What To Do About Catastrophizing:
Feeling Low Or Depressed
Its very common to feel sadness about stroke and the changes to your life. You might also feel low, which can include feeling sad or angry, like you cant cope, and not enjoying things like you usually do.
A low mood can happen to anyone from time to time. But if you feel this way for a long period, and its affecting your ability to enjoy life, it could be a sign of depression.
Depression is common after a stroke, and we know that at least one-third of stroke survivors will have some form of depression within the first year. But you may not have it straight away. It can appear at any point, perhaps months or even years down the line.
It can also return over and over again. So its important to know what to look out for and how to get help and support if you need it.
Signs of depression
Depression affects people in different ways, but these are some of the more common signs that could last for some time:
-
Feeling sad or down in the dumps.
-
Feeling worthless, helpless or guilty.
-
Feeling hopeless or desperate.
-
Not going out or avoiding other people.
-
Finding it difficult to concentrate or make decisions.
-
Having problems sleeping or sleeping too much.
-
Losing your appetite or eating too much.
-
Losing interest in sex.
How to get help with low mood and depression
-
Talk to your stroke nurse or GP. They can help you find out whats wrong, and get any treatment you need.
How To Get Rid Of The Stress
Here are some habits you can implement in your day-to-day life to ensure that you arent too stressed!
1. Exercise!People who exercise regularly are less likely to experience anxiety as against people who dont. Exercise helps release endorphins, which improve your mood and act as natural painkillers. Exercising regularly can also help regulate your sleep patterns, and boost your confidence by improving your overall appearance!
2. Maintain A Healthy Diet!Make sure your diet includes a healthy mix of green leafy vegetables, water, and less caffeine. High doses of coffee, tea, chocolate and energy drinks can increase anxiety! Test your sensitivity to caffeine before cutting down on it entirely.
3. Laugh A Lot!Laughing can help relieve tension by relaxing the muscles. In the long term too, laughter can improve your immune system and mood.
A study among people with cancer found that people in the laughter intervention group experienced more stress relief than those who were simply distracted.
4. Spend Time With Family and Friends!Having a rich social life can alleviate stress. Spending time with the people you love releases oxytocin that is a natural stress reliever!
5. Learn To Say No!Not all factors causing stress are within your control. But, you can always try to be selective of the responsibilities you take on, especially when it comes to work. Taking on more than you can handle, and then trying to juggle it all successfully, can cause a lot of stress.
Don’t Miss: Does Schizophrenia Skip A Generation
What Can I Do About The Way I Feel
1. Get some help
Theres a lot to cope with when youve had a stroke, so dont be afraid to ask for some help. If youre worried about the way youre feeling, or you think you may be experiencing some of the problems weve described, then you need to speak to your GP, stroke nurse or therapist about it. They will be able to tell you about the support thats available. Emotional problems are often missed by doctors and sometimes it can be difficult to get them taken seriously. However, you need to trust that you know yourself better than they do, so dont be afraid to keep asking to get the support you need. If you dont think youre getting the right support from your GP or stroke team, then contact our Stroke Helpline.
2. Talk to someone about it
Talking about the way youre feeling with someone who understands can really help. You may want to do this with a counsellor or therapist or it could be a family member or friend whoever you feel most comfortable talking to. Many people also find support groups helpful, because you can talk about your problems with people who are going through the same thing. Stroke clubs and groups are a good way to meet other stroke survivors and get advice and support, but there are all sorts of groups out there.
I wasnt able to cope with it all on my own. Talking to my doctor and getting some counselling was the best thing I ever did.Craig
3. Stay informed
4. Take it easy on yourself
5. Find new goals
6. Be as active as you can
You Have Catastrophic Thoughts
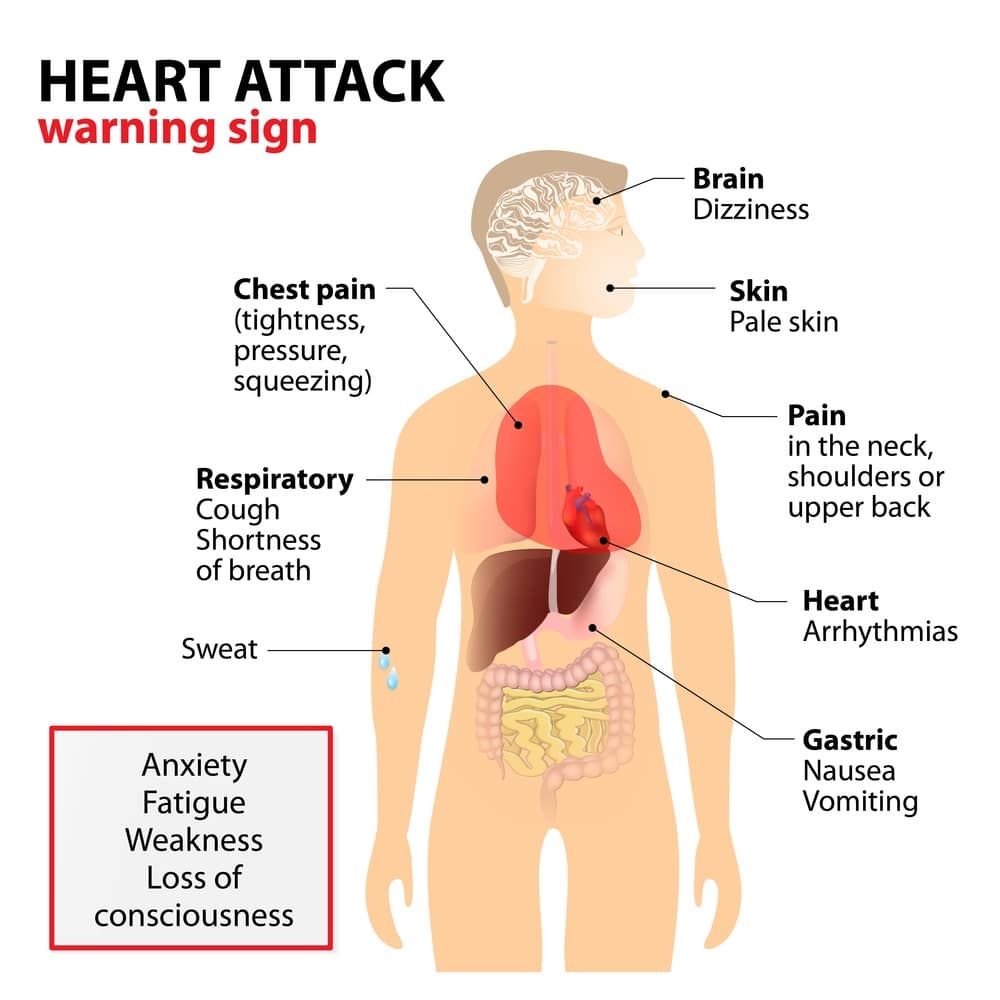
Many people have fearful thoughts during their attacks, and it is common to think you are having a heart attack, stroke, or “going crazy.” Some people fear they will lose control or will faint during one. Others fear that an attack will never end.
When you have scary thoughts about panic attacks, it keeps you on alert and makes the attacks more likely to occur. In addition, these scary thoughts during an attack can cause even more anxiety, making them even more intense.
Read Also: A Road Back From Schizophrenia A Memoir
Panic Attack Vs Heart Attack: How To Tell The Difference
Heartmail
Your heart suddenly begins racing. You feel pain in your chest and you are short of breath.
Are you having a heart attack? Or could it be a panic attack?
“Any of these symptoms can be extremely frightening,” says Patricia Tung, MD, of Arrhythmia Services at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Although they share a number of similarities, the two conditions result from very different disease processes. Panic attacks arise when stress hormones trigger the body’s “fight or flight” response, often resulting in racing heart, chest pain and shortness of breath.
In the case of a heart attack, a blockage in a coronary artery may result in the same symptoms. “Chest pain, rapid heartbeat and breathlessness may result when an insufficient amount of blood reaches the heart muscle,” says Tung.
One of the key distinctions between the two is that a heart attack often develops during physical exertion, whereas a panic attack can occur at rest.
A heart attack is more likely to develop when the work load of the heart increases, for example while a person is shoveling snow or running up the stairs, especially in people who do not routinely engage in physical exertion.
Another difference is duration: Panic attacks tend to gradually subside and resolve on their own within about 20 minutes. A heart attack, however, will often continue and may worsen over time.
When Your Heart Skips a Beat
Heart Attack
Can An Anxiety Attack Feel Like A Stroke
January 16, 2015 by Jenny
Hi. Its Jenny at AnxietyBoss.com. Our question today comes to us from Scott in Reserve, Montana. Can an anxiety attack feel like a stroke?
Generally, the symptoms of a panic attack can feel more like a heart attack than a stroke. Anxiety attacks, also known as panic attacks, are an acute activation of your bodys alarm system in the absence of a threat. We are all wired with what is called the flight-fight-freeze system. If there is a threat to our survival or something in our environment or our thoughts which we believe is a threat to our survival, we will experience dilated pupils, dry mouth, sweating, flushed or pale skin, a rapid heartrate, elevated blood pressure, hyperventilating, muscle tension, including tightness and discomfort in the chest and stomach, tingling or numbness in the hands or feet, and also the urge to withdraw from a threat, engage the threat, or we may lock up and be unable to move.
Many people who experience panic attacks go to or are brought by ambulance to an ER, or emergency room, because they believe they are having a cardiac event or a heart attack. The symptoms of a panic attack overlap the symptoms of a heart attack, but the cause is very different. A panic attack is your bodys alarm system activated in the absence of a real threat like the smoke alarm that keeps going off when youre cooking burgers on the stovetop. You know the house is not on fire, but the smoke alarm is insisting otherwise.
Also Check: Is Schizophrenia A Mental Disability
Emotional And Personality Changes After Stroke
If you have suffered a stroke, it is common to have changes in your mood and personality. Some emotional changes may be caused by damage to the brain from the stroke, but you can also experience a range of emotions, as well as depression, as a response to the change in your situation.Depression is common in the first year after a stroke, but it is particularly common in people who have trouble understanding, finding words and communicating after a stroke.The symptoms of depression include:
- feeling sad most of the time
- losing a sense of pleasure in activities you used to enjoy
- losing interest in food or eating too much
- losing weight or gaining weight.
After a stroke, people can also have anxiety either on its own or with depression. Anxiety is more than just feeling stressed. People who are anxious can:
- find it difficult to calm down
- feel worried most of the time
- feel frightened by intense panic
- have recurring thoughts that increase their anxiety
- avoid situations that can cause them to be anxious.
Personality and behavioural changes are also common and can include:
- irritability reacting to things that would normally not annoy you
- aggressiveness physical or verbal
- apathy or lack of motivation
- repetitive behaviour becoming stuck in the repetition of words or behaviours
- disinhibition tendency to say and do things that are socially inappropriate
- impulsiveness can also include sudden and socially inappropriate actions.
Why Do I Feel Different
A stroke is sudden and shocking. It can affect every part of your life. Its a lot to deal with, so its likely to have an effect on your emotional wellbeing.
Everyones experience of stroke is unique, but for many people it feels like theyve lost the life they had before. Feelings of shock, denial, anger, grief and guilt are normal when youre faced with such a devastating change. Dealing with them can be hard, and everyone does it in their own way.
Not only are you going through all these emotions yourself, but the people around you might be too. Often people dont want to admit how theyre feeling and put on a brave face. So the people around you may not realise what youre going through.
Others may assume that everything is fine, which can make it hard to tell them if its not. Communication problems may mean that you cant explain how youre feeling, even if you want to.
All of this can be hard to cope with. But if you dont acknowledge the way youre feeling and find things that can help you deal with it, these emotions can become overwhelming and lead to problems. Emotional problems can also affect your recovery, if you arent feeling motivated to take part in therapies, for instance.
Grief and loss after a strokeA stroke can come with feelings of loss and grief. Its a major life event, and for many people it leads to sudden changes at home, at work and in relationships. A stroke survivor might feel shock, anger and sadness at the changes and losses in their life.
Recommended Reading: Do Nurses Suffer From Ptsd
After Stroke Anxiety Is Common In Women
Please note: This article was published more than two years ago, so some information may be outdated. If you have questions about your health, always contact a health care professional.
Angie Read Doyal was unsure if she’d be the same after her stroke. So, when she felt ready to return to work after only seven weeks of intense physical, speech and occupational therapy, she was confident.
But that self-assurance quickly was undermined by severe anxiety, panic attacks and depression.
New research adds to the evidence that Doyal’s experience is all too common.
A new study finds that one in four stroke survivors report experiencing moderate to severe anxiety two to eight weeks after their stroke, with incidence more common in women and those who are single, divorced or widowed.
“We believe there is a bi-directional relationship between stroke and anxiety,” said the study’s lead researcher Jennifer Beauchamp, a researcher at the University of Texas Health Institute for Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases in Houston. The findings were reported this week at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference in Honolulu.
The researchers analyzed the health records of 194 ischemic stroke survivors. An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel to the brain is obstructed, cutting off blood flow. It accounts for about 87 percent of the nearly 800,000 strokes that occur in the United States each year.
Angie Read Doyal experienced debilitating anxiety after her stroke.
How To Tell The Difference Between Anxiety And A Mini Stroke
Only a doctor can tell you with 100% certainty if what you’ve experienced is stroke-like symptoms from an anxiety attack or an actual stroke. But generally there are several ways to tell the difference between the two, including:
As you can see, the differences are subtle. But they are definitely there, and if you are willing to think about the attack logically you’ll often find that it’s clear what occurred. However, it is critical to rule out a cerebrovascular event first.
Read Also: Are There Different Types Of Depression
Anxiety And The Development Of Heart Disease
Its my view and my personal clinical experience that anxiety disorders can play a major role in heart disease, says McCann. I believe that a really careful look at anxiety would reveal the ways it can severely impact heart disease, both as a contributing factor and as an obstacle in recovery.
A natural reaction to a sudden heart attack can be similar to post-traumatic stress disorder:
- Youre likely to be shocked by your near-death experience and extremely hesitant to do the things you used to do.
- You might constantly relive the life-threatening event, and avoid the activity or place associated with the heart attack.
- Recurring anxious thoughts may impede your ability to get regular sleep.
- Your thoughts about what lies ahead may be extremely negative and cause a drastically foreshortened outlook of the future.
Identifying Anxiety Disorders After Stroke
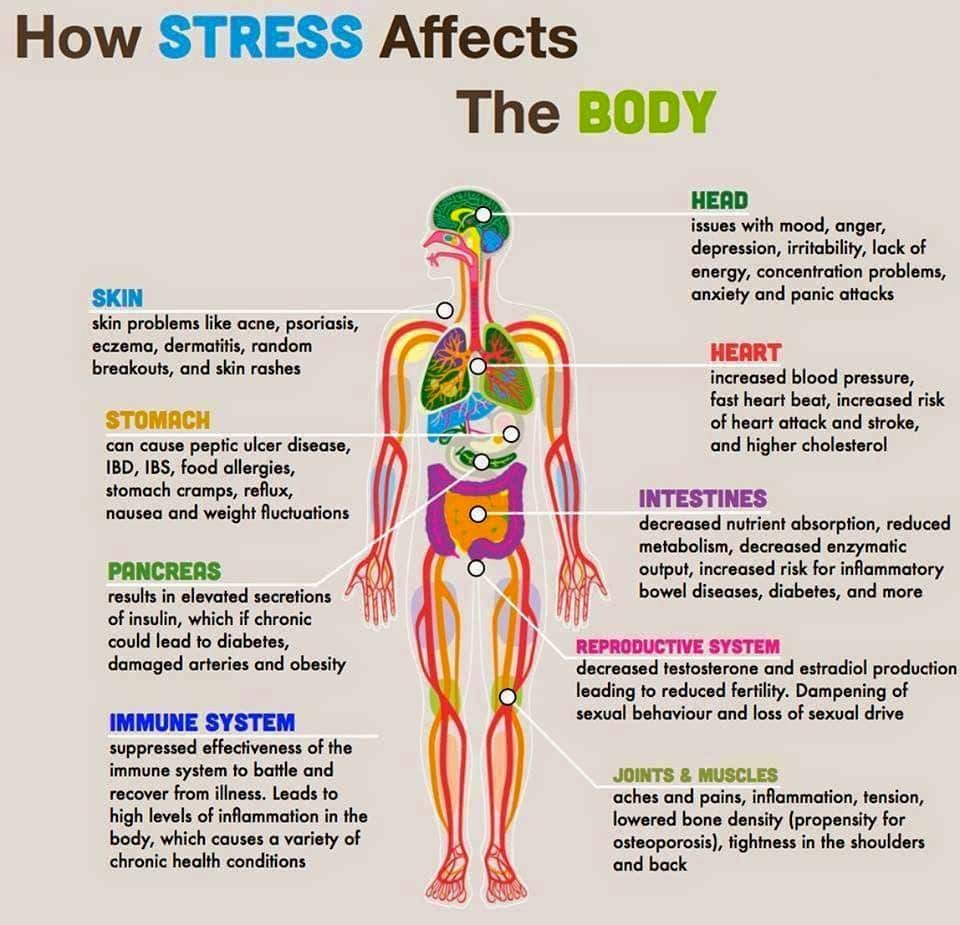
Anxiety disorders cause more than just a constant feeling of worry, even though that is part of it.
Instead, what distinguishes anxiety disorders from normal anxiety is their intensity. Everybody feels nervous at times, but for someone with an anxiety disorder after stroke, this nervousness overwhelms them. It can even stop them from doing the things they love.
Other signs that you might have an anxiety disorder include:
- Feeling irritable
- Constant fatigue and sleep problems
- Persistent thoughts about the things that worry you
- Continual feelings of impending danger, with physical sensations such as restlessness and rapid heart rate
Most anxiety disorders after stroke are caused bypsychological and biological changes in the brain. This means they may requiremore complex treatment approaches.
You May Like: Can A Bipolar Person Own A Gun In Texas
American Heart Association News Stories
American Heart Association News covers heart disease, stroke and related health issues. Not all views expressed in American Heart Association News stories reflect the official position of the American Heart Association. Statements, conclusions, accuracy and reliability of studies published in American Heart Association scientific journals or presented at American Heart Association scientific meetings are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the American Heart Associations official guidance, policies or positions.
Copyright is owned or held by the American Heart Association, Inc., and all rights are reserved. Permission is granted, at no cost and without need for further request, for individuals, media outlets, and non-commercial education and awareness efforts to link to, quote, excerpt or reprint from these stories in any medium as long as no text is altered and proper attribution is made to American Heart Association News.
Other uses, including educational products or services sold for profit, must comply with the American Heart Associations Copyright Permission Guidelines. See full terms of use. These stories may not be used to promote or endorse a commercial product or service.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Panic Attack
A panic attack is a sudden attack of overwhelming fear or anxiety. Panic attacks are not life-threatening, but they interfere with your quality of life and mental well-being.
People who have regular or frequent panic attacks may have a panic disorder, a type of anxiety disorder. But an isolated panic attack can happen to anyone, even without a panic disorder diagnosis.
- Feeling of squeezing or, says Dr. Miller, like an elephant sitting on your chest.
- Achy or burning sensation, like heartburn.
Panic attacks often cause:
- Sharp or stabbing pain .
- Heart racing or chest discomfort thats hard to describe.
The triggers
Heart attacks tend to happen after physical strain or exertion a sign not found in panic attacks. A heart attack might happen after shoveling snow or walking up a long flight of stairs, Dr. Miller says. But you wouldnt have a panic attack after exercise unless there was an emotional stress trigger with it.
But what if the symptoms hit you at night? Both panic attacks and heart attacks can wake you from sleep. But theres a key difference: People who have nighttime, or nocturnal, panic attacks usually have daytime panic attacks, too.
So if you wake up with chest pain or other symptoms, and you dont have a history of panic attacks, that might be a sign of a heart attack.
How long it lasts
Panic attack symptoms last a few minutes or up to an hour. Then, the symptoms disappear, and you feel better. But a heart attack wont let up.
Also Check: Can Low Testosterone Cause Depression