What Happens In The Brain When Youre Stressed Or Anxious
There are two parts of the brain that are thought to be key players in the production and processing of anxiety the amygdala and the hippocampus.
The amygdala is an almond-shaped structure deep in the brain that is believed to be a communications hub between the parts of the brain that process incoming sensory signals and the parts that interpret these signals. It can alert the rest of the brain that a threat is present and trigger a fear or anxiety response.
The emotional memories stored in the central part of the amygdala may play a role in anxiety disorders involving very distinct fears, such as fears of dogs, spiders, or flying. The hippocampus is the part of the brain that encodes threatening events into memories. .
Once the brain has encountered a threat , it releases a surge of chemicals, like cortisol and norepinephrine. These chemicals give us a natural boost in reflex time, perception, and speed. They cause our hearts to pump faster in order to get more blood and oxygen circulating through our bodies we essentially go into survival mode.
In This Article We Will Understand How Anxiety Affects Our Brain And How Important The Hippocampus And Amygdala Are To The Brain
Surely we have all felt anxiety in some situation, tingling in the stomach, tremors, tension, or an excessive heart rate.
These symptoms correspond to a concept that we will have heard about, and this one has a crucial role in the brain. We would say that anxiety has accompanied us in multiple situations throughout our lives.
Thus, it can be said that, despite being unpleasant, it is not pathological in itself and, in fact, fulfills an adaptive function.
However, this may change. When it disproportionately affects and interrupts daily activities, it no longer fulfills such an adaptive function. In this way, it can cause physical and mental health problems and a decrease in our performance.
Giving way to clinical entities such as phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, or panic attacks, among others. Let’s look at the effects of anxiety on the brain.
How Does Anxiety Affect The Brain
Anxiety weakens the connections between the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex , brain maps called Quantitative Electroencephalography may show a large amount of high beta brain waves on the right lobe of the prefrontal cortex in those with a generalized anxiety disorder or any other anxiety disorder.
This is an indication of anxiety, and the more anxiety someone has the more these waves are present.
The PPC is responsible for emotion regulation, rational decision-making, and other cognitive processes. The amygdala is responsible for fear processing.
Recommended Reading: How Is Schizophrenia Different From Dissociative Identity Disorder
Treatment For Children And Teenagers With Ptsd
For children and teenagers who are struggling to recover after a traumatic event, the recommended treatment is trauma-focussed cognitive behavioural therapy . This treatment involves:
- learning about the type of traumatic event experienced and common reactions to trauma
- teaching how to relax and manage anxiety
- helping to create a coherent story of the traumatic event, and correct any unhelpful beliefs about the event such as self-blame
- gradual exposure to trauma-related objects or situations that are feared or avoided
- helping to get back into everyday activities.
Environmental Influences And Stressful Life Experiences As A Cause Of Social Anxiety
Stressful life events and trauma during childhood can influence the development of social anxiety problems. Some of the exposures known to have predictive value for severe social anxiety include:
- Physical, sexual, or emotional abuse
- Family conflicts, domestic violence, and divorce
- Death of or desertion by a parent
- Maternal stress during pregnancy or infancy
Traumatic experiences can reinforce the idea that the world is a scary and unpredictable place, and it can be especially shocking and disheartening to kids to discover that their caregivers are capable of selfish or hurtful behavior.
Begin Your Recovery Journey.
Also Check: How Long Is Ptsd Treatment
Anxiety Changes How Your Brain Looks At Food
A constantly anxious brain will have trouble with the most basic functions. This includes thinking about or wanting to eat. Anxiety basically tells your brain and body that youre in a dangerous situation, whether its something you perceive as dangerous or an actual emergency, and sends you into a fight or flight mode.
This type of survival mode is supposed to subside when the danger passes but dealing with constant anxiety will keep your brain in this mode indefinitely. While some people who struggle with anxiety disorders have trouble eating, others feel the need to eat more. These changes in appetite are a direct result of how anxiety affects the brain.
Brain And Mental Health
There are also changes in chemicals found in receptors in the brain. Depression is believed to be caused by the lack of the neurotransmitter serotonin found in various receptors. Dopamine can be an important neurotransmitter in treating schizophrenia1.
The key takeaway is that various mental illnesses physically and chemically impact the human brain. Mental health disorders that can affect the brain include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder , generalized anxiety disorder , schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder , and depression.
Also Check: How Common Are Eating Disorders
What Causes Anxiety In The Brain
No one knows exactly what causes anxiety. But researchers have some ideas about how it develops in the brain. The amygdala is an almond-shaped structure in the brain that plays a big role in emotions and memory.
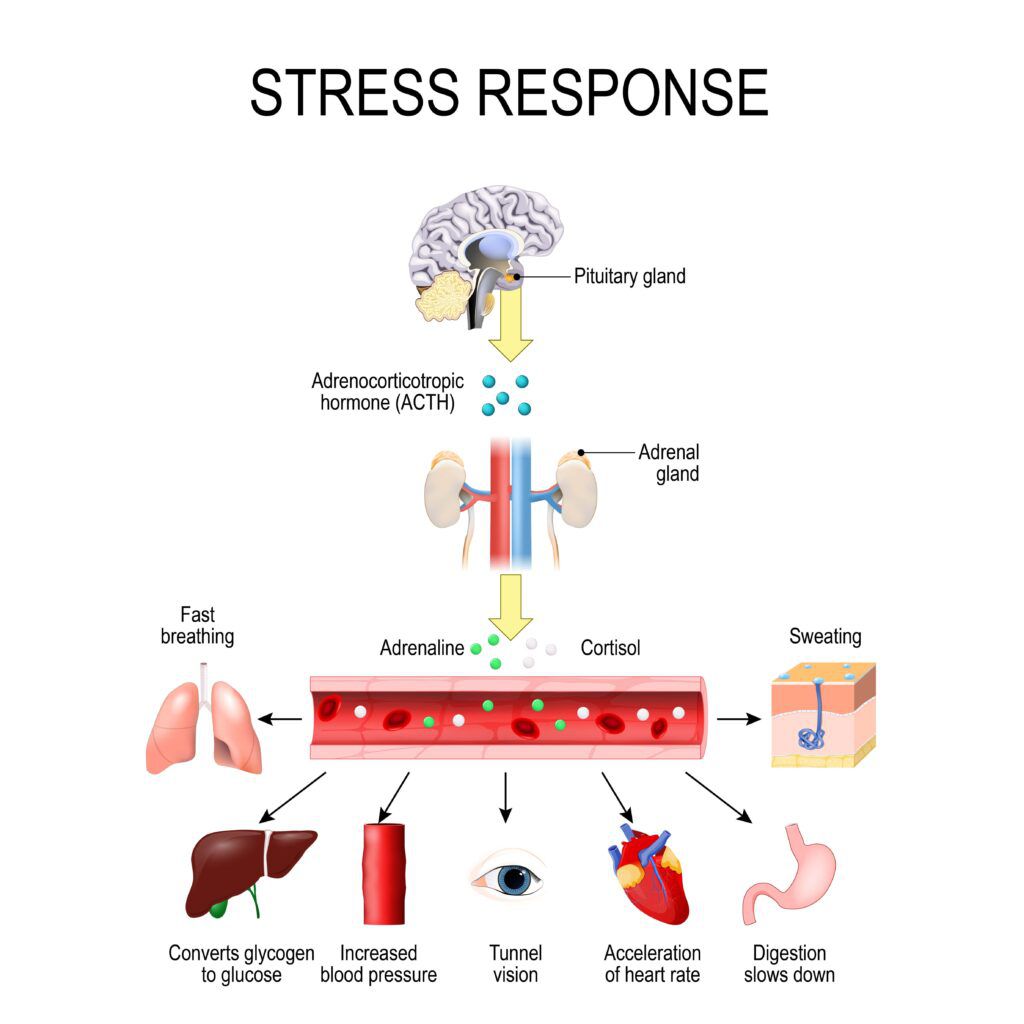
When youre stressed, your amygdala might send signals to other parts of your brain. Those signals tell your body to release adrenaline, which can cause physical reactions like quick breathing, sweating, and a fast heart rate.
Your amygdala might also activate parts of your brain associated with fear and worry. That can make you feel anxious or frightened.
What triggers anxiety in the brain?
The anxiety trigger is when your amygdala realizes that there is potential danger or even perceived potential danger, it sends signals to the hypothalamus. As discussed above, the hypothalamus is the part of the brain that controls the fight or flight response. So the signal activates the system.
This means your heart rate and blood pressure increase, and you might even shake. The amygdala also sets off alarms in the brain that tell your body to release certain hormones.
These hormones can make you feel anxious or stressed. Sometimes, people with anxiety become so alarmed that they react in an extreme way. They might scream or cry out of fear for no reason.
Major Effects Of Anxiety On The Brain
#1. Anxiety Floods Your Brain with Stress Hormones
- When you feel anxious, your body goes on alert, prompting your brain to prepare itself for flight or fight mode. In an attempt to help you fight off whatever has made you anxious, your brain floods your central nervous system with adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones tell your body that something scary is about to happen. Their role is to help you cope with danger. In order to do that, they sharpen your senses and make your reflexes faster. In a non-anxious brain, when the danger is gone, the sympathetic part of your nervous system takes over and calms you down. But when you suffer from anxiety, you may not be able to reach that sense of calm. Instead, the rush of stress hormones causes your brain to release even more stress hormones until youre simply overwhelmed.
#2. Anxiety Makes Your Brain Hyperactive to Threats
#3. Anxiety Can Make It Hard for Your Brain to Reason Rationally
#4. Anxiety Can Train Your Brain to Hold Onto Negative Memories
Read Also: What’s The Difference Between A Panic Attack And Anxiety Attack
It Can Lead To Depression
Anxiety and depression are two conditions that, while different, often go hand in hand.
Anxiety can often lead to symptoms of depression, Anastasiou says.
According to the MayoClinic, depression can commonly be triggered by an anxiety disorder, and anxiety is typically a symptom of depression. These conditions also share similar treatments primarily psychological counseling. If you are having difficulties coping with symptoms of depression or anxiety, it may be time to seek out professional help.
What Stress And Anxiety Do To The Brain Over Time
This survival response is helpful and necessary when we encounter a real threat, but in excess, can cause long-term damage to our bodies. The effects of chronic stress have been linked to a weakened immune system, weight gain, and heart disease, among other issues.
But new research is finding a possible correlation between prolonged stress and anxiety, and structural degeneration of the hippocampus,
and impaired functioning of the prefrontal cortex. This means that the wear and tear caused to the brain by chronic stress or anxiety could be tied to an increased risk of depression and dementia.
The good news is that some of the damage incurred from chronic stress and anxiety is not completely irreversible, according to some experts. It was long believed that once a brain lost volume, it was gone forever, but we now know thats not entirely true. Our brains are plastic, meaning theyre capable of change. This plasticity allows our brains some degree of regrowth and regeneration.
The best way, however, to protect your brain and body from the effects of chronic stress and anxiety is to find a way to manage it before it begins to affect your health. Luckily, there are many different options for managing these conditions.
Start Precision Breathing Training for FREE when you download the Neuropeak Pro App.
#GeneralizedAnxietyDisorder #Anxiety #GeneralizedAnxiety #Chronicstress #Stress
Also Check: Is Sleeping A Sign Of Depression
Anxiety Effects Of Brain
Your brain is responsible for controlling all of your actions and reactions. Your brain also influences your emotions. There could be many causes of anxiety. So, when we talk about brain effects, we mean those things directly related to your brain.
So let us try to understand that how anxiety impacts your brain.
What Does Anxiety Make Your Brain Feel Like
People with anxiety always have difficulty concentrating and focusing, unclear thoughts, short-term memory problems, an inability to completely relax, and racing thoughts. When you experience anxiety, a certain part of your brain is triggered.
Researchers have found that the amygdala is often involved in anxiety. The amygdala is an almond-shaped group of nuclei located deep within the brain. It plays a role in how we process emotion and memory.
It also helps us respond to threats, which can lead to high levels of anxiety if your brain interprets a situation as dangerous or threatening. Anxiety affects people differently, but one thing is clear: it can make it hard to think clearly and perform well on tasks that require mental agility.
Anxiety can affect how much you sleep, too, by making it more difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
You May Like: Can Low Iron Cause Anxiety
Aims Of The Present Study
The short literature review above indicates that WM performance can be sensitive to stress- or anxiety-related interference. These effects have been extensively studied in clinical and older adult populations. However, less is known about the effects of stress and anxiety on WM in non-depressed adult populations. This lack of research is baffling given the increasing prevalence of stress in a working age population . Experiencing stress and feelings of anxiety are common in otherwise healthy populations, but we know very little about how these mental states are associated with cognitive performance. Many previous studies are also hampered by the fact that they have used only single WM measures . Therefore, the present exploratory study investigated the relationships between WM performance and stress and state anxiety in a large non-depressed adult sample by using questionnaires and an extensive WM test battery including both verbal and visuospatial task variants.
The Effects Of Anxiety On The Body
Anxiety is a normal part of life. For example, you may have felt anxiety before addressing a group or in a job interview.
In the short term, anxiety increases your breathing and heart rate, concentrating blood flow to your brain, where you need it. This very physical response is preparing you to face an intense situation.
If it gets too intense, however, you might start to feel lightheaded and nauseous. An excessive or persistent state of anxiety can have a devastating effect on your physical and mental health.
Anxiety disorders can happen at any stage of life, but they usually begin by middle age. Women are more likely to have an anxiety disorder than men, says the National Institute of Mental Health .
Stressful life experiences may increase your risk for an anxiety disorder, too. Symptoms may begin immediately or years later. Having a serious medical condition or a substance use disorder can also lead to an anxiety disorder.
There are several types of anxiety disorders. They include:
Don’t Miss: Can You Get A Job With Ptsd
What Are The Effects Of Ptsd
There are many. They may include disturbing flashbacks, trouble sleeping, emotional numbness, angry outbursts, and feelings of guilt. You might also avoid things that remind you of the event, and lose interest in things that you enjoy.
Symptoms usually start within 3 months of a trauma. But they might not show up until years afterward. They last for at least a month. Without treatment, you can have PTSD for years or even the rest of your life. You can feel better or worse over time. For example, a news report about an assault on television may trigger overwhelming memories of your own assault.
PTSD interferes with your life. It makes it harder for you to trust, communicate, and solve problems. This can lead to problems in your relationships with friends, family, and coworkers. It also affects your physical health. In fact, studies show that it raises your risk of heart disease and digestive disorders.
Effects Of Chronic Stress On The Brain
While stress itself is not necessarily problematic, the buildup of cortisol in the brain can have long-term effects. Thus, chronic stress can lead to health problems.
Cortisols functions are part of the natural process of the body. In moderation, the hormone is perfectly normal and healthy. Its functions are multiple, explains the Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science. In addition to restoring balance to the body after a stress event, cortisol helps regulate blood sugar levels in cells and has utilitarian value in the hippocampus, where memories are stored and processed.
But when chronic stress is experienced, the body makes more cortisol than it has a chance to release. This is when cortisol and stress can lead to trouble. High levels of cortisol can wear down the brains ability to function properly. According to several studies, chronic stress impairs brain function in multiple ways. It can disrupt synapse regulation, resulting in the loss of sociability and the avoidance of interactions with others. Stress can kill brain cells and even reduce the size of the brain. Chronic stress has a shrinking effect on the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for memory and learning.
Don’t Miss: Why Do You Have Panic Attacks At Night
Brain Structures Associated With Anxiety Disorders
Previous studies have shown that the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis , hippocampus, striatum, anterior insula, anterior cingulate cortex and hypothalamus were closely related to anxiety disorders. For instance, the activation in the hippocampus, amygdala and anterior insula during negative emotion processing was enhanced in patients with anxiety disorders. In addition, abnormal thalamic volume is an indicator of social anxiety, especially in children and adolescents. The neural networks that regulate social vigilance mainly comprise the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and prefrontal cortex. Patients with anxiety disorders usually show behavioural avoidance, and the avoidance neural network includes the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, anterior insula, sublenticular extended amygdala and temporal pole. Notably, the functional connectivity between the amygdala and the anterior insula is associated with the degree of avoidance. These structures, which are closely related to anxiety, may play unique roles in the development of cognitive and emotional capabilities among adolescents.
Defining Social Anxiety And Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety can profoundly affect someones ability to socialize and communicate with other people. For those suffering from full-blown social anxiety disorder, which in any given year includes up to seven percent of the adult population, the symptoms of social anxiety can be overwhelming, debilitating, and beyond their ability to control.
* Intense fear of social interactions in a wide variety of contexts
* Anticipatory anxiety that leads social anxiety sufferers to avoid opportunities for conversation or public speaking
* Extreme symptoms of anxiety experienced during unwanted or stressful social interactions
* Poor verbal communication skills, complicated by a persons inability to think clearly while experiencing anxiety
* Overly critical self-evaluations of performance after conversations or spoken presentations are finished
* Low self-esteem and a lack of self-confidence, which are reinforced by constant self-criticism
When not interacting with close friends or family, people with severe social anxiety have a deep-seated fear of being judged, rejected, embarrassed or humiliated during social interactions. As irrational as those fears may be, they are difficult to escape.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is It To Get In Phobia