Coping With Flashbacks And Dissociation In Ptsd
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Many people with post-traumatic stress disorder struggle in coping with flashbacks and dissociation, which may occur as a result of encountering triggers, that is, reminders of a traumatic event.
To the extent that people are not aware of their triggers, flashbacks and dissociation can be incredibly disruptive and unpredictable events that are difficult to manage. However, you can take steps to better manage and prevent flashbacks and dissociation and stay in the present.
Prevalence And Symptoms Of Ptsd
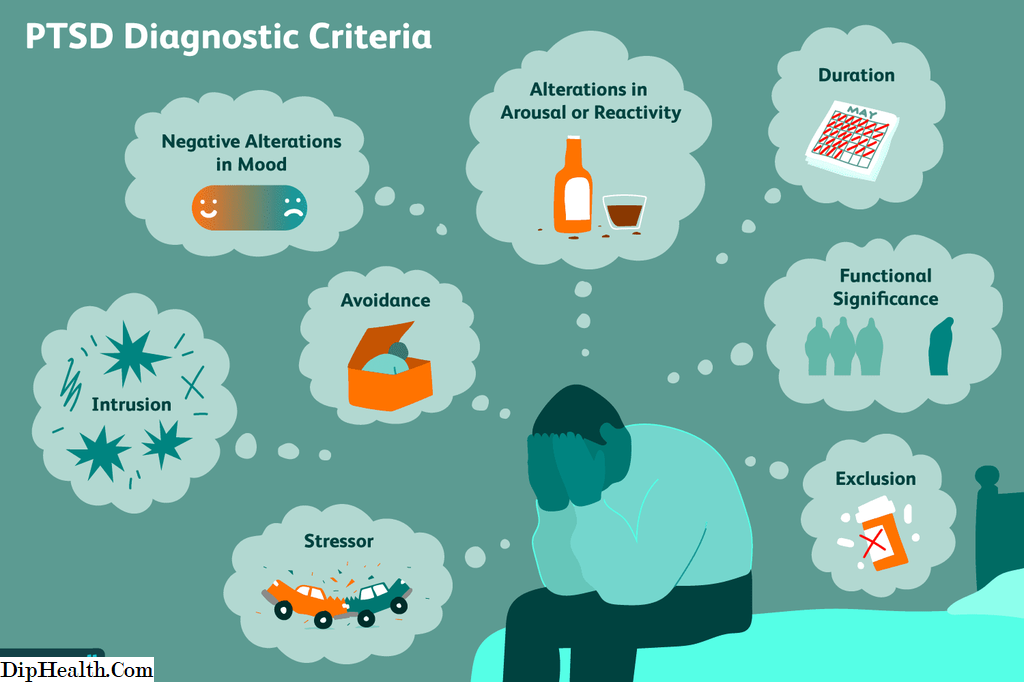
According to the National Center for PTSD, approximately 7-8% of people in the U.S. will develop PTSD during their life10% of women and 4% of men. To be diagnosed with this condition, a person will have symptoms that include several of these:
- Recurrent and distressing memories or dreams of the traumatic event
- Prolonged or noticeable psychological and/or physiological reactions to cues resembling the experience
- Flashbacks of the event or emotional/psychological dissociation when triggered
- Avoidance of thoughts, feelings, people, places, or any reminders of what happened
- Difficulty remembering details of the event
- Changes in mood, memory, or thinking patterns
- Hypervigilance, sleep problems, anger outbursts, or self-destructive behavior
While all these symptoms can cause significant impairment, some are more challenging to manage than others. This is largely due to the amygdala, a structure deep in the brain that is best known for our fight or flight response. When in danger, the amygdala assigns an emotional tag to any experience that could be life-threatening, and its function is automatically prioritized over other areas of the brain, including those that govern reasoning and memory.
Ptsd Symptoms In Children
In children especially very young children the symptoms of PTSD can differ from those of adults and may include:
- Fear of being separated from their parent.
- Losing previously-acquired skills .
- Sleep problems and nightmares.
- Somber, compulsive play in which themes or aspects of the trauma are repeated.
- New phobias and anxieties that seem unrelated to the trauma .
- Acting out the trauma through play, stories, or drawings.
- Aches and pains with no apparent cause.
- Irritability and aggression.
Do you have PTSD?
If you answer yes to three or more of the questions below, you may have PTSD and its worthwhile to visit a qualified mental health professional.
- Have you witnessed or experienced a traumatic, life- threatening event?
- Did this experience make you feel intensely afraid, horrified, or helpless?
- Do you have trouble getting the event out of your mind?
- Do you startle more easily and feel more irritable or angry than you did before the event?
- Do you go out of your way to avoid activities, people, or thoughts that remind you of the event?
- Do you have more trouble falling asleep or concentrating than you did before the event?
- Have your symptoms lasted for more than a month?
- Is your distress making it hard for you to work or function normally?
Don’t Miss: Fear Of Long Words Name
Living With Someone With Ptsd
PTSD doesnt only affect the person who has it. Its effects can affect those around them.
The anger, fear, or other emotions that people with PTSD are often challenged with can strain even the strongest relationships.
Learning all you can about PTSD can help you be a better advocate and supporter for your loved one. Joining a support group for family members of people living with PTSD can give you access to helpful tips from people whove been or are currently in your shoes.
Try to make sure that your loved one is getting proper treatment which can include therapy, medication, or a combination of the two.
Also, try to recognize and accept that living with someone who has PTSD isnt easy. There are challenges. Reach out for caregiver support if you feel the need to do so. Therapy is available to help you work through your personal challenges like frustration and worry.
Helping A Veteran With Ptsd
When a loved one returns from military service with PTSD, it can take a heavy toll on your relationship and family life. You may have to take on a bigger share of household tasks, deal with the frustration of a loved one who wont open up, or even deal with anger or other disturbing behavior.
Dont take the symptoms of PTSD personally. If your loved one seems distant, irritable, angry, or closed off, remember that this may not have anything to do with you or your relationship.
Dont pressure your loved one into talking. Many veterans with PTSD find it difficult to talk about their experiences. Never try to force your loved one to open up but let them know that youre there if they want to talk. Its your understanding that provides comfort, not anything you say.
Be patient and understanding. Feeling better takes time so be patient with the pace of recovery. Offer support but dont try to direct your loved one.
Try to anticipate and prepare for PTSD triggers such as certain sounds, sights, or smells. If you are aware of what causes an upsetting reaction, youll be in a better position to help your loved one calm down.
Take care of yourself. Letting your loved ones PTSD dominate your life while ignoring your own needs is a surefire recipe for burnout. Make time for yourself and learn to manage stress. The more calm, relaxed, and focused you are, the better youll be able to help your loved one.
Read Also: Why Is Liam Afraid Of Spoons
Ways To Help Someone Experiencing Dissociation
Our bodies seem to want to protect us when our environments or even our own heads feel too scary to sit with. I believe this is why dissociation occurs. Dissociation is a protective measure. It is a way of disconnecting ourselves from the triggers that are making us feel unsafe or out of control.
Dissociation feels different for every person. For me, it feels like being in control of my own actions and my own body, but feeling like I am in a dream. Nothing around me feels real, even if I logically know it is truly happening. It is like watching my life happen around me, but being more dead than I am alive. When I come out of these dissociative episodes, I often dont remember what happened during the episode, and sometimes am disoriented about where I currently am. The aftermath of a dissociative episode can bring up panic, fear, embarrassment and so many other feelings. It is important to know that dissociation occurs within the context of post-traumatic stress disorder , anxiety disorders, depressive disorders and other mental illnesses. It can also occur without the context of a mental illness. Many people may find that they dissociate during times of everyday stressful situations, but may not know that what happened was dissociation.
Heres how you can help someone having a dissociative episode cope with this truly frightening feeling. These tips can also be applied to yourself if you are struggling with dissociation.
1. Take the person to a safe space.
Tip : Anticipate And Manage Triggers
A trigger is anythinga person, place, thing, or situationthat reminds your loved one of the trauma and sets off a PTSD symptom, such as a flashback. Sometimes, triggers are obvious. For example, a military veteran might be triggered by seeing his combat buddies or by the loud noises that sound like gunfire. Others may take some time to identify and understand, such as hearing a song that was playing when the traumatic event happened, for example, so now that song or even others in the same musical genre are triggers. Similarly, triggers dont have to be external. Internal feelings and sensations can also trigger PTSD symptoms.
Read Also: Can You Go To Urgent Care For Panic Attacks
Common External Ptsd Triggers
- Sights, sounds, or smells associated with the trauma.
- People, locations, or things that recall the trauma.
- Significant dates or times, such as anniversaries or a specific time of day.
- Nature .
- Conversations or media coverage about trauma or negative news events.
- Situations that feel confining .
- Relationship, family, school, work, or money pressures or arguments.
- Funerals, hospitals, or medical treatment.
Why Do Some People Develop Ptsd And Other People Do Not
Not everyone who lives through a dangerous event develops PTSDmany factors play a part. Some of these factors are present before the trauma others become important during and after a traumatic event.
Risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing of PTSD include:
- Exposure to dangerous events or traumas
- Getting hurt or seeing people hurt or killed
- Childhood trauma
- Feeling horror, helplessness, or extreme fear
- Having little or no social support after the event
- Dealing with extra stress after the event, such as loss of a loved one, pain and injury, or loss of a job or home
- Having a personal history or family history of mental illness or substance use
Resilience factors that may reduce the likelihood of developing PTSD include:
- Seeking out support from friends, family, or support groups
- Learning to feel okay with ones actions in response to a traumatic event
- Having a coping strategy for getting through and learning from a traumatic event
- Being prepared and able to respond to upsetting events as they occur, despite feeling fear
Recommended Reading: Is Sex Good For Depression
Work Through Survivors Guilt
Feelings of guilt are very common among veterans with PTSD. You may have seen people injured or killed, often your friends and comrades. In the heat of the moment, you dont have time to fully process these events as they happen. But lateroften when youve returned homethese experiences come back to haunt you. You may ask yourself questions such as:
- Why didnt I get hurt?
- Why did I survive when others didnt?
- Could I have done something differently to save them?
You may end up blaming yourself for what happened and believing that your actions led to someone elses death. You may feel like others deserved to live more than youthat youre the one who should have died. This is survivors guilt.
Finding A Therapist For Ptsd
When looking for a therapist, seek out mental health professionals who specialize in the treatment of trauma and PTSD. You can ask your doctor or other trauma survivors for a referral, call a local mental health clinic, psychiatric hospital, or counseling center.
Beyond credentials and experience, its important to find a PTSD therapist who makes you feel comfortable and safe. Trust your gut if a therapist doesnt feel right, look for someone else. For therapy to work, you need to feel comfortable and understood.
Also Check: Phobia Medical Definition
Living With Someone Who Has Ptsd
When a partner, friend, or family member has post-traumatic stress disorder it affects you, too. PTSD isnt easy to live with and it can take a heavy toll on relationships and family life. You may be hurt by your loved ones distance and moodiness or struggling to understand their behaviorwhy they are less affectionate and more volatile. You may feel like youre walking on eggshells or living with a stranger. You may also have to take on a bigger share of household tasks and deal with the frustration of a loved one who wont open up. The symptoms of PTSD can even lead to job loss, substance abuse, and other problems that affect the whole family.
Its hard not to take the symptoms of PTSD personally, but its important to remember that a person with PTSD may not always have control over their behavior. Your loved ones nervous system is stuck in a state of constant alert, making them continually feel vulnerable and unsafe, or having to relive the traumatic experience over and over. This can lead to anger, irritability, depression, mistrust, and other PTSD symptoms that your loved one cant simply choose to turn off.
With the right support from you and other family and friends, though, your loved ones nervous system can become unstuck. With these tips, you can help them to finally move on from the traumatic event and enable your life together to return to normal.
Arousal And Reactivity Symptoms
- Having difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Feeling irritable and having angry or aggressive outbursts
- Engaging in risky, reckless, or destructive behavior
Arousal symptoms are often presentthey can lead to feelings of stress and anger and may interfere with parts of daily life, such as sleeping, eating, or concentrating.
Read Also: Dehydration Causes Anxiety
How To Recognize Ptsd
How to recognize PTSD without raising tensions is to look for avoidance symptoms, such as unreasonable guilt, fretfulness and depression. Observe if your loved one avoids the place, objects or events that pertain to the traumatic experience. Determine if a lack of enthusiasm for activities that were previously enjoyable is present. Also, be aware of hyperarousal symptoms. These can be outbursts of anger, sleep disturbances, tension or being easily startled.
Where To Find Help For Ptsd
If you are struggling with panic, anxiety, depression, rage or other life-controlling issues following a traumatic incident, you may be dealing with PTSD. If someone you love is being haunted by this crippling disease, you can play a role in their recovery. Call our toll-free helpline, , 24 hours a day to speak to an admissions coordinator about available treatment options. We are here for you. Call us now.
1 PTSD: National Center for PTSD. What Is PTSD?Negative Coping and PTSD PTSD: National Center for PTSD. 1 Jan. 2007.
2 PTSD Treatments.Monitor on Psychology, American Psychological Association. 21 July 2017.
3 Tull, Matthew, and Steven Gans. Is There a Cure for PTSD?Verywell Mind . 3 May 2018.
You May Like: Definition Phobia
Emotional And Psychological Trauma
If youve experienced an extremely stressful eventor series of eventsthats left you feeling helpless and emotionally out of control, you may have been traumatized. Psychological trauma often has its roots in childhood, but any event that shatters your sense of safety can leave you feeling traumatized, whether its an accident, injury, the sudden death of a loved one, bullying, domestic abuse, or a deeply humiliating experience. Whether the trauma happened years ago or yesterday, you can get over the pain, feel safe again, and move on with your life.
How Common Is Ptsd
According to the National Center for PTSD, about half of all women and 60 percent of all men will experience trauma at some point in their lives. Yet, not everyone who lives through a traumatic event will develop PTSD.
According to a 2017 study, theres at least a 10 percent prevalence of PTSD in women during their lifespan. For men, theres at least a 5 percent prevalence of PTSD during their lifetime. Simply stated, women are twice as likely as men to develop PTSD.
Theres limited available research on the prevalence of PTSD in children and adolescents.
An early review showed that theres a 5 percent lifetime prevalence for adolescents ages 13 to 18 years of age.
Don’t Miss: Aphobia Definition
Deal With Flashbacks Nightmares And Intrusive Thoughts
For veterans with PTSD, flashbacks usually involve visual and auditory memories of combat. It feels as if its happening all over again so its vital to reassure yourself that the experience is not occurring in the present. Trauma specialists call this dual awareness.
Dual awareness is the recognition that there is a difference between your experiencing self and your observing self. On the one hand, there is your internal emotional reality: you feel as if the trauma is currently happening. On the other hand, you can look to your external environment and recognize that youre safe. Youre aware that despite what youre experiencing, the trauma happened in the past. It is not happening now.
State to yourself the reality that while you feel as if the trauma is currently happening, you can look around and recognize that youre safe.
Use a simple script when you awaken from a nightmare or start to experience a flashback: I feel because Im remembering , but as I look around I can see that the event isnt happening right now and Im not in danger.
Describe what you see when you look around .
Try tapping your arms as you describe what you see to help bring you back to the present.
Continue Your Daily Routine
Avoid letting your loved one hole up for too long. Try to help them stick to a routine similar to the one they followed before the trauma. Without being pushy or overbearing, please encourage them to spend time with friends and family and socialize in settings with no connection to the traumatic experience. Make sure they also pursue physical activity so their body can release those happiness-boosting endorphins.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Fear Of Vomit Called
Ptsd Treatment And Therapy
Treatment for PTSD can relieve symptoms by helping you deal with the trauma youve experienced. A doctor or therapist will encourage you to recall and process the emotions you felt during the original event in order to reduce the powerful hold the memory has on your life.
During treatment, youll also explore your thoughts and feelings about the trauma, work through feelings of guilt and mistrust, learn how to cope with intrusive memories, and address the problems PTSD has caused in your life and relationships.
The types of treatment available for PTSD include:
Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy involves gradually exposing yourself to feelings and situations that remind you of the trauma, and replacing distorted and irrational thoughts about the experience with a more balanced picture.
Family therapy can help your loved ones understand what youre going through and help you work through relationship problems together as a family.
Medication is sometimes prescribed to people with PTSD to relieve secondary symptoms of depression or anxiety, although they do not treat the causes of PTSD.
EMDR incorporates elements of cognitive-behavioral therapy with eye movements or other forms of rhythmic, left-right stimulation, such as hand taps or sounds. These techniques work by unfreezing the brains information processing system, which is interrupted in times of extreme stress.