Sex Differences In Symptoms
As shown in , there are sex differences in the symptoms of schizophrenia. For example, men with schizophrenia appear to have more negative symptoms and more severe clinical features than females, particularly in social withdrawal, substance abuse and blunted or incongruent affects than female patients. Women with schizophrenia often present with more mood disturbance and depressive symptoms as well as affective symptoms. Interestingly, such sex-specific symptoms in male schizophrenia patients were also observed in subjects with high risk for this disease. The age of onset is also associated with type of symptoms. For example, studies showed that women with late onset of schizophrenia may have less severe negative symptoms and present with more positive symptoms, particularly sensory hallucinations and persecutory delusions.
Sex differences in distribution of various symptoms between male and females patients
Note: Data source: http://dysphrenia. hpage. co. in/research phenomenological study of thinking and perceptual disorders in schizophrenia fulltext 76041325.html and
Possible Causes Of Schizophrenia Development
There are many studies which tried to find the exact cause of this disorder and most of them came to the conclusion that there are many possible causes which usually act simultaneously. The possible causes of schizophrenia include:1. Genetic causes Since schizophrenia tends to run in families, experts have been trying to find the specific genes which increase a person’s chance of developing this illness. Most studies, especially those performed on twins, have found that heredity plays an important role in the development of schizophrenia. If one of the identical twins who have been raised separately develops schizophrenia, the chance that the other twin will also develop it is 50%.Some studies have proposed that an imbalanced level of a specific neurotransmitter such as dopamine and serotonin could be the cause of shizophrenia and this theory ius known as Neurotransmitter theory. 2. Abnormal brain development Many studies of people with schizophrenia have found abnormalities in their brain structure.The most common abnormalities are:
- enlargement of the ventricles, fluid-filled cavities, in the interior of the brain,
- decreased size of certain brain regions
- decreased metabolic activity in certain brain regions
- complications in pregnancy including bleeding and diabetes
- abnormal fetal growth and development including conditions such as low birth weight
- complications of delivery including asphyxia and emergency Caesarean section
When Does Schizophrenia Develop
Schizophrenia is now a chronic, frequently debilitatingmental illness that affects around 1% of the global population. After a centuryof research, the etiology of schizophrenia remains unclear.
Treatments, particularly pharmaceutical treatments,have been widely used for almost half a century, although there is no evidencethat they have significantly improved results for the majority of people withschizophrenia.
These present dismal outcomes may improve when we viewschizophrenia as a neurodevelopmental condition with psychosis as a late,perhaps avoidable stage of the illness.
This rethinking of as aneurodevelopmental disorder, which is radically different from how we haveviewed the illness for the last century, offers fresh promise for preventionand treatment over the next two decades.
You may view several experiments that were done onschizophrenia patients at the very end of the article.
Schizophrenia: The 7 Keys To Self
Seek social support. Friends and family vital to helping you get the right treatment and keeping your symptoms under control. Regularly connecting with others face-to-face is also the most effective way to calm your nervous system and relieve stress. Stay involved with others by continuing your work or education. If thats not possible, consider , joining a schizophrenia support group, or taking a class or joining a club to spend time with people who have common interests. As well as keeping you socially connected, it can help you feel good about yourself.
Manage stress. High levels of stress are believed to trigger schizophrenic episodes by increasing the bodys production of the hormone cortisol. As well as staying socially connected, there are plenty of steps you can take to reduce your stress levels. Try adopting a regular relaxation practice such as yoga, deep breathing, or .
Get regular exercise. As well as all theemotional and physical benefits, exercise may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, improve your focus and energy, and help you feel calmer. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days, or if its easier, three 10-minute sessions. Try rhythmic exercise that engages both your arms and legs, such as walking, running, swimming, or dancing.
Schizophrenia In Men And Women: Whats The Difference
Schizophrenia in men and women has the same diagnostic criteria , but differences are known between the genders. Schizophrenia in men tends to develop between the ages of 15-20 whereas for women, schizophrenia tends to develop between 20-25 years of age. Moreover, not only does schizophrenia in men occur earlier, men are often hit harder by the disease. Estrogen, a hormone found in greater amounts in women, may be protective against some of the effects of schizophrenia.
What To Look For
Symptoms in teens can come on gradually over days, weeks, several months or more. This is called the prodromal period. The early symptoms of schizophrenia can sometimes look like those of other problems such as or .
Especially at first, symptoms may look like the stuff of typical teen years: bad grades, changing friends, , or irritability.
But there are some early warning signs in teens that show up as changes in thinking, emotions, and behavior.
What The Warning Signs Look Like
You may notice changes in yourself before your friends and family do. Once your loved ones do become aware, they might try to explain these changes as “just a phase” you’re going through or due to something stressful in your life. Because of that, many people don’t seek help until later on, when more severe symptoms start to emerge.
Signs that you may be in a prodrome include trouble with your memory or problems with paying attention and staying focused.
Mood swings and can happen. You may have and feel guilty about things or mistrust others. You could even have thoughts of .
Another sign is lack of energy. You could have weight loss or no interest in meals. problems could crop up.
You might lose interest in things you once cared about and back away from socializing with family and friends. There could be a drop-off in your level of achievements at work or school.
Your friends may notice changes in how you look. You might not be keeping up with hygiene like you used to.
Some other things that you or others might become aware of:
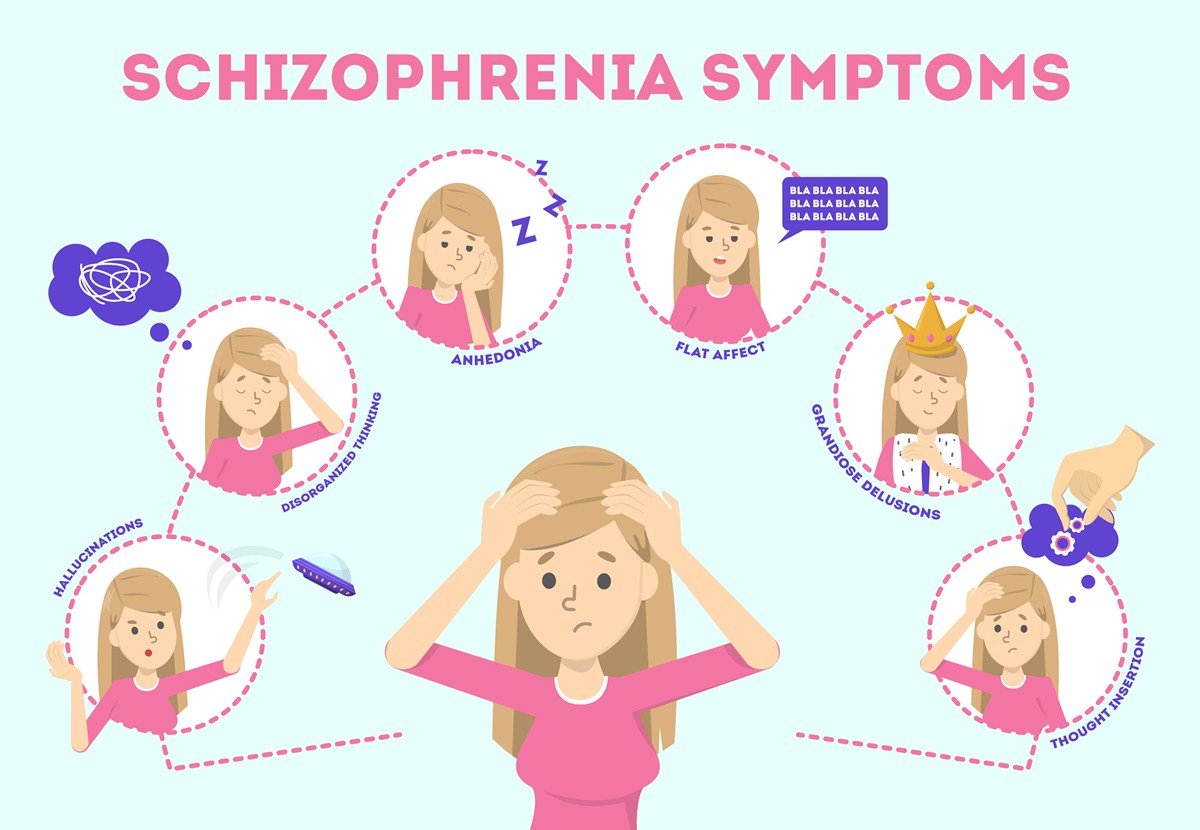
- Hearing or seeing something that’s not there
- A strange way of writing or talking
- An angry, scared, or bizarre response to loved ones
- Extreme interest in religion or the occult
Differences Between Schizophrenia In Men And Schizophrenia In Women
Delusions and hallucinations are the most well-known and generally prominent schizophrenia symptoms but other more subtle symptoms, like cognitive deficits, exist as well. Cognitive deficits represent any problem with the way a person is able to think.
In the case with schizophrenia in men, they tend to suffer more with the following symptoms:
- Lack of will and directed energy; a tremendous sense of inertia
- Inability to plan and complete things
- Making decisions
Men with schizophrenia may also react less positively to medication.
Because the symptoms of schizophrenia in women are less severe, women are more likely to:
- Marry
- Hold down a job
Men tend to have more trouble with joblessness and homelessness.
Schizophrenia is more likely in women who have been born to mothers who have been exposed to a viral infection, whereas men with schizophrenia are more likely to be born where birth trauma is involved. Why there is a gender difference among these risk factors is unknown.
What Is The Treatment
Even though schizophrenia is a serious mental illness it is also treatable, especially when the signs are caught early. Many people with schizophrenia live satisfying lives when they get good treatment. As with other mental illnesses, there are a few approaches to treatment that, when used all together, work the best. One approach is taking medicine prescribed by a psychiatrist or psychiatric nurse practitioner. Another approach is through individual or group therapy. There are also community programs that can help with daily living and job goals. Its helpful for family members to become educated so the person dealing with this illness is never alone in the journey.
Late Onset Schizophrenia And Dementia
Many researchers have wondered whether late onset of schizophrenia is somehow related to dementia. Brain studies have suggested that although tempting, this theory is not strong enough given that proof of brain degenerative causes for late onset of schizophrenia have not yet been confirmed.
Certain psychotic symptoms are the main symptoms of both and schizophrenia and this is the primary reason these two are linked. Etiologically, the disorders are different and only related to each other symptomatically.
Hope For The Patient And Family
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is life-changing for those affected and everyone who loves them. But, with hard work and dedication, you can help your loved one enjoy a meaningful life.
People with schizophrenia can finish college, work jobs, get married, have families and enjoy a reasonably healthy life, stresses Dr. Bowers.
But it requires a combination of good medication, supportive counseling and being connected to community resources.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness offers support groups for the mentally ill and their families. And organizations like Recovery International and Emotions Anonymous are excellent resources for patients, she says.
Social And Environmental Factors
Social cognition and social functioning
Premorbid social functioning and social cognition, robust predictors of relapse in this population, differ significantly between men and women. Men have poorer overall premorbid social functioning and social cognition, which is associated with higher rates of isolation, loneliness, and lower quality of life. Social cognitive and functional deficits are also related to the increased expression of negative symptoms observed in men. Additionally, these factors are also associated with reduced social network size and lower marriage rates in men with schizophrenia compared to women. Younger age at onset in men may also negatively impact community reintegration following the illness onset by delaying the development of life skills necessary to develop strong social support networks and foster self-perceptions of and agency.
Substance abuse and dependence
Women Tend To Develop Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Later Than Men And Often Exhibit Different Symptoms
There is no disparity in the occurrence and prevalence of schizophrenia between men and women, though schizophrenia is more closely associated with younger men. This may be due to the fact that women are more likely to experience the onset of schizophrenia later than men. Women tend to develop symptoms in their late 20s whereas the onset in men is typically in their early 20s.1 Also, because women with tend to be more socially active, their schizophrenia may be less detectable.
Positive And Negative Symptoms
What psychiatrists call the positive symptoms of schizophrenia are more obvious:
- Abnormal thinking and inappropriate emotions.
- Hallucinations, delusions and odd communication.
What they call the negative symptoms are more subtle and can last longer:
- Not talking much.
- Blunted feelings/little facial expression.
- Staying in bed to avoid people.
Whether their symptoms are positive or negative, people with schizophrenia dont seem to interact with the world in a healthy way, says Dr. Bowers.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
A diagnosis for schizophrenia is often first made in the active stage. This is when symptoms become most obvious. Other people may recognize the disordered thoughts and behavior patterns for the first time.
At that point, a doctor may work with friends and family members to understand when early symptoms began. Symptoms of the first phase are often not recognized until a person is in the active phase.
Once a diagnosis is made, a doctor will also be able to determine when the active phase is over based on symptoms and behaviors.
Where to Find Help
Advocacy organizations can help you find immediate help. They can also connect you with local resources that can help you find sustained, long-term treatment. These mental health resources include:
Most people with schizophrenia arent diagnosed until the second phase, once symptoms worsen and become more obvious.
At this point, treatment options include:
Where to Seek Emergency Care
If you or a loved one is experiencing suicidal thoughts or dangerous behaviors, seek emergency care:
- Dial 911 or your local emergency number
- Visit a hospital or emergency department
Life Challenges For Women With Schizophrenia
Typically, women with schizophrenia function better socially than men, often because a later age of onset indicates a less severe form of mental illness. Women with schizophrenia are likely to experience fewer hospitalizations and shorter visits while in the hospital compared to men. Some researchers believe that this later onset is because hormones like estrogen have a protective effect.4 However, this disparity in the age of onset is not present in all ethnic groups. For example, multiple studies in the country of India have found no difference in the mean age of onset between men and women.5
What Parents Should Know About Schizophrenia And Teens
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder that people can develop at any age. Some studies show that not only can teenagers start showing signs of the disorder, but males who develop schizophrenia most often do so in the teen years and early 20s. Females tend to develop it in their 20s and 30s, but its possible for them to have signs earlier.
Despite the prevalence in teens, fewer than 20 percent of people who have psychosis say that their parents noticed the symptoms and did something to help. All parents can do their part to reverse this sad trend by learning about the disorder, the symptoms of schizophrenia in teens, and what to do if someone they know shows these signs.
Child And Adolescent Brain Development
The increased spatial resolution available with magnetic resonance imaging allows a reliable, automated quantitative measurement of several brain regions, which combined with periodic rescanning in pediatric and adult populations, allows us to examine trajectories of brain change longitudinally. Over the past 20 years, longitudinal anatomic brain imaging of children and adolescents has established the trajectories of brain gray matter and white matter volumes, cortical thickness, along with finer maps of GM and WM development across time.
Early Warning Signs And Symptoms
Usually, a person with schizophrenia has gradual changes in their thoughts and perceptions. Families are often the first to see early signs of psychosis and schizophrenia in a loved one.
Before the first episode of psychosis, you go through what is known as a premorbid period. This is the 6 months before the first symptoms of psychosis. During this period, you might experience gradual changes.
Although sleep disturbances are not included in the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia, people with the condition consistently report them.
Early warning signs include:
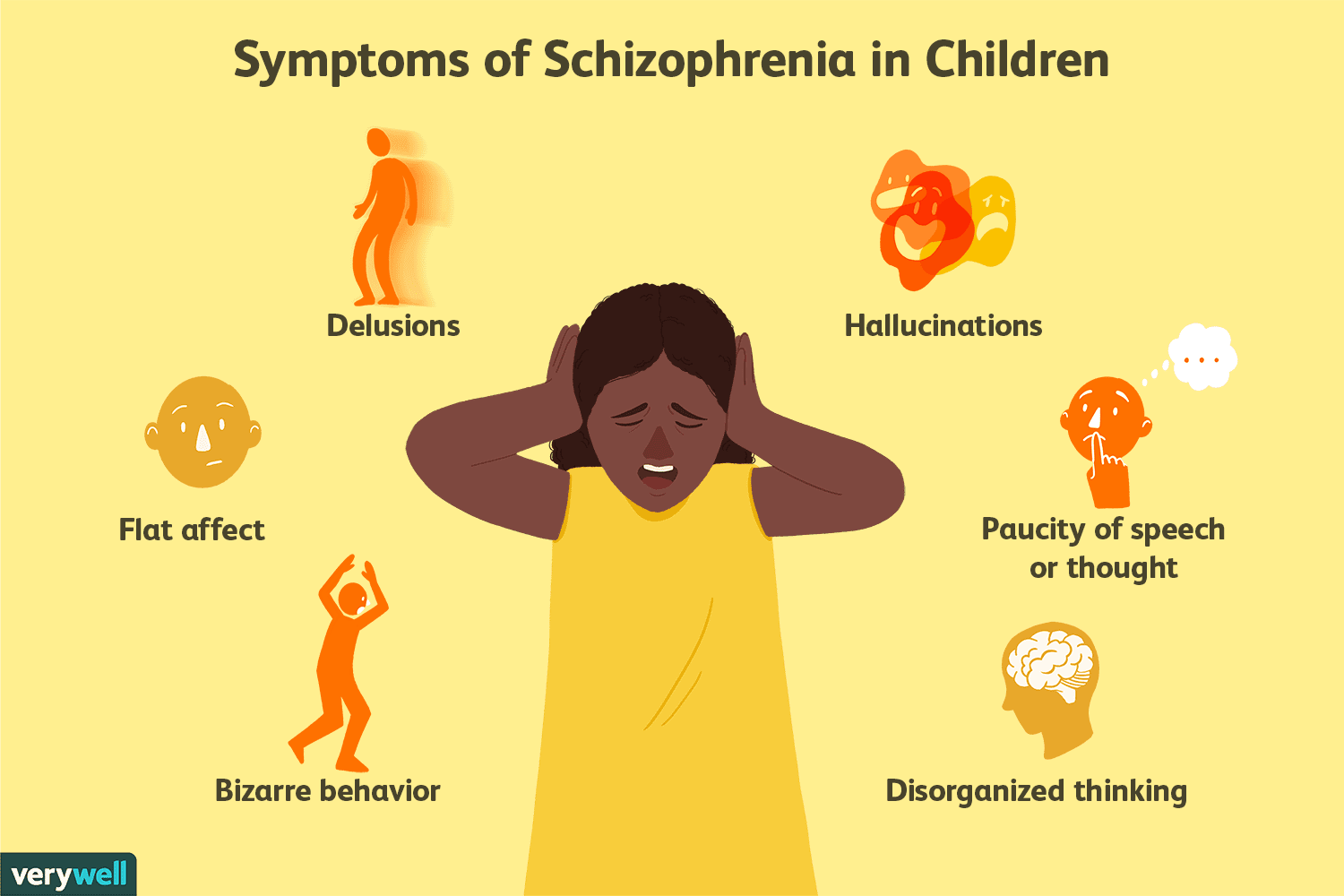
Childhood Schizophrenia Signs And Symptoms
Some children who develop schizophrenia first go through a period called the prodrome or the prodromal phase. They might withdraw from daily life, with more anxiety and less interest in school or friends. Not all children who show these signs will have a psychotic disorder, so its important to talk to your doctor if you notice any issues.
Early childhood schizophrenia symptoms
A or may have signs of schizophrenia that are different from those in older children, , and adults.
The disorder affects how your develops. You may notice things like:
- Long periods in which theyre sluggish or not active
- Floppy arms or legs
- Delays in crawling, walking, or talking
- Odd movements such as rocking or flapping their arms
- A limp or slumped posture
Some of these symptoms show up in children with other problems besides schizophrenia. And some happen in kids without any mental health conditions. Only your child’s doctor can figure out what’s really going on.
Later childhood schizophrenia symptoms
In older kids, you might notice the behavior changes of schizophrenia over time or suddenly, as if out of nowhere. Your child may act withdrawn and clingy, or they may talk about strange and disturbed ideas and fears.
Tell your doctor as soon as you see symptoms of schizophrenia. It’s important to get a diagnosis and start treatment before your youngster shows signs of a break from reality, called .
Symptoms in older children include:
The Phases And Recovery Of Schizophrenia

Recovery from psychotic episodes is not something that can be predicted. Some people may only experience one psychotic episode that is full-blown. Others have several different episodes. Some people may recover completely, however it is recommended that patients continue with lifelong treatment and support so as to avoid relapsing.
What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
There are at least three stages to the progression of schizophrenia: prodrome, initial episode, and chronic phase.
The prodrome, the initial episode, and the long-term chronic phase are all stages of the disease. It’s also true that there’s a pre-morbid period before the prodrome, during which delays in early neurodevelopmental indicators, such as early paediatric milestones, might indicate a higher chance of schizophrenia in the future.
Why Sex Differences In Schizophrenia
1Beijing Key Laboratory of Mental Disorders, Beijing Anding Hospital Capital Medical University, Beijing 100088, China
2Center of Schizophrenia, Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing 100069, China
3Center for Hormone Advanced Science and Education, Roskamp Institute, Sarasota, FL 34243, USA
When Schizophrenia Symptoms Start
Symptoms usually start to develop in early adulthood, between late adolescence and the early 30s. The disorder typically becomes evident slightly earlier in men than in women. Symptoms often emerge between late adolescence and the early 20s in men and between the early 20s and the early 30s in women.
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Stop Happening
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function involving thinking, behavior, and perception. You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. A doctor will call this anhedonia.
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. Doctors call this alogia.
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. When they talk, their voice can sound flat, like they have no emotions. They may not smile normally or show usual facial emotions in response to conversations or things happening around them. A doctor might call this affective flattening.
- Withdrawal. This might include no longer making plans with friends or becoming a hermit. Talking to the person can feel like pulling : If you want an answer, you have to really work to pry it out of them. Doctors call this apathy.
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. They may stop bathing or taking care of themselves.
- No follow-through. People with schizophrenia have trouble staying on schedule or finishing what they start. Sometimes they can’t get started at all. A doctor might call this avolition.
has some of the same symptoms, too. They can be hard to spot, especially in teens, because even healthy teens can have big emotional swings between highs and lows.
How You Get A Diagnosis
If you or someone you shows any of these signs, see a doctor right away. The symptoms of prodrome are subtle and easy to miss. Many also overlap with other mental health issues, like and substance misuse.
To rule out other health problems, your doctor may order lab tests and imaging tests. You’ll also be asked to answer detailed questions about your health, feelings, thoughts, and daily habits. How you respond will help your doctor decide if you are in a schizophrenia prodrome and if so, what kind.
To reach the right diagnosis, your family doctor may refer you to a who treats schizophrenia.
How Can You Help A Person With Schizophrenia
People with schizophrenia can get help from professional case managers and caregivers at residential or day programs. However, family members usually are a patient’s primary caregivers.
People with schizophrenia often resist treatment. They may not think they need help because they believe their delusions or hallucinations are real. In these cases, family and friends may need to take action to keep their loved one safe. Laws vary from state to state, and it can be difficult to force a person with a mental disorder into treatment or hospitalization. But when a person becomes dangerous to himself or herself, or to others, family members or friends may have to call the police to take their loved one to the hospital.
Treatment at the hospital. In the emergency room, a mental health professional will assess the patient and determine whether a voluntary or involuntary admission is needed. For a person to be admitted involuntarily, the law states that the professional must witness psychotic behavior and hear the person voice delusional thoughts. Family and friends can provide needed information to help a mental health professional make a decision.
People with schizophrenia can get help from professional case managers and at residential or day programs.
What About Substance Abuse
Some people who abuse drugs show symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. Therefore, people with schizophrenia may be mistaken for people who are affected by . Most researchers do not believe that substance abuse causes schizophrenia. However, people who have schizophrenia are much more likely to have a substance or alcohol abuse problem than the general population.
Substance abuse can make treatment for schizophrenia less effective. Some drugs, like and such as or , may make symptoms worse. In fact, research has found increasing evidence of a link between and schizophrenia symptoms. In addition, people who abuse drugs are less likely to follow their treatment plan.
Schizophrenia and
to is the most common form of substance abuse in people with schizophrenia. They are addicted to at three times the rate of the general population .
The relationship between and schizophrenia is complex. People with schizophrenia seem to be driven to smoke, and researchers are exploring whether there is a biological basis for this need. In addition to its known health hazards, several studies have found that may make antipsychotic drugs less effective.
Why The Difference In Schizophrenia Symptoms In Men And Women

While researchers continue to study this important question, one thing is known: Males and females have different schizophrenia symptoms and experiences because of differences in the brain. Multiple areas within the brain have been implicated in schizophrenia .
The areas of damageincluding, but not limited to, the inferior parietal lobe in the cerebral cortexthat are associated with this mental illness are different in men and women. Schizophrenia damages male brains differently than female brains.
Men and women can have different symptoms of schizophrenia, and those symptoms affect lives uniquely. One isnt better or worse, because schizophrenia is a mental illness that is challenging for everyone who lives with it. Also, while there is no cure for schizophrenia, people of both genders can work to minimize symptoms and live a quality life. When someone with schizophrenia is viewed as an individual with symptoms and strengths, the gender differences dont seem as big.
What Is Schizophrenia Or Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a challenging brain disorder that often makes it difficult to distinguish between what is real and unreal, to think clearly, manage emotions, relate to others, and function normally. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, and sees the world.
The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia, or schizophrenia with paranoia as its often called. People with paranoid schizophrenia have an altered perception of reality. They may see or hear things that dont exist, speak in confusing ways, believe that others are trying to harm them, or feel like theyre being constantly watched. This can cause relationship problems, disrupt normal daily activities like bathing, eating, or running errands, and lead to alcohol and drug abuse in an attempt to .
Many people with schizophrenia withdraw from the outside world, act out in confusion and fear, and are at an increased risk of attempting suicide, especially during psychotic episodes, periods of depression, and in the first six months after starting treatment.
Take any suicidal thoughts or talk very seriously
If you or someone you care about is suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-TALK, visit orto find a helpline in your country, or readSuicide Prevention.