Treatment And Support For Schizophrenia
The best place to start in getting a diagnosis is a GP. They can make an assessment and provide a referral to a psychiatrist for full diagnosis and treatment if needed.
Schizophrenia takes time to diagnose some people might receive a predicted diagnosis of schizophrenia quickly, but it can take six months or longer to be confirmed. A diagnosis may also change over time. For example, after new information or experiences are identified. This is normal.
Early intervention can be helpful. Although the process can be scary, it can be very useful to identify a risk of developing schizophrenia early to develop a care plan. This may include case management, support for families and carers, group programs, and minimising disruptions to school and work .
If someone develops schizophrenia, antipsychotic medications are usually a first line of treatment. Psychological therapies can also be beneficial, including cognitive behavioural therapy, psychodynamic therapy, and open dialogue . Community support programs are also available to help with social connection, physical health, accommodation, and work or school.
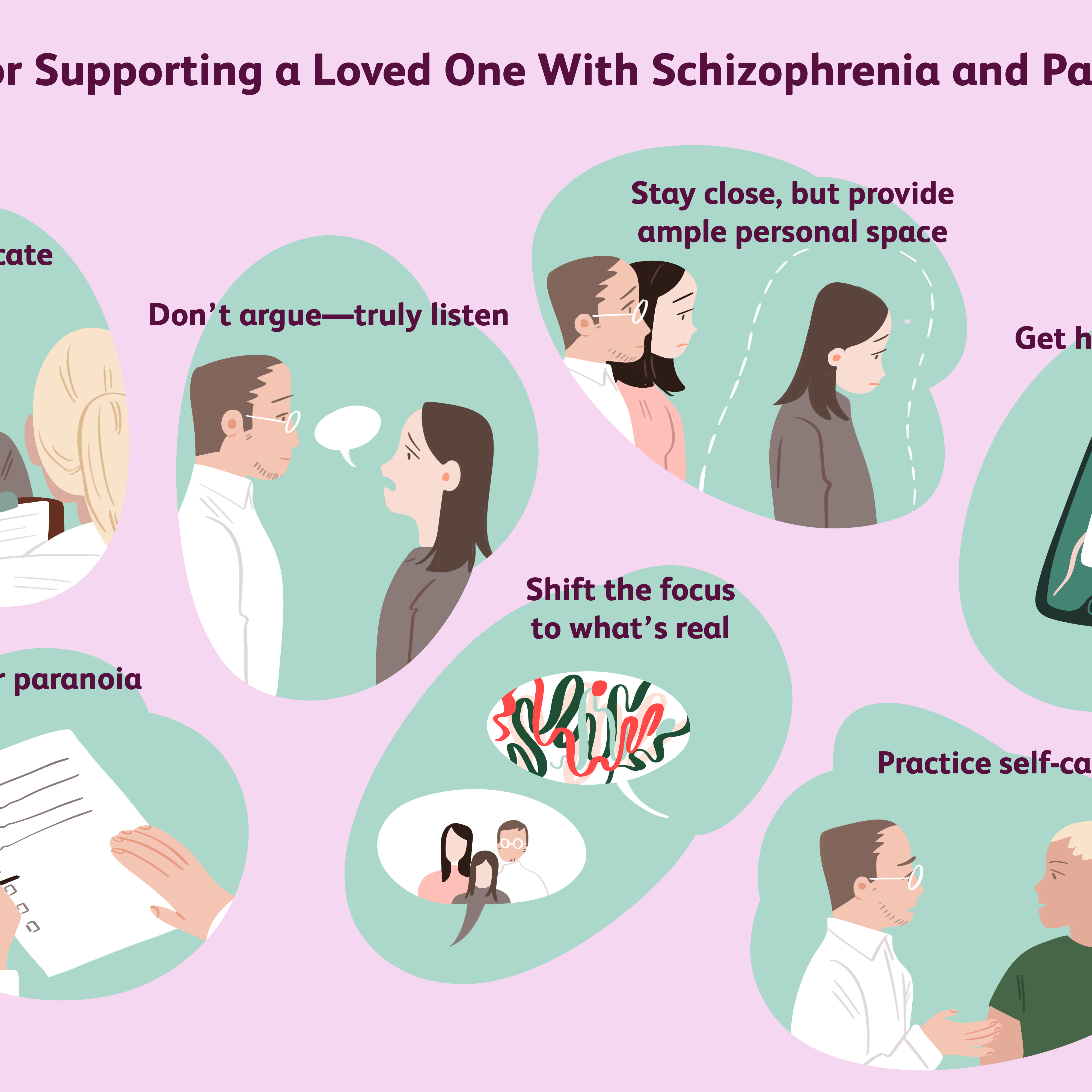
It is important that people experiencing symptoms of schizophrenia collaborate with their healthcare providers and are empowered to make their own treatment choices, wherever possible. Though not always easy, sticking with treatment and medication is important, especially for people experiencing paranoia.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
Symptoms may intensify in the run-up to an acute episode of psychosis in schizophrenia. The warning signs include:
- A worrying drop in grades or job performance
- New difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating
- Suspiciousness of or uneasiness with others
- Withdrawing socially, spending a lot more time alone than usual
- Unusual, overly intense new ideas, strange feelings, or having no feelings at all
- Difficulty telling reality from fantasy
- Confused speech or trouble communicating
While these changes might not be concerning by themselves, if you or a loved one are experiencing a number of these symptoms, you should contact a mental health professional. It can be difficult for those with schizophrenia to want to get help, especially if they are experiencing symptoms such as paranoia.
If you or your loved one is thinking of or talking about harming themselves, contact someone who can help right away. You can call the toll-free, 24-hour National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-237-8255.
If you require immediate emergency care, call 911 for emergency services or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Cognitive Symptoms & Thinking Problems
These symptoms reflect how well the personâs brain learns, stores, and uses information.
Someone with schizophrenia might have a hard time with their working memory. For example, they may not be able to keep track of different kinds of facts at the same time, like a phone number plus instructions.
Along with having trouble paying attention, it can be hard for them to organize their thoughts and make decisions.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: Is An Eating Disorder A Disease
Finding Mental Health Services
There are a few different options available for clinical treatment. Your choice will depend on cost, severity of your symptoms and convenience, but not all services are available everywhere. For people in rural and remote areas, treatment options can be reduced, involve long travel, or alternatively can be delivered through telehealth services. Ask your GP for advice about the best options available for you.
Research Shows Cellular Clean
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Schizophrenia Center sampled the smell neurons pictured here, from individuals with and without schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Through examining these cells, neuropsychiatrist Koko Ishizuka, in collaboration with Kyoto University, found a protein that is usually cleared out by the cellular waste management. Her work suggests that the link between these brain disorders and the cellular clean-up system deserves a closer look.
-
Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder. It often runs in families and can cause troubling symptoms.
-
It’s caused by a chemical imbalance and other changes in the brain.
-
Symptoms include hearing voices, feeling that people are out to get you, and having false beliefs that are not based in reality.
-
These symptoms can make it very hard to function in the world and take care of yourself.
-
Treatment includes antipsychotic medicines, support services, and a healthy lifestyle.
Don’t Miss: What Does A Ptsd Episode Feel Like
Schizophrenia: The 7 Keys To Self
Seek social support. Friends and family vital to helping you get the right treatment and keeping your symptoms under control. Regularly connecting with others face-to-face is also the most effective way to calm your nervous system and relieve stress. Stay involved with others by continuing your work or education. If thats not possible, consider volunteering, joining a schizophrenia support group, or taking a class or joining a club to spend time with people who have common interests. As well as keeping you socially connected, it can help you feel good about yourself.
Manage stress. High levels of stress are believed to trigger schizophrenic episodes by increasing the bodys production of the hormone cortisol. As well as staying socially connected, there are plenty of steps you can take to reduce your stress levels. Try adopting a regular relaxation practice such as yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
Get regular exercise. As well as all the emotional and physical benefits, exercise may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, improve your focus and energy, and help you feel calmer. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days, or if its easier, three 10-minute sessions. Try rhythmic exercise that engages both your arms and legs, such as walking, running, swimming, or dancing.
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often appear several years before somebody experiences their first acute schizophrenic episode.
These initial negative symptoms are often referred to as the prodromal period of schizophrenia.
Symptoms during the prodromal period usually appear gradually and slowly get worse.
They include the person becoming more socially withdrawn and increasingly not caring about their appearance and personal hygiene.
It can be difficult to tell whether the symptoms are part of the development of schizophrenia or caused by something else.
Negative symptoms experienced by people living with schizophrenia include:
- losing interest and motivation in life and activities, including relationships and sex
- lack of concentration, not wanting to leave the house, and changes in sleeping patterns
- being less likely to initiate conversations and feeling uncomfortable with people, or feeling there’s nothing to say
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often lead to relationship problems with friends and family as they can sometimes be mistaken for deliberate laziness or rudeness.
Read Also: Do You Think A Depressed Person Could Make This
Moving Into Adulthood: A Turning Point
Schizophrenia is typically diagnosed after age 18, most often in a persons 20s or early 30s.
It may be fairly well-controlled early in life, but moving from home to college and encountering new rules, or no rules exposes vulnerable young people to things theyre not prepared to deal with, says Dr. Bowers.
Living with a college roommate can prove difficult. It may seem easier to avoid talking or eating with others. You tend to isolate yourself and seem preoccupied with your own world, she says.
Increased exposure to alcohol or drug use is also a trigger.
Among 50 college students who smoke pot, a few may get a drug-induced psychosis that clears in weeks, says Dr. Bowers. But one may go on to develop a serious mental health disorder.
Exposure to disturbing news events or potentially false information on the internet and social media can provoke extreme reactions in the vulnerable.
They misperceive whats happening in the environment and develop delusions, she says. They may not make sense or become too aggressive.
Its easy to become so distracted by thoughts that schoolwork and jobs get neglected.
If someone constantly plays video games or focuses only on personal interests, and offers an irrational explanation for avoiding studies or work, thats a warning sign, says Dr. Bowers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality. Although schizophrenia is not as common as other mental disorders, the symptoms can be very disabling.
Schizophrenia is a severe and debilitating brain and behavior disorder affecting how one thinks, feels and acts. People with schizophrenia can have trouble distinguishing reality from fantasy, expressing and managing normal emotions and making decisions. Thought processes may also be disorganized and the motivation to engage in lifes activities may be blunted. Those with the condition may hear imaginary voices and believe others are reading their minds, controlling their thoughts or plotting to harm them.
While schizophrenia is a chronic disorder, it can be treated with medication, psychological and social treatments, substantially improving the lives of people with the condition.
A moving presentation by Dr. Kafui Dzirasa on Schizophrenia
View Webinar on Identifying Risk Factors and Protective Pathways for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia affects men and women equally. It occurs at similar rates in all ethnic groups around the world. Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30.
Learn more about childhood-onset schizophrenia from this expert researcher:
Find answers to more questions about Schizophrenia in our Ask the Expert section.
You May Like: What Is The Definition Of Ptsd
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Stop Happening
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function involving thinking, behavior, and perception. You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. A doctor will call this anhedonia.
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. Doctors call this alogia.
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. When they talk, their voice can sound flat, like they have no emotions. They may not smile normally or show usual facial emotions in response to conversations or things happening around them. A doctor might call this affective flattening.
- Withdrawal. This might include no longer making plans with friends or becoming a hermit. Talking to the person can feel like pulling teeth: If you want an answer, you have to really work to pry it out of them. Doctors call this apathy.
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. They may stop bathing or taking care of themselves.
- No follow-through. People with schizophrenia have trouble staying on schedule or finishing what they start. Sometimes they can’t get started at all. A doctor might call this avolition.
Depression has some of the same symptoms, too. They can be hard to spot, especially in teens, because even healthy teens can have big emotional swings between highs and lows.
Environment: Triggers And Influences
Research is continuing to reveal what influences a persons chances of developing schizophrenia. Some of those factors are:
- your biological mothers health during pregnancy or complications with your birth
- substance misuse
- difficult social circumstances and stressful life events
- trauma during childhood, such as abuse, neglect, parental death and bullying.
However, many people who experience these factors don’t develop schizophrenia. Were understanding more about the causes of schizophrenia all the time, but theres some way to go. What we do know is that there is no single cause.
Recommended Reading: Why Do You Get Panic Attacks
What Is Schizophrenia Or Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a challenging brain disorder that often makes it difficult to distinguish between what is real and unreal, to think clearly, manage emotions, relate to others, and function normally. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, and sees the world.
The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia, or schizophrenia with paranoia as its often called. People with paranoid schizophrenia have an altered perception of reality. They may see or hear things that dont exist, speak in confusing ways, believe that others are trying to harm them, or feel like theyre being constantly watched. This can cause relationship problems, disrupt normal daily activities like bathing, eating, or running errands, and lead to alcohol and drug abuse in an attempt to self-medicate.
Many people with schizophrenia withdraw from the outside world, act out in confusion and fear, and are at an increased risk of attempting suicide, especially during psychotic episodes, periods of depression, and in the first six months after starting treatment.
Take any suicidal thoughts or talk very seriously
If you or someone you care about is suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-TALK, visit IASP or Suicide.org to find a helpline in your country, or read Suicide Prevention.
Common Early Signs Of Schizophrenia

1. Associative problems
Associative problems are the most common signs of schizophrenia. In associate problems, people face difficulty in understanding the cause and effects of relationships.
2. Changes in Behavior and Personality
People who experience schizophrenia show different types of behavioral and personality changes in the early stages. These changes basically occur in the first psychotic event.
3. Drugs or Alcohol Abuse
People experiencing schizophrenia at early stages are likely to be involved in drug or alcohol abuse. They get involved in such intakes because it helps in easing their anxiety or other symptoms.
4. Disorganized thinking
Disorganized thinking is the other early common sign of schizophrenia. People experiencing schizophrenia experience difficulty in solving problems or comprehending information.
5. Disorganized speech
The most common early sign of schizophrenia is troubling speech. The person might get confused while having a conversation. If your teenager is not able to put words in the proper sentence or not able to write a proper essay, you must start looking for the other signs as well.
6. Expressionless or flat stare
You are likely to find that people experiencing schizophrenia at an early stage always have a flat or blank expression on their face always.
7. Hallucination and delusions
8. Inappropriate Social Behavior
9. Late or delayed development
10. Mood swings
11. Struggling with school
12. Suspiciousness
13. Slow movements
Takeaway
Read Also: What Is A Depression On A Topographic Map
Difficulty With Abstract Thinking
Another classic sign of schizophrenia is the struggle to form generalizations or think beyond a solid idea or concept.
People with the condition may have a hard time understanding things that arent physical or real. They may also have difficulty understanding a proverb, simile, or metaphor because they can only interpret things literally.
They tend to get distracted by whats real and literal, and may be unable to understand what a story means or the comparison thats being made.
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Each person may feel symptoms differently. These are the most common symptoms:
-
False beliefs not based on reality
-
Seeing, hearing, smelling, or feeling things that are not real
-
Disorganized speech and behavior
-
Feeling like someone or something is out to get them
-
Withdrawal from others
-
Inflated self worth
These symptoms can make it very hard to function in the world and take care of yourself. People with this illness are usually not violent.
The symptoms of schizophrenia may look like other problems or mental health conditions. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: What Age Is Bipolar Disorder Diagnosed
Functioning In Social And Professional Situations
When social and work functioning is impaired, it may be helpful to consult with a doctor. Because the symptoms tend to develop over time, it can be hard to realize that someone is experiencing difficulty in these areas. Noticing that a pattern has developed can be a signal to consult with a professional.
Early Warning Signs And Symptoms
Usually, a person with schizophrenia has gradual changes in their thoughts and perceptions. Families are often the first to see early signs of psychosis and schizophrenia in a loved one.
Before the first episode of psychosis, you go through what is known as a premorbid period. This is the 6 months before the first symptoms of psychosis. During this period, you might experience gradual changes.
Although sleep disturbances are not included in the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia, people with the condition consistently report them.
Early warning signs include:
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Anxiety Without Panic Attacks
When Schizophrenia Appears
Experts offer guidance for newly diagnosed patients and their families
People with schizophrenia can have a hard time telling whatâs real and whatâs not. They may see things that arenât there or hold firm beliefs that fly in the face of fact. Understanding schizophreniaâs nature can help patients and their loved ones regain a sense of control.
What Causes These Phases
Its unclear why individuals develop schizophrenia. Likewise, its unclear exactly how or why a person moves through the stages at the pace they do.
Researchers believe a combination of factors set off chemical and structural changes in the brain. Ultimately, these changes lead to schizophrenia. Those same factors may influence when or how quickly a person progresses from one phase to another.
Researchers believe these factors may contribute to developing schizophrenia:
- Genetics. If you have a family history of the illness, youre more likely to develop it. However, having a family history doesnt mean you certainly will have the illness.
- Hormonal changes. Researchers believe that hormones and physical changes in the body may be a factor. Symptoms of the illness often begin in young adulthood, during a time of major change. On average, men show first signs in their late teens and early 20s. Women develop the illness later. For them, symptoms typically first appear in their mid 20s to early 30s.
- Biological. Neurotransmitters relay signals between cells in the brain, and chemical changes may damage or impair them. This could lead to the illness.
- Structure. Changes to the shape or structure of the brain could interfere with communication between neurotransmitters and cells, too.
- Environmental. Researchers believe exposure to some viruses at an early age could lead to schizophrenia. Likewise, lifestyle choices may impact risk. These choices can include narcotic use or misuse.
Also Check: How Do Eating Disorders Affect The Brain