Common Symptoms Of Anxiety In Children
Thumping heart, rapid breathing, sweating, tense muscles, nausea, and dread are familiar symptoms of anxiety that accompany a fight, flight, or freeze reaction triggered by real or imagined threats, like a snarling dog or new social experience. Anxious children may be clingy, startle easily, cry or have tantrums, sleep poorly, and have headaches or stomachaches.
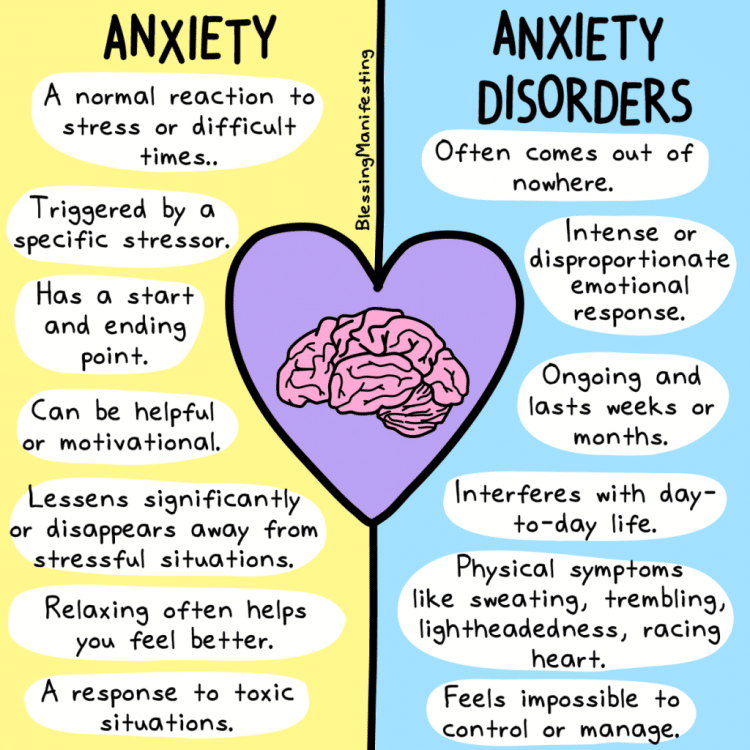
But anxiety is not all bad. It can motivate us, or help us avoid danger, says Dr. Mona Potter, medical director of McLean Anxiety Mastery Program and McLean Child and Adolescent Outpatient Services. The problem is when anxiety gets out of hand and makes decisions for us that are no longer helpful maybe even paralyzing. By that point, normal anxiety may have become an anxiety disorder.
Types Of Anxiety Disorders
There are five types of anxiety disorders in children and youth.
Its normal for young children to have fears about being left with someone new, but they are usually able to get used to the situation. A child with separation anxiety continues to have a hard time being away from caregivers. For example, for some children even being in a different room in the same home can provoke anxiety. This fear gets in the way of children doing things by themselves when they otherwise would be capable of doing so.
Children with separation anxiety disorder may:
- refuse or avoid going to school
- cry and cling to a caregiver
- express worries that something bad might happen to the caregiver
- complain of physical symptoms like tummy aches before, during and after separation
Social Anxiety Disorder
Children and youth with social anxiety disorder have a strong fear of embarrassing themselves and of other people thinking badly of them. For example, they may worry about wearing the wrong clothing or doing or saying the wrong thing. They can at times feel deeply uncomfortable as if a spotlight is on them or they are the centre of attention, even when that is not the case.
Children and youth with social anxiety disorder may feel deeply uncomfortable when, or avoid completely:
Specific Phobias
Anxiety Canada
Anxiety In Kids Is On The Rise
CDC data shows about 5.8 million children 3-17 years old were diagnosed with anxiety, and about 2.7 million were diagnosed with depression between 2016 and 2019. But there are signs that mental health issues have gotten worse since the pandemic. Weekly visits to emergency departments in children 5-17 increased for self-harm, drug poisoning, and psychosocial concerns during 2020, 2021, and 2022 when compared to 2019. And last year, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry called the mental health crisis in kids a national emergency. The AAP said doctors witnessed dramatic increases in emergency department visits for all mental health emergencies, including suspected suicide attempts.
Plus, the US Department of Health and Human Services published a study this year that showed the number of kids 3-17 years old diagnosed with anxiety grew by 29% from 2016 to 2020.
Mental health disorders like ADHD, anxiety, and depression are more common among older kids. One study that looked at the 2016 National Survey on Childrens Health found that anxiety was most common in kids 12-17 years old. Separation anxiety, selective mutism, and GAD are more common in younger kids . Social anxiety and specific phobias usually happen in older kids.
Also Check: How To Live In The Moment With Anxiety
Common Symptoms Of Generalized Anxiety Disorder For Children At School
According to Child Mind Institute, your childs anxiety may manifest at school in several ways. Keep an eye out for these signs:
- Refusing to go to school or having a hard time at school drop-offs
- Difficulty participating in class and interacting with peers
- Excessive worry about everyday things
- Trouble answering questions when called on by the teacher
- Disruptive behavior
- Frequent trips to the nurse
- Avoiding socializing or group work
- Not turning in homework
If you notice several of the above, ask your childs doctor to perform an in-depth screening of his or her mental and physical health to rule out a mood disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder , or a specific phobia, all of which can look like GAD. Certain physical conditions, like thyroid disorders or heart conditions, can also mimic anxiety-like symptoms. Your doctor can rule out most of these with simple blood and urine tests though some more complicated conditions may require x-rays or physical stress tests.
What Types Of Anxiety Are Common In Children
- Very anxious and upset when parted from parents and caregivers refusal to attend camp, sleepovers, or play dates worry that bad things will happen to self or loved ones while separated.
- Social anxiety: Strong fear of social situations very anxious and self-conscious around others worry about being judged or humiliated.
- Specific phobia: Severe, irrational fear set off by a situation or thing, such as thunderstorms, worry about vomiting, or insects.
Also Check: Can Being Molested Cause Ptsd
Positive Activities For Behavioral Activation Worksheet
When patients suffer from more debilitating emotional issues like depression and severe anxiety it can be difficult for them to keep from falling into bad habits like isolating and cutting off things that bring them joy. Of course this is understandable, as with such mental illnesses it can be difficult for a patient to enjoy
How Does Diagnosis Of Anxiety Differ In Children
The DSM-5 includes diagnostic criteria for the different anxiety disorders. Children must meet different diagnostic criteria than adults to be diagnosed with an anxiety disorder. For example, to be diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder, children only need to meet one of the six symptoms listed below, whereas adults need three of the six: · Restlessness
Recommended Reading: How To Fix Binge Eating Disorder
Identifying And Treating Anxiety In Children
Childhood anxiety can sometimes be missed because it often appears as difficult or bizarre behaviors that some may believe will simply be ‘outgrown.’ However, if any of these symptoms or behaviors persist, consult with a Psychologist who uses a Cognitive Behavioral approach in treating anxiety. As childhood anxiety can also be exhausting for you, the parent, be certain to gain support for yourself through a parent support group for children who suffer from anxiety. You could also consider psychological support to offer support and guidance as you work with your child towards decreased anxiety.
What Is The Outlook For Children With Anxiety
Children are very resilient. With the right interventions, including treatment and support, they can learn to manage anxiety symptoms and live a full life.
For some kids, anxiety may be a lifelong condition, but for others, the symptoms and effects may be temporary and related to a particular situation. The good news is that treatment is very effective, and the outlook for children, adolescents, and teens is very promising.
Your childs doctor should ensure, however, that the anxiety symptoms arent the side effects of a particular medication. Medications that may cause anxiety symptoms include:
- bronchodilators
Also Check: How To Handle Panic Attacks
Get Help Finding Treatment
Here are tools to find a healthcare provider familiar with treatment options:
- Psychologist Locatorexternal icon, a service of the American Psychological Association Practice Organization.
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist Finderexternal icon, a research tool by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry .
- Find a Cognitive Behavioral Therapistexternal icon, a search tool by the Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies.
- If you need help finding treatment facilities, visit MentalHealth.govexternal icon.
Help For Kids With Anxiety And Panic Attacks In Davidson Nc
Anxiety doesnt have to run your childs life and call the shots in your house. If you feel like youre bending over backwards to avoid things that set off your childs worries, therapy can help. Kids can learn coping skills to feel more in control of anxiety and panic, like the ones I teach in Worry-Free Tweens, my online class for kids.
Child-friendly styles of therapy like Play Therapy and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy have been proven to help anxious kids feel better in a relatively short period of time. With a little practice, your child wont have to dread their next panic attack, because shell know exactly what to do if she feels one coming on.
I love helping anxious kids and tweens in my Davidson, NC child therapy office. I also provide play therapy and CBT online to kids throughout North Carolina, New York, and Florida. I use these approaches because Ive seen them work, and I know theyre effective. Whether you work with me or another counselor, I hope your family finds therapy helpful, too.
Read Also: How Can You Tell If Someone Is Depressed
Can A Child Have Both Anxiety And Panic
Yep! A child can have both anxiety and panic attacks. In fact, its pretty common. Being anxiety-prone or sensitive to stress may put a child at risk for experiencing panic attacks. Sometimes, panic attacks happen on their own, and this is called Panic Disorder. Its also very common for panic attacks to go hand-in-hand with other forms of anxiety, like Social Anxiety, Generalized Anxiety, and Agoraphobia.
If a child is struggling with both anxiety and panic attacks, she probably has lower-level anxiety on an ongoing basis that gets punctuated by brief moments of intense fear. For example, a child may struggle with perfectionism and worries about not doing a good enough job on school assignments. This could lead to problems like avoiding turning in homework, stomach aches on school days, and fitful sleep. Before a test, however, this child might experience a full-blown panic attack with rapid breathing and dizziness.
Anxiety and panic are both tough. Dealing with them both is even harder. The good news is, there are great therapy options to help kids with anxiety, panic, or a mix of both. Its possible to get worries under control and learn to soothe panic responses in the body, so your child can get back to enjoying life.
How Serious Can It Be

Long-term anxiety can severely interfere with a child’s personal development, family life and schooling.
Anxiety disorders that start in childhood often persist into the teenage years and early adulthood. Teenagers with an anxiety disorder are more likely to develop clinical depression, misuse drugs and feel suicidal.
This is why you should get help as soon as you realise it’s a problem.
You May Like: What Ptsd Is Really Like
What Causes Anxiety Disorders
Several things play a role in causing the overactive “fight or flight” that happens with anxiety disorders. They include:
Genetics. A child who has a family member with an anxiety disorder is more likely to have one too. Kids may inherit genes that make them prone to anxiety.
Brain chemistry. Genes help direct the way brain chemicals work. If specific brain chemicals are in short supply, or not working well, it can cause anxiety.
Life situations. Things that happen in a child’s life can be stressful and difficult to cope with. Loss, serious illness, death of a loved one, violence, or abuse can lead some kids to become anxious.
Learned behaviors. Growing up in a family where others are fearful or anxious also can “teach” a child to be afraid too.
Signs Your Child Is Having Panic
Panic comes on suddenly, and it can be debilitating. Its possible for a child to go about her day with anxiety, but a panic attack will stop her in her tracks. While anxiety gradually waxes and wanes, panic is like a light switch flipping on and off. The good news is that although panic attacks are intense, they dont usually last very long. If your child has a panic attack, it will most likely be over in 15 minutes.
If your child is having a panic attack, you may notice things like:
-
Shaking hands or full-body shivering
-
Increased sweating
-
Tingling feelings in the fingers or hands
-
A sense of losing control
-
Intense terror, as if something bad is about to happen
Your child may or may not be worried about something in particular when a panic attack occurs. Sometimes, panic attacks seem to appear out of the blue, when a child isnt thinking about anything in particular. Over time, though, your child may start feeling worried about the panic attacks themselves. If shes already had a few, she may dread the possibility of having another one.
Read Also: Does Valium Stop Panic Attacks
Wheel Of Emotions For Kids Worksheet
During childhood, we learn how to identify and cope with our emotions. It is important to encourage children to understand and embrace their emotions at an early age. That way, they develop a level of emotional intelligence that will help them develop a healthy relationship with themselves and with others. Emotions can be triggered in
How We Treat Generalized Anxiety Disorder
If you suspect your child may have GAD, it is essential to speak with a qualified mental health professional as soon as possible. Children with GAD respond well to treatment that is administered by trained mental health clinicians. By closely working with the treatment team, you can help your child go on to enjoy an active and fulfilling life.
Evidence-based treatments for GAD in children and adolescents includes cognitive behavioral therapy, medication, or a combination of medication and therapy. Here at Boston Childrens Hospital, medication is used in conjunction with therapy for treatment of GAD. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants are currently first-line medications in the pharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders in children. These antidepressants are powerful anxiolytics with a broader spectrum that may improve comorbid affective disorders and symptoms of anxiety.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When Friend Is Having Panic Attack
Feeling Anxious For Most Of The Time For No Apparent Reason
While it’s normal for children to frequently have fears and worries, some anxious children may grow up to develop a long-term condition called generalised anxiety disorder when they become a teenager or young adult.
Generalised anxiety disorder causes you to feel anxious about a wide range of situations and issues, rather than one specific event.
People affected by it feel anxious most days and often struggle to remember the last time they felt relaxed.
Teach The Child Relaxation Techniques
Yoga, deep breathing, and other self-calming techniques are highly effective. Look into classes for kids offered in your area. Some kids have developed their own ways to calm themselves when worry strikes hugging a pillow, playing with a pet, or simply holding a favorite toy. Ultimately, it’s up to the child to curb his own anxiety.
Read Also: Who To Talk To About Depression
Autism And Anxiety Symptoms
There is a lot of overlap between autism and anxiety symptoms. Many people with autism also have anxiety, and vice versa. This is not surprising, as both autism and anxiety can be characterized by difficulties with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. People with autism may have a hard time understanding social cues, which can lead to anxiety in social situations. They may also have trouble communicating, which can lead to anxiety about being misunderstood. And, finally, people with autism may engage in repetitive behaviors as a way of coping with anxiety.
Understanding and Treating Anxiety in Autism, written by Jessica Kingsley Publishers, is now available for purchase. Anxiety disorders, which affect approximately 18% of the general population, are the most common type of mental illness. Repetitive behavior, rigidity in routine, rituals, flat affects, and limited social interactions are some of the most common symptoms of anxiety disorders. When a person is under stress, their appetite or ability to eat normally may be reduced. A sleeping problem is possible. Anxiety can look a lot like anger or fear at times. There are several possible explanations for autism and anxiety overlap, including: how to spot anxiety symptoms and whether this is a one-time or persistent problem.
What Should You Do When You Think Your Child Needs Anxiety Treatment

If you think your child is struggling with anxiety, seeking professional help is recommended. As a chronic condition, anxiety is not likely to go away on its own.
But support is available. If youre not sure where to start, your pediatrician can provide a referral to a therapist or psychologist who specializes in anxiety disorders.
The type of treatment depends on the specific anxiety disorder, but the first line of treatment is often cognitive-behavioral therapy . CBT helps children learn how to identify and manage their anxious thoughts and feelings. In structured sessions, children are given the tools to recognize their cognitive distortions and learn how to respond to them in a healthy way.
Read Also: Can You Have Ptsd Without Trauma
What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worry about a variety of events. It is often accompanied by physical symptoms such as headaches, muscular tension, restlessness, heart palpitations, and stomach upset. Children and adolescents with GAD may worry excessively about their performance and competence at school or in sporting events, about personal safety and the safety of family members, or about natural disasters and future events.
The difference between normal feelings of anxiety and the presence of generalized anxiety disorder is that children with GAD worry more often and more intensely than other children in the same circumstances. Children with GAD tend to worry about the same things as their non-anxious peers, but they do so in excess. These worries and associated symptoms cause significant distress and impair daily functioning. Children with GAD are often overly self-critical and avoid activities in which they feel that may not be able to perform perfectly. They also tend to seek frequent reassurance from caregivers, teachers, and others about their performance, although this reassurance provides only fleeting relief from their worries.