Understanding The Location Structure And Function Of Bipolar Neurons
Bipolar neurons have 2 processes – axonal and dendritic. They have 2 distinct structures to carry out these processes. These neurons are chiefly involved in transporting electrical signals from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system.
Bipolar neurons have 2 processes axonal and dendritic. They have 2 distinct structures to carry out these processes. These neurons are chiefly involved in transporting electrical signals from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system.
Bipolar Neurons: Features Location And Functions
The Bipolar neurons Are a type of cells that are characterized by two extensions: an axon and a dendrite.
East Type of neurons Are less prevalent at the brain level than Multipolar neurons but more prevalent than Unipolar neurons .
Bipolar neurons are mainly sensory and are specialized in the transmission of nerve signals that come from specific senses. In this way, they form very important cells in the reception of olfactory, gustatory and auditory stimuli. In turn, they are also part of the vestibular functions.
These types of cells are found in the spinal ganglia when they are embryonic.
In The Spinal Ganglia
Bipolar cells are also found in the , when the cells are in an condition.
Sometimes the extensions, also called , come off from opposite poles of the cell, and the cell then assumes a spindle shape.
In some cases where two fibers are apparently connected with a cell, one of the fibers is really derived from an adjoining nerve cell and is passing to end in a ramification around the ganglion cell, or, again, it may be coiled helically around the nerve process which is issuing from the cell.
Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
- B.A., Biology, Emory University
- A.S., Nursing, Chattahoochee Technical College
Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system and nervous tissue. All cells of the nervous system are comprised of neurons. The nervous system helps us to sense and respond to our environment and can be divided into two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of sensory and motor nerve cells that run throughout the rest of the body. Neurons are responsible for sending, receiving, and interpreting information from all parts of the body.
What Are Unipolar Neurons
A unipolar neuron is a neuron that possesses only one protoplasmic process. So, unipolar neurons have only one structure extending from the cell body or soma.
Figure 03: Unipolar Neuron
Generally, unipolar neurons are present in invertebrates, especially in insects in order to stimulate muscles or glands. In mammals, they are primarily found in the afferent division of the PNS.
Morphology Of Bipolar Neurons
The soma of bipolar neurons has two cytoplasmic extensions, which in turn are also branched. One of these extensions acts as a dendrite, Which allows to receive electrochemical impulses sent by presynaptic neurons, and the other in axon form, transmitting stimulation generated by the neuronal body to other cells.
Bipolar neurons are more common in the central nervous system of humans than unipolar neurons, although much less so than multipolar neurons. Unlike the latter, which act as motor neurons and interneurons, bipolar they mainly perform the function of sensory neurons.
In addition to being characterized by the separation between its two extensions, bipolar neurons therefore have a particularly elongated shape compared to unipolar, which are more rounded, and multipolar, which in many cases have been compared to stars.
In addition to being relatively common in certain regions of the human body, particularly the sensory pathways, bipolar neurons they are very numerous in the spinal ganglia of fish. People also have bipolar neurons in this section of the spinal cord during embryonic development.
Difference Between Unipolar Neurons And Pseudounipolar Neurons
In case of true unipolar neurons, which are primarily found in invertebrates, dendrites dont arise directly from the cell body. These have a single process that extends from the cell body. This single process gets divided into two branches, with one of the branches projecting to the periphery, and the other projecting to the central nervous system. Thus, the single process functions as the axon, as well as the dendrites.
In case of pseudounipolar neurons, the axon and the dendrite are fused, which give the appearance of a single process. Basically, these neurons begin as bipolar neurons during development. While these neurons dont have true dendrites, a single axon emerging from the cell body moves in two opposite directions. While one end heads for the skin, joints, and muscles, the other end moves to the spinal cord. The pseudounipolar neurons are the most common type of sensory neurons in the human nervous system. These can sense pressure, touch, and pain. These can be found in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal nerves, as well as the sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves . The baroreceptor-sensitive cells in the nodose ganglion are examples of this type. These cells sense changes in the systemic blood pressure, after which they transmit this information to the neurons in the dorsal medulla. These neurons are found in the ganglia that lie outside the brain, as well as the spinal cord.
In The Vestibular Nerve
Bipolar neurons exist within the vestibular nerve as it is responsible for special sensory sensations including hearing, equilibrium and motion detection. The majority of the bipolar neurons belonging to the vestibular nerve exist within the vestibular ganglion with axons extending into the maculae of utricle and saccule as well as into the ampullae of the semicircular canals.
The Nervous System: Introduction
The nervous system coordinates the bodys voluntary and involuntary actions and transmits signals between different parts of the body. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms approximately 550 to 600 million years ago. In most types of vertebrate animals, it consists of two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system . The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are long fibers that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. The PNS includes motor neurons , the autonomic nervous system , and the enteric nervous system .
The nervous system performs several functions simultaneously. For example, as you are reading, the visual system is processing what is seen on the page; the motor system controls the turn of the pages ; the prefrontal cortex maintains attention. Even fundamental functions, like breathing and regulation of body temperature, are controlled by the nervous system. A nervous system is an organisms control center: it processes sensory information from outside the body and controls all behaviors, from eating to sleeping to finding a mate.
What Is The Difference Between Multipolar Bipolar And Unipolar Neurons
Multipolar neurons contain three or more protoplasmic processes, especially one axon and many dendrites, while bipolar neurons have two protoplasmic processes, especially one axon and one dendrite extending from the soma and unipolar neurons have only one process extending from the soma. So, this is the key difference between multipolar bipolar and unipolar neurons. In humans, more than 99% of the total neurons are multipolar neurons, while bipolar neurons are rare and unipolar neurons are very rare.
Moreover, multipolar neurons are found in the CNS and the efferent division of the PNS while bipolar neurons are found in the retina of the eye, and the olfactory system and unipolar neurons are found primarily in the afferent division of the PNS and in insects. Thus, this is another difference between multipolar bipolar and unipolar neurons.
Where Would You Find Bipolar Neuron
Bipolar neuronsneuronsMultipolar neuronsneuron
Unipolar neurons are typically sensory neurons with receptors located within the skin, joints, muscles, and internal organs. The axons of such neurons are usually long, terminating in the spinal cord.
Secondly, are bipolar neurons motor? Answer and Explanation: Motor neurons are multipolar neurons with several dendrites and an long axon that reaches muscles and glands. Bipolar neurons are pretty rare and they
Consequently, where are neurons located in the body?
Myelinated neurons are typically found in the peripheral nerves , while non-myelinated neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord. Dendrites or nerve endings.
Where would you find interneurons other than in the brain?
Interneurons are neurons that are found exclusively in the central nervous system. That means that they are found in the brain and spinal cord and not in the peripheral segments of the nervous system.
Structure Of Jo Neurons
FIGURE 2.7. The chordotonal mechanosensory cilium.
Schematic of the tip of the chordotonal neuron dendrite showing the sensory cilium . Some of the proteins localized to each part are shown in colored text. Sas-4 and PLP are centrosomal/basal body proteins. Eys is a secreted protein that forms a prominent luminal band surrounding the cilium. The other proteins are mentioned in the text. Immunofluorescence of pupal JO chordotonal neurons expressing a GFP-tagged axonemal dynein light intermediate chain marking the proximal cilia zone and with NompC marking the distal zone .
The mechanosensory mechanism is only partially known. The primary mechanosensory molecule is thought to be the TRPN channel encoded by nompC, which localizes to the membrane of the distal ciliary zone . The evidence suggests that it is expressed in and required for the subset of JO neurons that responds specifically to sound . The protein has ankyrin repeats that have been proposed to form a coiled spring. The membrane of the proximal ciliary zone contains TRPV channels formed by proteins encoded by inactive and nanchung . These genes are essential for chordotonal neuron function and appear to be involved in membrane potential propagation downstream of the initial mechanotransduction event and also in gain control of the nonlinear neuronal response to sound . Unlike nompC, the TRPV genes are expressed in all JO neurons .
Jahangir Moini, Pirouz Piran, in, 2020
Neuron Structure And Classification
Neurons have four specialized structures that allow for the sending and receiving of information: the cell body , dendrites, axon and axon terminals .
Cell body or soma: The cell body is the portion of the cell that surrounds the nucleus and plays a major role in synthesizing proteins.
Dendrites: Dendrites are short, branched processes that extend from the cell body. Dendrites function to receive information, and do so through numerous receptors located in their membranes that bind to chemicals, called neurotransmitters.
Axon: An axon is a large process that extends from the cell body at a point of origin-called the axon hillock-and functions to send information. In contrast to the shorter dendrites, the axon can extend for more than a meter. Because of this length, the axon contains microtubules and is surrounded by myelin. Microtubules are arranged inside the axon as parallel arrays of long strands that act as highways for the movement of materials to and from the soma. Specialized motor proteins “walk” along the microtubules, carrying material away from the soma or back to the soma . This system can move materials down the axon at rates of 400mm/day . Myelin consists of totally separate cells that coil and wrap their membranes around the outside of the axon. These are essential for electrical insulation and to speed up action potential propagation.
Image produced by BYU-Idaho Student Jared Cardinet 2013
Image shows Anterograde and Retrograde transport in an axon.
Anatomy Of The Neurons
The components of a neuron include: Cell body Telodendria Ganglia
While the cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles, dendrites are shorter processes extending from the cell body. Dendrites are shorter and have many branches. They act as receptors, receiving impulses from the nearby neurons at the synapses, and transmitting them to the cell body. An axon refers to a long, slender cytoplasmic process that conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body. The axons that are coated with myelin sheath can transmit impulses at a very high speed. Some of the axons are very long, and these could transmit impulses at a high speed of up to 300 feet in a mere second. The terminal branches of an axon are called telodendria. These come in contact with other neurons at synapses, which are small gaps at the end of the neuron that facilitate the passage of information from one neuron to the next one. Ganglia refers to the groups of neuron cell bodies that lie peripheral to the central nervous system in vertebrates.
Bipolar Disorder And Endocrinology
Neurotransmitters are not the only important chemical messengers in the body. The body also uses hormones as chemical messengers. Produced in the endocrine system, hormones circulate from one organ to another through the bloodstream. Receiving organs in the body interpret hormonal signals and respond to their messages.
The endocrine and nervous systems are linked by the hypothalamus. This is a centrally located ‘switching station’ within the brain. The hypothalamus is an exceptionally complex brain region. It controls many different body functions such as blood pressure, appetite, immune responses, body temperature, maternal behavior, and body rhythms dealing with circadian and seasonal rhythms. This coordination of circadian and seasonal body rhythms is particularly important when discussing bipolar disorder. .
Another component of the endocrine system which is known to cause mood fluctuations when not being regulated correctly is the reproductive system. As reproductive hormones are known to affect mood, most prominently in women, the source of this effect is thought to be the ovaries which secrete estrogen and testosterone. Although the role sex hormones play in mood conditions are well documented , exactly how these hormones affect mood is unclear. There is little information available currently regarding their possible role in causing or maintaining bipolar symptoms.
Characteristics Of Bipolar Neurons
Bipolar neurons are those that present a cellular body elongating where at each of its ends possesses a single dendrite.
These cells are therefore characterized by two branches external to the soma or neuronal body. It differs from the unipolar because it has two extensions and the multipolar ones because they contain only one dendrite .
The axons of the bipolar neurons are responsible for performing the functions of information transmission, while the dendrites perform the processes of capturing information from other neurons.
The nucleus of the bipolar neuron is located in the center. Each of its sides contains a branch. On one side the axon and on the other the dendrite.
In general, bipolar neurons are afferent. That is, they are responsible for transmitting information from the senses to the central nervous system.
The presence of this type of neurons becomes especially prominent in the spinal ganglia of the fish. Its main properties are.
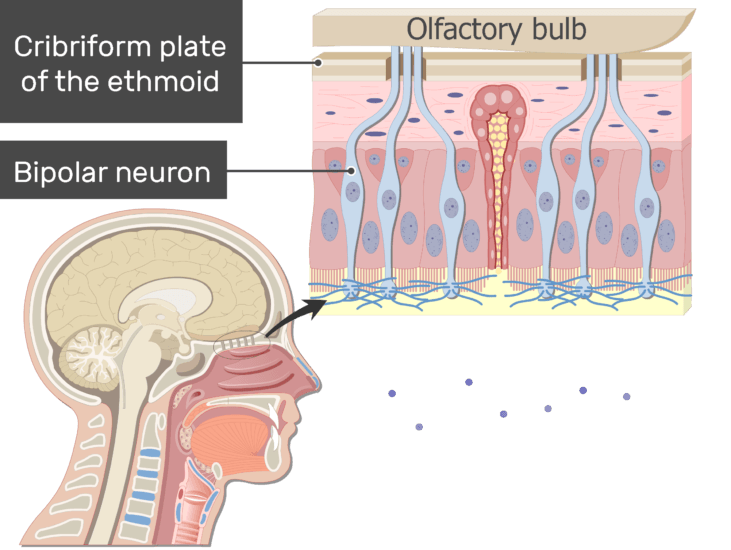
In The Olfactory Epithelium
Bipolar neurons perform the function of olfactory receptors in the olfactory epithelium, Located on the roof of the nasal cavity. The dendrites of these neurons have cilia, which hold odor molecules in the lining. By binding to these, the neuron transmits electrical impulses to the olfactory bulb through the cribiform plate of the skull.
Summary Multipolar Bipolar Vs Unipolar Neurons
Based on the number od protoplasmic processes coming out from the soma, there are four types of neurons as unipolar, bipolar, multipolar and pseudounipolar. Multipolar neurons have one axon and many dendrites extending from the cell body. Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite. Unipolar neurons have only one protoplasmic process extending from the cell body. Thus it is the key difference between multipolar bipolar and unipolar neurons. Multipolar neurons are the commonest while there are many bipolar neurons. However, there are unipolar neurons present in the nervous system, but their number is very low compared to the other two types.
Reference:
1. 12.2 Nervous Tissue. Anatomy and Physiology, OpenStax, 6 Mar. 2013, Available here.2. Neurons & the Nervous System. Human Physiology Neurons & the Nervous System, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. Blausen 0657 MultipolarNeuron By BruceBlaus Own work via Commons Wikimedia2. Bipolar Interneuron By Artwork by Holly Fischer CNS Slide 12; PNS Slide 18 via Commons Wikimedia3. Unipolar Sensory Neuron By Artwork by Holly Fischer CNS Slide 12; PNS Slide 18 via Commons Wikimedia
Vestibular Ganglion And Nerve
Vestibular nerve fibers are the afferent projections from the bipolar neurons of Scarpa’s ganglion. The vestibular nerve transmits afferent signals from the labyrinths through the internal auditory canal . In addition to the vestibular nerve, the IAC also contains the cochlear nerve , the facial nerve, the nervus intermedius , and the labyrinthine artery. The IAC travels through the petrous portion of the temporal bone to open into the posterior fossa at the level of the pons. The vestibular nerve enters the brain stem at the pontomedullary junction and contains two divisions, the superior and inferior vestibular nerves. The superior vestibular nerve innervates the utricle, as well as the superior and lateral canals. The inferior vestibular nerve innervates the posterior canal and the saccule. Because a common disorder of the vestibular nerve, vestibular neuritis, often spares the inferior division, clinical situations can arise in which there is a partial injury to the vestibular nerve.4
Alexander de Lahunta DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVP, Eric Glass MS, DVM, DACVIM , in, 2009
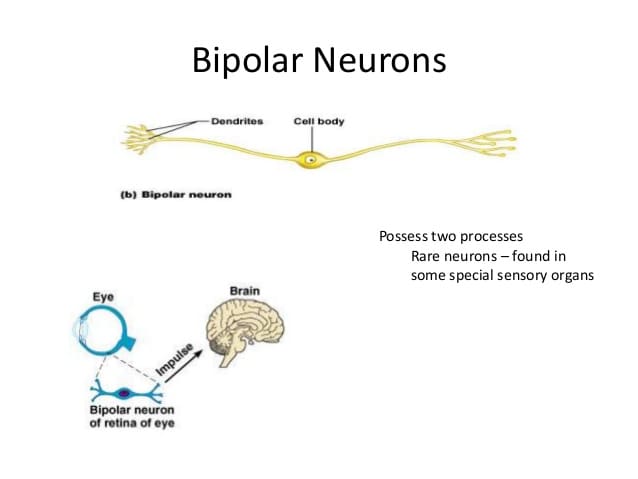
What Are Bipolar Neurons
Bipolar neurons are a type of neurons that have two processes extending from the cell body. Generally, these two processes run in opposite directions from the cell body. One process is an axon while the other process is a dendrite.
Figure 02: Bipolar Neuron
In comparison to multipolar neurons, bipolar neurons are few in number. They are found in the retina of the eye and the olfactory system.
Retinal Anatomy And Function
- In photoreception: Neural transmission
rear of the retina, the bipolar cells, and finally the ganglion cells, whose axons make up the optic nerve. Forming a network between the photoreceptors and the bipolar cells are the horizontal cells , and between the bipolar cells and the ganglion cells, there exists a similar
- In human eye: The retina
neurons called the bipolar cells. These bipolar cells connect with the innermost layer of neurons, the ganglion cells; and the transmitted messages are carried out of the eye along their projections, or axons, which constitute the optic nerve fibres. Thus, the optic nerve is really a central
Spiral Ganglion And Auditory Nerve
Figure 5. ANF tuning curves for fibers tuned to 2000 Hz and 15,000 Hz . The y axis is threshold in decibels sound pressure level.
Inputoutput functions of ANFs are described by four parameters: spontaneous rate, threshold, maximum or saturation discharge rate, and dynamic range. Thresholds at CF for ANFs with high spontaneous rates generally follow the behavioral sensitivity curve, and thresholds at CF for ANFs with low spontaneous rates progressively increase by 1040 dB as the spontaneous rate decreases to zero. Maximum discharge rates for ANFs range from 100 to 400 spikes/sec and, like threshold, correlate with spontaneous rate. That is, the higher the spontaneous rate, the higher the maximum discharge rate tends to be. Dynamic range refers to the intensity range over which an ANF’s response increases from the resting rate to the maximum rate. Dynamic ranges for most ANFs are typically 2030 dB, but some low-spontaneous-rate ANFs can have dynamic ranges up to 70 dB.
Figure 6. Inputoutput functions of ANFs with different spontaneous rates.
Jahangir Moini, Pirouz Piran, in, 2020
Difference Between Multipolar Bipolar And Unipolar Neurons
The key difference between multipolar bipolar and unipolar neurons is that multipolar neurons have many and one axon, while bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite and unipolar neurons have only one protoplasmic process.
A neuron or a nerve cell is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It is an electrically excitable cell. Neurons receive signals from the external world via the sensory organs and send them to the central nervous system in order to process. Then, neurons transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body, especially to muscles and gland cells. In this manner, neurons facilitate communication within our body.
A neuron has three major components: an axon, dendrites and a cell body. Neurons receive signals from the dendrites. Then the signal travels via the cell body to the axon. From the axon, the signal goes to the next neuron through the . Neurons can be unipolar, pseudounipolar, bipolar or multipolar. Most neurons are multipolar, while many are bipolar. However, there are unipolar and pseudounipolar neurons, as well.
Location Structure And Functions Of The Unipolar Neuron
Neurons refer to nerve cells that perform the vital function of conducting nerve impulses. This Bodytomy post provides information on unipolar neurons, which are neurons that have just one extension from the cell body.
Neurons refer to nerve cells that perform the vital function of conducting nerve impulses. This Bodytomy post provides information on unipolar neurons, which are neurons that have just one extension from the cell body.
This Problem Has Been Solved
1) Bipolar Neurons: a) comprise about 20%of all neurons. b) are typically motorneurons. c) are found in thecochlea. d) all of theabove. e) none of the above.
2) The peripheral nervous system: a) includesthe spinal cord. b) includes the medullaoblongata. c) includes 12 pair of cranialnerves. d) all of theabove. e) none of the above.
3) Motor neurons: a) carry actionpotentials from the brain. b) innervate musclesand glands. c) are also called efferentneurons. d) all of theabove. e) none of the above.
4) Which of the followingdoesnt belong? a)Schwann cell. b) ependymalcell. c)oligodendrocyte.
d) astrocyte. e)microglia.
Type Ii Multidendritic Sensilla
Besides the sensilla that are innervated by bipolar neurons, the insect sensory system comprises another set of multidendritic subepidermal neurons which act as receptors for pressure and stretch . A subset of these sensory neurons is accompanied by specialized ligament cells by which they stretch out alongside muscles; examples are the wing hinge stretch receptors and pleural stretch receptors. Most multidendritic neurons are naked, extending complex dendritic arbors at the basal surface of the epidermis . These neurons, which have been identified in soft-bodied insects are called dendritic arbor neurons. In Manduca and Drosophila, four classes with different dendritic complexity, axonal termination, and physiological properties were defined . Members of one class completely tile the epidermis. Thus, dendritic branches of a given da neuron form a dense mesh in a given domain of the epidermis. Another da neuron of the same class innervates a domain that is contiguous, yet nonoverlapping with the first one. In this manner, the entire epidermis is completely covered with the innervation domains of the da neurons of a given class.
S.S. Schiffman, in, 2007
In The Vestibulocochlear Nerve
The vestibular and cochlear branches of the eighth cranial pair they are made up of bipolar cells. While the vestibular branch transmits information about balance to the brain, the cochlear is related to the sense of hearing. Bipolar neurons are located in the vestibular ganglion and their axons extend to the semicircular canals.
What Are Multipolar Neurons
Multipolar neurons are the commonest type of neurons, having three or more protoplasmic processes. Generally, these neurons have one axon and many dendrites. More than 99% of the total neurons in humans are multipolar. Therefore, they are the major type of neurons found in the central nervous system and the efferent division of the peripheral nervous system.
Figure 01: Multipolar Neurons
Bipolar Disorder And Neurochemistry

The brain uses a number of chemicals as messengers to communicate with other parts of the brain and nervous system. These chemical messengers, known as neurotransmitters, are essential to all of the brain’s functions. Since they are messengers, they typically come from one place and go to another to deliver their messages. Where one neuron or nerve cell ends, another one begins.
In between two linked neurons is a tiny space or gap called a synapse. In a simple scenario, one cell sends a neurotransmitter message across this gap and the next cell receives the signal by catching the messenger chemical as it floats across the gap. The receiving neuron’s capture of the neurotransmitter chemicals alerts it that a message has been sent, and this neuron in turn sends a new message off to additional neurons that it is connected to, and so on down the line.
Neurons cannot communicate with each other except by means of this synaptic chemical message. The brain would cease to function in an instant if chemical messengers were somehow removed. By providing a way for allowing neurons to communicate with one another, neurotransmitters literally allow the brain to function. There are millions and millions of individual synapses, or gaps, in the brain. The neurotransmitter traffic and activity happening inside those gaps is constant and complicated.