Etiology And Risk Factors
Genetics have an important role in the etiology of schizophrenia, even though most patients diagnosed with the disease have no family history of psychosis. The genetic variation responsible for the disease has not been identified. Relatives of persons with schizophrenia are also at risk of schizoaffective disorder, schizotypal personality disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, and autism spectrum disorder.1,5
Environmental factors may have a role.1 Possible environmental factors include being born and raised in an urban area, cannabis use, infection with Toxoplasma gondii,2,6,7 obstetric complications, central nervous system infection in early childhood, and advanced paternal age .1
Schizophrenia And Dangerous Behaviour
Schizophrenia and Dangerous Behaviour
It is one of the commonest and most enduring myths around schizophrenia that all people suffering from this condition are violent. In public opinion schizophrenia is most often associated with violence than with any other type of disordered behaviour.
This is undoubtedly fed and reinforced by rancorous and ill-informed media reporting of the subject. Articles and current affairs programmes that focus on violence in schizophrenia whilst ignoring all of the other features of this complex condition, particularly the high suicide rate and telling us very little about the illness in general, are sadly all too common. A study carried out in 1994 of the British news media found that stories about violence by people with schizophrenia outweighed sympathetic news stories about the condition by about four to one.11
Sadly this subject is one that many people engaged in the caring professions feel particularly uncomfortable discussing. Dangerous behaviour is very often seen by them as a failure on the part of the doctors rather than as a feature of a society which undervalues people with mental illness and under-funds mental health services. In addition, at times of tragedy, they are often faced with hostile reporting by the media which seeks to point fingers of blame at the doctors rather than at societys attitudes to treating mental illness.
Are people with schizophrenia dangerous?
Schizophrenia and suicide
Schizophrenia and violence
References
Early Warning Signs And Symptoms
Usually, a person with schizophrenia has gradual changes in their thoughts and perceptions. Families are often the first to see early signs of psychosis and schizophrenia in a loved one.
Before the first episode of psychosis, you go through what is known as a premorbid period. This is the 6 months before the first symptoms of psychosis. During this period, you might experience gradual changes.
Although sleep disturbances are not included in the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia, people with the condition consistently report them.
Early warning signs include:
Read Also: How To Conquer Panic Attacks
Lack Of Emotional Expressions
A characteristic symptom of schizophrenia is a lack of emotional expression. People with this condition may show little or no reactions to good or bad news.
They also begin to show fewer facial expressions and gestures when they talk. Their voice may become flat when they speak.
Interestingly, suggests that while they appear to have a wooden expression, what they express outward may not be the same as what they feel inside.
Sometimes, they can have unexplained and seemingly inappropriate reactions to things, like overwhelming anger or inappropriate laughter.
What Are The Types Of Schizophrenia

There are different types of schizophrenia. The International Classification of Diseases manual describes them as below.
Paranoid schizophrenia
- Pranks, giggling and health complaints.
- Usually diagnosed in adolescents or young adults.
Catatonic schizophrenia
- Unusual movements, often switching between being very active and very still.
- You may not talk at all.
Simple schizophrenia
- Negative symptoms are prominent early and get worse quickly.
- Positive symptoms are rare.
Undifferentiated schizophrenia
Your diagnosis may have some signs of paranoid, hebephrenic or catatonic schizophrenia, but doesnt obviously fit into one of these types alone.
Residual schizophrenia
This type of schizophrenia is diagnosed in the later stages of schizophrenia. You may be diagnosed with this if you have a history of schizophrenia but only continue to experience negative symptoms.
Other schizophrenia
There are other types of schizophrenia according to the ICD-10, such as.
- Cenesthopathic schizophrenia. This is where people experience unusual bodily sensations.
- Schizophreniform. Schizophreniform disorder is a type of psychotic illness with symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. But symptoms last for a short period.
Unspecified schizophrenia
Symptoms meet the general conditions for a diagnosis, but do not fit in to any of the above categories.
Don’t Miss: Does Bipolar Mean Your Crazy
Difficulty With Abstract Thinking
Another classic sign of schizophrenia is the struggle to form generalizations or think beyond a solid idea or concept.
People with the condition may have a hard time understanding things that arent physical or real. They may also have difficulty understanding a proverb, simile, or metaphor because they can only interpret things literally.
They tend to get distracted by whats real and literal, and may be unable to understand what a story means or the comparison thats being made.
How Does Schizophrenia Affect Families
Schizophrenia takes an enormous toll on afflicted families. Many people with schizophrenia have difficulty maintaining a job or living independently, though it is important to recognize that treatment, especially at the onset of symptoms, allows individuals with a diagnosis of schizophrenia to lead meaningful, productive lives.
Also Check: Is Stress Eating An Eating Disorder
Positive Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Start Happening
Positive symptoms are highly exaggerated ideas, perceptions, or actions that show the person canât tell whatâs real from what isnât. Here the word “positive” means the presence of symptoms. They can include:
- Hallucinations. People with schizophrenia might hear, see, smell, or feel things no one else does. The types of hallucinations in schizophrenia include:
- Auditory. The person most often hears voices in their head. They might be angry or urgent and demand that they do things. It can sound like one voice or many. They might whisper, murmur, or be angry and demanding.
- Visual. Someone might see lights, objects, people, or patterns. Often itâs loved ones or friends who are no longer alive. They may also have trouble with depth perception and distance.
- Olfactory and gustatory. This can include good and bad smells and tastes. Someone might believe theyâre being poisoned and refuse to eat.
- Tactile. This creates a feeling of things moving on your body, like hands or insects.
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Stop Happening
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function involving thinking, behavior, and perception. You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. A doctor will call this anhedonia.
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. Doctors call this alogia.
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. When they talk, their voice can sound flat, like they have no emotions. They may not smile normally or show usual facial emotions in response to conversations or things happening around them. A doctor might call this affective flattening.
- Withdrawal. This might include no longer making plans with friends or becoming a hermit. Talking to the person can feel like pulling teeth: If you want an answer, you have to really work to pry it out of them. Doctors call this apathy.
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. They may stop bathing or taking care of themselves.
- No follow-through. People with schizophrenia have trouble staying on schedule or finishing what they start. Sometimes they can’t get started at all. A doctor might call this avolition.
Depression has some of the same symptoms, too. They can be hard to spot, especially in teens, because even healthy teens can have big emotional swings between highs and lows.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Service Dog Do For Someone With Ptsd
Is It Possible To Recover From Schizophrenia
Many people who live with schizophrenia have recovery journeys that lead them to live meaningful lives.
Recovery can be thought of in terms of:
- clinical recovery, and
- personal recovery.
What is clinical recovery?
Your doctor might have talked to you about recovery. Some doctors and health professionals think of recovery as:
- no longer having mental illness symptoms, or
- where your symptoms are controlled by treatment to such a degree that they are not significantly a problem.
Sometimes this is called clinical recovery.
Everyones experience of clinical recovery is different.
- Some people completely recover from schizophrenia and go on to be symptom free.
- Some who live with schizophrenia can improve a great deal with ongoing treatment.
- Some improve with treatment but need ongoing support from mental health and social services.
What is personal recovery?
Dealing with symptoms is important to a lot of people. But some people think that recovery is wider than this. We call this personal recovery.
Personal recovery means that you can live a meaningful life.
What you think of as being a meaningful life might be different to how other people see it. You can think about what you would like to do to live a meaningful life and work towards that goal.
Below are some ways you can think of recovery.
What can help me recover?
You may want to think about the following questions.
The following things can be important in recovery.
Helping Someone With Schizophrenia Tip : Encourage Treatment And Self
Encouraging treatment and self-help is a cornerstone of helping a loved one with schizophrenia. While medication is an important element of schizophrenia treatment, your loved ones recovery depends on other factors as well. Self-help strategies such as changing to a healthy diet, managing stress, exercising, and seeking social support can have a profound effect on your loved ones symptoms, feelings, and self-esteem. And the more someone does for themselves, the less hopeless and helpless theyll feel, and the more likely their doctor will be able to reduce their medication. Your encouragement and support can be crucial to your loved one starting and continuing a program of self-help.
You May Like: Is Binge Eating Disorder Dangerous
What Myths Are There About Schizophrenia
There are some myths or mistaken beliefs about schizophrenia which come from the media. For example,
- Schizophrenia means someone has a split personality
This is not the case. The mistake may come from the fact that the name ‘schizophrenia’ comes from two Greek words meaning ‘split’ and ‘mind’.
- People who live with schizophrenia are dangerous
Those who live with schizophrenia arent usually dangerous. People who live with schizophrenia are far more likely to be harmed by other people than harm others.
There is a higher risk of violent behaviour from those who live with schizophrenia. But, as with people who dont live with schizophrenia, much of the risk is linked to the use of street drugs or alcohol.
Sometimes people who live with schizophrenia commit violent crimes. The media often report them in a way which emphasises the persons mental health diagnosis. This can create fear and stigma in the general public. But it should be remembered that:
- violent crimes are also committed by people who dont live with schizophrenia,
- its often later found that the person was failed or neglected by the mental health system, and
- the crime might have been prevented if the person had received the care and support they needed.
So, its not right to say that schizophrenia equals dangerous.
What Causes Schizophrenia
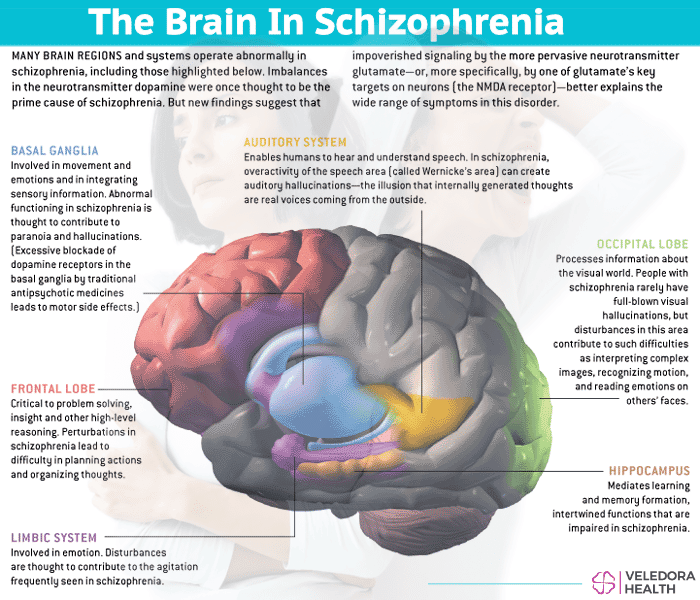
Nobody knows exactly what causes schizophrenia, it is likely to be the result of several factors. For example:
- Stress. Some people can develop the illness as a result of a stressful event, such as the death of a loved one or the loss of a job.
- Genetics. You are more likely to develop schizophrenia if you have a close relation with the illness.
- Brain damage. This is usually damage that has stopped your brain from growing normally when your mother was pregnant. Or during birth.
- Drugs and alcohol. Research has shown that stronger forms of cannabis increase your risk of developing schizophrenia.
- A difficult childhood. If you were deprived, or abused, as a child this can increase your risk of developing a mental illness. Including schizophrenia.
There is research to suggest that may be an association between menopause and schizophrenia. This may be due to the hormonal changes during this stage of life for women.
You can find more information about:
- Does mental illness run in families? by clicking here.
- Drugs, alcohol and mental health by clicking here.
- Cannabis and mental health by clicking here.
Don’t Miss: How To Overcome Depression Without Medication
Tip : Monitor Medication
Once in treatment, careful monitoring can ensure that your loved one stays on track and gets the most out of medication.
Take side effects seriously. Many people with schizophrenia stop taking their medication because of side effects. Bring any distressing side effects to the attention of the doctor, who may be able to reduce the dose, switch to another antipsychotic, or add medication to counter the side effect.
Encourage your loved one to take medication regularly. Even with side effects under control, some people with schizophrenia refuse medication or have trouble remembering their daily dose. Medication reminder apps, weekly pillboxes, and calendars can help. Some medications are available as long-lasting weekly or monthly injections instead of daily pills.
Be careful to avoid drug interactions. Help your loved one avoid any dangerous drug interactions by giving the doctor a complete list of the drugs and supplements theyre taking. Mixing alcohol or illegal drugs with schizophrenia medication is harmful, so talk to the doctor if your relative has a substance abuse problem.
Track your family members progress. A mood-tracking app, journal, or diary is a good way to track changes in your family members behavior, outlook, and other symptoms in response to medication.
A Different View Of Schizophrenia
I am glad that they have found empirical evidence for what I have always believed that our illness is not without purpose. Perhaps this will give psychologists and psychiatrists a new perspective on Schizophrenia, and view it less as an abomination and more as a normal part of nature.
I know that my family has found my illness difficult to deal with. Episodes have caused disruption within our family unit and caused me great pain. I am certain my siblings and parents will always view my illness as a blight and problem. Maybe their six figure salaries, patents, Ivy league educations, creative and scientific genius were dependent on what they hated most about me. I am certain they will never thank me for my illness, but perhaps they should.
Recommended Reading: How To Spot An Eating Disorder In A Child
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
People diagnosed with schizophrenia may display a variety of symptoms. These symptoms will often come and go, and in some cases, the individual may learn how to deal with the symptoms, so they are not noticeable. There are three categories of symptoms: positive symptoms, negative symptoms and cognitive symptoms.Positive symptoms include:
The Turning Point: Adolescence
An interaction between something in your genes and something in your environment probably causes the disease. Researchers still have a lot to learn about it, but it’s likely that many things play a role. Some, like exposure to a virus or malnutrition , might have happened while you were still in your mother’s womb. For vulnerable individuals, cannabis use can increase the risk of developing psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.
No one knows exactly why it usually crops up in late adolescence, but there are many theories.
Your brain changes and develops a lot during puberty. These shifts might trigger the disease in people who are at risk for it.
Some scientists believe it has to do with development in an area of the brain called the frontal cortex. Others think it has to do with too many connections between nerve cells being eliminated as the brain matures.
Hormones also play a major role in puberty. One theory is that women get schizophrenia later than men because they go through puberty earlier and the hormone estrogen might somehow protect them. Know how to recognize the signs of schizophrenia in teens.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Eating Disorders
Changes In Behaviour And Thoughts
A person’s behaviour may become more disorganised and unpredictable.
Some people describe their thoughts as being controlled by someone else, that their thoughts are not their own, or that thoughts have been planted in their mind by someone else.
Another feeling is that thoughts are disappearing, as though someone is removing them from their mind.
Some people feel their body is being taken over and someone else is directing their movements and actions.
How Our Helpline Works
For those seeking addiction treatment for themselves or a loved one, the PsychGuides.com helpline is a private and convenient solution.
We are standing by 24/7 to discuss your treatment options. Our representatives work solely for AAC and will discuss whether an AAC facility may be an option for you.
Our helpline is offered at no cost to you and with no obligation to enter into treatment. Neither PsychGuides.com nor AAC receives any commission or other fee that is dependent upon which treatment provider a visitor may ultimately choose.
For more information on AACâs commitment to ethical marketing and treatment practices, or to learn more about how to select a treatment provider, visit our About AAC page.
If you wish to explore additional treatment options or connect with a specific rehab center, you can browse top-rated listings or visit SAMHSA.
Read Also: What To Say At A Ptsd Exam
Changed Feelings And Psychosis
Psychosis can lead to changes in emotions. How a person feels can change for no obvious reason. Examples may include: feeling strange and cut off from the worldmood swings, feeling unusually excited or depressedfeeling or showing less emotion feeling distanced or detached from one’s body or thoughts