What Treatments Are Available For Phobias
With the exception of severe social phobia, medication is rarely prescribed for the treatment of phobias. If medication is needed, it is often for treating the panic symptoms associated with confronting a phobia. These medications can include tranquilizers or beta blockers.
Exposure therapy, also called systematic desensitization, incorporates the use of imagery, has shown very effective in treating phobias. The therapist asks the client to recall an event and confront the thoughts and feelings that occurred during that event, but this time in a safe environment. Gradually, the patient is introduced to the fear. For example, a patient with a fear of water may first look at pictures of water then work his/her way up to touching water and finally being submerged in water. Hypnosis can also be helpful at reducing anxiety caused by a phobia.
Flooding uses the same approach as exposure therapy but does so rapidly rather than gradually. While it has the benefit of being much faster than exposure therapy, flooding can in some cases worsen phobias rather than alleviate them. In order to control the physical symptoms associated with phobia exposure, the patient may be given a low dosage of a sedative before the treatment.
The Drake Institute Can Help
Since 1980, the Drake Institute has been successfully treating patients for their anxiety disorder symptoms.
By using Biofeedback in conjunction with brain-map guided Neurofeedback and Neuromodulation, the Drake Institute is able to create non-drug treatment protocols custom-tailored to each patients specific needs and requirements.
In addition to these advanced treatment methodologies, the Drake Institute also utilizes Heart Rate Variability training to improve the homeostasis or balanced functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
During Bio- or Neurofeedback, the physiologic recordings are provided back to the patient instantaneously through auditory and/or visual feedback, which enables the patient to reduce and potentially eliminate their tension through achieving deep relaxation, creating healthy homeostasis and physiological balance. This deep relaxation may not be possible without the physiologic feedback provided from the instruments.
Once the physiological tension is reduced, the anxiety symptoms begin to reduce as well. For example, if a patient is dealing with tension headaches, the process of Bio- or Neurofeedback can assist with lowering the individuals blood pressure and allows them to release the abnormal muscle tension that that carry in their face and head, subsequently causing the headaches to dissipate.
How Phobias Differ From Other Mental Disorders
Many mental health disorders show similar symptoms. However, there are important differences that mental health professionals look for in order to provide an accurate diagnosis. Provided here is a brief look at the differences between phobias and other mental health disorders.
You May Like: Can You Go To Urgent Care For Panic Attacks
What Are The Symptoms Of Specific Phobias
Symptoms of specific phobias may include:
- Excessive or irrational fear of a specific object or situation
- Avoiding the object or situation or enduring it with great distress
- Physical symptoms of anxiety or a panic attack, such as a pounding heart, nausea or diarrhea, sweating, trembling or shaking, numbness or tingling, problems with breathing , feeling dizzy or lightheaded, feeling like you are choking
- Anticipatory anxiety, which involves becoming nervous ahead of time about being in certain situations or coming into contact with the object of your phobia for example, a person with a fear of dogs may become anxious about going for a walk because they may see a dog along the way.
Children with a specific phobia may express their anxiety by crying, clinging to a parent, or throwing a tantrum.
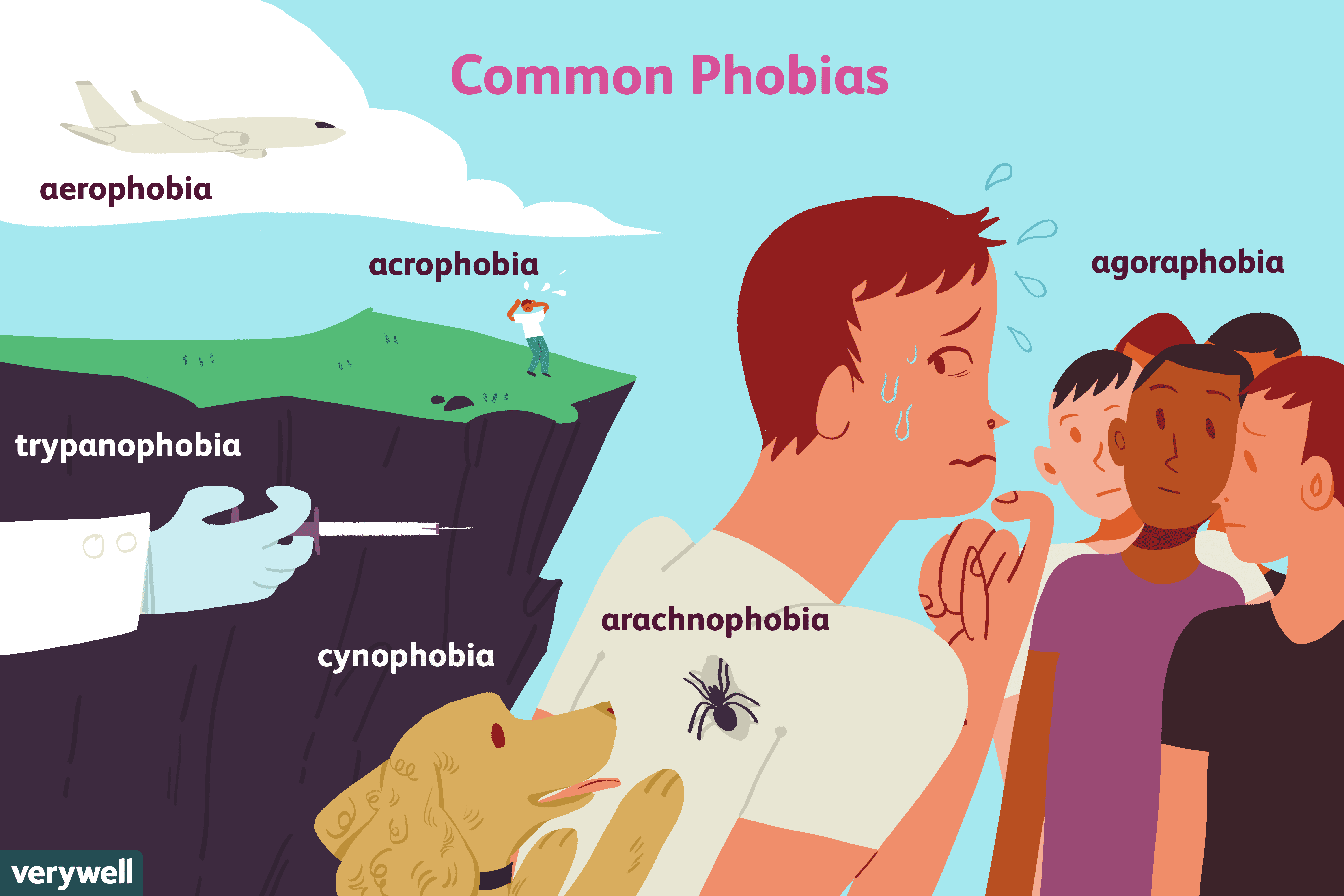
Types Of Specific Phobias

A specific phobia is defined as an extreme, irrational fear or aversion to a particular thing or situation such as a thunderstorm or being in small, tight places, etc. The fear is so intense it interferes with the way you live. Whats key here is that the object or situation usually does not pose significant danger, and yet the fear of it is intense and often interferes with your life.1
Within specific phobias, there are five different categories:1
- Phobias of animals or insects like dogs, snakes, or spiders
- Phobias of natural phenomena like heights, storms, or water
- Phobias of blood or injury like getting a blood test or needles
- Phobias of specific situations like flying in planes, driving cars, or being in confined places
- Other phobias like choking, vomiting, or catching an illness
Its estimated that 12.5% of US adults and 19.3% of teens will deal with a specific phobia at some time in their lives, making it the most common type of phobia and the most common type of anxiety disorder overall. Adult women tend to develop specific phobias at twice the rate as men, while the numbers among teens are closer. Anxiety disorders across the board are more prevalent among women than men. The reasons for this are still being explored, but it likely relates to hormonal differences.4,5
Recommended Reading: Premorbid Schizophrenia
Types Of Anxiety Disorder That Causes An Individual Irrational Fear
- |
- Pages: 2
- This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students’ samples.
Having an anxiety disorder can lead to serious complications in the life of a person, it can increase the risk of depression, take away time and focus from other activities, impair the ability to perform tasks quickly and efficiently due to difficulty in concentration. It can also lead to or worsen some physical health conditions like headaches and migraines, heart-health issues, sleep problems and insomnia, chronic pain, and illness. Anxiety disorder often occurs along with other mental health problems like phobias, depression, substance abuse, and suicidal thoughts.
How Common Are Specific Phobias
The National Institute of Mental Health estimates that about 5%-12% of Americans have phobias. Specific phobias affect an estimated 6.3 million adult Americans.
Phobias usually first appear in adolescence and adulthood, but can occur in people of all ages. They are slightly more common in women than in men. Specific phobias in children are common and usually disappear over time. Specific phobias in adults generally start suddenly and are more lasting than childhood phobias. Only about 20% of specific phobias in adults go away on their own .
Also Check: How To Get Motivated To Exercise When Depressed
Causes Of Specific Phobia
The reasons why phobias develop are not fully understood. Specific phobias tend to begin in children, whose developing brains are still developing patterns about how to respond to the world around them. A common example of this is a child who develops a phobia of dogs after being bitten by one, but there are many more subtle ways that a childs brain can take in information that teaches them to fear something. For example, they could learn to fear a dog by watching a movie that features a scary dog or watch a family member flinch in response to a dogs bark.1
Still, experiences in childhood are only one of many potential reasons why one may go on to develop a specific phobia. Genetics may also play a role.1Many specific phobias may be due to a complex interplay between genetics and life experiences. The same goes for social anxiety disorders and agoraphobia. Teens are more vulnerable to developing social anxiety disorders, likely because the teen years are marked by hormonal changes and new social pressures. Agoraphobia and panic disorders have a lot of overlap, and they both tend to start in young adulthood.6,11,12
Can Anxiety Disorders Be Prevented
You cant prevent anxiety disorders. But you can take steps to control or reduce your symptoms:
- Check out medications: Talk to a healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking over-the-counter medications or herbal remedies. Some of these contain chemicals that may make anxiety symptoms worse.
- Limit caffeine: Stop or limit how much caffeine you consume, including coffee, tea, cola and chocolate.
- Live a healthy lifestyle: Exercise regularly and eat a healthy, balanced diet.
- Seek help: Get counseling and support if you experienced a traumatic or disturbing event. Doing so can help prevent anxiety and other unpleasant feelings from disrupting your life.
You May Like: Spasmenagaliaphobia
How Are Anxiety Disorders Diagnosed
If you have symptoms of an anxiety disorder, talk to your healthcare provider. Theyll start with a complete medical history and physical examination.
There are no lab tests or scans that can diagnose anxiety disorders. But your provider may run some of these tests to rule out physical conditions that may be causing symptoms.
How Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome Related To Anxiety Disorders
Some people feel the effects of stress in their stomachs. People with IBS have uncomfortable problems with digestion, including stomach pain, constipation and diarrhea. They also frequently have anxiety and depression, which can make symptoms worse.
The connection between IBS and anxiety comes from the nervous system partly controlling the colon. The nervous systems response to stress may affect the stomach. Among people who get treated for IBS, anywhere from 50% to 90% may also have an anxiety disorder or depression. Treatment for IBS may include stress management and psychotherapy to relieve symptoms.
Read Also: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Who Can Diagnose Anxiety Disorders
If your provider finds no signs of physical illness, they may refer you to a psychiatrist or psychologist. These mental health professionals specialize in diagnosing and treating mental illnesses. They may use specially designed interview and assessment tools to figure out if you have an anxiety disorder. Typically, the provider bases a diagnosis on:
- Your reported symptoms, including how intense they are and how long they last.
- Discussion of how the symptoms interfere with your daily life.
- The providers observation of your attitude and behavior.
Providers also consult the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . The American Psychiatric Association publishes the DSM-5. Its the standard reference manual for diagnosing mental illnesses.
Are You Suffering From Anxiety
Take our 2-minute anxiety quiz to see if you may benefit from further diagnosis and treatment.
A phobia is an intense as well as irrational fear toward one or more things or situations for which the level or intensity of fear does not match the actual danger of what you fear.
A phobia can be specific, like a fear of dogs or being high off the ground. But it can also be overarching, like being in any social setting or public place.2
While fear is a natural and universal human emotion, having a phobia is a medical diagnosis and not a word to be tossed around lightly. To understand phobias, it is helpful to have a deeper understanding of fear and why we experience it.
Also Check: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
What Can I Do About It
Most people who experience problems with anxiety recognize that their fears are irrational but dont think they can do anything to control them. The good news is that anxiety disorders are treatable. Recovery isnt about eliminating anxiety. Its about managing anxiety so you can live a fulfilling life.
Some physical health problems, such as heart or thyroid problems, can cause anxiety symptoms. Your doctor will look at all possible options to make sure that another medical problem isnt behind your experiences.
How Are Specific Phobias Treated
Treatment for specific phobias may include one or a combination of:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy: Psychotherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for specific phobias. Treatment usually involves a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, called systematic desensitization or exposure and response prevention therapy, in which patients are gradually exposed to what frightens them until their fear begins to fade.
- Medication: For situational phobias that produce intense, temporary anxiety , short-acting sedative-hypnotics such as alprazolam orà lorazepamà à may be prescribed on an occasional, as-needed basis to help reduce anticipatory anxiety. Unless a phobia is accompanied by other conditions such as depression or panic disorder, long-term or daily medicines are generally not used. Occasionally, serotonergicà antidepressantsà such asescitalopram oxalate , à fluoxetine ,à andà paroxetine may have potential value for some patients. More recently, common blood pressure drugs called beta-blockers have been used to treat anxiety related to specific phobias.
- Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, may also help reduce anxiety symptoms.
Also Check: Definition Phobia
Specific Or Simple Phobias
Specific or simple phobias centre around a particular object, animal, situation or activity.
They often develop during childhood or adolescence and may become less severe as you get older.
Common examples of simple phobias include:
- animal phobias such as dogs, spiders, snakes or rodents
- environmental phobias such as heights, deep water and germs
- situational phobias such as visiting the dentist or flying
- bodily phobias such as blood, vomit or having injections
- sexual phobias such as performance anxiety or the fear of getting a sexually transmitted infection
Who Is At Risk For Anxiety Disorders
A mix of genetic and environmental factors can raise a persons risk for developing anxiety disorders. You may be at higher risk if you have or had:
- Certain personality traits, such as shyness or behavioral inhibition feeling uncomfortable with, and avoiding, unfamiliar people, situations or environments.
- Stressful or traumatic events in early childhood or adulthood.
- Family history of anxiety or other mental health conditions.
- Certain physical conditions, including thyroid problems and heart arrhythmias .
Anxiety disorders occur more often in women. Researchers are still studying why that happens. It may come from womens hormones, especially those that fluctuate throughout the month. The hormone testosterone may play a role, too men have more, and it may ease anxiety. Its also possible that women are less likely to seek treatment, so the anxiety worsens.
Recommended Reading: Feratrophobia
The Difference Between Fear And Phobia
The term phobia gets thrown around a lot these days, but having a fear and having a phobia arent exactly the same thing.
Essentially, fear is temporary phobia isnt.
Having a phobia creates a stumbling block in your life, and the fear it causes can be so strong that youll do anything to avoid the object of that phobia. Phobia that becomes debilitating is a type of anxiety disorder. Take, for example, a job offer. You made it through the hardest partlanding your dream positiononly to find out that your office will be on the 20th floor of an office buildingand you have a phobia of heights. In order to avoid being so high off the ground, you turn the position down and pass up a significant job opportunity because of your phobia.1
Phobias can be debilitating and crippling, and they can keep you from enjoying the things you love with the people you love. But it doesnt have to be this way. There is hope and help for people with phobias.
How Do I Know If My Child Has An Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety-related problems in children share four common features. The anxiety:
- Is typically a fear or fixation that interferes with the ability to enjoy life, get through the day or complete tasks.
- Is puzzling to both the child and parents.
- Does not improve after logical explanations to address the worries.
- Is treatable.
Also Check: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
How Fear Works In The Brain
One of the ways the brain helps keep you alive is by warning you of dangers. When the brain senses danger, an internal alarm system is activated, sending out various signals that trigger feelings of fear or anxiety. These are physical and cognitive reactions triggered in response to whatever it is that your brain perceives as dangerous or scary.
Sometimes, we should be fearfulwithout fear, we would unknowingly put ourselves into life-threatening situations without taking proper precautions. But the difference between having healthy, occasional bouts of fear and having a phobia is that a phobia is by definition irrational: Despite the intense fear you feel, the circumstance or object of your fear poses little or no actual threat to you.3
Think of a phobia as the brains alarm system in overdriveit overestimates the threat of a particular situation, triggering intense anxiety and leading you to avoid that situation in the future. That avoidance actually makes a phobia worse because it solidifies the brains overblown association between the situation and its threat level.
How Do Anxiety Disorders Affect Children
Its normal for children to feel some amount of anxiety, worry or fear at certain points. For example, a child may feel scared of a thunderstorm or barking dog. A teenager might get anxious about an upcoming test or school dance.
But sometimes, children approach these situations with overwhelming dread or they cant stop thinking about all the fears tied to one of these events. It may seem that none of your comforts help. These children often get stuck on their worries. They have a hard time doing their daily activities, like going to school, playing and falling asleep. Theyre extremely reluctant to try something new.
When thinking about your childs anxiety levels, getting stuck is key. It separates the regular worries of childhood from an anxiety disorder that needs professional help. If the anxiety or worry interferes with your childs ability to function, it may be time to seek help
Also Check: Psychological Symptoms Definition
How Many People Are Affected By Phobias
Approximately 5% of the general population suffers from at least one phobia, although there are large differences amongst countries. In the United States, nearly 9% of the population has been diagnosed with a specific phobia while, for example, that number drops to .2% in Northern Ireland. Approximately 4.6% of the worlds population suffers from a social phobia.
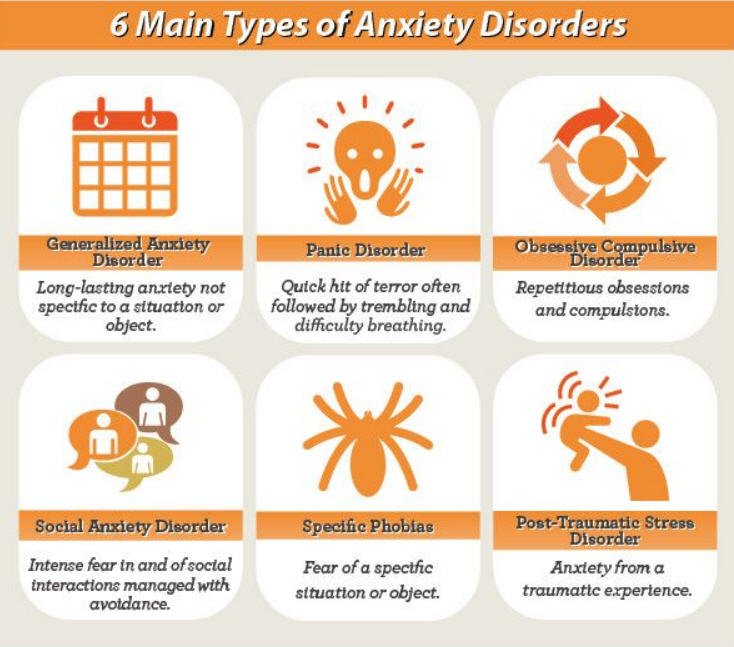
What Are The Five Major Types Of Anxiety Disorders
The five major types of anxiety disorders are:
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, OCD, is an anxiety disorder and is characterized by recurrent, unwanted thoughts and/or repetitive behaviors . Repetitive behaviors such as hand washing, counting, checking, or cleaning are often performed with the hope of preventing obsessive thoughts or making them go away. Performing these so-called “rituals,” however, provides only temporary relief, and not performing them markedly increases anxiety.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, PTSD, is an anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to a terrifying event or ordeal in which grave physical harm occurred or was threatened. Traumatic events that may trigger PTSD include violent personal assaults, natural or human-caused disasters, accidents, or military combat.
- Social Phobia Social Phobia, or Social Anxiety Disorder, is an anxiety disorder characterized by overwhelming anxiety and excessive self-consciousness in everyday social situations. Social phobia can be limited to only one type of situation – such as a fear of speaking in formal or informal situations, or eating or drinking in front of others – or, in its most severe form, may be so broad that a person experiences symptoms almost anytime they are around other people.
Recommended Reading: Which Type Of Therapy Has Been Used Widely With Those Suffering An Anxiety Disorder In Old Age