Is It Drugs Or Is It Bipolar Disorder
Since the symptoms of both of these disorders can be very similar, the patient needs to be assessed by a caregiver who is a specialist in dual diagnosis. Symptoms can overlap, and it is often very difficult to distinguish between one and the other.
One of the mitigating factors they look for is whether the patient was having episodes prior to the onset of the drug abuse. If the behavior was present without the drugs, it is easier to determine that bipolar may be the core issue. If the bipolar behavior began as a result of the drug abuse, it can be much harder to tell. The importance of obtaining the correct diagnosis cannot be stressed enough, as both issues can be treated separately or together, but in the case of drug abuse, and depending on the patients drug of choice, some medications may not be as effective or can even exacerbate the behavior.
Medications that are strictly for bipolar disorder can bring a great deal of relief to a patients life, helping them to normalize their moods and to better function in their day-to-day lives. Some of these drugs include:
Bipolar Disorder And Relationships
Bipolar disorder can affect any of your relationships. But these effects might show up most clearly in your closest relationships, like those with family members and romantic partners.
When it comes to managing a relationship while living with bipolar disorder, honesty can always help. Being open about your condition can help your partner better understand your symptoms and how they can offer support.
You might consider starting with a few basic details, including:
- how long youve had the condition
- how episodes of depression usually affect you
- how episodes of mania usually affect you
- your treatment approach, including therapy, medication, and coping strategies
- anything they can do to help
Want more tips on maintaining a healthy relationship when you or a partner has bipolar disorder? Our guide can help.
What Diseases Can Mimic Mental Illness
There are many diseases which can display symptoms of mental illness. These diseases are mental disorders and so its not easy to tell them apart from psychiatric disorders. A few diseases which mimics mental illness are: Parkinsons disease, Alzheimers disease, sleep disorders, anorexia nervosa, dyslexia etc..
Recommended Reading: How Much Vitamin D For Depression
Unspecified Vs Specified Bipolar Disorder
As mentioned, the American Psychiatric Association prefers the terms unspecified or other specified for bipolar disorder to better reflect the uncertainty of the diagnoses. .
Other specified bipolar disorder may be diagnosed when a person displays specific symptoms of bipolar , but the full criteria for those symptoms aren’t met.
Unspecified bipolar may be the diagnosis when a person’s symptoms resemble the symptoms of bipolar disorder, but the clinician chooses not to specify the reason the criteria are not met for a specific bipolar disorder, such as in an emergency room where there is insufficient information to make a more specific diagnosis.
What If Im Not Happy With My Treatment

If you arent happy with your treatment you can:
- talk to your doctor about your treatment options,
- ask for a second opinion,
- get an advocate to help you speak to your doctor,
- contact Patient Advice and Liaison Service , or
- make a complaint.
There is more information about these options below.
How can I speak to my doctor about my treatment options?
You can speak to your doctor about your treatment. Explain why you arent happy with it. You could ask what other treatments you could try.
Tell your doctor if there is a type of treatment that you would like to try. Doctors should listen to your preference. If you arent given this treatment, ask your doctor to explain why it isnt suitable for you.
Whats a second opinion?
A second opinion means that you would like a different doctor to give their opinion about what treatment you should have. You can also ask for a second opinion if you disagree with your diagnosis.
You dont have a right to a second opinion. But your doctor should listen to your reason for wanting a second opinion.
What is advocacy?
An advocate is independent from the mental health service. They are free to use. They can be useful if you find it difficult to get your views heard.
There are different types of advocates available. Community advocates can support you to get a health professional to listen to your concerns. And help you to get the treatment that you would like. NHS complaints advocates can help you if you want to complain about the NHS.
Read Also: A Fear Becomes A Phobia When
Can You Get A Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis Removed Or Reversed
A diagnosis for bipolar disorder usually is not removed because its a lifelong disorder.
But if you feel that your condition has been misdiagnosed, do not hesitate to advocate for yourself and seek a second medical opinion. Additional healthcare professionals may be able to reverse or amend a misdiagnosis of bipolar disorder.
Depressive Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
The depressive symptoms of bipolar disorder include:
- Very low mood state
- A loss of interest in things that previously gave pleasure
- Dysregulation of appetite
- Significant weight loss or gain
- Change in sleeping habits
- Altered physical agitation rate
- Feelings of fatigue, worthlessness, or inappropriate guilt
- Difficulty concentrating
- Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide
Read Also: How To Handle A Panic Attack At School
Neurotransmitters: The Kynurenine Pathway Of Tryptophan Degradation
One of the first hypotheses concerning mood disorders etiology was related to neurotransmitters alterations: psychopharmaceutical development has highlighted an important role of different neurotransmitter systems into the functional and clinical aspects of mood disorders. However, although existing literature tends to emphasize specificity in drugs’ mechanisms of actions, many effective treatments target multiple mechanisms and a multitarget approach to treatment could be better suited for a multifactorial illness such as MDD .
Two of the previously described cytokines, TNF- and IFN-, play a major role in influencing one fundamental biological pathway in the brain: the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation. Alterations in the kynurenine pathway, that begins with tryptophan degradation, have been hypothesized in depression models this pathway is the starting point for serotonin and melatonin biosynthesis, both quantitatively altered in BD .
Moreover, ventral, striatal-ventrolateral, and orbitofrontal cortical reward processing circuitry have been proposed to define an endophenotype specific of BD , and consistent evidence associates inflammation with decreased dopamine synthesis, packaging, and release, leading to decreased dopamine and dopamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid, and decreased availability of striatal dopamine, which resultsat the behavioral levelin depressive symptoms related to motivation and motor activity .
How Do Doctors Diagnose Bipolar Disorder
The main symptoms of bipolar disorder are mood swings. Doctors will first rule out other medical conditions that can cause mood changes. A stroke, brain tumor, or overactive or underactive thyroid can cause mood changes. Your doctor may order imaging tests, brain scans, or blood tests.
Your doctor will question you about your symptoms. A diagnosis of bipolar disorder is based on markers such as:
- severity of the manic or depressive episodes
- length of an episode or how long the episodes have persisted
- frequency of an episode
- frequency of symptoms
- experiences over a lifetime
Sometimes, people may seek help for depressive disorders, but manic episodes can go unnoticed. This is one reason bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose. In addition, bipolar disorder can mimic psychotic symptoms and be misdiagnosed as schizophrenia. Conditions such as thyroid disease, some medications, and drug use can mimic symptoms or worsen mood. These contribute to difficulty of diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Is Anxiety A Chronic Illness
Manic Symptoms In Children
Symptoms of mania in children can include:
- acting very silly and feeling overly happy
- talking fast and rapidly changing subjects
- having trouble focusing or concentrating
- doing risky things or experimenting with risky behaviors
- having a very short temper that leads quickly to outbursts of anger
- having trouble sleeping and not feeling tired after sleep loss
Talking To A Health Care Provider About Your Mental Health
If you or someone you know is in immediate distress or is thinking about hurting themselves, call or text the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org. You can also contact the Crisis Text Line . For medical emergencies, call 911.
Communicating well with a health care provider can improve your care and help you both make good choices about your health. Find tips to help prepare for and get the most out of your visit. For additional resources, including questions to ask a provider, visit the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality website.
Read Also: What Does An Eating Disorder Therapist Do
Can Ptsd Mimic Bipolar Disorder
Yes, Post-traumatic stress disorder can mimic certain aspects of bipolar disorder. Patients with bipolar disorder exhibit manic, depressive or hypomanic episodes, each of which can be accompanied by a variety of symptoms. In the manic phase, patients may feel euphoric, have inflated self-esteem, become highly involved in pleasurable activities that have a high potential for painful consequences , and have increased irritability and anger. In the depressive phase, patients may feel sad, hopeless, and discouraged, and their sleep and appetite may be affected. PTSD patients will often exhibit the same symptoms during their flashbacks. For example, a PTSD patient may start hyperventilating during a flashback because they believe they are going to die. If you or a loved one experiences PTSD symptoms, it is important to seek treatment from a psychiatrist, who will be able to make the proper diagnosis..
The Challenges Of Diagnosing A Patient With Bipolar Disorder
In part 1 of this 2-part episode, W. Clay Jackson, MD, DipTH, speaks about diagnosing patients with bipolar disorder, other disorders commonly confused with bipolar disorder, and the risk factors and the prevalence of bipolar disorder.
For more information on bipolar disorder, visit the Resource Center.
Listen to part 2 of this episode here.
W. Clay Jackson, MD, DipTh, is an assistant professor of clinical psychiatry and family medicine at the University of Tennessee College of Medicine .
TRANSCRIPTION:
Jessica Bard: Hello, everyone. And welcome to another installment of Podcast 360, your go-to resource for medical news and clinical updates. I’m your moderator, Jessica Bard, with Consultant360, a multidisciplinary medical information network.
Nearly 3% of US adults had bipolar disorder in the past year, according to the National Institutes of Health. Dr Clay Jackson is here to speak with us today about bipolar disorder. Dr Jackson is an assistant professor of Clinical Psychiatry and Family Medicine at the University of Tennessee College of Medicine in Memphis, Tennessee.
Thank you for joining us today, Dr Jackson. Please describe mania, hypomania, and major depressive episode. And what are the differences between each?
Jessica Bard: Yeah, absolutely. So, we talked about the symptoms, but how is bipolar disorder diagnosed when we’re talking about maybe physical examination?
Jessica Bard: When is bipolar disorder typically diagnosed?
Dr Clay Jackson:
Also Check: How To Deal With Bipolar Depression
Can You Be Wrongly Diagnosed With Mental Illness
Yes. It is possible to be wrongly diagnosed with mental illness. There are so many forms of mental illness and it is not always easy for a medical professional to determine the difference between mental illness and non-mental illness. A general practitioner or a psychiatrist may not always be able to diagnose mental illness successfully. There are many factors that can influence the effectiveness of a mental health clinic. The first factor is the personal situation of the patient. For example, if a patient has a history of drug addiction, then it is likely that a mental health clinic will diagnose the patient with a drug addiction or an addiction to something else. Nor is it always possible to determine whether a person is actually suffering from mental illness. Sometimes, a person may just be going through a difficult period in their life..
How Getting The Wrong Diagnosis Can Be Harmful
For individuals who are misdiagnosed with bipolar disorder, one potential pitfall may involve health problems that result from taking the prescription drugs used to treat the condition, according to Zimmerman. He notes that some medications, including atypical antipsychotics, can increase the risk for high cholesterol and diabetes, while others, such as lithium, have been linked to thyroid and kidney problems.
Conversely, up to 20 percent of people with bipolar disorder may be mistakenly diagnosed with depression by their primary care doctors, according to a study published in July 2011 in the British Journal of Psychiatry. And another study, published in August 2017 in the journal Bipolar Disorders, analyzed the delay in diagnosis of 382 people with bipolar disorder and found that 90 of those individuals initially received a diagnosis of depression before being correctly diagnosed. According to the study, the lag between diagnoses was about nine years. The patients who were originally diagnosed with depression tended to be younger, have more manic symptoms, and have better coping skills, which perhaps helped them function throughout the day and contributed to the delay in getting the correct diagnosis.
These findings arent surprising, says Jeremy Schwartz, a psychotherapist in Brooklyn, New York. Bipolar disorder can be hard to diagnose, he says, because people often seek professional help only during their down periods and neglect to mention their up, or manic, periods.
Also Check: Can Bipolar 1 Become Bipolar 2
Bipolar Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
When a diagnosis is suggestive rather than indicative of bipolarity
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Laurence Mouton / Getty Images
Bipolar disorder not otherwise specified is one of those psychiatric terms that can cause more confusion than clarity, especially to the person being diagnosed. Bipolar disorder NOS is usually diagnosed when a patient shows some symptoms of bipolar disorder but doesn’t necessarily meet all the criteria as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
The term bipolar disorder NOS was used in the fourth edition of the DSM however, the DSM-5 actually uses the terms “unspecified bipolar and related disorder” or “other specified bipolar and related disorder” to diagnose conditions that were previously called bipolar disorder NOS.
Can Brain Scans Or Imaging Tests Help With The Bipolar Diagnosis
While doctors donât rely on brain scans or imaging tests for making a bipolar diagnosis, some high-tech neuroimaging tests may help doctors make specific neurologic diagnoses that can account for psychiatric symptoms. An MRI or CT scan is therefore sometimes ordered in patients who have had a sudden change in thinking, mood, or behavior to assure that a neurological disease is not the underlying cause.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health, studies are underway to examine whether electroencephalograms and magnetic resonance imaging studies of the brain can reveal differences between bipolar disorder and related behavioral syndromes. But bipolar disorder remains a clinical diagnosis, and no imaging study or other lab test has yet been established to confirm its diagnosis or guide its treatment.
You May Like: What Is The Phobia Of Dying
Hypomania Can Go Unnoticed
Some people with bipolar II who present to clinicians do not have a clear history of hypomania.
What is Hypomania?
Hypomania refers to an elevation in mood that is less drastic than mania. Hypomania may sometimes be enjoyable due to the increased energy and confidence that often come with it. However, it can still lead to impulsive behaviour with adverse consequences, such as overspending and damaging personal relationships. Because it is more subtle in how it is experienced, it is harder to pick up.
Because it is enjoyable, people with bipolar II may not seek treatment during a hypomanic episode. Research suggests that people with bipolar II are more likely to seek treatment for a depressive episode than a hypomanic episode. Hypomania also does not tend to involve psychotic symptoms , or a serious break from reality. Furthermore, hypomania does not tend to end in hospitalisation, as mania sometimes does.
Hypomania is therefore less likely to be recognised by mental health professionals, the person with h bipolar II or their family and close friends. This could explain the research finding that misdiagnosis of bipolar disorder as unipolar depression is more common in bipolar type II than in bipolar type I7.
Ruling Out Other Conditions
There are no specific blood tests or brain scans to diagnose bipolar disorder. Even so, a doctor may perform a physical exam and order lab tests, including a thyroid function test and urine analyses. These tests can help determine if other conditions or factors could be causing your symptoms.
A thyroid function test is a blood test that measures how well your thyroid gland functions. The thyroid produces and secretes hormones that help regulate many bodily functions.
If your body does not receive enough of the thyroid hormone, which is known as hypothyroidism, your brain may not function as expected. As a result, you may have problems with depressive symptoms or develop a mood disorder.
Sometimes, certain thyroid issues cause symptoms that are similar to those of bipolar disorder. Symptoms may also be a side effect of medications. After other possible causes are ruled out, your doctor will likely refer you to a mental health specialist.
Recommended Reading: Does Melatonin Make You Depressed
Neuroinflammation In Bipolar Depression
- 1Psychiatry and Clinical Psychobiology Unit, Division of Neuroscience, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele Hospital, Milano, Italy
- 2University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milano, Italy
- 3PhD Program in Molecular Medicine, University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Italy
- 4Clinical Neuroimmunology Unit, Institute of Experimental Neurology, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele, Milano, Italy
What Are The Long
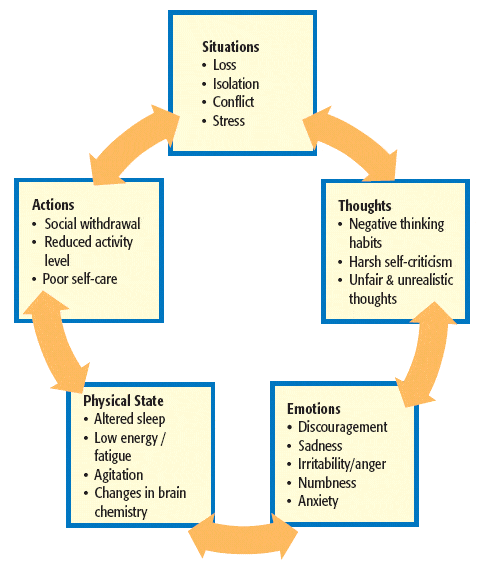
Bipolar disorder is a life-long and often recurring illness. You may need long term support to help manage your condition.
What medication options are there?
Your doctor will look at what medication worked for you during episodes of mania or depression. They should ask you whether you want to continue this treatment or if you want to change to lithium.
Lithium usually works better than other types of medication for long-term treatment. Your doctor should give you information about how to take lithium safely. If lithium doesn’t work well enough or causes you problems, you may be offered:
Your doctor should monitor your health. Physical health checks should be done at least once a year. These checks will include:
- measuring your weight,
- checking your liver and heart, and
- checking your pulse and blood pressure.
What psychological treatments are recommended?
You should be offered a psychological therapy that is specially designed for bipolar disorder. You could have individual or group therapy.
The aim of your therapy is to stop you from becoming unwell again. This is known as relapse. Your therapy should help you to:
- understand your condition,
- think about the effect that your thoughts and behaviour have on your mood,
- monitor your mood, thoughts and behaviour,
- think about risk and distress,
- make plans to stay well,
- make plans to follow if you start to become unwell,
- be aware of how you communicate, and
- manage difficulties you may have in day to day life.
- support needs, and
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Paranoid Schizophrenia Patient