What’s It Like Living With Bipolar Disorder
In this video, Laura, Steve and Joe talk about their experiences of living with bipolar disorder.
In this podcast, Siobhan talks about her experiences of bipolar disorder.
Content warning: this podcast mentions suicide, but it doesn’t include details on methods.
Find out more about or subscribe to our podcast on iTunes or Audioboom.
Falret And Baillarger: A Cycling Disease
From antiquity through to the 19th century, mania and melancholia were considered to be two completely different disorders which embraced a wide variety of psychiatric syndromes. Jean-Pierre Falret created the first concept of a new and separate psychiatric disorder which encompassed both mania and depression and published his description of this disease in 1851, which he termed folie circulaire, a mental disorder characterized by a continuous cycle of depression, mania, and free intervals of varying lengths between these two extremes . His contemporary Jules Baillarger described folie à double forme in which mania and melancholia change into one another but with no requirement for an free interval between the two, in contrast to Falrets description which would include those with a long interval between the two mood states to still receive a diagnosis of folie circulaire . These discrepant hypotheses regarding this aspect of cycling, with pauses between mood episodes still regarded as linked shifts between mood states regardless of length, created a rift in understanding when instead they may have been describing two sides of the same coin. Regardless, these competing descriptions spread from France via supporters of either description, and the concept of a cycling mood disease was accepted before the end of the century .
Brain Structure And Function
Research shows that the brain structure and function of people with bipolar disorder may differ from those of people who do not have bipolar disorder or other mental disorders. Learning about the nature of these brain changes helps researchers better understand bipolar disorder and, in the future, may help predict which types of treatment will work best for a person with bipolar disorder.
Read Also: How To Help Anxiety Nausea
What Is Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a mental illness that can be chronic or episodic . People sometimes refer to bipolar disorder with the older terms manic-depressive disorder or manic depression.
Everyone experiences normal ups and downs, but with bipolar disorder, the range of mood changes can be extreme. People with the disorder have manic episodes, or unusually elevated moods in which the individual might feel very happy, irritable, or up, with a marked increase in activity level. They might also have depressive episodes, in which they feel sad, indifferent, or hopeless, combined with a very low activity level. Some people have hypomanic episodes, which are like manic episodes, but not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning or require hospitalization.
Most of the time, bipolar disorder symptoms start during late adolescence or early adulthood. Occasionally, children may experience bipolar disorder symptoms. Although symptoms may come and go, bipolar disorder usually requires lifelong treatment and does not go away on its own. Bipolar disorder can be an important factor in suicide, job loss, ability to function, and family discord. However, proper treatment can lead to better functioning and improved quality of life.
Prevalence Of Bipolar Disorder Among Adults
- Based on diagnostic interview data from National Comorbidity Survey Replication , Figure 1 shows past year prevalence of bipolar disorder among U.S. adults aged 18 or older.1
- An estimated 2.8% of U.S. adults had bipolar disorder in the past year.
- Past year prevalence of bipolar disorder among adults was similar for males and females .
Figure 1
| Demographic |
|---|
| 0.7 |
Also Check: What Are Some Symptoms Of An Eating Disorder
What Types Of Therapy Are Used To Treat Bipolar Disorder
Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, can be an effective part of the treatment plan for people with bipolar disorder.
Psychotherapy is a term for a variety of treatment techniques that aim to help you identify and change troubling emotions, thoughts and behaviors. Working with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, can provide support, education and guidance to you and your family.
Different types of therapy for bipolar disorder include:
What Risks And Complications Can Bipolar Disorder Cause
There can be complications and risks for people who live with bipolar disorder. But these risks can be lessened with the right support and treatment.
What about suicide and self-harm?
You might have an illness where you experience psychosis, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Your risk of suicide is estimated to be between 5% and 6% higher than the general population.
You are more likely to try to take your own life if you have a history of attempted suicide and depression. It is important that you get the right treatment for your symptoms of depression and have an up to date crisis plan.
There is also research that suggests you are 30% – 40% more likely to self-harm if you live with bipolar disorder.
What about financial risk?
If you have mania or hypomania you may struggle to manage your finances. You may spend lots of money without thinking about the effect that it may have on your life.
You could make a Lasting Power of Attorney. This is a legal process. This means that you pick someone that you trust to manage your finances if you lack mental capacity to manage them by yourself.
You can work with your carer and mental health team. You can form an action plan. This can say what they can do if you have a period of mania or hypomania and you start to make poor financial decisions.
What about physical health risk?
What about alcohol and drugs risk?
If you want advice or help with alcohol or drug use contact your GP.
What about driving risk?
You May Like: Can Caffeine Cause Panic Attacks Anxiety
Pregnancy And Treatment For Bipolar Disorder
You should discuss any pregnancy plans with your psychiatrist. Together, you can arrange how to manage your mood during the pregnancy and for the first few months after the baby arrives. Lithium and sodium valproate should not be prescribed if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
If you become are pregnant while taking lithium, it’s best to discuss with your psychiatrist whether you need to stop lithium. Although lithium is safer in pregnancy than the other mood stabilisers, there is a significant risk to the baby of heart problems. This risk will need to be weighed against the risk of you becoming depressed or manic.
The risk is greatest during the first three months of pregnancy. Lithium is safe after the 26th week of pregnancy, although you should not breastfeed your baby if you are taking lithium as it can be toxic for your baby12.
It will be worth the discussing the possibility of starting some of the psychological treatments mentioned above.
During pregnancy, everyone involved – the obstetrician, midwives, health visitors, GP, psychiatrist, and community psychiatric nurse need to keep in close touch with each other.
During a depressive episode, or in between episodes of mania and depression, psychological treatments can be helpful1 5 11. These can include:
- other options if the above choices have not helped.
Bipolar Disorder Due To Another Medical Or Substance Abuse Disorder
Some bipolar disorders dont have a specific pattern or dont match the three categories of disorders listed above and yet, they still align with the criteria for abnormal mood changes. For example, a person may experience mild depressive or hypomanic symptoms that last less than the specified amount for cyclothymia. Additionally, a person might experience depressive episodes, but have symptoms of mood elevation that are too mild or brief to be diagnosed as mania or hypomania.
These instances can be determined to be characteristic of bipolar disorder, but arent classified under the aforementioned types of bipolar disorder.
Read Also: Which Symptom Is Associated With Social Anxiety Disorder
How Is Bipolar Disorder Treated
Treatment can help many people, including those with the most severe forms of bipolar disorder. An effective treatment plan usually includes a combination of the following therapies:
- Psychotherapy .
- Self-management strategies, like education and identifying the early symptoms of an episode or possible triggers of episodes.
- Helpful lifestyle habits, such as exercise, yoga and meditation. These can support, but not replace, treatment.
- Other therapies, such as electroconvulsive therapy in cases that are poorly responsive to medication or where rapid control of symptoms is necessary to prevent harm.
Bipolar disorder is a lifelong condition, so treatment is a lifelong commitment. It can sometimes take several months to years before you and your healthcare provider find a comprehensive treatment plan that works best for you. Although this can be discouraging, its important to continue treatment.
Episodes of mania and depression typically come back over time. Between episodes, many people with bipolar disorder dont have mood changes, but some people may have lingering symptoms. Long-term, continuous treatment can help manage these symptoms.
Again, even though it may be difficult to treat these conditions, its not impossible. Be sure to stay committed to finding a treatment plan that works for you.
What Are The Side Effects Of Bipolar Disorder Medications
Side effects of bipolar disorder medications are common and vary by medication. Its important to talk with your healthcare provider about what you can expect when taking certain medications. Its also important to tell them if youre experiencing side effects.
Never stop taking your medication unless your healthcare provider tells you to do so. Abruptly stopping medication can cause severe side effects and trigger severe episodes.
The most common side effects of bipolar disorder medications include:
- Akathisia feelings of restlessness and agitation with a compelling need to move, rock or pace.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Ptsd
Kahlbaum And Kraepelin: A Comprehensive Description Of Mood Dysfunction
Manic-depressive insanityincludes on the one hand the whole domain of so-called periodic and circular insanity, on the other hand simple mania, the greater part of the morbid states termed melancholia and also a not inconsiderable number of cases of amentia . Lastly, we included here certain slight and slightest colourings of mood, some of them periodic, some of them continuously morbid, which on the one hand are to be regarded as the rudiment of more severe disorders, on the other hand pass without sharp boundaries into the domain of personal predispositionI have become more and more convinced that all of the above-mentioned states only represent manifestations of a single morbid process
In this concept, all possible expressions of mood states exist in one categorical spectrum . This would include together our modern definitions of depressive and manic states, psychosis, mixed states, and the subdromal expressions.
The Concept Of Bipolar Disorder Is Surprisingly Modern

The terms used for the bipolar extremes, melancholy and mania both have their origins in Ancient Greek. Melancholy derives from melas black and chole bile, because Hippocrates thought that depression resulted from an excess of black bile. Mania is related to menos spirit, force, passion mainesthai to rage, go mad and mantis seer, and ultimately derives from the Indo-European root men- mind to which, interestingly, man is also sometimes connected.
The idea of a relationship between melancholy and mania can be traced back to the Ancient Greeks, and particularly to Aretaeus of Cappadocia, who was a physician and philosopher in the time of Nero or Vespasian . Aretaeus described a group of patients would would laugh, play, dance night and day, and sometimes go openly to the market crowned, as if victors in some contest of skill only to be torpid, dull, and sorrowful at other times. Although he suggested that both patterns of behaviour resulted from one and the same disorder, this idea did not gain currency until the modern era.
Interestingly, Kraepelin did not distinguish between people with both manic and depressive episodes and people with only depressive episodes with psychotic symptoms. This distinction dates back only to the 1960s, and is largely responsible for the modern emphasis on bipolarity, and hence on mood elevation, as the defining feature of the disorder.
Neel Burton is author of The Meaning of Madnessand other books.
Also Check: Is Zoloft Used For Anxiety
Symptoms Of Bipolar I Disorder
Manic Episode
A manic episode is a period of at least one week when a person is extremely high-spirited or irritable most of the day for most days, possesses more energy than usual, and experiences at least three of the following changes in behavior:
- Increased or faster speech
- Uncontrollable racing thoughts or quickly changing ideas or topics when speaking
- Distractibility
- Increased activity
- Increased risky behavior
These behaviors must represent a change from the persons usual behavior and be clear to friends and family. Symptoms must be severe enough to cause dysfunction in work, family, or social activities and responsibilities. Symptoms of a manic episode commonly require a person to receive hospital care to stay safe.
Some people experiencing manic episodes also experience disorganized thinking, false beliefs, and/or hallucinations, known as psychotic features.
Hypomanic Episode
A hypomanic episode is characterized by less severe manic symptoms that need to last only four days in a row rather than a week. Hypomanic symptoms do not lead to the major problems in daily functioning that manic symptoms commonly cause.
Major Depressive Episode
A major depressive episode is a period of at least two weeks in which a person has at least five of the following symptoms :
- Intense sadness or despair
- Frequent thoughts of death or suicide
Can Bipolar Disorder Be Prevented
While theres no guaranteed way to prevent someone from developing bipolar disorder, many people successfully manage it with the right treatment and support. A successful strategy may include medication, therapy and other self-help strategies.
If you have a family history of bipolar disorder, its important to be aware of early warning signs, and for friends and family to be aware of them too. Avoid taking substances that can trigger manic or hypomanic episodes such as:
- recreational drugs such as cocaine, ecstasy and amphetamines
- excessive amounts of caffeine
Other ways to prevent relapses or episodes include learning to manage your stress and getting enough sleep.
Also Check: Which Of The Following Is True About Panic Attacks
Improving Treatment Options For Bipolar Disorder
As the labels for psychiatric disorders evolved and changed, so, too, did the range of treatments for those with bipolar disorder, says Gardenswartz. She points to the use of sedatives and barbiturates prior to the 1950s patients were also institutionalized to separate them from others. Prefrontal lobotomies and early forms of electroconvulsive shock therapy emerged as two more radical treatment options.
Starting in the mid-1900s, with the advent of psychiatric and antipsychotic mood-stabilizing medications, patients were able to be viewed more as human beings suffering from illnesses that could be treated, Gardenswartz affirms. Additionally, doctors and the public began toview various health conditions as the separate entities that they were: schizophrenia, ongoing without breaks or relief from symptoms when untreated or bipolar, in which people could typically function normally during periods between this cyclical illness.
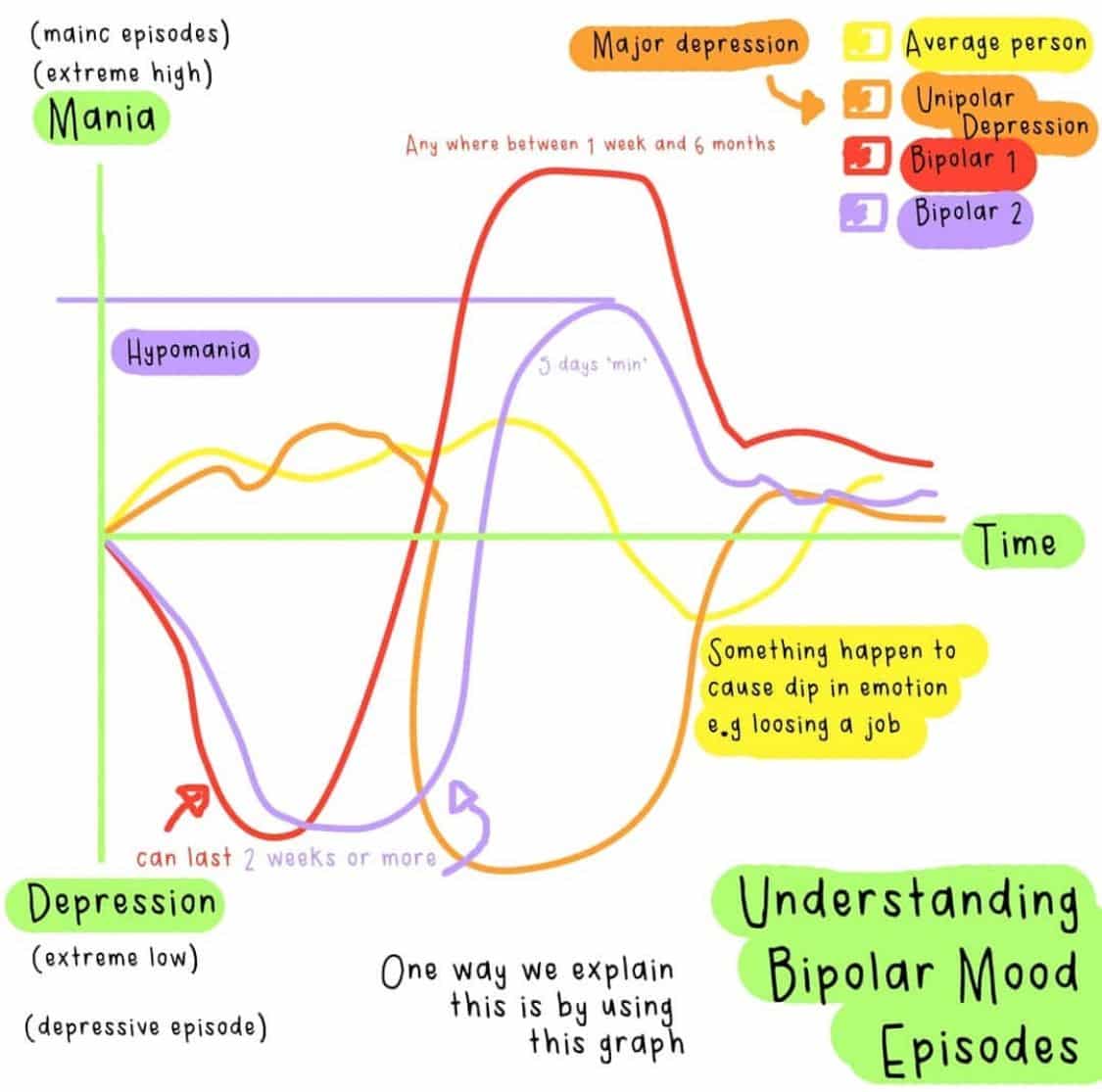
What Are The Different Types Of Bipolar Disorder
There are different types of bipolar disorder.
What is bipolar disorder I disorder?
A diagnosis of bipolar I disorder means you will have had at least 1 episode of mania that lasts longer than 1 week. You may also have periods of depression. Manic episodes will generally last 3-6 months if left untreated. Depressive episodes will generally last 6-12 months without treatment.
What is bipolar II disorder?
A diagnosis of bipolar II disorder means it is common to have symptoms of depression. You will have had at least 1 period of major depression. And at least 1 period of hypomania instead of mania.
What is bipolar I or II disorder with mixed features?
You will experience symptoms of mania or hypomania and depression at the same time. You may hear this being called mixed bipolar state. You may feel very sad and hopeless at the same time as feeling restlessness and being overactive.
What is bipolar I or II disorder with rapid cycling?
Rapid cycling means you have had 4 or more depressive, manic or hypomanic episodes in a 12-month period.
What is bipolar I or II with seasonal pattern?
Seasonal pattern means that either your depression, mania or hypomania is regularly affected in the same way by the seasons. For example, you may find that each winter you have a depressive episode, but your mania doesnt regularly follow a pattern.
There can be some similarities between bipolar I or II with seasonal pattern and another conditional called seasonal affective disorder.
Read Also: How To Help Kids With Anxiety
Staying Active And Eating Well
Eating well and keeping fit are important for everyone. Exercise can also help reduce the symptoms of bipolar disorder, particularly depressive symptoms.
It may also give you something to focus on and provide a routine, which is important for many people.
A healthy diet, combined with exercise, may also help limit weight gain, which is a common side effect of medical treatments for bipolar disorder.
Some treatments also increase the risk of developing diabetes, or worsen the illness in people that already have it. Maintaining a healthy weight and exercising are an important way of limiting that risk.
You should have a check-up at least once a year to monitor your risk of developing cardiovascular disease or diabetes.
This will include recording your weight, checking your blood pressure and having any appropriate blood tests.
Read more information about losing weight and improving fitness
What Are Bipolar Disorders
Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that causes changes in a person’s mood, energy, and ability to function. People with bipolar disorder experience intense emotional states that typically occur during distinct periods of days to weeks, called mood episodes. These mood episodes are categorized as manic/hypomanic or depressive . People with bipolar disorder generally have periods of neutral mood as well. When treated, people with bipolar disorder can lead full and productive lives.
People without bipolar disorder experience mood fluctuations as well. However, these mood changes typically last hours rather than days. Also, these changes are not usually accompanied by the extreme degree of behavior change or difficulty with daily routines and social interactions that people with bipolar disorder demonstrate during mood episodes. Bipolar disorder can disrupt a persons relationships with loved ones and cause difficulty in working or going to school.
Bipolar disorder is a category that includes three different diagnoses: bipolar I, bipolar II, and cyclothymic disorder.
People with bipolar I disorder frequently have other mental disorders such as anxiety disorders, substance use disorders, and/or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder . The risk of suicide is significantly higher among people with bipolar I disorder than among the general population.
You May Like: How Do You Make Yourself Have A Panic Attack