Research Shows Cellular Clean
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Schizophrenia Center sampled the smell neurons pictured here, from individuals with and without schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Through examining these cells, neuropsychiatrist Koko Ishizuka, in collaboration with Kyoto University, found a protein that is usually cleared out by the cellular waste management. Her work suggests that the link between these brain disorders and the cellular clean-up system deserves a closer look.
-
Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder. It often runs in families and can cause troubling symptoms.
-
It’s caused by a chemical imbalance and other changes in the brain.
-
Symptoms include hearing voices, feeling that people are out to get you, and having false beliefs that are not based in reality.
-
These symptoms can make it very hard to function in the world and take care of yourself.
-
Treatment includes antipsychotic medicines, support services, and a healthy lifestyle.
Possible Causes Of Bipolar Disorder
The cause of BPAD is uncertain, but we know more today than we did a decade ago.
Chemical ImbalanceThree brain chemicals norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine are involved in psychiatric disorders. Norepinephrine and serotonin are linked to mood disorders, such as depression and BPAD. Dopamine, is more closely linked to psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia. However, since these disorders have a number of symptoms in common, all three chemicals are likely involved in different phases of BPAD.
GeneticsMany studies have shown that BPAD runs in families, so relatives of persons diagnosed with BPAD or depression are more likely to have the disorder than the general public.
TriggersThe onset of BPAD is often triggered by a significant life stressor . These stressors do not cause BPAD, but can trigger the disorder to become active. Trigger events can also cause a person with BPAD to experience a relapse .
Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Because early treatment is thought to be most effective for schizophrenia, researchers are continually looking for ways to detect it before symptoms fully develop.
Hallucinations and delusions are the hallmark symptoms of psychosis and must be present for a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Although psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions are the most common aspects that present in schizophrenia, there are several symptoms involved. People with schizophrenia experience:
- Positive symptoms: The appearance of things that should not be there, like hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder .
- Negative symptoms: The absence of things that should be there, like loss of motivation, disinterest or lack of enjoyment in daily activities, social withdrawal, difficulty showing emotions, and difficulty functioning normally.
- Cognitive symptoms: Problems with attention, concentration, and memory.
Assessment of these symptoms is typically how schizophrenia is diagnosed, but the discovery of brain differences in people with schizophrenia could potentially mean an earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
While schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in the late teens to early thirties, subtle changes in cognition and social relationships may be noticeable before the actual diagnosis, even during adolescence. Often these early symptoms are apparent years before a person is diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Some of these early symptoms include:
You May Like: How To Get Over Ptsd Triggers
What Causes Schizophrenia Genetics Environment Brain Chemistry Brain Structure
Schizophrenia is a severe disease in which individuals are plagued with hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, as well as social dysfunction. Although an exact cause of the disease has not yet been discovered, researchers are aware that a number of factors may contribute to its development. Genetics, environment, brain structure, and brain chemistry can each be analyzed and broken down separately.
Is It Possible To Recover From Schizophrenia
Many people who live with schizophrenia have recovery journeys that lead them to live meaningful lives.
Recovery can be thought of in terms of:
- clinical recovery, and
- personal recovery.
What is clinical recovery?
Your doctor might have talked to you about recovery. Some doctors and health professionals think of recovery as:
- no longer having mental illness symptoms, or
- where your symptoms are controlled by treatment to such a degree that they are not significantly a problem.
Sometimes this is called clinical recovery.
Everyones experience of clinical recovery is different.
- Some people completely recover from schizophrenia and go on to be symptom free.
- Some who live with schizophrenia can improve a great deal with ongoing treatment.
- Some improve with treatment but need ongoing support from mental health and social services.
What is personal recovery?
Dealing with symptoms is important to a lot of people. But some people think that recovery is wider than this. We call this personal recovery.
Personal recovery means that you can live a meaningful life.
What you think of as being a meaningful life might be different to how other people see it. You can think about what you would like to do to live a meaningful life and work towards that goal.
Below are some ways you can think of recovery.
What can help me recover?
You may want to think about the following questions.
The following things can be important in recovery.
You May Like: What Is The Phobia Of Throwing Up
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Bipolar 2
Dopamine And Human Evolution
The role of dopamine in human evolution has hitherto received little theoretical attention. It is still unclear to what extent dopaminergic expansion in hominin evolution was due to genetic adaptations or epigenetic factors. Dopamine has expanded throughout primate and hominin evolution and that dopamine is especially concentrated in the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in higher order functioning. The dopaminergic hypothesis contends that climatic changes occurring in sub-Saharan Africa during the Pliocene and Pleistocene periods, which resulted in increases of the Savannah belt expanded hominin locomotory range. It is also speculated that some human groups ventured to the more habitable African southern coast leading to dietary changes that aided dopaminergic expansion . Dopamine increase may have also been linked with a concomitant elevation in thyroid hormone production. Higher T4 found in may have represented an early endocrinological difference between humans and other primates . In humans, T4 concentration is associated with tyrosine conversion to dopa deficiencies of T4 concentrations are linked with various neurological impairments .
What Are The Symptoms Of A Chemical Imbalance In The Brain
What are the symptoms of a chemical imbalance in the brain? Scientists in the late 1950s first proposed the idea that mental health conditions are caused by a chemical imbalance in the brain. Research at the time had focused on the role that chemicals in the brain play in depression and anxiety.
How are scientists proving the chemical imbalance theory?
Now, UC San Diego researchers may have found a way to prove this commonly-held theory of imbalance. Using a model derived from stem cells, the researchers showed how the brain cells of patients with schizophrenia secrete higher amounts of three neurotransmitters.
What causes schizophrenia in both men and women?
Schizophrenia is caused by a chemical imbalance and other changes in the brain. It tends to run in families, but the environment may also play a role. While it affects men and women the same, symptoms tend to start earlier in men than in women. Its rare in childhood.
Also Check: What Is The Phobia Of Holes Called
What Is The Dopamine Hypothesis Of Schizophrenia
The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia states that too much dopamine in the brain or too little could directly contribute to symptoms of schizophrenia, particularly those of psychosis such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thinking.
This theory was introduced decades ago due to an observational link between administering dopamine-blocking medications and an improvement of symptoms.
Experts naturally assumed that the medications worked because they reversed an underlying condition of the disorder.
In other words, if blocking dopamine helped, experts felt it meant that there was too much to begin with.
Keep Learning And Find Support
The most important thing is to keep learning about schizophrenia and find a safe place to ask questions and feel supported. We offer a free private Facebook group for families with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. You can also so that you can receive our latest blog posts.
Here are some additional articles you might find helpful:
Read Also: What Causes Sudden Panic Attacks
How Is Schizophrenia Prevented
Because the cause of schizophrenia remains unknown, theres no known way to prevent the disorder from occurring in the first place. Once schizophrenia has been diagnosed and an effective treatment plan is in place, however, relapses of symptoms can often be successfully prevented.
Its important to continue taking medications as directed by your healthcare providers, even after your symptoms have diminished. If the medication is causing side effects, it is much better to work with your provider to find a better solution than to simply stop taking the medication on your own.
*The medical information we gather and publish is vetted and intended to be up to date, accurate and express a spectrum of recognized scientific and medical points of view. The information comes from a nucleus of informed scientists, medical doctors, peer-reviewed scientific journals and the National Institute of Health. Please note, differing points of view among scientists and physicians are common. Every effort is employed to ensure the accuracy of these different points of view. That notwithstanding, it is incumbent on persons using this information to consult with his/her physician before reaching any conclusions. Our medical information and publications are not intended to be a substitute for consultation with ones physician.
Modelling Psychosis: The Use Of Animal Models
Potentially, the most useful avenue for animal models to assist in schizophrenia research will be identifying convergent aetiological pathways. Understanding which neurotransmitter systems and brain regions are most involved may help to identify the core neurobiological features of schizophrenia. For example, changes in dopaminergic systems are observed in animal models after manipulation of factors based on schizophrenia epidemiology, , genetics, pharmacology and related hypotheses. These include changes in early dopamine specification factors, , sensitivities to psychostimulants,,, and alterations in dopamine neurochemistry,,, . Evidence of subcortical dopaminergic hyperactivity or sensitivity in animal models is proposed to represent the face validity for psychosis in patients. The most commonly used behavioural assessments of positive symptoms in animal models include enhanced amphetamine-induced locomotion and deficits in prepulse inhibition . These tests are widely used because they are relatively simple to perform. However, we propose that given current knowledge of the neurobiology in schizophrenia, they have outlived their usefulness as measures of positive symptoms.
Read Also: Can You Have Anxiety Without Depression
Link Between Brain Chemical Cognitive Decline In Schizophrenia Demonstrated
- Date:
- University of California – Davis – Health System
- Summary:
- In one of the first such studies involving human patients with schizophrenia, researchers have provided evidence that deficits in a brain chemical may be responsible for some of the debilitating cognitive deficits — poor attention, memory and problem-solving abilities — that accompany the delusions and hallucinations that are the hallmarks of the disorder.
In one of the first such studies involving human patients with schizophrenia, researchers at UC Davis have provided evidence that deficits in a brain chemical may be responsible for some of the debilitating cognitive deficits — poor attention, memory and problem-solving abilities — that accompany the delusions and hallucinations that are the hallmarks of the disorder.
The study, published online March 10 in the Journal of Neuroscience, suggests an important avenue of inquiry for improving cognitive function in the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from schizophrenia, according to Jong H. Yoon, an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at UC Davis Health System and the study’s lead author.
Schizophrenia is characterized by psychosis — abnormalities in the perception or expression of reality. Sufferers may experience visual or auditory hallucinations and have paranoia, delusions and disorganized speech and thinking. But they also experience profound cognitive difficulties that interfere with daily functioning.
Story Source:
Debunking The Two Chemical Imbalance Myths Again

Moving toward a bio-psycho-sociocultural model of major depression.
& copy efks/AdobeStock
For reader feedback, see Chemical Imbalance? Readers Respond.
Dr Pies is Professor in the psychiatry departments of SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY and Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston. He is Editor in Chief Emeritus of Psychiatric Times .
A little learning is a dangerous thing. – Alexander Pope1
Like the legendary Count Dracula, who could be killed only by driving a stake through his heart, some myths seem almost immortal. For more than 8 years now, I have tried to drive a stake through the heart of two myths regarding the so-called chemical imbalance theory-but with only limited success, as a recent piece in the New Yorker brought home to me.2-5
Ironically, anti-psychiatry groups are quite right in heaping scorn on the chemical imbalance theory of mental illness, but not for the reasons they usually give. . The fact is, there could never have been a scientifically based, chemical imbalance theory of mental illness, because a genuine theory requires an integrated network of well-supported, interlinked hypotheses. And yes, the frequently ignored distinction between a theory and a hypothesis is crucial. It is the key to understanding why claims by antipsychiatry bloggers regarding the chemical imbalance theory nearly always crash and burn.
The theory that never was
Psychiatrists questioned the chemical imbalance theory
The bio-psycho-sociocultural model
Don’t Miss: How To Get Help For Depression And Anxiety
What Brain Chemical Causes Schizophrenia
Research suggests schizophrenia may be caused by a change in the level of 2 neurotransmitters: dopamine and serotonin. Some studies indicate an imbalance between the 2 may be the basis of the problem. Others have found a change in the bodys sensitivity to the neurotransmitters is part of the cause of schizophrenia.
What chemical is increased in schizophrenia?
Scientists have long known that dopamine is involved in the development of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. People with schizophrenia have an overactive dopamine system, releasing more dopamine than healthily people.
Does Too Much Dopamine Cause Schizophrenia
Increased activity of the mesolimbic pathway is related to positive symptoms of schizophrenia . This means that increasing the activity of dopamine receptors in this brain system could theoretically reduce delusions and hallucinations.
A closely related idea is that by blocking post-synaptic dopamine receptors, scientists can reduce the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia.
As mentioned previously, this is what most modern medications do: they block post-synaptic dopamine receptors in order to reduce psychotic symptoms. Unfortunately, when scientists block all available dopamine receptors they also produce a number of debilitating side effects such as extrapyramidal symptoms and tardive dyskinesia.
Also Check: How Does Exposure Therapy Work For Ptsd
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
To diagnose this disease, your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. You may also have a physical exam. You may also have lab tests to rule out other conditions.
Mental health care professionals diagnose and treat this illness. They often interview family members. This helps the healthcare team get a complete picture of the symptoms.
Researchers Are Working Hard To Understand Its Biology
In 2015, almost three million adults suffered from schizophrenia, a severe and often incapacitating disorder of the brain characterized by periods of psychosis, hallucinations, delusions, distortions of sensory perception, problems with some types of thinking, and social withdrawal. Though we can describe its symptoms, and doctors have some medications that are helpful for some people living with schizophrenia, the nature of this disorder is not well understood.
In this post, I will do my best to use my lay brain to summarize the findings of a few of these studies. I include sources for each study in references so that readers may look at more complete reports for themselves.
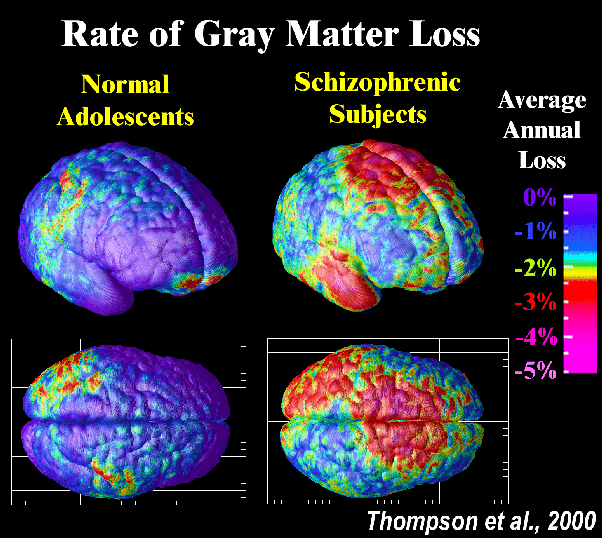
One of the most promising recent studies, conducted by the Broad Institute in Boston and reported in 2016, looked at the genomes of 65,000 people and for the first time identified a particular gene closely connected to schizophrenia. This research showed that an increase in the risk of schizophrenia by specific variants in C4, a gene involved in pruning the brains synapses, or points where neurons communicate. This is supported by the facts that many people first experience symptoms of schizophrenia during adolescence, when synaptic pruning is very active, and the brains of people with schizophrenia often have fewer than usual synapses.
References
You May Like: Does Bipolar Disorder Get Worse With Age
Don’t Miss: What Was Ptsd Called In The Past
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
Managing schizophrenia is a lifelong process. It can’t be cured. But symptoms can often be managed with medicine and therapy. Often, more than 1 method is needed. Types of treatment that may be helpful include:
-
Antipsychotic medicines. These are the main medicines used to reduce the most troubling symptoms such as delusions and paranoia.
-
Other medicines. These may include antidepressants or other mood stabilizers.
-
Therapy. Individual and family therapy .
-
Training. These may include learning social skills, job skills, or structured activity.
-
Self-help and support groups.
Early treatment and supportive services helps affected people live productive lives. It’s very important to take medicines exactly as prescribed and to keep taking them even if you feel better. Many people may still have some symptoms, even with treatment. At times, symptoms may get worse and treatment will need to be adjusted.
Always see your healthcare provider for more information.
What Is A Chemical Imbalance
A chemical imbalance occurs when the substances that help the body function the way it should become out of balance. Either too much or too little of these substances can cause a chemical imbalance that affects the bodys ability to function normally.
These chemical imbalances are often linked to health conditions. For example, a hormonal imbalance occurs with polycystic ovary syndrome , which in turn puts a person at risk for other conditions such as type 2 diabetes and infertility.
While too much or too little of these substances anywhere in the body is considered a chemical imbalance, the term chemical imbalance is usually associated with chemical imbalances in the brain and their potential effect on mental heath and related conditions.
Also Check: Which Is A Cardiac Complication Of An Eating Disorder