The 3d Elevation Programsupporting California’s Economy
IntroductionCalifornia faces unprecedented challenges presented by shifting weather patterns that are defining a “new normal.” The result has been extreme weather events, prolonged drought, flooding, and debris flows. These conditions drive severe tree mortality, increase wildfire occurrence and intensity, reduce water availability, and hasten…
Attribution:Core Science SystemsNational Geospatial Program
Part 4: Limitations Of Topographic Maps
There are a few limits to what all the lines and symbols on a topographic map can tell the map reader.
Too Static – The details on a topographical map can be dated, which is maybe the biggest disadvantage. The landscape and places on a map will change over time, so map readers should be aware of this. These changes may be caused by humans, such as a newly constructed road or structure. Larger shifts, such as the draining of a lake, may also occur. All of these factors, as well as others, must be considered when using the map.
Size – Since topographic maps are big and bulky, they can pose a problem for backpackers and other wilderness explorers who prefer to travel light. Instead of these, detailed trail maps are now commonly used.
Vegetation Issues – Another drawback of a topographic map is that the data shown isn’t always accurate. This is especially true when driving through areas where there are no roads or trails. In these cases, a topo map does not provide much detail about the vegetation’s composition. The map does not indicate if a forest is dense and bushy or whether it is dominated by tall trees with little undergrowth.
What Are Three Ways You Can Determine The Flow Of A River When Looking At A Topographic Map
If the map has elevation contour lines, then you can deduce the flow direction by finding two of these lines that cross the river, and working out their elevation; water will be flowing from the higher to the lower. If the map has spot heights that are near the river, you could deduce it from these in the same way.
How To Draw Contour Lines Manually
You can easily generate contour lines with the click of a button in CAD or GIS software. But what if you want to draw it by hand?
First, you have to choose a contour interval. For example, we’re going to use a contour interval of 10 meters. So this means that there will be a contour every 10 meters.
Between transition points of ten , add markers where to draw lines. Basically, draw or interpolate between the lines.
Now that we have points to connect, let’s draw smooth contour lines for each interval. Essentially, we are connecting the points with lines.
And there we have it.
Map Parts Orientation And Scale
A map is a plan view representation of an area on Earth’s surface. Topographic maps are maps that illustrate the topography of the mapped region. Geological maps are maps that illustrate the rock types, rock ages and other geological features of the mapped area.
Every map has a:
- map area or data frame: the part of the map illustrating the map area;
- legend: a guide to the different symbols used on the map, such as lines representing roads and streams;
- scale: this defines the relationship of distances on the map to real distances in the area that the map represents;
- north arrow: indicates the direction of geographic north; and
- title: a name that generally describes the location of the map area.
The topographic and geological maps produced by Natural Resources Canada , and the United States Geological Survey are oriented with north at the top of the map. Therefore if you move towards the top of the map you are moving in a northerly direction, and if you are moving towards the bottom of the map, you are moving towards the south. Any movement to the right or left will be towards the east or west, respectively.
The National Mapnew Data Delivery Homepage Advanced Viewer Lidar Visualization
As one of the cornerstones of the U.S. Geological Survey’s National Geospatial Program, The National Map is a collaborative effort among the USGS and other Federal, State, and local partners to improve and deliver topographic information for the Nation. The National Map is featuring direct links to new and improved GIS data access utilities…
Attribution:National Geospatial Program
Tips Tricks And Common Mistakessome Tips Tricks And Common Mistakes To Avoid When Reading Topographic Maps
The real art of map reading comes with interpreting how individual landscape features fit together in the terrain: saddles connect ridges to knolls to cliffs; gullies form into rivers and valleys. Interpreting how contour lines fit together helps understand the lay of the land and be able to navigate through it.
The big picture
1 – hill, 2 – valley, 3 – ridge, 4 – saddle, 5 – depression, 6 – gully, 7 – spur, 8 – cliff, 9 – cut, 10 – fill
This image describes a landscape by contours. In words:Running east to west across the complex landmass is a ridgeline. A ridgeline is a line of high ground, usually with changes in elevation along its top and low ground on all sides. The changes in elevation are the three hilltops and two saddles along the ridgeline. From the top of each hill, there is lower ground in all directions. The saddles have lower ground in two directions and high ground in the opposite two directions. The contour lines of each saddle form half an hourglass shape. Because of the difference in size of the higher ground on the two opposite sides of a saddle, a full hourglass shape of a saddle may not be apparent.
There are four prominent ridges. A ridge is on each end of the ridgeline, and two ridges extend south from the ridgeline. All of the ridges have lower ground in three directions and higher ground in one direction. The closed ends of the U’s formed by the contour lines point away from higher ground.
Spur
Gully
Knoll
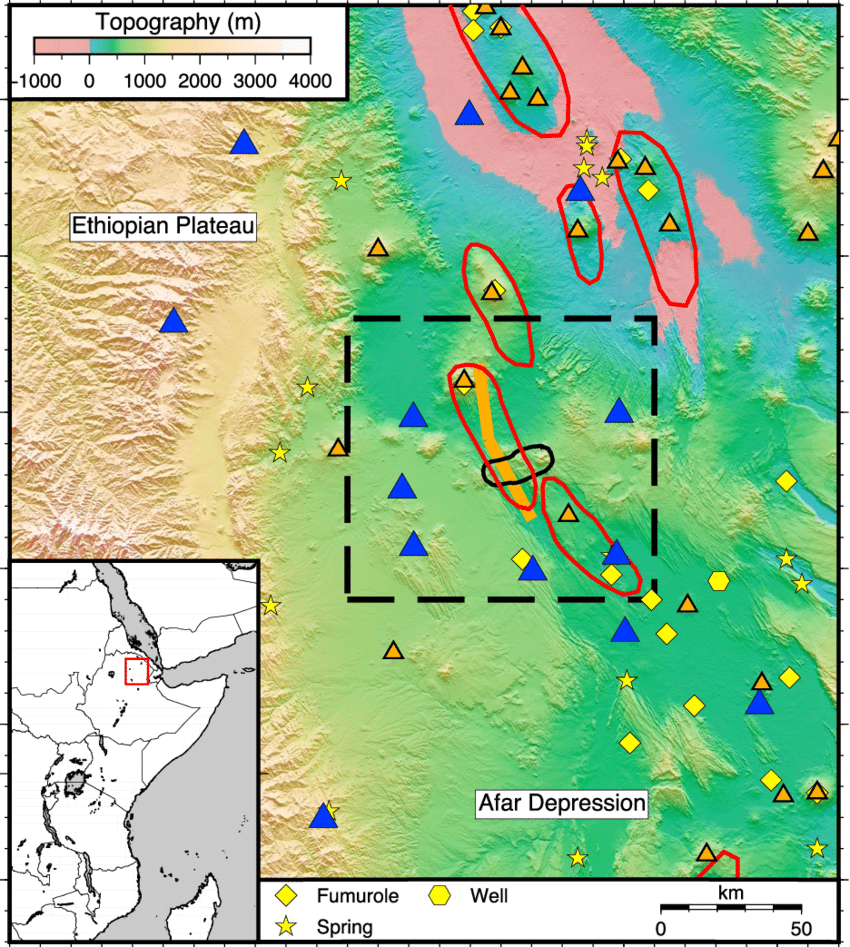
Depression
How Does Mount Fujis Contour Lines Look Like
In this case, closed contour lines indicate a mountain. The beautiful Mount Fuji stands 3,776 meters tall above sea level. At 250-meter spacing, here’s how the contour lines look:
When you see Mount Fuji in 3D, you can see that it’s quite steep as the contours are relatively closely spaced together.
So far, we’ve seen examples of two types of closed contours, but how do contours look like in valleys?
Maps From Specialty Companies
Several companies produce enhanced topographic maps. They highlight key features and update details regularly. These maps are more likely to be available for popular areas.
Additional features that can make a map more valuable include:
- Highlighted trails
- Distances between trail junctions and landmarks
- Primitive trails
The 3d Elevation Programflood Risk Management
Flood-damage reduction in the United States has been a longstanding but elusive societal goal. The national strategy for reducing flood damage has shifted over recent decades from a focus on construction of flood-control dams and levee systems to a three-pronged strategy to improve the design and operation of such structures, provide more…
Slope Percent From Topographic Map
The horizontal distance between points A and B can be measured with a scaled ruler and used to determine the slope percent.slope percent = rise/run × 100Example 4 – What is the slope percent in Exercise 2 above? slope percent = rise/run × 100.For this computation, the rise, or vertical ground distance, and run, or horizontal ground distance, are needed.Step 1. Measure the horizontal map distance between points A and B to get the vertical ground distance.The horizontal map distance measures 0.5 inches.Step 2. Use the appropriate conversion factor to convert the horizontal map distance to horizontal ground distance.0.5 in × 24,000 in/in = 12,000 inStep 3. The desired unit is feet. Set up the cancellation table so all units will cancel, except the desired unit, feet.Step 4. Use the slope percent equation and solve. The run is 1000 feet and the rise in elevation is 120 feet. slope percent = rise/run × 100slope percent = × 100 = 12%Slope Worksheet – Use the information from the example above and complete the slope worksheet. Line 1 starts with the contour interval, not the projection point. Slope Worksheet
| Line |
The Inner Depression Contour Lines Indicate Lower Elevations With The Elevation Increasing With Each Outer Layer
Depression on a topographic map. Are contour lines with ticks pointing downslope that indicate a depression on a topographic. Each world has more than 20 groups with 5 puzzles each. So look what weve done weve made up a new type of contour called a depression contourits marked with little teeth called hachuresfor hachured contours a point inside a contour is lower than the contour.
Just the opposite of ordinary unhachured contours. Landforms and terrain features such as mountain pass col or saddle cliff and depression are represented by contour lines in topographic maps. Hills valleys depression gullies ridges.
Codycross is an addictive game developed by fanatee. A depression is sort of the opposite of a hill. Contour lines fit together in many different ways and they form shapes which can be recognised by the user.
A topographic map of the atlantic coastal plain differs from a topographic map of the rocky mountains because the topographic map of the atlantic coastal plain has much higher altitudes. Topographic map called provisional some symbols and lettering are hand drawn. Some of the worlds are.
A topographic map is a map using contour lines to show relief height above sea level various physical features eg. Usually only depressions that are equal to or greater than the contour interval will be shown. Riversforest areas and features of the human environment eg.
Australian Topographic Map Symbols Relief
Lowest Land Points Below Sea Level Map Depression Elevations
Common Terrain Featuresunderstanding How Common Terrain Features Are Depicted On Topographic Maps
All terrain features are derived from a complex landmass known as a ridgeline, not to be confused with a ridge.
The US Army states that “A ridgeline is a line of high ground, usually with changes in elevation along its top and low ground on all sides from which a total of 10 natural or constructed terrain features are classified”.Army, U. S. “Map Reading and Land Navigation.” Washington, DC, fm: 3-25. By comparison, a ridge is a sloping line of high ground.
Major terrain features include hills, saddles, gullies, ridges, and depressions, and they each have characteristic contour lines that make it easy to pick them out in the landscape.
- Hills, peaks, knolls, mountains: A hill, peak, knoll or mountain is an area of high ground. From a hilltop, the ground slopes down in all directions. A hill is shown on a map by contour lines forming concentric circles. The inside of the smallest closed circle is the hilltop.
- Hill = an area of high ground; generally, a smaller and rounder than a mountain, and less steep.
- Knoll = small, rounded natural hill.
- Mountain = a very tall hill, generally with a minimum size of 600m, but varies around the world.
- Peak = a mountain with a pointed top.
- = a Scottish mountain taller than 3,000 feet .
Closed contour loops represent hills or bumps along the ridgeline.
How Do You Find Approximate Elevation
You can figure out the elevation of any point by finding the nearest labeled line, counting the number of lines above or below it, multiplying by the contour interval, and adding or subtracting the result from the nearest marked contour line. The more closely spaced the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
How Are Shoulder Bone Spurs Removed
Arthroscopic Debridement Removal of bone spurs and other tissue may provide noticeable pain relief and slow down the erosion of cartilage. To perform this procedure, a surgeon makes a very small incision in the shoulder to access the joint and then insert a long, slim instrument called an arthroscope.
A Depression Is A Low Point In The Ground Or A Sinkhole
What is a depression on a topographic map. These maps are prepared based on a detailed survey of the areas concerned. Click here to see list of references authorities sources and geographical terms as used in this glossary. The phrase usgs topographic map can refer to maps with a wide range of scales but the scale used for all modern usgs topographic maps is 1 24 000. And a point outsidea contour is higherthan the contour.
These maps are revised periodically to update. Use the drop down menus to answer the questions about the topographic map. A topographic map with points a and b labeled. Depression in this case essentially means a hole.
How are areas of depression represented on a topographic map answers a depression is shown by contour lines with small marks pointing toward the lowest point of the depression. It could be described as an area of low ground surrounded by higher ground in all directions or simply a hole in the ground. It is a ditch or gully or pit where the elevation decreases towards the center. So look what we ve done we ve made up a new type of contour called a depression contour.
They will appear as a series of closed circles one inside the other. Point b is on a contour line with number 6800 and image of a table. Point a is on a contour line with number 7000. A depression is sort of the opposite of a hill.
The symbol at point b indicates a area.
What Is A Topographic Map
The distinctive characteristic of a topographic map is the use of elevation contour lines to show the shape of the Earth’s surface. Elevation contours are imaginary lines connecting points having the same elevation on the surface of the land above or below a reference surface, which is usually mean sea level. Contours make it possible to show the height and shape of mountains, the depths of the ocean bottom, and the steepness of slopes.
USGS topographic maps also show many other kinds of geographic features including roads, railroads, rivers, streams, lakes, boundaries, place or feature names, mountains, and much more. Older maps show additional features such as trails, buildings, towns, mountain elevations, and survey control points. Those will be added to more current maps over time.
The phrase “USGS topographic map” can refer to maps with a wide range of scales, but the scale used for all modern USGS topographic maps is 1:24,000. That covers a quadrangle that measures 7.5 minutes of longitude and latitude on all sides, so these are also referred to as 7.5-minute maps, quadrangle maps, or “quad” maps . Each topographic map has a unique name.
Within this domain there are two product categories:
-
maps are the current topographic map series, published as digital documents from 2009 to the present.
-
The is scanned images of maps originally published as paper documents in the period 1884-2006.
Learn more:
Part 5: When And To Whom Are They Useful
Many hikers and backpackers bring a topographic map with them when they go camping. One of these maps, along with a compass, can be extremely useful for people embarking on a long backcountry trek across unknown territory. Military, architects, and mining companies also often use topographic maps.
Learn about map scale, political map and more types of maps.
Part 3: The Importance Of Topographic Maps
Since topographic maps may represent the three-dimensional landscape in two dimensions, they are a valuable tool. An individual who knows how to read a topo map can locate hills, valleys, ridges, and saddles, among other land features. On topo maps, you can see if you’ll be going uphill or downhill on a given road or trail.
Contour Lines – Contour lines link points of similar elevation on a topo map, marking elevations. Imagine walking in a loop around a mountain, never going uphill or downhill but remaining at the same elevation. A contour line on a map will be created if you followed the direction you walked.
Land Features – The contour lines’ shape will reveal the shape of the landforms in a given region. Concentric circles, for example, depict a peak, with the smallest circle indicating the summit. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep terrain, while widely spaced contour lines indicate relatively flat terrain.
USGS Maps – Highways, dirt roads, villages, and buildings are all depicted on USGS topo maps, as are other features found on standard road maps. Power lines, rivers, glaciers, and mines are also depicted on the charts.
Other Useful Map Details
Look closely at the map legend. It’s loaded with map-reading clues and navigational data. Start by studying what each line, symbol and color means. Generally, green indicates denser vegetation, while light or colorless areas suggest open terrain. And, as you’d expect, streams and lakes are shown in blue.
Practice reading features from a map of a familiar area. Visualize how the terrain on the major landmarks relates to the contour lines on your map. Pick out features like peaks and saddles. Identify subtler features like cliffs, which have contour lines grouped tightly together, and ridgelines, which connect peaks and have contour lines that decrease in elevation on each side. Valleys are low-elevation areas between ridgelines; some might have a creek running along the bottom, though that isn’t a requirement for a feature to be a valley.
Hone your map-reading skills on every trip. Pull it out at the trailhead, orient it correctly and mentally check off landmarks as you hike. Regular map readers rarely get lost.
What Three Things Do Topographic Maps Show
Contours make it possible to show the height and shape of mountains, the depths of the ocean bottom, and the steepness of slopes. USGS topographic maps also show many other kinds of geographic features including roads, railroads, rivers, streams, lakes, boundaries, place or feature names, mountains, and much more.
What Is A Depression On A Topographic Map
4.3/5depression contourcontourmapcontour
They are marked with short, straight lines inside the circle. The lines point toward the center of the depression. The difference in elevation between the highest and lowest points in the area on the map.
Additionally, what does a depression contour look like? Depression Contour: A contour that indicates a hole and is represented by a “hachured” brown line. A depression is a point inside a contour that is lower than the contour; a point outside the depression contour is higher than the contour.
Also asked, how do you draw a depression on a topographic map?
A depression is represented by a series of concentric closed contours with the inner contours having lower elevation than their outer surrounding. There are small tick marks or hachures on these contour lines pointing towards lower elevation.
What is a valley on a topographic map?
A valley is an elongated depression in the landscape that is formed by the action of water or carved out by glaciers . Valley bottoms are represented by “U” or “V” shaped contour lines with their closed end pointing towards higher elevation.
What About Ridges And Gullies
Over time, gullies form through erosion of running water on hillsides. A consequence of two eroded gullies is a spur at the center on the face of a hillside that sticks out. Both gullies and spurs run from ridgelines to valley bottoms.
Gullies are characterized by “U” or “V” shaped contour lines with their closed-end pointing towards higher elevation. On the other hand, spur contour lines point toward lower elevation.
In 2D, these valley landscape features are a bit more difficult to see. But it’s key to remember how ridges point downslope and gullies point upslope.
Usually Only Depressions That Are Equal To Or Greater Than The Contour Interval Will Be Shown
Depression on a topographic map. On maps depressions are represented by closed contour lines that have tick marks pointing toward low ground figure 10 21. Are you looking for never ending fun in this exciting logic brain app. Some of the worlds are.
A draw is a less developed stream course than a valley. It is a ditch or gully or pit where the. And a point outside a contour is higher than the contour.
Topographic map called provisional some symbols and lettering are hand drawn. On topographic maps contours represent the shape of the land. Geological survey reading topographic maps interpreting the colored lines areas and other symbols is the ? rst step in using topographic maps.
Are contour lines with ticks pointing downslope that indicate a depression on a topographic. Each world has more than 20 groups with 5 puzzles each. So look what weve done weve made up a new type of contour called a depression contourits marked with little teeth called hachuresfor hachured contours a point inside a contour is lower than the contour.
Features are shown as points lines or areas depending on their size and extent. Contour lines fit together in many different ways and they form shapes which can be recognised by the user. Just the opposite of ordinary unhachured contours.
Riversforest areas and features of the human environment eg. Features of the landscape that are useful to know are. Hills valleys depression gullies ridges.
Understanding Topographic Maps
Exercise 3: Topographic Map Symbols
To understand topographic maps, you need to understand thesymbols the maps use! Some symbols are like those on othermaps you have used, such as road maps. Others are lessobvious. Take a minute to look through the graphics belowto familarize yourself with USGS map symbols. Then answerthe questions — everything you need to answer them is found inthe symbol listings below.
How Do You Read A Topographic Map
Topographic maps use legends that have different colors. Legend explains what each symbols represents.
Explanation:
The following are the rules on how to read your topographic map easier:A. A contour line of one elevation never crosses or divides a contour line of another elevation. Each contour line represents only one elevation. The contour lines cannot intersect since one point cannot have two different elevations.B. Closely spaced contour lines represent a steep slope. The lines are closely spaced because the elevation of a steep slope changes greatly over a very short distance. Contour lines spaced far apart represent a gentle slope. The lines are far apart because the elevation of a gentle slope changes only slightly from one point to another.C. Contour lines that cross a valley are V shaped. If a stream flows through the valley, the V will point upstream, or in the direction opposite to the flow of the stream.D. Contour lines form closed loops around hilltops and depressions. Elevation numbers on the contour lines indicate whether a feature is a hilltop or depression. If the numbers increase toward the center of the closed loop, the feature is a hilltop. If the numbers decrease, the feature is a depression. Sometimes elevation numbers are not given. instead short dashes called hachures are used to indicate depression. Hachures are drawn perpendicular to the contour line that loops around a depression. The hachures point to the inside of the loop.
-prentice-hallES
What Depression Lines Indicate
Depression Contour: A contour that indicates a hole and is represented by a “hachured” brown line. A depression is a point inside a contour that is lower than the contour; a point outside the depression contour is higher than the contour. Contour lines are used in a map to portray differences in elevation.
Bench Mark And Mean Sea Level
A bench mark is a permanent mark established in a field to use as a reference point. A bench mark can be a concrete base in which an iron bar is fixed, indicating the exact place of the reference point.
A bench mark can also be a permanent object on the farm, such as the top of a concrete structure.
In most countries the topographical departments have established a national network of bench marks with officially registered elevations. All bench mark heights are given in relationship to the one national datum plane which in general is the mean sea level .
Fig. 52. A bench mark and mean sea level
EXAMPLE
In Figure 52, the elevation of point A in relation to the bench mark is 5 metres. The BM elevation relative to the mean sea level is 10 m. Thus, the elevation of point A relative to the MSL is 5 m + 10 m = 15 m and is called the reduced level of A.
QUESTION
What is the reduced level of point B in Figure 52.
ANSWER
The elevation of B relative to BM = 3 m
The elevation of BM relative to MSL = 10 m
Thus, the reduced level of B = 3 m + 10 m = 13 m
QUESTION
What is the difference in elevation between A and B? What does it represent?
ANSWER
The difference in elevation between A and B is the reduced level of A minus the reduced level of B = 15 m – 13 m = 2 m, which represents the vertical distance between A and B.