symptoms and criteria that they can use in order to diagnose patients with mental disorders. This guidebook helps to make diagnosis and communication about mental illness more consistent.
Over the years, the book has continued to be updated and revised as there is research consistently happening on an ongoing basis around mental health disorders. These revisions help to keep the book accurate for our current day in order to help the most amounts of people. The most recent additions to the book were made in order to include symptoms that people were commonly experiencing with mental disorders such as PTSD, but we’re not already included in the book.
Because mental health professionals are using this book in order to diagnose patients, a lack of the right symptoms being included could cause people not to be diagnosed. This would mean that they would not have access to the treatment that they would need in order to gain control of their mental health challenges.
Exposure To Ptes And Probable Ptsd Diagnosis
Responses on the HTQ revealed that participants in this sample had been exposed to multiple types of PTEs. On average, participants had experienced 5.68 types of PTEs, with the vast majority reporting exposure to at least one type of PTE. The frequency of exposure to PTEs are summarised in Table . Participants most commonly experienced lack of food or water and being close to death . Additionally, more than one third of the sample had experienced imprisonment and/or torture , and just under one fifth were survivors of rape or sexual abuse . A total of 51 participants were identified as having a probable diagnosis of PTSD.
Table 3 Frequency of Exposure to Potentially Traumatic Events
Recommended Reading: Was Audrey Hepburn Anorexia
Why Didnt The Dsm Include Complex Ptsd
According to the National Center for PTSD, complex PTSD wasnt included as a separate diagnosis in the DSM-5 because 92% of people with C-PTSD also met the criteria for PTSD.
A review of the literature by Resick in 2012 found insufficient evidence to support complex PTSD as a distinct diagnosis from PTSD, based on the way PTSD was defined in the DSM-5. This is in spite of what appears to be a significant body of research literature supporting complex PTSD as a separate diagnosis.
For example, a study by Powers and colleagues of African women found clear, clinically-relevant differences between the two conditions. C-PTSD was associated with a lower likelihood of having secure attachment, greater comorbidity with other mental illnesses, and increased emotional dysregulation and dissociation.
Bessel van der Kolks excellent book The Body Keeps the Score offers a very compelling argument for complex PTSD to be a distinct diagnosis. Hes advocated for the American Psychiatric Association to make that change, but unfortunately, it didnt happen for the release of the DSM-5.
Suicide Risk And Comorbidities
Traumatic events increase a persons suicide risk, and PTSD is strongly associated with suicidal ideation and suicidal attempts.
PTSD is also linked to other mental disorders. According to DSM-5, those with PTSD are 80% more likely than those without it to have symptoms that meet the diagnostic criteria for at least one other mental disorder, such as depressive, bipolar, anxiety, or substance abuse disorders. Although females are at greater risk of PTSD, males diagnosed with PTSD are more likely to have a comorbidity. Among Afghanistan and Iraq veterans, its been found that the co-occurrence of PTSD and a mild traumatic brain injury was 48%.
Don’t Miss: Is Bipolar The Same As Bpd
Criterion D: Negative Alterations In Cognitions And Mood
Many PTSD psychotherapy protocols focus on changing both assimilated beliefs and overgeneralized beliefs that are now characterized by PTSD Criteria D2 and D3. Therefore, an accurate assessment of PTSD Criteria D2 and D3 prior to initiating treatment will provide insight into the specific beliefs that should be targeted throughout the course of treatment. Of course, these symptoms should be regularly assessed during therapy to determine the extent to which they are being modified by the intervention. Finally, because dysfunctional cognitions which remain after treatment may continue to produce high levels of distress , clinicians should assess for the continued existence of these beliefs during follow-up assessments.
The addition of symptom D4, the presence of a persistent negative emotional state , also has important implications for PTSD assessment within the context of treatment. The introduction of D4 is a reflection of the re-categorization of PTSD as a trauma- and stressor-related disorder rather than as an anxiety disorder. This new classification is a reflection of research that has suggested that, although the reaction to a traumatic event may be anxiety- or fear-based, it may also be most prominently expressed through dysphoric, externalizing, or dissociative symptom profiles .
Criterion C: Avoidance Symptoms
The third criterion for a PTSD diagnosis is avoidance of reminders of the trauma.
This could be an avoidance of thoughts or feelings about the event or avoidance of trauma-related reminders altogether. A person who suffered sexual assault may display avoidance of thoughts and feelings of the assault and do their best to never think about the event.
Someone who witnessed a person drowning may avoid trauma-related reminders and stay away from pools or bodies of water, for example.
In the case of military veterans, they may avoid any depictions of violence to avoid reminders of their own trauma. For a diagnosis of PTSD, the presence of at least one of these symptoms is required.
Read Also: Prodromal Symptoms Schizophrenia
What Is The Dsm V
DSM 5 Substance Use Disorder. DSM is an acronym for the Diagnostic Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders, a standard text used by mental health and drug treatment professionals. The DSM V designation indicates that this is the fifth edition of the manual with the first edition published in 1952, according to the American Journal
Assessment In Ptsd Treatment

Assessment of PTSD can be conducted using a range of available instruments, each possessing varying strengths and weaknesses. Structured, standardized diagnostic interviews are considered the gold standard for assessing PTSD symptoms. However, because such structured interviews are time-consuming and must be administered by a trained clinician, it may not be feasible to administer them in every situation. Self-report measures of PTSD symptomatology can be used when time and resources are scarcer but they have their own limitations. Specifically, self-report instruments have fixed item content and rating scale formats, and their accuracy is contingent upon the patient understanding each item and answering truthfully.
After treatment, assessment of the symptoms that were targeted during treatment allows the clinician to determine the degree of symptom improvement by calculating reliable change and clinically significant change scores. Reliable change scores indicate the extent to which changes on scores of a particular measure are greater than the expected measurement error . Clinically, significant change scores indicate the extent to which the patients end state scores on a particular measure compare with scores observed in clinically meaningful comparison groups .
Don’t Miss: Phobia Definition Medical
Criterion E: Alterations In Arousal And Reactivity
For a diagnosis of PTSD, at least two of the following symptoms that began or worsened after the stressor must be present:
- Irritability or aggression
- Risky or destructive behavior
- Hypervigilance
- Increased startle reaction
- Difficulty concentrating or sleep disturbances.
These alterations in arousal and reactivity are a defense mechanism for preventing further trauma.
How Do The Dsm
Overall, the symptoms of PTSD are generally comparable between DSM-5 and DSM-IV. A few key alterations include:
- The revision of Criterion A1 in DSM-5 narrowed qualifying traumatic events such that the unexpected death of family or a close friend due to natural causes is no longer included.
- Criterion A2, requiring that the response to a traumatic event involved intense fear, hopelessness, or horror, was removed from DSM-5. Research suggests that Criterion A2 did not improve diagnostic accuracy .
- The avoidance and numbing cluster in DSM-IV was separated into two criteria in DSM-5: Criterion C and Criterion D . This results in a requirement that a PTSD diagnosis includes at least one avoidance symptom.
- Three new symptoms were added:
- Criterion D : Overly negative thoughts and assumptions about oneself or the world and, negative affect
- Criterion E : Reckless or destructive behavior
Continuing Education
PTSD Overview and Treatment
The course describes the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for PTSD and evidence-based treatments. Videos of Veterans with PTSD and clinicians are included.
Read Also: Schizophrenia Prodromal Phase
Changes From Previous Pcl For Dsm
Several important revisions were made to the PCL in updating it for DSM-5:
- PCL for DSM-IV has three versions, PCL-M , PCL-C , and PCL-S , which vary slightly in the instructions and wording of the phrase referring to the index event. PCL-5 is most similar to the PCL-S version. There are no corresponding PCL-M or PCL-C versions of PCL-5.
- Although there is only one version of the PCL-5 items, there are three formats of the PCL-5 measure, including one without a Criterion A component, one with a Criterion A component, and one with the Life Events Checklist for DSM-5 and extended Criterion A component.
- The PCL-5 is a 20-item questionnaire, corresponding to the DSM-5 symptom criteria for PTSD. The wording of PCL-5 items reflects both changes to existing symptoms and the addition of new symptoms in DSM-5.
- The self-report rating scale is 0-4 for each symptom, reflecting a change from 1-5 in the DSM-IV version. Rating scale descriptors are the same: “Not at all,” “A little bit,” Moderately,” “Quite a bit,” and “Extremely.”
- The change in the rating scale, combined with the increase from 17 to 20 items means that PCL-5 scores are not compatible with PCL for DSM-IV scores and cannot be used interchangeably.
What Are The Three Symptom Categories Of Ptsd
The diagnosis of PTSD is further characterized by three distinct symptom clusters: re-experiencing of the traumatic event through such phenomena as dreams, flashbacks, and intrusive, distressing thoughts avoidance and numbing, characterized by such phenomena as avoidance of trauma reminders and numbing of
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Mimic Diabetes
Specify If: With Dissociative Symptoms
In addition to meeting criteria for diagnosis, an individual experiences high levels of either of the following in reaction to trauma-related stimuli:
Criterion A: The Gatekeeper
The definition of a qualifying stressor, the so-called gatekeeper criterion, has the greatest impact on the prevalence of PTSD. The two central questions for Criterion A are first, must the stressor involve a life-threatening or serious injury ? Second, must exposure to this event be direct, such as experiencing or witnessing, or are indirect exposures, such as being confronted with or learning about, sufficiently intense to justify labeling them traumatic stressors?
Regarding the first question, there is no bright line separating trauma that produces PTSD from trauma that does not. Some research suggests that events that are not life threatening, such as serious conflicts in a relationship, loss of a job, separation, and serious financial stress may be as likely to cause symptoms of PTSD as those that involve serious threat to bodily integrity. Despite these findings, the DSM-5 Anxiety, Obsessive-Compulsive Spectrum, Posttraumatic, and Dissociative Disorders Work Group felt that the weight of the research indicated that, in most cases, PTSD does not develop unless the individual is exposed to events that are intensely stressful, constituting watershed events in the life of the patient .
You May Like: Acute Phase Of Schizophrenia
What Is The Criteria For Dsm 5
4.9/5DSM5CriteriaDSM5fivein-depth answer
Criterion DElevated self-blame or blame of others about the cause or consequence of a traumatic event3? A negative emotional state that is pervasive. Loss of interest in activities that you used to enjoy. Feeling detached from others.
Also Know, what are the components of a DSM 5 diagnosis? DSM consists of three major components: the diagnostic classification, the diagnostic criteria sets, and the descriptive text. The diagnostic classification is the official list of mental disorders recognized in DSM.
Correspondingly, what is the DSM 5 and what is it used for?
The DSM–V is the standard classification of mental disorders used by mental health and other health professionals, and is used for diagnostic and research purposes. During this time, the APA will conduct three phases of field trials to test some of the proposed diagnostic criteria in real-world clinical settings.
What are the four types of PTSD?
There are five main types of post-traumatic stress disorder: normal stress response, acute stress disorder, uncomplicated PTSD, comorbid PTSD and complex PTSD.
What Can The Dsm

The DSM can diagnose mental disorders. It provides a classification system for such disorders and lists the diagnostic criteria for them. It is used by clinicians to diagnose mental health conditions in the United States.
The DSM-V includes the five categories: disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence mental disorders due to general medical conditions substance use disorders schizophrenia and other psychotic disorder mood, anxiety, and related disorder.
Read Also: What Is A Depression Contour
Ptsd And Criminal Law
PTSD has been offered as a basis in criminal defenses including insanity, unconsciousness, self-defense, and diminished capacity, as well as in sentence mitigation proceedings, although, in one study, PTSD was advanced as the basis for an insanity defense in only 0.3 percent of all insanity pleas. The expanded criteria as well as the newly added symptoms in the DSM-5 are likely to increase the use of PTSD diagnoses by defendants in both the guilt and sentencing phases. As summarized by Berger et al., the successful use of PTSD in an insanity defense has been predicated on a demonstration of the presence of dissociative phenomena, primarily flashbacks, that transiently cause defendants to misperceive their circumstances and act as would be reasonable in the context of the flashback. This approach would be applicable in a jurisdiction using the M’Naughten standard. In jurisdictions applying an American Law Institute standard, the argument would shift to the impact of PTSD on volition, and specifically, whether the instant offense was a spontaneous, unpremeditated reenactment of the prior trauma.