Finding Mental Health Services
There are a few different options available for clinical treatment. Your choice will depend on cost, severity of your symptoms and convenience, but not all services are available everywhere. For people in rural and remote areas, treatment options can be reduced, involve long travel, or alternatively can be delivered through telehealth services. Ask your GP for advice about the best options available for you.
Comparing Delusions And Obsessions
Scientists have long studied the relationship between OCD and schizophrenia, as a great many of their symptoms overlap. Doctors can often differentiate the disorders by the delusions seen in schizophrenia and the obsessions seen in OCD.
- Delusions are defined as false thoughts that are held to be true despite evidence to the contrary. Often times, the affected person will feel that they possess special powers, is being persecuted, or has an extraordinary connection to events, people, or objects that dont exist. Moreover, persons experiencing a delusion will usually not recognize the irrationality of their thoughts.
- Obsessions, by contrast, are similar in that they are also irrational but are more related to concepts of uncleanliness, disorder, or asymmetry. And, unlike schizophrenic delusions, persons experiencing an obsession are usually aware of their irrationality and are simply unable to control it.
While this is not always the case, of course, it does provide a framework by which psychiatrists can individually identify and treat the two co-existing conditions.
Read Also: How To Get A Service Dog For Anxiety And Ptsd
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
You May Like: Definition Of A Phobia
You May Like: What Does Ptsd Look Like
What Conditions Fall Under The Schizophrenia Spectrum
According to the American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition , the disorders in the schizophrenia spectrum are:
- Schizoaffective disorder.
- Catatonia is a syndrome that can include a lack of movement, unusual movements, unusual repetitive behaviors, not speaking and social withdrawal. It can also complicate schizophrenia, as well as other psychiatric and medical conditions.
- Other schizophrenia spectrum disorders . This diagnosis allows healthcare providers to diagnose unusual variations of schizophrenia.
What Kind Of Symptoms Might People With Schizophrenia Have

People with schizophrenia may have a number of psychotic symptoms. These symptoms can come and go in phases, or they can happen only once or twice in a lifetime. When the illness begins, psychotic symptoms are usually sudden and severe.
During psychotic phases, the person may still understand parts of reality. He or she may lead a somewhat normal life, doing basic activities such as eating, working and getting around. In other cases, the person may be unable to function. Symptoms during psychotic phases include:
- Seeing, hearing, feeling or smelling things that are not real .
- Having strange beliefs that are not based on facts . For example, the person may believe that people can hear his or her thoughts, that he or she is God or the devil, or that people are putting thoughts into his or her head.
- Thinking in a confused way, being unable to make order out of the world, shifting quickly from one thought to the next.
- Having emotions, thoughts and moods that do not fit with events.
People with schizophrenia also may:
- Have a lot of energy or be overly active, or become catatonic, a state in which the body becomes rigid and cannot be moved.
- Talk in sentences that do not make sense.
- Not wash or groom.
Recommended Reading: Can Bipolar Disorder Cause Panic Attacks
The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
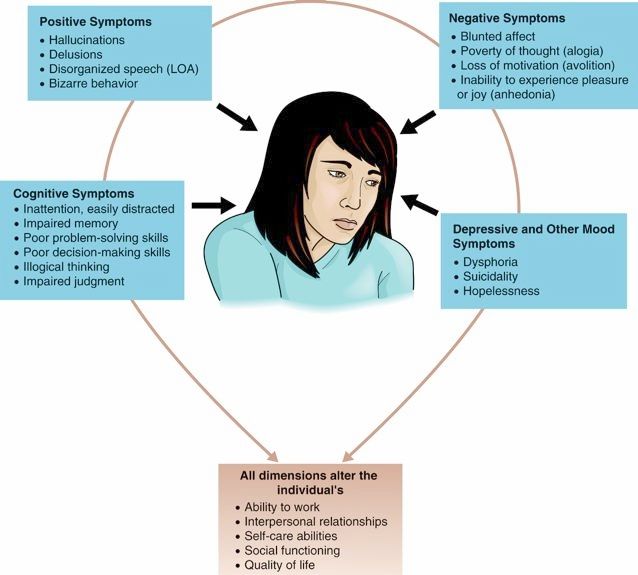
As you can see from the DSM criteria, no single symptom positively identifies schizophrenia. On top of that, an individuals symptoms can change over time. The symptoms of schizophrenia are generally divided into three categories: positive, negative and cognitive symptoms.
Positive symptoms are also known as psychotic symptoms because the person has lost touch with reality in certain ways. The term positive symptoms refers to mental experiences that are added on to a persons usual experiencetypically these are hallucinations and delusions.
- Hallucinations cause a person to hear voices inside or outside their heads or, less commonly, see things that do not exist.
- Delusions occur when someone believes ideas that are clearly false, such as that people are reading their thoughts or that they can control other peoples minds.
Negative symptoms do not refer to negative thinking, but rather reflect symptoms that indicate reduction of a capacity, such as motivation. Negative symptoms often include emotional flatness or lack of expressiveness, an inability to start and follow through with activities, speech that is brief and lacks content and a lack of pleasure or interest in life. Difficulties with social cues and relationships are common. These symptoms challenge rehabilitation efforts, as work and school goals require motivation as well as social function. Negative symptoms can also be confused with clinical depression.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed Dsm
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that deeply affects people. Because a correct schizophrenia diagnosis can improve someones quality of life, its important that it be made as soon as possible after the symptoms of schizophrenia appear.
Currently, no tests can provide a schizophrenia diagnosis. To determine whether someone has the disorder, doctors follow established criteria for a schizophrenia diagnosis.
Also Check: How Many Kids Have Eating Disorders
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
In some people, schizophrenia appears suddenly and without warning. But for most, it comes on slowly, with subtle warning signs and a gradual decline in functioning, long before the first severe episode. Often, friends or family members will know early on that something is wrong, without knowing exactly what.
In this early phase of schizophrenia, you may seem eccentric, unmotivated, emotionless, and reclusive to others. You may start to isolate yourself, begin neglecting your appearance, say peculiar things, and show a general indifference to life. You may abandon hobbies and activities, and your performance at work or school can deteriorate.
Other Considerations In Diagnosing Schizophrenia
The DSM-5 includes other things that can help determine schizophrenia. Theyre not necessary diagnostic criteria, but their presence points to this serious mental illness.
- Inability to understand someones intentions
- Thinking insignificant things are highly, personally meaningful
In addition to these, people with schizophrenia often experience what is known as neurological soft sign, subtle abnormalities that arent severe enough to fit into any disorder but are problematic and indicative of a bigger problem, like schizophrenia. They can include:
- Coordination problems
- Left-right confusion
- Difficulty with complex movement
To diagnose schizophrenia, professionals examine all of the symptoms and features that are present . They also must look at what is not present.
Also Check: Can You Develop Bipolar Disorder Later In Life
How Do Doctors Test For Schizophrenia
There are no laboratory tests to diagnose schizophrenia. Instead, a doctor will perform a physical evaluation, review your medical history, and may use various diagnostic tests, such as a blood test, MRI, or CT scan to rule out any other conditions. If there are no physical reasons for the symptoms, the individual is referred to a psychiatrist or psychologist, for further assessment. A diagnosis is made based on the symptoms the person is experienced and the psychiatrists observation of their behavior.
Dont Miss: Can You Be Bipolar And Have Bpd
Patients Are Commonly Misdiagnosed With Schizophrenia
A retroactive review of patients referred to a psychiatric consultant found that most patients left with a different diagnosis.
Russell L. Margolis, MD
Schizophrenia may have become a trigger-happy diagnosis.
A retroactive analysis of patients referred to a psychiatry consultation clinic with an initial schizophrenia diagnosis found that about half of all such diagnoses were inaccurate upon further review.
The study, from the Johns Hopkins Early Psychosis Intervention Clinic , reported that a multitude of factors may influence a physician too readily diagnosing a patient with schizophrenianot the least of which being a desire to treat the chronic psychiatric condition with speed and efficacy.
Early detection of schizophrenia is very important, so the patient can get the correct pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic care they need to stay on the best possible path of their life, study author Russell L. Margolis, MD, told MD Magazine®.
The investigators conducted a retroactive chart review of 78 patients who has been referred to EPIC with an early psychosis diagnosis. Of the 78 observed patients, 43 had a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia spectrum disorder at the time of their referral. Among those 43 cases, 22 concluded with a different diagnosis following the consultation, and 18 were not diagnosed with any form of primary psychotic disorder.
There can be an overreaction to mental health conditions, he explained.
Also Check: Pristiq Dosage For Anxiety
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Schizophrenia From Acid
Positive And Negative Symptoms
The diagnosis of schizophrenia is established with a structured clinical interview that excludes other disorders that present similarly but are of known other cause . Symptom severity is often assessed with the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, which probes three main dimensions: positive symptoms, negative symptoms, and general psychopathology. Positive symptoms are symptoms added to the experience of a person and include delusions, conceptual disorganization, hallucinatory behavior, excitement, grandiosity, suspiciousness, and hostility. Negative symptoms are features of the experience of a person that are taken away, and include blunted affect, emotional withdrawal, poor rapport, social withdrawal, difficulty in abstract thinking, lack of spontaneity and flow of conversation, and stereotyped thinking. General psychopathology refers to other, more difficult-to-classify symptoms, such as disorientation, poor attention, and lack of judgment.
Cindy M. Yee, Marian D. Sigman, in, 1998
Statistical Methods And Measurement Caveats
The prevalence rate of schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders is difficult to estimate using typical household survey methods alone. Accurate assessment of schizophrenia is best achieved using clinicians trained in the diagnosis of mental illnesses. The U.S. prevalence studies cited here were selected based on their use of U.S. population samples and use of methods that involved clinical diagnosis, either via clinical reappraisal studies or clinical record studies.3,4,5
Individuals with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders may be under-counted in prevalence estimation studies. These individuals may be under-represented in household surveys because they may reside in prisons, other institutions, or may lack a permanent address. Similarly, some people with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders may not be fully reflected in medical records data because they may not have a documented diagnosis, and/or may receive little or no health care.
Information on statistical methods and measurement caveats can be found in the papers cited on this page and listed in the reference section. Below we provide additional background information for large datasets used in two studies cited on this page.3,5
National Comorbidity Survey Replication
Also Check: What Is Ptsd Classified As
Also Check: What Does Bipolar Mean Urban Dictionary
United States And International Statistics
The lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia has generally been estimated to be approximately 1% worldwide. However, a systematic review by Saha et al of 188 studies drawn from 46 countries found a lifetime risk of 4.0 per 1000 population prevalence estimates from countries considered least developed were significantly lower than those from countries classed as emerging or developed. Immigrants to developed countries show increased rates of schizophrenia, with the risk extending to the second generation.
Iischizophrenia And Neurocognitive Impairment: A Challenge For Drug Development
The diagnosis of schizophrenia requires the presence of positive symptoms , negative symptoms , and social/occupational dysfunction over a period of time, as defined by the DSM . Dozens of studies have also identified neurocognitive impairment as a core component of the disorder, characterized by deficits in global cognition, problem solving, and learning and memory. Despite decades of clinical trials leading to the development of dozens of antipsychotics that can be effective in treating positive and negative symptoms, there is little evidence that these agents can modulate neurocognitive impairment in an enduring, meaningful way. This limitation presents a significant obstacle for treatment as neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia is linked to functional disability and poor outcomes. Fortunately, many groups have identified and validated neurophysiological biomarkers, discussed in the succeeding text, which show great promise in aiding development of procognitive agents aimed at targeting neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia.
Jeffrey M. Lyness, in, 2012
Also Check: Is Schizoaffective Disorder Worse Than Schizophrenia
What Can I Do If A Loved One Shows Signs Of Schizophrenia Or A Similar Condition
Because people with schizophrenia often cant recognize their symptoms or condition, they often dont believe they need medical care or treatment. That can be frustrating or frightening for both the person with the symptoms and those who care about them.
If you notice a loved one showing signs of schizophrenia or a related condition, you can try helping them by doing the following:
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Schizophrenia can be a frightening condition for the people who have it and their loved ones. Despite stereotypes, this isnt a condition where any thought of recovery or living a happy, fulfilling life is impossible. If you think you have symptoms of schizophrenia, its important to talk to a healthcare provider as soon as you can. Their job is to help you, and healthcare providers especially those who specialize in mental health conditions like schizophrenia have the training to help you not feel judged, ashamed or embarrassed. If you notice a loved one struggling with symptoms of psychosis or schizophrenia, encourage them gently and supportively to get care. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a big difference in helping people recover and manage this condition.
The Most Common Early Warning Signs Include:
While these warning signs can result from a number of problemsnot just schizophreniathey are cause for concern. When out-of-the-ordinary behavior is causing problems in your life or the life of a loved one, seek medical advice. If schizophrenia or another mental problem is the cause, getting treatment early will help.
Don’t Miss: Which Assessment Finding Is Associated With Depression
What The Warning Signs Look Like
You may notice changes in yourself before your friends and family do. Once your loved ones do become aware, they might try to explain these changes as just a phase youre going through or due to something stressful in your life. Because of that, many people dont seek help until later on, when more severe symptoms start to emerge.
Signs that you may be in a prodrome include trouble with your memory or problems with paying attention and staying focused.
Mood swings and depression can happen. You may have anxiety and feel guilty about things or mistrust others. You could even have thoughts of suicide.
Another sign is lack of energy. You could have weight loss or no interest in meals. Sleep problems could crop up.
You might lose interest in things you once cared about and back away from socializing with family and friends. There could be a drop-off in your level of achievements at work or school.
Your friends may notice changes in how you look. You might not be keeping up with hygiene like you used to.
Some other things that you or others might become aware of:
- Hearing or seeing something thats not there
- A strange way of writing or talking
- An angry, scared, or bizarre response to loved ones
- Extreme interest in religion or the occult
Why Support And Treatment Are Key
While it may be tempting for someone with schizophrenia to think they dont need support or treatment, facing this diagnosis alone is not a good idea. Dr. Nelson cited studies that show, in fact, that one of the best protective factors for living well with the diagnosis is to be married, possibly because this close support can help to ensure that the condition is managed well.
Given the symptoms of this diagnosis, Dr. Nelson recommended that professional and long-term supportive case management or other services be on board to help a patient live at their best. He noted that if a person with schizophrenia has mild symptoms and practices good self-care, they may find the disruptions to their life are relatively minor. On the other hand, though, a patient with severe symptoms and no insight or management of their illness will not do well and will often be unwilling to participate in services that could benefit them.
As with any life issue, it is always best to have a good support system, Dr. Nelson said. The same trusted advice might be given to a family facing another serious medical condition.
Dont Miss: Fear Of Bees And Wasps Phobia
Don’t Miss: Why Is Anxiety Worse At Night
What Are The Types Of Schizophrenia
There are different types of schizophrenia. The International Classification of Diseases manual describes them as below.
Paranoid schizophrenia
- Pranks, giggling and health complaints.
- Usually diagnosed in adolescents or young adults.
Catatonic schizophrenia
- Unusual movements, often switching between being very active and very still.
- You may not talk at all.
Simple schizophrenia
- Negative symptoms are prominent early and get worse quickly.
- Positive symptoms are rare.
Undifferentiated schizophrenia
Your diagnosis may have some signs of paranoid, hebephrenic or catatonic schizophrenia, but doesnt obviously fit into one of these types alone.
Residual schizophrenia
This type of schizophrenia is diagnosed in the later stages of schizophrenia. You may be diagnosed with this if you have a history of schizophrenia but only continue to experience negative symptoms.
Other schizophrenia
There are other types of schizophrenia according to the ICD-10, such as.
- Cenesthopathic schizophrenia. This is where people experience unusual bodily sensations.
- Schizophreniform. Schizophreniform disorder is a type of psychotic illness with symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. But symptoms last for a short period.
Unspecified schizophrenia
Symptoms meet the general conditions for a diagnosis, but do not fit in to any of the above categories.