First How Common Is Anxiety
Anxiety is so much more prevalent in the United States today than is recognized. Currently over 40 million Americans suffer from some form of anxiety EVERYDAY. Anxiety is the experience of environmental stressors which is marked by continued excessive worry, feeling nervous or on edge, sleep abnormalities, difficulty concentrating, emotional swings, fatigue, gastrointestinal upset, increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and restlessness. Anxiety is not only stressful emotionally, but overtime can be very stressful physically on the brain and body.
Awareness of how anxiety can affect quality of life for both the individual experiencing the anxiety and the loved ones around them is extremely important. Anxiety is very treatable, even without medication, yet only less than 40% of those with anxiety are treated successfully and with the right approach.
What Are Signs Of High Anxiety
Carrie Simon |
Some common symptoms of high-functioning anxiety include:
- Constantly overthinking and overanalyzing.
- Fear of failure and striving for perfection.
- Insomnia and fatigue.
- The need to please others and difficulty saying no.
- Tendency to dwell on past mistakes.
- Nervous habits such as nail-biting, hair twirling, or leg shaking.
What Are The Types Of Anxiety
When a pattern of anxiety attacks and its symptoms emerge, mental health professionals will seek out a specific type of anxiety disorder. The kind of anxiety disorders will usually break down in the following categories: ²
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder marked by excessive anxiety for no logical reason. The Anxiety and Depression Association of America estimates that GAD affects about 6.8 million American adults per year.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder a type of anxiety in which people have disorderly, continuous thoughts and behaviors .
- Panic Disorder a type of anxiety that causes sudden feelings of terror when there is no real danger, better known as panic attacks. ³
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder when someone experiences a mental and emotional stress due to a severe psychological shock .
- Social Anxiety Disorder fear of social situations involving large crowds or social interactions with other people. Often comes from fear of being judged or humiliated by others.
You may only struggle with one of the above types of anxiety. However, in some cases, people struggle with more than one.
Also Check: What Is The Fear Of Feet Phobia Called
What Is An Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in the U.S. One in five Americans, or 40 million people, suffer from anxiety disorders each year. There are many different types of anxiety disorders, but they all cause excessive worry and fear that lead to emotional distress and impairment.
There are several different types of anxiety disorders: generalized anxiety disorder, specific phobia, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder , social phobia , post-traumatic stress disorder , and separation anxiety disorder.
Some people might get anxious about very specific things, like animals or heights. Others might be afraid of a wide range of things. All types of anxiety disorders share one thing in common: They cause excessive worry and fear that lead to emotional distress and impair everyday functioning.
Biological Causes Of Anxiety Disorders
Genetics and biology play a role in the creation of anxiety disorders. Not only does anxiety appear to run in families – if you take two people with similar experiences, one may have an anxiety disorder, one may not, and the only difference between them may be genetic, or at least influenced by the body more than the mind. Biological causes include:
You May Like: What Is The Definition Of Schizophrenia
How Do I Shut My Brain Off From Anxiety
There are many ways to get relief from anxiety. You can talk to a friend, or call a hotline. You can take time for yourself and do something soothing like taking a bath, reading, playing video games, or drinking tea.
You can also try mindful meditation where you focus on your breathing quietly for five minutes. It might be helpful to write down your thoughts in order to rename them Im nervous becomes Im feeling some anxiety right now.
And finally, you can take action- do something that would make you feel more confident, like going for a walk or doing yoga.
Hormones And Other Internal Factors
Fight or flight cannot be invoked without the help of hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers sent out from places like the amygdala. Estrogen and testosterone are hormones, but so are cortisol, GABA, and adrenaline. Our hormones play a huge role in our moods, growth, and physiological functioning.
Hormonal imbalances may be a direct cause of anxiety. On a good day, our hormones are balanced and there is no need for us to go into fight-or-flight mode. But hormones may fall out of balance because of stressful events or other factors. The menstrual cycle may lead to hormonal imbalances. Thyroid issues, chronic stress, or birth control may also lead to hormonal imbalances. With the wrong imbalance, you may experience anxiety or even a panic attack.
Hormones remain in balance when our bodies are healthy. Anything that threatens our health may actually be threatening hormone production and distribution. This is why keeping a healthy body and mind is so crucial to preventing anxiety!
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know Your Depressed
Do Bananas Help Anxiety
Yes, potassium-rich foods such as bananas or pumpkin seeds can help combat anxiety. Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress. If youre feeling anxious about an upcoming test, a job interview, or meeting new people, its OK. Anxiety is a normal part of life. But when you have too much anxiety, it can become a problem. You might feel tense, nervous, or stressed. Anxiety can make you afraid of certain things, or it can make you feel worried and tense all the time.
How Does Anxiety Affect The Brain
Anxiety weakens the connections between the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex , brain maps called Quantitative Electroencephalography may show a large amount of high beta brain waves on the right lobe of the prefrontal cortex in those with a generalized anxiety disorder or any other anxiety disorder.
This is an indication of anxiety, and the more anxiety someone has the more these waves are present.
The PPC is responsible for emotion regulation, rational decision-making, and other cognitive processes. The amygdala is responsible for fear processing.
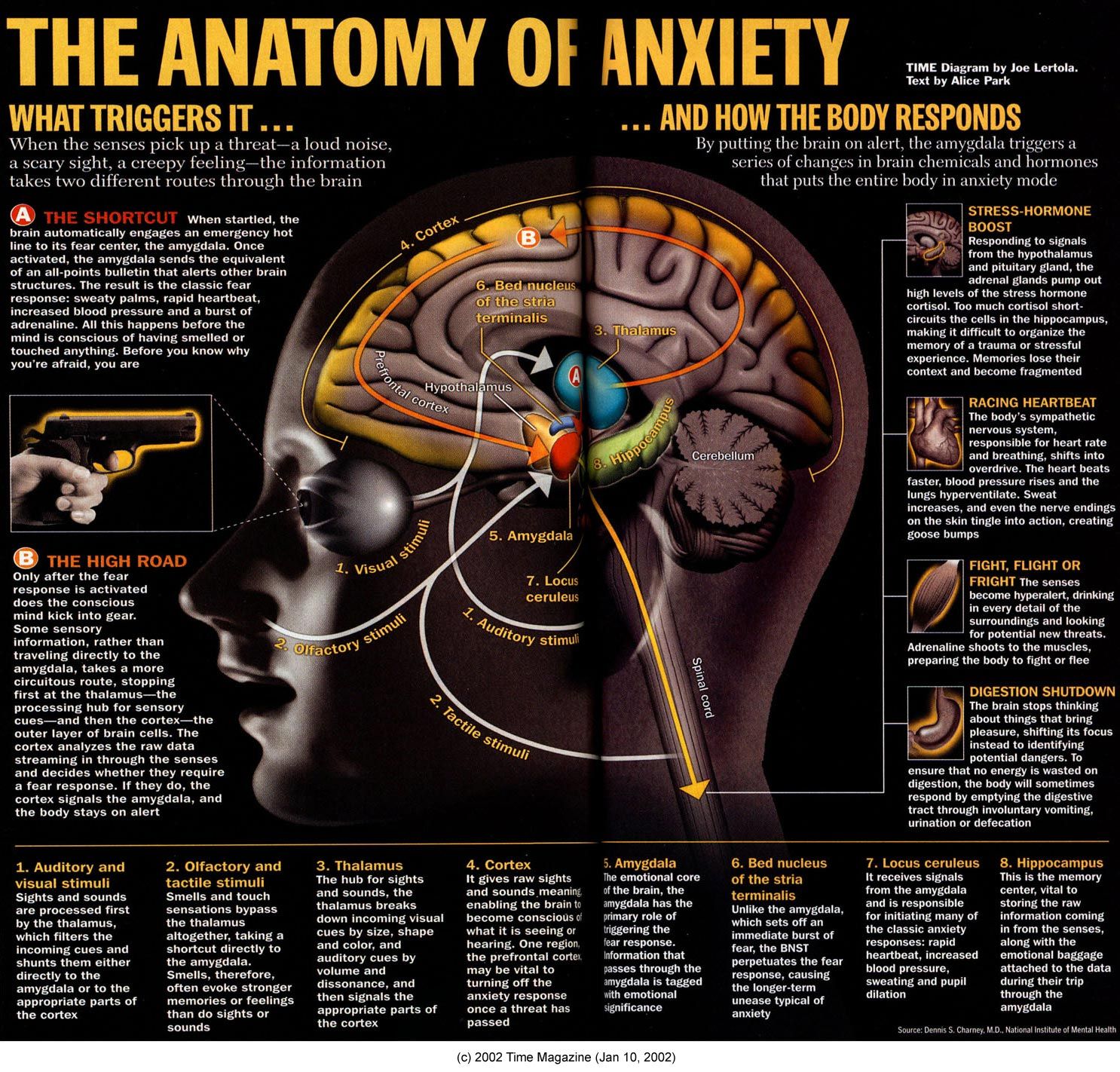
Number 1: The Amygdala
Patients with anxiety disorders often show heightened amygdala response to anxiety cues. The amygdala is connected to the prefrontal cortex and is responsible for much of the brains fight or flight response. It is also linked to the hypothalamus.
The amygdala and the PFC are linked in a way that heightens anxiety responses. This is what causes panic attacks to feel so intense, for example. The amygdala sends a signal to the PFC when you sense something that triggers your anxiety and it responds accordingly by sending signals that trigger your fight or flight response.
The amygdala is a small, almond-shaped part of the brain. Its located deep in your brain next to the PFC and the hippocampus. The amygdalas main job is to control emotional reactions to things like fear and stress.
Number 2: Anxiety Floods Your Brain with Stress Hormones
Number 3: The Hippocampus
Number 4: The Ventral Tegmental Area
Don’t Miss: How Do You Develop Bipolar Disorder
Permanent Changes Take Consistency Persistence And Repetition
It does work, but it takes persistence, practice, and repetition. The brains neural pathways must change so that your beliefs, thoughts, and perceptions become more rational. This can only occur if you change your neural pathways by practicing repetitiously the new methods and concepts learned in cognitive therapy.
Cognitive therapy is nothing more than learning the appropriate methods, strategies, and concepts to help your brain develop new neural pathways that are more rational than the old anxiety-ridden pathways.
This is more fully explained in the audio therapy series, Overcoming Social Anxiety: Step By Step and the cognitive therapy provided throughout this series directly relates to overcoming social anxiety altogether.
This, as you can see, takes practice, persistence, and repetition. But, it works. It has to work because, as you continue, your mind really does change. You are developing new neural pathways and associations as you learn appropriate cognitive strategies.
The Effect Of Parenting Styles On Social Anxiety
Extensive research has confirmed a connection between negative parenting styles and anxiety disorders, including social anxiety disorder.
When parents are overcontrolling, quick to criticize, reluctant to show affection, or overly concerned with the opinions of others, a childs self-image and impression of the world can be shaped by words and actions associated with these characteristics.
Children and adolescents may become more fearful and less trustful of other people when they are raised in this environment, and their self-esteem and self-confidence may be negatively impacted as well. In these instances, parents dont realize their actions are harmful, but their focus on the negative inadvertently can set their children up for trouble later in life.
Social anxiety disorder is usually not diagnosed until sufferers reach adulthood, but symptoms tend to first manifest in late childhood or early adolescence, which bolsters the idea that parental influences are playing a formational role in the development of the disorder.
You May Like: How Common Is Bipolar Disorder Uk
Effects Of Chronic Stress On Amygdalar Function And Anxiety
A large bulk of evidence suggests that chronic stress and early exposure to stress not only induce persistent anxiety even after 21 days from the end of stress , but also induce a series of functional and morphological changes in the brain. In the amygdala, changes in neural plasticity and electrophysiological responses including suppression of gamma-Aminobutyric acid currents , as well as a persistent increase in dendritic arborization of spiny neurons and amygdalar hypertrophy, have been reported as a result of chronic stress, effects are not restored by ceasing the stress , but can be restored with short environmental enrichment . Interestingly, some of these changes may be prevented by intraBLA antagonism of corticotrophin releasing factor , which is a critical hypothalamic activator of the HPA axis and mediator of stress responses in the brain.
Other brain areas involved in anxiety have also been reported to suffer changes and even damage as a result of chronic stress . For example, in animal models of chronic stress, the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex show atrophy, which may lead to memory impairments, whereas the amygdala hypertrophy may lead to increased anxiety and aggression .
Connections Between The Amygdala And Other Brain Regions Associated With Anxiety
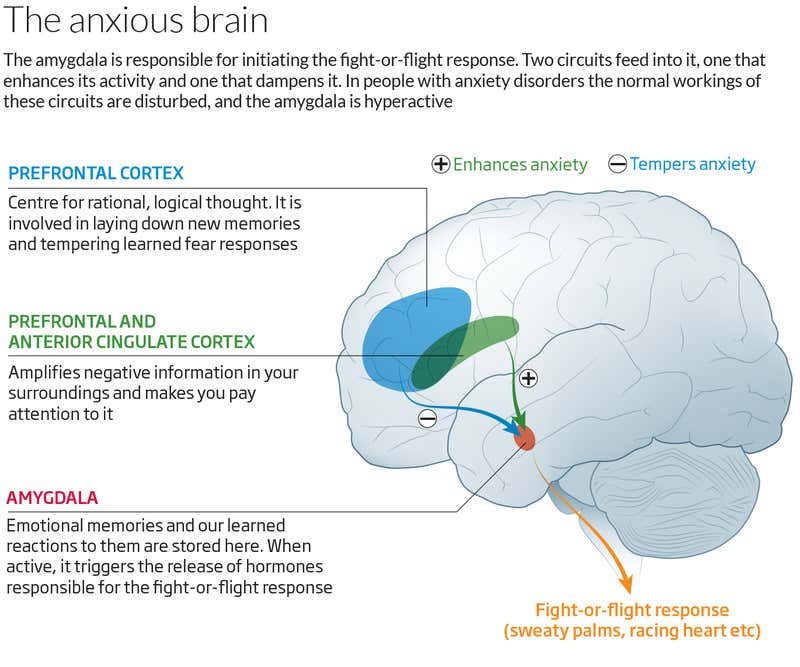
The recent development of optogenetic approaches allowing the activation or inhibition of specific cell types or neuronal projections using the inducible expression of channel rhodopsins has begun to allow a much greater understanding of the circuitries associated with anxiety. In a recent study, it was shown that inhibition of vHPC input to the mPFC and bilateral, but not unilateral inhibition of the input to the BLA disrupts anxiety . In the same line, the activation of BLA inputs to the mPFC produces anxiogenic effects in the EPM and openfield tests, whereas inhibition of the structure produces anxiolytic effects . Furthermore, systemic activation of Kapa opiod receptors was shown to inhibit glutamate release from BLA projections to the BNST and prevent the anxiolytic effects induced by optogenetic activation of BLABNST projections, while deletion Kapa opiod receptors from amygdala neurons induces anxiolytic effects . In yet another study, it was reported that the stimulation of VTAprojecting BNST glutamatergic neurons has anxiogenic effects, while the activation of VTAprojecting BNST GABAergic neurons has anxiolytic effects, similar to the effects of direct inhibition of VTA GABAergic neurons .
Figure 2.
You May Like: How To Tell If Depressed
How Does Anxiety Affect Your Mind
Anxiety reduces the strength of the connections between the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex . When the amygdala warns the brain to danger, the prefrontal cortex should step in and assist you in responding rationally and logically. However, with anxiety, these signals are not received well by the PFC, so it has less control over thinking and acting properly.
Here are some other ways that anxiety affects the mind:
Anxious people are more likely to think negatively about their surroundings and themselves. They may also have problems focusing on one task for an extended period of time. Anxiety can cause people to make poor decisions about things like which jobs to apply for or what relationships to enter into. It can also lead them to neglect basic self-care, such as eating properly or getting enough sleep.
With anxiety, people tend to focus on potential negative outcomes rather than positive ones. This is called “catastrophizing”– imagining worst-case scenarios that usually don’t come true. For example, someone who is anxious might imagine that saying “yes” instead of “no” will cause him or her to lose control of his or her job. Or that asking someone out on a date will make the person reject him or her. Or that agreeing to go somewhere will result in never being able to go anywhere again!
Neurotransmitter And Neuroendocrine Signaling In Social Anxiety Disorder
Amino acid neurotransmitters
Increased excitatory glutamatergic activity has been reported in patients who have SAD. Compared with matched control subjects, patients who had SAD had a 13.2% higher glutamate/creatine ratio in the ACC as measured by MRS. The glutamate/creatine ratio correlated with symptom severity, suggesting a causal role between excitatory signaling in the ACC and psychopathology .
Monoamines
A recent study assessed whether a DA agonist or antagonist influenced response to anxiogenic challenge such as verbal tasks and autobiographical scripts in patients who had SAD. The anxiogenic effect of the behavioral challenges was significantly increased in patients who had untreated SAD following administration of either drug. After successful treatment with SSRIs, however, administration of pramipexole seemed to dampen the behavioral provocation-induced anxiety, whereas sulpiride administration continued to enhance the anxiogenic effects of these tasks. These authors suggested that instability in the dopaminergic response to social stress contributes to anxiety severity and is normalized only partly by successful treatment, perhaps via SSRI-induced desensitization of postsynaptic D3 receptors.108
Neuropeptides
Corticotropin-releasing factor and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
Also Check: What Does The Average Person Know About Ptsd
How To Treat Anxiety
When it comes to treating anxiety, there is good news and bad news. The good news is there are a number of ways to ease anxiety. The bad news is there is no way to completely treat anxiety so that it never comes back.
It shouldnt be forgotten that anxiety is a natural response our brains have to threat. An anxiety disorder is when that response kicks in during moments when no threat is present.
The best way to ease an anxiety disorder is by using psychological resources, such as psychotherapies. These can appear in various approaches, from immersion therapy to talk therapy. ¹¹
Most often, when a medical professional diagnoses you with an anxiety disorder, youll also receive medication that can help alongside psychotherapies. However, we at Bedlamite Publications warn that these medications can be addictive and should only be taken as a medical professional recommends.
A Permanent Solution Involves Changing The Brain
The only permanent solution is to change your neural pathways and associations. This can only be done by learning new strategies, rational concepts, and new methods to extinguish social anxiety. Then, these new strategies and methods must be practiced and practiced. This is why we always talk about repetition.
Without repetition, neural pathways and associations cannot change. To have a permanent solution for social anxiety, our neural pathways and associations MUST change.
When our neural pathways and associations change, our brain chemistry also changes. This is a permanent change, because you have practiced the new methods and concepts into your brain repetitiously, thus creating new neural associations. The more dense these neural associations are, the more you have recovered from social anxiety.
Everything in life works like this. Whatever you really learn causes new neural pathways in the brain, and, over time, with repetition, you gradually become better and better at something. Find the best method of support for you and get started.
Read Also: Can Anxiety Go Away On Its Own
Recommended Reading: How To Relax After A Panic Attack
What Part Of The Brain Controls Fear And Anxiety
The amygdala in the brain appears to be important in controlling fear and anxiety. Anxiety disorder patients frequently have a heightened amygdala reaction to anxiety stimuli. The amygdala and other limbic system components are linked to areas of the prefrontal cortex. It is possible that deficits in this connection may play a role in anxiety disorders.
The amygdala reacts to threats in our environment by triggering a stress response mediated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. This response involves the release of hormones such as cortisol from the adrenal glands which helps us deal with danger. Studies using brain imaging have shown that the amygdala is activated when people are exposed to threatening images or situations even if they do not expect to face a threat. This suggests that the amygdala plays a role in causing the physical changes associated with the stress response.
Anxiety disorders are some of the most common mental illnesses in the United States. They affect nearly 40 million Americans, mostly women. Young adults under 30 account for half of all cases of anxiety disorders.
A Lack Of Rationalization
If youve been dealing with anxiety for a while, it can weaken the connection between the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. The prefrontal cortex is the part of the brain that makes it possible to problem-solve and work through difficult situations. It allows you to think rationally, rather than relying on impulses.
When that connection is weak, youre less likely to process information correctly. Instead of coming up with a logical response to a perceived threat, youre more likely to think irrationally, and even partake in impulsive and potentially dangerous behaviors.
Also Check: How To Manage Panic Attacks