How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Schizophrenia is a condition that has severe effects on a persons physical and mental well-being. This is because it disrupts how your brain works, interfering with your thinking ability, memory, how your senses work and more.
Because your brain isnt working correctly, having schizophrenia often causes you to struggle in many parts of your day-to-day life. Schizophrenia often disrupts your relationships . It can also cause you to have trouble organizing your thoughts, and you might behave in ways that put you at risk for injuries or other illnesses.
What If I Am A Carer Friend Or Relative
It can be distressing if you are a carer, friend or relative of someone who has schizophrenia. You can get support.
How can I get support for myself?
You can do the following.
- Speak to your GP about medication and talking therapies for yourself.
- Speak to your relatives care team about family intervention. For more information about family intervention see the further up this page.
- Speak to your relatives care team about a carers assessment.
- Ask for a carers assessment.
- Join a carers service. They are free and available in most areas.
- Join a carers support group for emotional and practical support. Or set up your own.
What is a carers assessment?NICE guidelines state that you should be given your own assessment through the community mental health team to work out what effect your caring role is having on your health. And what support you need. Such as practical support and emergency support.
The CMHT should tell you about your right to have a carers assessment through your local authority. To get a carers assessment you need to contact your local authority.
How do I get support from my peers?You can get peer support through carer support services or carers groups. You can search for local groups in your area by using a search engine such as Google. Or you can call our advice service on 0808 801 0525. They will search for you.
How can I support the person I care for?
You can do the following.
There is no definition for what high risk means. It could include:
Research Shows Cellular Clean
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Schizophrenia Center sampled the smell neurons pictured here, from individuals with and without schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Through examining these cells, neuropsychiatrist Koko Ishizuka, in collaboration with Kyoto University, found a protein that is usually cleared out by the cellular waste management. Her work suggests that the link between these brain disorders and the cellular clean-up system deserves a closer look.
-
Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder. It often runs in families and can cause troubling symptoms.
-
It’s caused by a chemical imbalance and other changes in the brain.
-
Symptoms include hearing voices, feeling that people are out to get you, and having false beliefs that are not based in reality.
-
These symptoms can make it very hard to function in the world and take care of yourself.
-
Treatment includes antipsychotic medicines, support services, and a healthy lifestyle.
Don’t Miss: What Does High Functioning Bipolar Look Like
What Can I Do To Manage Schizophrenia
People deal with their experience in different ways. You might need to try different things before finding something that works.
Support groups
You could join a support group. A support group is where people come together to share information, experiences and give each other support. Hearing about the experiences of others can help you feel understood. This may help you feel less alone and boost your self-confidence.
You might be able to find a local group by searching online. Rethink Mental Illness have support groups in some areas. You can find out what is available in your area, or get help to set up your own support group if you follow this link:
Or you can call our advice service on 0808 801 0525 for more information.
Recovery College
Recovery colleges are part of the NHS. They offer free courses about mental health to help you manage your experiences. They can help you to take control of your life and become an expert in your own wellbeing and recovery. You can usually self-refer to a recovery college. But the college may tell your care team.
Unfortunately, recovery colleges are not available in all areas. To see if there is a recovery college in your area you can use a search engine such as Google. Or you can call our advice service on 0808 801 0525 for more information.
Peer support through the NHS
- recognising and coping with symptoms,
- what to do in a crisis,
- meeting other people who can support you, and recovery.
Self-management techniques
- talk back to them,
What Are The Types Of Schizophrenia

There are different types of schizophrenia. The International Classification of Diseases manual describes them as below.
Paranoid schizophrenia
- Pranks, giggling and health complaints.
- Usually diagnosed in adolescents or young adults.
Catatonic schizophrenia
- Unusual movements, often switching between being very active and very still.
- You may not talk at all.
Simple schizophrenia
- Negative symptoms are prominent early and get worse quickly.
- Positive symptoms are rare.
Undifferentiated schizophrenia
Your diagnosis may have some signs of paranoid, hebephrenic or catatonic schizophrenia, but doesnt obviously fit into one of these types alone.
Residual schizophrenia
This type of schizophrenia is diagnosed in the later stages of schizophrenia. You may be diagnosed with this if you have a history of schizophrenia but only continue to experience negative symptoms.
Other schizophrenia
There are other types of schizophrenia according to the ICD-10, such as.
- Cenesthopathic schizophrenia. This is where people experience unusual bodily sensations.
- Schizophreniform. Schizophreniform disorder is a type of psychotic illness with symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. But symptoms last for a short period.
Unspecified schizophrenia
Symptoms meet the general conditions for a diagnosis, but do not fit in to any of the above categories.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Treated For Depression
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
People with schizophrenia should do the following to help care for themselves and manage their condition:
- Take medications as prescribed. One of the most critical things a person with schizophrenia can do to help themselves is to take their medications. If you have schizophrenia, you should not stop your medication without talking to your healthcare provider. Sudden stopping of medication often speeds up the return of psychosis symptoms. Side effects are common with antipsychotics. However, there are many antipsychotic medications, so its often possible to work with your healthcare provider to find one that both works well for you and has minimal or no side effects.
- See your healthcare provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your condition.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Schizophrenia is more likely to respond and have a good outcome with early diagnosis and treatment.
- Avoid alcohol and recreational drug use. Alcohol and drug use can make schizophrenia symptoms worse and can lead to other issues. This includes using prescription medications in a way other than prescribed.
- Consider seeking support. Organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness can offer resources and information that can help.
Causes And Pathophysiology Of Schizophrenia
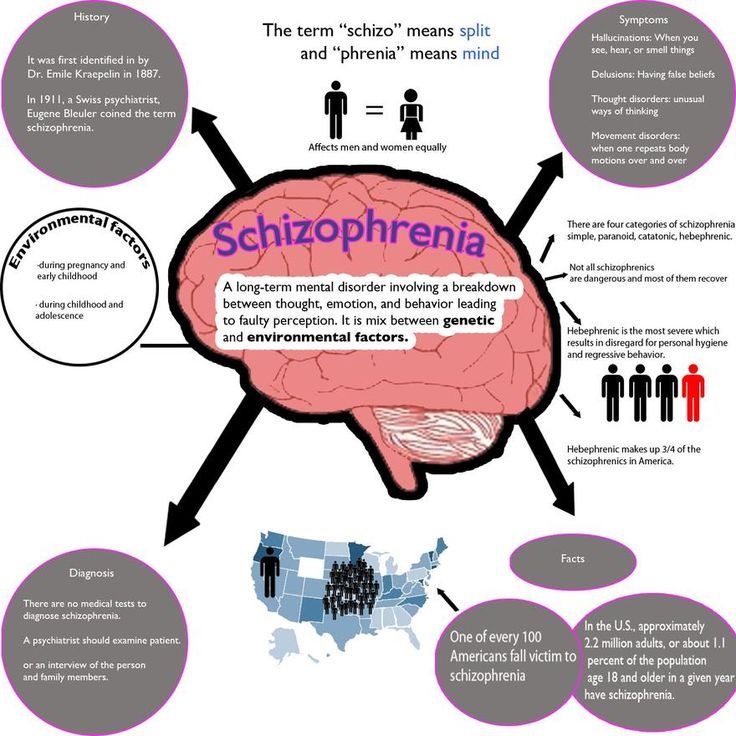
The causes of schizophrenia are unknown so far. Therefore, the term schizophrenia refers to an empirically defined syndrome characterized by a combination of certain symptoms which occur in a particular temporal pattern. The idea that schizophrenia is a distinct brain disorder is rooted in Emil Kraepelins concept of dementia praecox . This concept emphasized one particular aspect of the disorder: the onset of persistent cognitive disturbances early in life. The term schizophrenia was coined by Eugen Bleuler , who wanted to emphasize the loss of coherence between thought, emotion, and behavior which represents another important feature of the disorder. Bleuler actually spoke about schizophrenias, implying a group of diseases rather than one distinct disease entity. The present diagnostic systems compiled by the World Health Organization and the American Psychiatric Association distinguish various subtypes of schizophrenia which are classified according to particular symptom combinations, and according to certain aspects of the course and prognosis of the disease. However, these subtypes are defined in a phenomenological manner which neither implies distinct causes for any of the subtypes nor any particular treatment.
Table 1. Subtypes of schizophrenia according to the major classification systems
| ICD-10 |
|---|
James W. Little DMD, MS, Nelson L. Rhodus DMD, MPH, in, 2013
You May Like: How Often Do Panic Attacks Occur
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The word “negative” here doesnât mean “bad.” It notes the absence of normal behaviors in people with schizophrenia. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia include:
- Lack of emotion or a limited range of emotions
- Withdrawal from family, friends, and social activities
- Loss of pleasure or interest in life
- Poor hygiene and grooming habits
What Is Schizoaffective Disorder
People with schizoaffective disorder typically show symptoms of a mood disorder, such as mania or depression, alongside schizophrenia symptoms.
In the past, the process of diagnosing schizoaffective disorder may have been imprecise. Today, there is a distinction between having schizophrenia and mood episodes and having schizoaffective disorder.
Because the symptoms can overlap, it is not always clear whether a person has bipolar disorder or depression with psychotic features, post-traumatic stress disorder , or a schizophrenia-like illness, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
Read Also: How To End A Panic Attack
Psychosocial Factors During Pregnancy And Delivery
Some studies suggest an association between antenatal stress and schizophrenia. The children of mothers whose husband died while they were pregnant have been found to have a significantly increased rate of schizophrenia compared with children who lost their father in infancy in the first year of life. In The Netherlands, rates of schizophrenia have been found to be very slightly higher in individuals exposed in utero to war and flood disaster than in reference subjects.
In the Northern Finland 1966 Birth Cohort the risk of later schizophrenia among unwanted children was elevated 2.4-fold compared with wanted or mistimed children, even after adjustment for confounding by sociodemographic, pregnancy and perinatal variables. Unwantedness might be a marker for features associated with risk in either the mother or the child. In the same cohort, the level of schizophrenia in the offspring of antenatally depressed mothers was elevated by a factor of 1.5-foldly, but the association was not statistically significant. Those mothers of schizophrenia patients with a psychotic first-degree relative had suffered from depressed mood during pregnancy twice as often as other mothers. The familial risk for psychosis, including genetic risk for psychosis, might explain the elevated prevalence of depressed mood during pregnancy among the mothers of the offspring who went on to develop schizophrenia.
Neurotransmitters As A Cause Of Schizophrenia
Problems with brain chemistry may also be a cause of schizophrenia. In particular, this includes neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate. If there is an imbalance of these chemicals, it can affect the way the brain reacts to stimuli.
Issues with responding to stimuli can result in problems with how the individual perceives sensory information, such as sound, smell, taste, and sight. This may lead to hallucinations or delusions.
Findings from a 2020 study suggest that there is some relevance in linking dopamine and glutamate to schizophrenia. Researchers continue to study this relationship to gain a better understanding.
You May Like: How To Deal With Relationship Anxiety
Treatment And Medical Options For Schizophrenia
Over the past 30 years, researchers have identified more than 100 genes that may increase the risk of schizophrenia, and they have begun finding novel pathways and making other discoveries that may help identify new targets for drug therapy.
There is no cure for schizophrenia, and as with many diseases that can be managed but not cured, early detection and treatment are important.
Seek medical treatment if you or someone you know might be experiencing signs of psychosis or schizophrenia. Early treatment can improve a persons chance for a successful recovery. Whats more, proper treatment helps minimize symptoms and improve quality of life. Yet even after symptoms have ceased and schizophrenia is managed, most people with schizophrenia require ongoing drug and nondrug treatment.
Recommended Reading: Meaning Of Phobic
Is It Possible To Recover From Schizophrenia
Many people who live with schizophrenia have recovery journeys that lead them to live meaningful lives.
Recovery can be thought of in terms of:
- clinical recovery, and
- personal recovery.
What is clinical recovery?
Your doctor might have talked to you about recovery. Some doctors and health professionals think of recovery as:
- no longer having mental illness symptoms, or
- where your symptoms are controlled by treatment to such a degree that they are not significantly a problem.
Sometimes this is called clinical recovery.
Everyones experience of clinical recovery is different.
- Some people completely recover from schizophrenia and go on to be symptom free.
- Some who live with schizophrenia can improve a great deal with ongoing treatment.
- Some improve with treatment but need ongoing support from mental health and social services.
What is personal recovery?
Dealing with symptoms is important to a lot of people. But some people think that recovery is wider than this. We call this personal recovery.
Personal recovery means that you can live a meaningful life.
What you think of as being a meaningful life might be different to how other people see it. You can think about what you would like to do to live a meaningful life and work towards that goal.
Below are some ways you can think of recovery.
What can help me recover?
You may want to think about the following questions.
The following things can be important in recovery.
Read Also: What Are The Types Of Schizophrenia
Who Does It Affect
Schizophrenia typically starts at different ages, depending on sex. It usually starts between ages 15 and 25 for men and between 25 and 35 for women. It also tends to affect men and women in equal numbers.
Schizophrenia in children, especially before age 18, is possible but rare. However, these cases are usually very severe. Earlier onset tends to lead to a more severe, harder-to-treat condition.
About 20% of new schizophrenia cases occur in people over age 45. These cases tend to happen more in women. Delusion symptoms are stronger in these cases, with less-severe negative symptoms and effects on the ability to think and focus.
Major Life Events And Traumas
Although a major life event is unlikely to be a single cause of schizophrenia, it may act as a trigger for someone who is already susceptible to it because of another factor.
A major stressful event such as the death of a loved one or becoming unemployed causes big changes in someones hormone levels as they try and recover from the shock. It is not known exactly how, but these changes are thought to be involved in the development of schizophrenia.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Prescribed Anxiety Medication
Which Functional Pathways Are Affected
When we looked at the functions of the 49 genes that were expressed differently in healthy people and those with schizophrenia, we could see that they were involved in biochemical pathways that affected specific functions in the brain: synaptic neurotransmission, signal transduction, cytoskeletal dynamics and neurodevelopment.
Figure 2: From brain to synapse: gene expression changes in schizophrenia are highly localised to the synapse.Click to enlarge image
To understand this, we need to take a closer look at brain cells: neurons. Typically, a neuron consists of a cell body, containing the nucleus many extensions of the cell body, known as dendrites and a single extension, called an axon, which may be as long as 1 m .
The 49 genes that were expressed differently in people with schizophrenia, therefore, are involved in fundamental brain processes that determine how the cells in the brain respond to external signals and to nerve impulses elsewhere in the brain these responses include a change in the density of dendritic spines at the synapse. This is consistent with the decreases in synapse density observed microscopically in post-mortem examinations of the brains of people with schizophrenia. Such changes at the synapse are known to be key to the adaptive changes that occur during learning and development changes known as synaptic plasticity.
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
In some people, schizophrenia appears suddenly and without warning. But for most, it comes on slowly, with subtle warning signs and a gradual decline in functioning, long before the first severe episode. Often, friends or family members will know early on that something is wrong, without knowing exactly what.
In this early phase of schizophrenia, you may seem eccentric, unmotivated, emotionless, and reclusive to others. You may start to isolate yourself, begin neglecting your appearance, say peculiar things, and show a general indifference to life. You may abandon hobbies and activities, and your performance at work or school can deteriorate.
Read Also: How Does A Panic Attack Happen
Family Education And Support
Educational programs for family members, significant others, and friends offer instruction about schizophrenia symptoms and treatments, and strategies for assisting the person with the illness. Increasing key supporters understanding of psychotic symptoms, treatment options, and the course of recovery can lessen their distress, bolster coping and empowerment, and strengthen their capacity to offer effective assistance. Family-based services may be provided on an individual basis or through multi-family workshops and support groups. For more information about family-based services in your area, you can visit the family education and support groups page on the National Alliance on Mental Illness website.
Differences In Brain Chemistry
Studies show that people can be more likely to experience schizophrenia if their brain development was disrupted during pregnancy or early childhood. Changes in brain structure do not appear in everyone with schizophrenia though.
Some chemicals also seem to behave differently in the brains of people who experience schizophrenia. These chemicals are thought to include dopamine, which helps to carry messages between brain cells.
Some research suggests that an imbalance between certain neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin, may be one of the causes behind schizophrenia.
Antipsychotics, which are sometimes used to treat schizophrenia, can help to lower dopamine levels.
For more information see our pages on antipsychotics.
More recently my physical health has deteriorated. I have become more agoraphobic and find group settings harder than before.
You May Like: How To Diagnose Binge Eating Disorder