What Are The Types Of Bipolar Disorders
Bipolar disorder can be further divided into four types. These include:
Lithium Treatment And Suicide
An association of reduced risk of suicides and attempts during long-term treatment with lithium in BD is supported consistently by most , but not all studies . At least 10 placebo-controlled, randomized trials not specifically designed with suicide risk as the primary outcome measure, but involving more than 110,000 person-years of risk, found five- to sixfold reductions in suicidal acts . Based on such studies, several expert reports recommend long-term lithium treatment to limit risk of suicidal behavior in BD patients .
What Is The Difference Between Depression And Bipolar Disorder
Depression and bipolar disorder are two mood disorders that have many similarities. However, they have key differences that are essential to understand for the sake of effective treatment.
Mental health is becoming more of a mainstream topic, an incredible advancement that normalizes the experiences of many. As such, isnt uncommon to hear someone say theyre feeling depressed.
However, clinical depression, also known as major depressive disorder, isnt just feeling sad. It is a persistent feeling of hopelessness and emptiness, losing interest in things that used to excite you, and several other symptoms including changes in sleep, appetite, and thinking.
-
Persistent feeling of hopelessness and emptiness
-
Changes in appetite, sleep, thinking
-
Significant fatigue
-
May cause impairment or require hospitalization
-
May have feelings of extreme energy when manic
Similarly, some may casually say theyre bipolar because theyre feeling a wide range of moods. But bipolar disorder is marked by episodes of mania or hypomania and depression that significantly impact your life.
Read on to learn more about the symptoms, causes, and treatment for these two disorders.
Recommended Reading: How Can Social Media Cause Depression
Learn The Signs And Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
The symptoms of bipolar disorder can show up in people differently. Learn the signs of depressive and manic episodes. It can help to directly ask your friend things like:
- What do your manic or depressive symptoms look like?
- Is getting worse or better?
- Are there signs that I should look out for that things are getting worse or getting better?
- What are the coping strategies that work for you?
Bipolar Disorder Due To Another Medical Or Substance Abuse Disorder

Some bipolar disorders dont have a specific pattern or dont match the three categories of disorders listed above and yet, they still align with the criteria for abnormal mood changes. For example, a person may experience mild depressive or hypomanic symptoms that last less than the specified amount for cyclothymia. Additionally, a person might experience depressive episodes, but have symptoms of mood elevation that are too mild or brief to be diagnosed as mania or hypomania.
These instances can be determined to be characteristic of bipolar disorder, but arent classified under the aforementioned types of bipolar disorder.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Nocturnal Panic Attacks
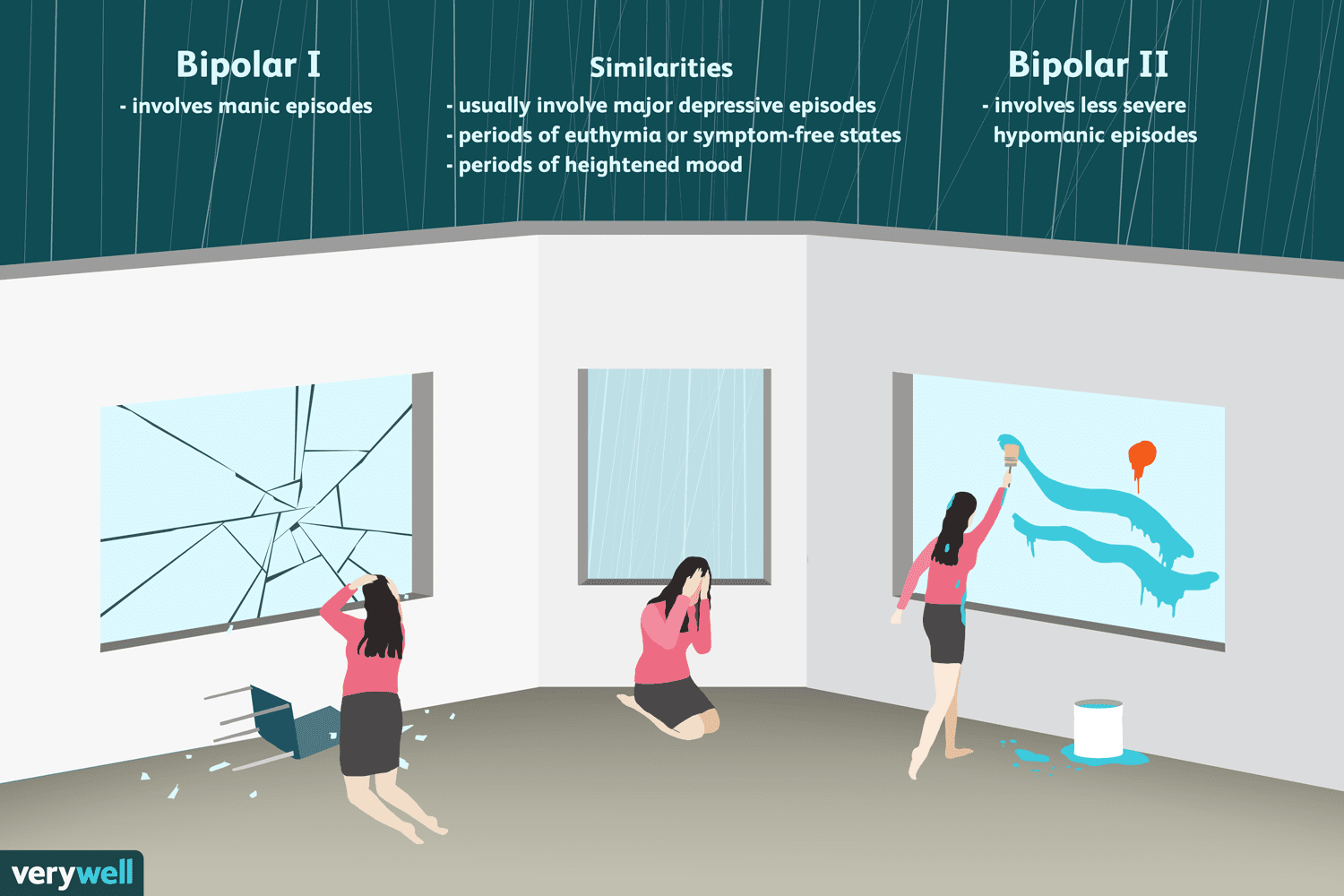
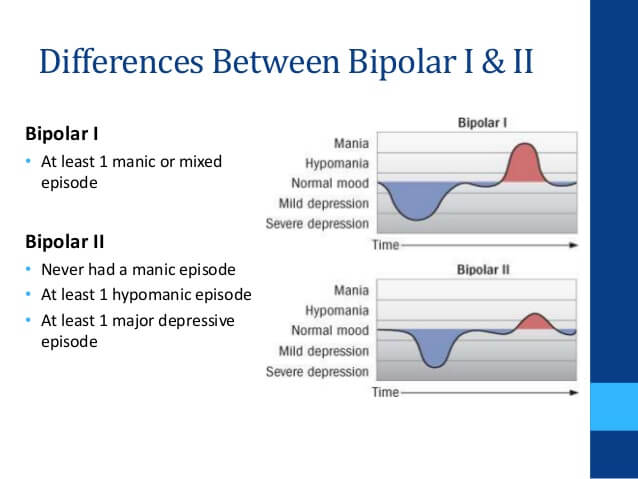
What Is Bipolar 2 Disorder
Bipolar 2 disorder involves a major depressive episode lasting at least two weeks and at least one hypomanic episode . People with bipolar 2 typically dont experience manic episodes intense enough to require hospitalization.
Bipolar 2 is sometimes misdiagnosed as depression, as depressive symptoms may be the major symptom at the time the person seeks medical attention. When there are no manic episodes to suggest bipolar disorder, the depressive symptoms become the focus.
As mentioned above, bipolar 1 disorder causes mania and may cause depression, while bipolar 2 disorder causes hypomania and depression. Lets learn more about what these symptoms mean.
Signs And Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder can look very different in different people. The symptoms vary widely in their pattern, severity, and frequency. Some people are more prone to either mania or depression, while others alternate equally between the two types of episodes. Some have frequent mood disruptions, while others experience only a few over a lifetime.
There are four types of mood episodes in bipolar disorder: mania, hypomania, depression, and mixed episodes. Each type of bipolar disorder mood episode has a unique set of symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Can Schizophrenia Develop Over Time
Symptoms Of Bipolar I Disorder
Manic Episode
A manic episode is a period of at least one week when a person is extremely high-spirited or irritable most of the day for most days, possesses more energy than usual, and experiences at least three of the following changes in behavior:
- Increased or faster speech
- Uncontrollable racing thoughts or quickly changing ideas or topics when speaking
- Distractibility
- Increased activity
- Increased risky behavior
These behaviors must represent a change from the persons usual behavior and be clear to friends and family. Symptoms must be severe enough to cause dysfunction in work, family, or social activities and responsibilities. Symptoms of a manic episode commonly require a person to receive hospital care to stay safe.
Some people experiencing manic episodes also experience disorganized thinking, false beliefs, and/or hallucinations, known as psychotic features.
Hypomanic Episode
A hypomanic episode is characterized by less severe manic symptoms that need to last only four days in a row rather than a week. Hypomanic symptoms do not lead to the major problems in daily functioning that manic symptoms commonly cause.
Major Depressive Episode
A major depressive episode is a period of at least two weeks in which a person has at least five of the following symptoms :
- Intense sadness or despair
- Frequent thoughts of death or suicide
Unipolar And Bipolar Depression: Different Disorders
The prevailing model is that the depressions within unipolar and bipolar disorders are qualitatively different in etiology and phenomenology. This type of duality is exemplified in the DSM diagnostic system, with unipolar and bipolar disorders categorized as separate branches on the mood disorder diagnostic tree. This separate branch includes both mania and bipolar depression on the bipolar âbranch,â rather than depression without mania, depression and mania, and monopolar mania. Drawing on the strong evidence that mania is biologically driven, bipolar depression has been seen as more endogenous than unipolar depression. As a consequence of this dichotomy in the diagnostic nomenclature, research in mood disorders tends to focus on either bipolar disorder as a whole, failing to account for episode polarity in bipolar disorder, or unipolar depression. Few researchers have directly compared unipolar and bipolar depression.
Also Check: Why Eating Disorders Are On The Rise
Whats The Difference Between Borderline Personality Disorder And Bipolar Disorder
While borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder have similar symptoms and are often confused for each other, theyre distinct conditions.
BPD involves a longstanding pattern of abrupt, moment-to-moment swings in moods, behavior and self-image that are often triggered by conflicts in interactions with other people. Nonsuicidal self-injury is also common in BPD but not in bipolar disorder.
Bipolar disorder is different from BPD because it involves distinct, longer-lasting episodes of mania/hypomania and/or depression. Several things can trigger manic or depressive episodes, such as sleep changes, stress, medications and substance use.
What Is Manic Depression
In older days, general Bipolar disorder was also known as manic depressive disorder, since it also has alternating periods of mania and depression. But, after the identification of subcategories under Bipolar disorder, Bipolar 1, which is characterized by full-blown episodes of mania alternating with periods of depression, began to be called as manic depression.
A person who is in a manic phase will indicate high feelings or euphoria, intense energy, and activity, restlessness, insomnia, agitation or irritability and tendency to engage in risky things recklessly, e.g., fast driving.
In contrast, a person who is in a depressive phase will feel hopeless and empty. He or she will have low energy, trouble sleeping or increased sleepiness, have trouble concentrating, poor insight, loss of appetite and tendency to develop feelings of suicide.
Additionally, people may also develop both mania and depression at once, in a single episode which is then referred to as an episode of mixed features where there will be extreme low moods which suddenly convert into euphoria.
Manic depression can be effectively treated with anti-psychotic and anti-depressants combined with psychotherapy, family-focused therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Suffer From Panic Attacks
Difference Between Major Depression And Bipolar Disorder
The main difference between the two is that depression is unipolar, meaning that there is no up period, but bipolar disorder includes symptoms of mania. To differentiate between the two disorders, it helps to understand the symptoms of each one. What is the difference between major depression and bipolar disorder quizlet? What is the difference between depression and bipolar disorder? Depression is
Treatment Of Bipolar Depression
As noted, depressive, dysthymic, and mixed states account for the majority of illness-burden in BD, and are strongly predicted by initial depressive, mixed, or anxious episodes . Remarkably few treatments are proved to be highly and consistently effective in acute episodes of bipolar depression, and there is even less evidence supporting substantial long-term protection from recurrences . In particular, there is continued controversy about the value and risks of antidepressant drugs in bipolar depression . Lack of highly effective treatments encourages widespread drug-combinations and other off-label treatments largely untested for effectiveness and safety.
Table 4 Placebo-controlled trials for acute depression in bipolar disorder
Relative paucity of experimental treatment studies for bipolar depression may reflect a broadly accepted view that major depression is similar in its clinical characteristics as well as treatment responses in BD and MDD . Instead, their characteristics differ, e.g., in family history, sex-distribution, onset-age, long-term diagnostic stability, episode duration, recurrence rates, and treatment-responses . The assumption of similarity probably contributes to the rarity of direct comparisons of treatment responses with depression in BD vs. MDD, and leaves bipolar depression as a leading challenge for psychiatric therapeutics .
You May Like: How To Get Over Dental Anxiety
Bipolar Disorder And Depression: Understanding The Difference
Depression and Bipolar disorder are two mental health conditions often confused with each other due to certain similarities in the nature and phases of both. There are mixed views about the two disorders, as some sources claim Bipolar disorder just to be a type of Depression, while others think they are two completely different branches of Mental disorders.
Talk To Someone You Trust
It is important to have someone to talk to who understands what you are going through. Find a friend, family member, or another support system to help you through tough times. When you share your experiences with someone who listens without judgment, you can gain a better understanding of your thoughts and feelings.
Don’t Miss: Can Vitamin D Help With Depression
Help Is Available For All Types Of Bipolar Disorder
Treatment is available for all types of bipolar disorder. The first step to recovery is to seek help from a medical doctor or licensed mental health care provider such as a psychiatrist. The professional will likely provide you with a psychological assessment for bipolar disorder and work with you to create a treatment plan specifically for you. You might also be asked to monitor your daily moods and sleep patterns through a mood chart to help with diagnosis.
Treatment for this disorder usually includes a variety of strategies to manage the condition over the long term such as psychotherapy and medication. Since bipolar disorder is a chronic illness, treatment must be ongoing.
Medications are typically an important part of treatment and might include mood stabilizers, antipsychotic medications, or antidepressants. Such medications usually need to be taken regularly to be effective. If you have been diagnosed with bipolar disorder, you and your doctor will work together to find the right medication or combination of medications for your unique needs. As everyone responds to medication differently, you may have to try several different medications before you find one that relieves your symptoms.
With treatment and through an individuals own efforts, people with all types of bipolar disorder can live rich, rewarding lives.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Yourself From Depression
How To Treat Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder are both treatable. To diagnose bipolar disorder, your healthcare provider may carry out a physical exam and a mental health evaluation to learn more about your symptoms.
If appropriate, you may receive a mental health referral. Your mental health provider may talk to you about your symptoms and overall mental wellbeing. You may be asked about your personal or family history of bipolar disorder or other forms of mental illness.
You can also seek treatment from home with our online psychiatry service, which allows you to connect with a licensed psychiatry provider online for an evaluation.
Although theres no way to cure bipolar disorder, it can usually be treated with a combination of medication and psychotherapy.
The most common medications for treating bipolar disorder are mood stabilizers and atypical, or second-generation, antipsychotics. These medications work by preventing highs and lows that can occur with bipolar disorder and stopping delusions, hallucinations and paranoid thoughts.
In some cases, antidepressants are also used to treat bipolar depression.
If youre prescribed medication to treat bipolar disorder, make sure to use it exactly as instructed by your healthcare provider. Inform your healthcare provider if you develop any side effects from your medication.
You May Like: Does Anxiety Medication Cause Weight Gain
Difficulty Taking Care Of Oneself
Bipolar disorder can make it hard to take care of day-to-day responsibilities, such as eating healthy, exercising, and getting enough sleep. This can lead to problems with weight, energy levels, and overall health. People with bipolar disorder may also have trouble keeping a job or managing their finances.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
Wondering how to know if you are bipolar? Signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder in men or women can range, depending on the state theyre in. Symptoms, when someone is in a manic state, can widely vary from what they experience when theyre in a depressive state. Severity of bipolar symptoms in either state can differ as well.
In a manic state, manic symptoms may include:
- Extreme overexcitement that lasts for a long time
- Inability to focus
Also Check: What To Do When Someone With Ptsd Pushes You Away
What Are The Types Of Depression
The Difference Between Anxiety Depression And Bipolar Disorder
Obtaining a diagnosis is the first step in seeking mental and behavioral healthcare. Once you understand your specific mental health condition, you can obtain the support you need to thrive. However, it can be tricky to understand the nuances between the many diagnoses, especially when discussing anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder.
Heres how to distinguish between these common conditions.
Recommended Reading: Is Stress Eating A Disorder
Loss Of Interest In Activities
When people are depressed, they may lose interest in activities or hobbies that they once enjoyed. This can be one of the first signs that something is wrong. For example, someone who used to love going out on walks may suddenly stop doing so. And it might not just be one activity they may lose interest in many things.
The Difference Between Anger And Bipolar Anger
That said, the majority of people with bipolar disorder have experienced bipolar anger, a level of rage and hostility outside of the normal range. But, what exactly is bipolar anger? The Difference between Anger and Bipolar Anger Everyone gets angry. Anger is a normal human emotion and one that serves a valuable purpose.
Also Check: What Is The Best Mood Stabilizer For Bipolar