Signs And Symptoms Of Asd And Ptsd
ASD and PTSD share common symptoms, and what differentiates them is the duration of the symptoms. Symptoms are of four kinds:
- Re-experiencing the trauma: This happens through flashbacks, vivid memories and nightmares. There may be intense emotional or physical reactions, such as heart palpitations, sweating or panic, when reminded of the event.
- Avoiding reminders of the event: The person deliberately avoids thoughts, feelings, activities, places and people that they associate with the event.
- Negative changes in mood and thoughts: The person feels low or numb, and no longer enjoys their favourite activities and hobbies. Its common to feel detached from reality, to have difficulty remembering things , and to feel guilty, angry or fearful.
- Increased anxiety and easily wound up: The person may feel on edge or jumpy, and find it difficult to relax, sleep or concentrate. They might also be irritable or prone to angry outbursts.
What Are The Differences Between Pts And Ptsd
Its easy to confuse post-traumatic stress and post-traumatic stress disorder . In addition to sharing similar names, theres considerable overlap in symptoms between the two conditions. Both PTS and PTSD are associated with feeling fearful and/or nervous, avoiding the activity or place associated with the traumatic event, and nightmares. However, there are significant differences in symptom intensity, duration, and treatment.
Preventing Ptsd By Treating Asd
According to a 2000 study with Bryant and Harvey, cognitive behavioral interventions during the acute aftermath of trauma exposure have yielded the most consistently positive results in terms of preventing subsequent posttraumatic psychopathology. These interventions focus on the development of personal coping strategies that target solving current problems and changing unhelpful patterns in cognitions , behaviors, and emotional regulation.
One of the biggest differences between ASD and PTSD is the greater emphasis on dissociative symptoms for ASD. Dissociation is defined as being out of consciousness either fully or partially. Dissociative symptoms include amnesia which is temporary, depersonalization , and derealization . An ASD diagnosis requires that a person experience three symptoms of dissociation , while the PTSD diagnosis does not include a dissociative symptom cluster.
Read Also: What’s The Phobia Of Throwing Up
The Relationship Between Ptsd And Asd
The symptoms of PTSD and ASD are generally very similar. Usually, ASD precedes PTSD . ASD is diagnosed within one month of the traumatic incident and cannot be diagnosed as ASD after that time. PTSD, however, can be diagnosed years later because symptoms may not develop immediately after a traumatic event. PTSD is often thought to be a more serious version of ASD because of this. One of the things that you need to know is that if you have ASD, it could lead to PTSD. In fact, ASD leads to PTSD in 80% of cases. Some of the symptoms that both disorders share include emotional numbness, restlessness, anxiety, uncharacteristic irritability, problems focusing or concentrating, flashbacks, and sleep disturbance.
While the concept of PTSD has been discussed as early as 1952, ASD was only introduced into the DSM-IV in 1994. Similarly to PTSD, a veteran can be diagnosed through an interview with a physician. Specifically, the Acute Stress Disorder Interview is the only structured clinical interview that has been validated for ASD. It appears to meet standard criteria for internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and construct validity. The interview was validated by comparing it with independent diagnostic decisions made by clinicians with experience in diagnosing both PTSD and ASD.
Acute Stress Disorder And Post

Acute stress disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder are specific manifestations of symptoms referable to an extremely traumatic event. The event by definition must involve exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence, as reported directly by the patient or by family members or friends. Patients suffer from repeated or extreme exposure to aversive details of the event. It is important to recognize that acute stress disorder or PTSD does not develop in all individuals exposed to a single traumatic event . Some individuals may instead develop other anxiety disorders, major depression, mania, or psychosis, and many may never develop diagnosable psychopathology.
The 12-month prevalence of PTSD in the United States is about 3%, with projected lifetime risk approaching 9%. About half of adults with PTSD have complete recovery within 3 months, but PTSD may persist for many months or years. Both cognitive-behavioral and psychodynamic psychology perspectives are useful in informing psychotherapeutic treatments.A13 Antidepressants also have demonstrated efficacy in PTSD. Ketamine can provide rapid relief in patients with chronic PTSD.A14 Other agents have been used as well, including prazosin and second-generation antipsychotics, such as risperidone and quetiapine.
J.F. Aili Low, … Christopher R. Thomas, in, 2012
Also Check: Apiphobia Definition
Treatment At Bridges To Recovery
At Bridges to Recovery, we specialize in diagnosing and treating psychiatric and emotional issues such as acute stress disorder and PTSD. We provide compassionate and effective care in a serene residential setting so clients can focus on their treatment and recovery without the worries of external pressures and stressors.
Distinguishing Between Asd And Ptsd
May 30, 2018
Studies show that about 20 percent of fire fighters and paramedics will experience post-traumatic stress disorder at some point in their career, compared to 3.5 percent of the general population. However, acute stress disorder is lesser known. You may not recognize the signs of this specific mental health disorder.
ASD can occur in the month following a trauma. The symptoms associated with ASD overlap with those of PTSD. A notable difference is that a PTSD diagnosis cannot be given until symptoms have lasted for at least one month.
Daily exposure to trauma can take a toll and cause cumulative stress. Sometimes, a particular incident pierces your emotional defenses. Both ASD and PTSD are very personal responses to these sorts of traumatic events. Following a potentially traumatic incident, an entire department might appear to be coping adequately on the surface, but some maybe could be experiencing ASD symptoms.
Read Also: Phobia Of Puke
Acute And Posttraumatic Stress Disorders In Children And Adolescents
, MD, Nemours/A.I. duPont Hospital for Children
Posttraumatic stress disorder is recurring, intrusive recollections of an overwhelming traumatic event recollections last > 1 month and begin within 6 months of the event. The pathophysiology… read more in adults.)
ASD and PTSD are trauma- and stressor-related disorders. They used to be considered anxiety disorders but are now considered distinct because many patients do not have anxiety but have other symptoms instead.
Because vulnerability and temperament are different, not all children who are exposed to a severe traumatic event develop a stress disorder. Traumatic events commonly associated with these disorders include assaults, sexual assaults, car accidents, dog attacks, and injuries . In young children, domestic violence is the most common cause of PTSD.
Children do not have to directly experience the traumatic event they may develop a stress disorder if they witness a traumatic event happening to others and posttraumatic stress disorder are reactions to traumatic events. The reactions involve intrusive thoughts or dreams, avoidance of reminders of the event… read more ) or learn that one occurred to a close family member.
Symptoms And Signs Of Asd And Ptsd
Symptoms of ASD and PTSD are similar and generally involve a combination of the following:
-
Intrusion symptoms: Recurrent, involuntary, and distressing memories or dreams of the traumatic event dissociative reactions and distress at internal or external cues that resemble some aspect of the trauma
-
Avoidance symptoms: Persistent avoidance of memories, feelings, or external reminders of the trauma
-
Negative effects on cognition and/or mood: Inability to remember important aspects of the traumatic event, distorted thinking about the causes and/or consequences of the trauma , a decrease in positive emotions and an increase in negative emotions , general lack of interest, social withdrawal, a subjective sense of feeling numb, and a foreshortened expectation of the future
-
Altered arousal and/or reactivity : Jitteriness, exaggerated startle response, difficulty relaxing, difficulty concentrating, disrupted sleep , and aggressive or reckless behavior
-
Dissociative symptoms: Feeling detached from one’s body as if in a dream and feeling that the world is unreal
Typically, children with ASD are in a daze and may seem dissociated from everyday surroundings.
Also Check: Prodromal Psychotic Symptoms
Can You Be Diagnosed With Ptsd And Anxiety Together
While yes that is a possibility since a veteran with a history of anxiety before service could have been exposed to a traumatic experience in active duty, we still have to consider several factors. A common issue with differentiating between mental health conditions is that many of them have very similar symptoms . That makes it so challenging to determine, especially in one session, which diagnosis a veteran may have. Add the fact that most of us do not want to go into a room and talk to a stranger about our most traumatic life events, and then the diagnosis can get even more challenging to make. This is why we see veterans diagnosed with one condition, then later be diagnosed with a different one, or an additional one, or two. There are also theories that some chronic trauma disorders such as PTSD cause a person to create coping skills that mimic other disorders such as Borderline Personality disorder or Bipolar disorder. If someone has been coping with PTSD for several years, or even decades, often times they have created coping mechanisms that hide their symptoms so well they are misdiagnosed with other disorders they may not actually have originally had but developed as a protective measure.
Main Differences Between Adjustment Disorder And Acute Stress Disorder
Don’t Miss: Feretrophobia Define
How Common Is Acute Stress Disorder
The prevalence of acute stress disorder varies according to the individual, context, and traumatic experience. According to the DSM-5, the prevalence of acute stress disorder is 20 to 50 percent among survivors of interpersonal traumatic events, such as assaults, rapes, or mass shootings. The prevalence is less than 20 percent among those who experienced traumatic events that do not involve interpersonal assaults, such as car accidents, mild traumatic brain injury, or burns.
Adjustment Disorder Vs Acute Stress Disorder
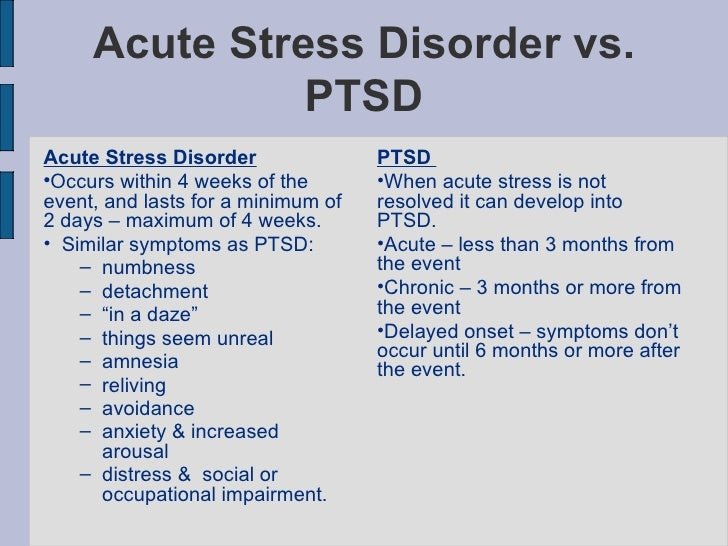
The difference between Adjustment Disorder and Acute Stress Disorder is that as an adjustment disorder people will begin to feel stress in whatever events or activities they do. In Acute Stress Disorder, people will feel lonely and will not be in the mood to speak with others. The symptoms of adjustment disorder are behavior and emotions. The symptoms of acute stress disorder are the depression that will occur due to our surroundings.
Adjustment Disorder is a type of stress that we should not ignore when the moment we sense it. We should seek professional and medical help in this case because if it exceeds more than six months then it will lead to chronic disorder which will be very difficult to cure. People call this an emotional disability as well.
Acute Stress Disorder is one of the stresses that will happen when you are not feeling or mood in the speak to others. It is not something worse when you are in the early stage because a light medication and treatment will help you to get rid of it. But when you avoid speaking it with others and try to run away from it then it will haunt you.
You May Like: Spasmenagaliaphobia
How Are Stress And Anxiety Related
Although stress and anxiety share many of the same emotional and physical symptoms, including uneasiness, tension, headaches, high blood pressure, and sleep loss, they have very different origins. Determining which one youre experiencing is critical to finding an effective treatment plan and feeling better.
Stress is caused mostly by external factors such as being fired or arguing with a family member. Anxiety, alternatively, is often caused by internal factors and can be classified in a variety of ways, including:
- Obsessive-Disorder
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Social Anxiety
Unlike stress, anxiety can persist long-term. If left untreated, acute stress disorderthe most immediate response to a traumatic eventcan quickly transform to more chronic anxiety known as PTSD.
Regardless of their differences, anxiety, and stress are prominent mental health concerns impacting millions. An estimated 40 million Americans are currently living with some type of anxiety disorder. In Colorado, nearly 18% of residents face challenges, including substance abuse, often brought forth by mental illness. Currently, anxiety disorders are viewed as the most common mental health illness. Anxiety, as it relates to stress and trauma, is highly treatable. Still, only 37% receive the treatment they need.
What Help Is Available
Although there are things you can do following a traumatic experience to help you cope, if youre experiencing some of the symptoms listed above, and are struggling to get back into your daily routine, its important to seek help from a mental health professional. The first step you can take is to contact your GP to discuss the best options for you. They might refer you to a clinical psychologist, who can offer you strategies and skills to help with processing the trauma. Your doctor may also suggest that you see a psychiatrist, who can prescribe medication to help ease your symptoms.
It can be difficult to talk about a traumatic experience even when youve decided to seek help. Ask a friend or family member to come along with you to your GP for support, or write down how you feel and how your life is being impacted. Remember that mental health professionals have a lot of experience of working with people who have experienced trauma and will understand if you might not be ready to talk about everything right away.
Check out the Blue Knot Foundation for more information about ASD and PTSD, and for suggestions for coping with or treating it.
Don’t Miss: What Does A Phobia Mean
Epidemiology And The Natural History Of Trauma Reactions
Epidemiological studies indicate that exposure to potentially traumatic events is common in the general population and that PTSD is one of the most prevalent anxiety disorders. For example, the National Comorbidity Survey , a large-scale nationally representative epidemiological study of psychiatric disorders in the United States, found the majority of respondents had experienced one or more potentially traumatic events, with men being more likely to be exposed than women . Not only was exposure to potentially traumatic events common in the NCS sample, but among those participants who were exposed to at least one potentially traumatic event, 56.3 percent of the men and 48.7 percent of the women experienced at least two potentially traumatic events and 16.8 percent of the men and 12.4 percent of the women reported experiencing four or more potentially traumatic events. The overall lifetime prevalence of PTSD in the NCS was 7.8 percent. Despite the higher rate of trauma exposure among men, lifetime PTSD was twice as common among women than men .
Physical Findings & Clinical Presentation
DSM-5 criteria are met when the following criteria are satisfied:
-
Exposure to actual or threatened serious injury, death, or sexual violation in one or more of the following ways:
- 1.
-
Witnessing a traumatic event as it occurred
- 3.
-
Learning that a traumatic event occurred to a family member or close friend
- 4.
-
Repeated or extreme exposure to the details of a traumatic event
-
Presence of nine or more of the following symptoms from any of the following five categories: intrusion, negative mood, dissociation, avoidance, and arousal:
- 1.
-
Recurrent, distressing, involuntary memories of the trauma
- 2.
-
Recurrent distressing dreams relating to the trauma
- 3.
-
Flashbacks to the event, in which the individual feels/acts as if the event is recurring
- 4.
-
Intense or prolonged psychological distress or physiological reaction in response to cues that are reminiscent of the trauma
- 5.
-
Continual inability to experience positive emotions
- 6.
-
Altered sense of reality
- 7.
-
Inability to recall components of the trauma
- 8.
-
Avoidance of memories, thoughts, or feelings associated with the event
- 9.
-
Avoidance of external reminders of the event
- 10.
-
Irritability and anger outbursts
- 12.
-
Exaggerated startle response
J.L. Rodriguez, E.A. Meadows, in, 2012
Also Check: Feretrophobia
Acute Stress Disorder Vs Ptsd
Traumatic events can significantly impact a persons psychological, emotional, and physical wellbeing, whether the trauma is experienced firsthand or witnessed. Trauma can also lead to mental health disorders, such as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Acute Stress Disorder .
PTSD and ASD share many symptoms, and both require early intervention and treatment for positive recovery outcomes. But there are key distinctions between them that result in different treatment methods. Heres an overview on how ASD and PTSD compare:
Symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder
ASD symptoms develop in the immediate aftermath of trauma and last anywhere from days to a month after the event. Symptoms of ASD include:
- Severe anxiety
- Withdrawal from social activities
- Avoidance of people, places, or experiences associated with the trauma
Another major symptom of ASD is dissociation and dissociative amnesia. Dissociation involves a sense of detaching from ones self from reality, while dissociative amnesia refers to difficulty remembering certain details about the traumatic event as a self-protection mechanism.
Symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Symptoms of PTSD develop later than symptoms of ASD. While ASD is often a precursor to PTSD, thats not always the case. PTSD symptoms can take months or years to develop, varying greatly in terms of severity. Symptoms of PTSD include:
Acute Stress Disorder vs. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
There are also differences in treatment: