What Is The Treatment For Mania Hypomania And Depression
You can check what treatment and care is recommended for bipolar disorders on the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence website.
NICE produce guidelines for how health professionals should treat certain conditions. You can download these from their website at:
The NHS doesnt have to follow these recommendations. But they should have a good reason for not following them.
What medications are recommended?
Mood stabilisers are usually used to manage mania, hypomania and depressive symptoms.
The mood stabilisers we talk about in this factsheet are:
- Lithium
- Certain benzodiazepine medication
Mania and hypomaniaYou should be offered a mood stabiliser to help manage your mania or hypomania. Your doctor may refer to your medication as antimanic medication.
If you are taking antidepressants your doctor may advise you to withdraw from taking them.
You will usually be offered an antipsychotic first. The common antipsychotics used for the treatment of bipolar disorder are:
- Haloperidol
- Quetiapine
- Risperidone
If the first antipsychotic you are given doesnt work, then you should be offered a different antipsychotic medication from the list above.
If a different antipsychotic doesnt work, then you may be offered lithium to take alongside it. If the lithium doesnt work you may be offered sodium valproate to take with an antipsychotic. Sodium valproate is an anticonvulsive medication.
Sodium Valproate shouldnt be given to girls or young women who might want to get pregnant.
How Does Pregnancy Affect Bipolar Disorder
Women who have bipolar disorder are at risk for experiencing an episode after giving birth, especially a depressive episode. Women who experience a depressive or manic episode after giving birth are also more likely to have episodes after other pregnancies. Women with bipolar disorder are at high risk of developing , which is a medical emergency.
Talk to your doctor or nurse if you are trying to get pregnant or are pregnant. Some medicines are not safe to take during pregnancy.
Dont Miss: What Is The Fear Of Spoons Called
Coping With Bipolar Disorder
Living with bipolar disorder can be challenging, but there are ways to help make it easier for yourself, a friend, or a loved one.
- Get treatment and stick with itrecovery takes time and its not easy. But treatment is the best way to start feeling better.
- Keep medical and therapy appointments, and talk with the provider about treatment options.
- Take all medicines as directed.
- Structure activities: keep a routine for eating and sleeping, and make sure to get enough sleep and exercise.
- Learn to recognize your mood swings.
- Ask for help when trying to stick with your treatment.
- Be patient improvement takes time. Social support helps.
Remember, bipolar disorder is a lifelong illness, but long-term, ongoing treatment can help control symptoms and enable you to live a healthy life.
Don’t Miss: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Bipolar Disorder And Suicide
The depressive phase of bipolar disorder is often very severe, and suicide is a major risk factor. In fact, people suffering from bipolar disorder are more likely to attempt suicide than those suffering from regular depression. Furthermore, their suicide attempts tend to be more lethal.
The risk of suicide is even higher in people with bipolar disorder who have frequent depressive episodes, mixed episodes, a history of alcohol or drug abuse, a family history of suicide, or an early onset of the disease.
Suicide warning signs include:
- Talking about death, self-harm, or suicide.
- Feeling hopeless or helpless.
What Does Mania Feel Like
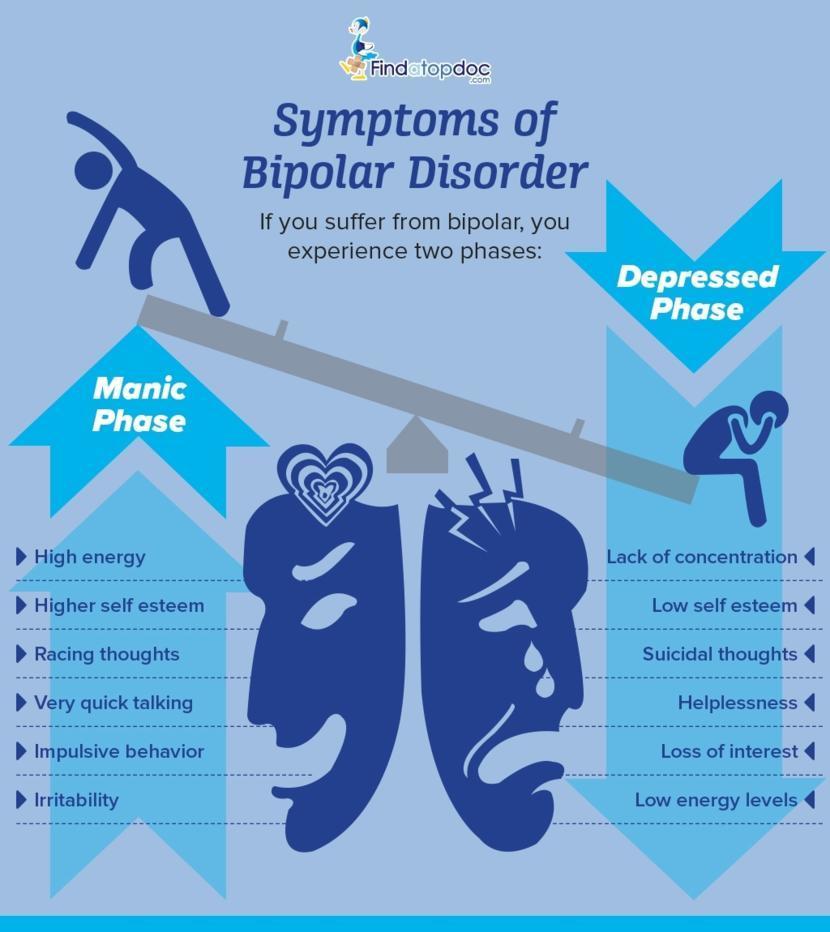
Mania symptoms exist in an equally wide range of forms for both men and women. It is important to understand that mania by no means translates to extreme behavior or physical aggression. It may, but symptoms are usually more internalized. Manic thinking and feeling sometimes veer on delusion, as in grandiose ideas of the self as having some special purpose to fulfill. During the stage of mania, the observation of the self ego struggles with behaviors, judgments, emotions, and actions in real time as they are manifesting and self-monitoring. Hallucinations also occur in extreme cases, wherein the individual is unable to distinguish the real from the unreal.
Manic states are often marked by sleeplessness the person does not have insomnia, but rather is so obsessed that they believe they require less sleep or choose to remain awake as long as possible. More commonly, however, mania feels like a stage of prolonged excitement. This may result in a negative or positive response the person may be agitated and anxious for hours or days, for no cause they can name, or they may be euphoric for the same extended period. Mania is essentially a heightened state of perception, feeling, and behavior, and the bipolar person cannot contain the mania. Manic states overwhelm the personality and cognitive processes, regardless of feeling abundantly happy or sad.
Also Check: Feretrephobia
Patterns Of Depression And Mania
If you have bipolar disorder, you may have episodes of depression more regularly than episodes of mania, or vice versa.
Between episodes of depression and mania, you may sometimes have periods where you have a “normal” mood.
The patterns are not always the same and some people may experience:
- rapid cycling where a person with bipolar disorder repeatedly swings from a high to a low phase quickly without having a “normal” period in between
- mixed state where a person with bipolar disorder experiences symptoms of depression and mania together for example, overactivity with a depressed mood
If your mood swings last a long time but are not severe enough to be classed as bipolar disorder, you may be diagnosed with a mild form of bipolar disorder called cyclothymia.
Brain Structure And Function
Researchers are learning that the brain structure and function of people with bipolar disorder may be different from the brain structure and function of people who do not have bipolar disorder or other psychiatric disorders. Learning about the nature of these brain changes helps doctors better understand bipolar disorder and may in the future help predict which types of treatment will work best for a person with bipolar disorder. At this time, diagnosis is based on symptoms rather than brain imaging or other diagnostic tests.
Also Check: What Is The Phobia For Bees
Treating A Dual Diagnosis
Dual diagnosis treatment is conducted as a meaningful collaboration among members of the treatment teams for each illness, and Destination Hopes Dual Diagnosis program draws on the most up-to-date research and proven best practices in treating patients with bi-polar and other mood disorders who also have a drug or alcohol addiction.
Integrated Group Therapy, which addresses the addiction and the bi-polar disorder simultaneously in a group setting, is a promising new therapy that was developed specifically for a dual diagnosis of addiction and bipolar disorder in recent years by researchers at Harvard Medical School.
We combine Integrated Group Therapy with individual therapy and family counseling and a number of other research-based therapies to address the broad range of issues unique to those with a dual diagnosis.
Bipolar Disorder And Sexual Health
Bipolar disorder is a mood disorder. People who have bipolar disorder experience high levels of both euphoria and depression. Their moods can go from one extreme to the other.
Life events, medication, and drug misuse can trigger mania and depression. Both moods can last from a few days to a few months.
Bipolar disorder can also affect your sexuality and sexual activity.
During a manic episode, you may experience hypersexuality, or an increase in sexual activity. It may place you at an increased risk for actions that may have negative effects, such as contracting a sexually transmitted infection .
During a depressive episode, you may lose interest in sex. These sexual issues can create problems in relationships and may lower your self-esteem.
During a manic episode, your sex drive and sexual impulses can often lead to sexual behavior thats atypical for you when you arent experiencing episodes of mania.
Examples of hypersexuality during a manic episode can include:
- greatly increased sexual activity without a feeling of sexual satisfaction
- sex with multiple partners, including strangers
Hypersexuality can be a challenging symptom if you have bipolar disorder.
More studies that look at prevalence of this condition are needed.
A 2016 study published in Psychiatry Journal compared the sexual behavior of two groups:
- people with bipolar disorder who were treated as outpatients in private practice
- people treated as outpatients who didnt have affective disorder or schizophrenia
Read Also: Schizophrenia Cured By Diet
Can Lifestyle Habits Increase The Risk Of Bipolar Disorder
Lack of sleep increases the risk of having an episode of mania in someone with bipolar disorder. In addition, antidepressants, particularly when taken as the only medication, may also trigger a switch into a manic state.
Excessive use of alcohol or drugs can also trigger bipolar symptoms. Research has shown that about 50% of bipolar sufferers have a substance abuse or alcohol problem. Sufferers often use alcohol or drugs in an effort to reduce unpleasant feelings during low mood periods, or as part of the recklessness and impulsivity associated with manic highs.
Understanding Manic Episodes Of Bipolar Disorder
The way bipolar disorder symptoms manifest, the duration of symptoms, and the overall effect on a person may vary greatly from person to person. The manic symptoms of bipolar disorder may be especially difficult for some people to understand as people may react differently during these episodes. For example, when manic episodes occur, one person may experience mania or hypomania episodes with feelings of frustration or irritability while another may exhibit a decreased need for sleep, accelerated thinking, or hyperactivity.
When manic symptoms of bipolar disorder emerge, its not uncommon for one to experience feelings of creativity, heightened energy, or euphoria. Some people may feel they are destined for greatness or are invincible.
While the overall feeling of increased energy and euphoria may feel good at first, manic episodes can cause a spiral in emotions. For instance, during this phase, some people engage in dangerous or inappropriate behavior. They may become sexually promiscuous, gamble, or go on spending sprees. Some people are easily angered, may start fights or lash out at others, or blame those who criticize their behavior.
Some common symptoms of manic episodes include:
- Sleeping less, but feeling extremely energetic
- Racing thoughts that jump from one subject to another quickly
- Talking rapidly
- Difficulty concentrating, easily distracted
Recommended Reading: What Does The Suffix Phobia Mean
What Exactly Causes Bipolar Disorder And Who Does It Affect The Most
Usually, bipolar disorder is passed down from your family. If your parents or blood relatives ever suffered from bipolar disorder or depression, it raises the risk of the condition in you.
However, you could also develop the disorder due to childhood trauma, or because of losing someone, or other mental health crisis. In most cases, genetics is the reason for bipolar disorder, and people are born with it.
A highly imbalanced chemical function in the brain that controls certain brain functions acts differently, which causes Bipolar disorder.
Studies suggest that men and women are almost equally affected by Bipolar disorder, so is the case of race.
The highest point of bipolar disorder is the age of 20-40, whereas the condition typically starts affecting people aged 15-19.
Also, leaving the disorder untreated could create more and more mental health issues and damage in your daily life as you grow old.
Other Treatments For Bipolar Disorder
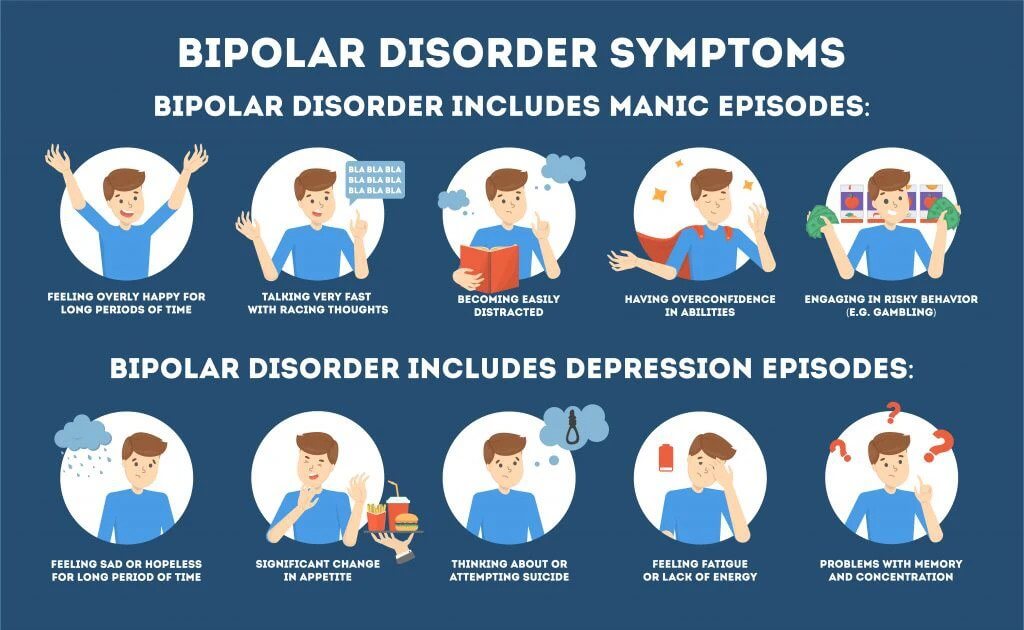
There are other potential treatments for bipolar disorder if medication and psychotherapeutic interventions are not successful, or if the condition is extreme.
Electroconvulsive therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy is a treatment that sends electrical current through the brain to trigger an epileptic seizure. The electricity is administered under general anesthetic and with the use of muscle relaxants, so the body does not convulse.
ECT is only advised for rapid, short-term relief of severe depression, mania or psychosis, where other interventions have failed and/or when the condition is considered life-threatening.
ECT causes memory loss, which is usually short-term but can be very disorienting.
New treatments
There is ongoing research into new mood-stabilizing drugs. Other, non-medication therapies, are also being investigated, including vagal nerve stimulation, transcranial magnetic stimulation and light therapy.
Also Check: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Manic Symptoms In Children
Symptoms of a childs manic episode caused by bipolar disorder can include:
- acting very silly and feeling overly happy
- talking fast and rapidly changing subjects
- having trouble focusing or concentrating
- doing risky things or experimenting with risky behaviors
- having a very short temper that leads quickly to outbursts of anger
- having trouble sleeping and not feeling tired after sleep loss
What Risks And Complications Can Bipolar Disorder Cause
There can be complications and risks for people who live with bipolar disorder. But these risks can be lessened with the right support and treatment.
What about suicide and self-harm?
You might have an illness where you experience psychosis, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Your risk of suicide is estimated to be between 5% and 6% higher than the general population.
You are more likely to try to take your own life if you have a history of attempted suicide and depression. It is important that you get the right treatment for your symptoms of depression and have an up to date crisis plan.
There is also research that suggests you are 30% – 40% more likely to self-harm if you live with bipolar disorder.
What about financial risk?
If you have mania or hypomania you may struggle to manage your finances. You may spend lots of money without thinking about the effect that it may have on your life.
You could make a Lasting Power of Attorney. This is a legal process. This means that you pick someone that you trust to manage your finances if you lack mental capacity to manage them by yourself.
You can work with your carer and mental health team. You can form an action plan. This can say what they can do if you have a period of mania or hypomania and you start to make poor financial decisions.
What about physical health risk?
What about alcohol and drugs risk?
If you want advice or help with alcohol or drug use contact your GP.
What about driving risk?
Also Check: What Is The Phobia Of Throwing Up
What Are The Signs And Symptoms
A person with bipolar disorder will go through episodes of mania and at other times experience episodes of depression . These aren’t the normal periods of happiness and sadness that everyone experiences from time to time. Instead, the episodes are intense or severe mood swings, like a pendulum that keeps arcing higher and higher.
Symptoms of mania include:
- anger, worry, and anxiety
- thoughts of death or suicide
In adults, episodes of mania or depression usually last for weeks or months, although they can be shorter in length. In children and adolescents, though, these episodes can be much shorter, and a kid or teen can even go back and forth between mania and depression throughout the day.
Episodes of mania or depression may happen irregularly and follow an unpredictable pattern or they may be linked, with a manic episode always following a period of depression, or vice versa. Sometimes episodes have a seasonal pattern. Mania in the spring, for example, may be followed by depression in the winter.
Between episodes, someone with bipolar disorder usually returns to normal functioning. For some people, though, there is little or no “break period” between their cycles. These mood swing cycles can change slowly or rapidly, with rapid cycling between mania and depression being much more common in women, children, and adolescents.
P
Bipolar Disorder And Relationships
When it comes to managing a relationship while you live with bipolar disorder, honesty is the best policy. Bipolar disorder can have an impact on any relationship in your life, perhaps especially on a romantic relationship. So, its important to be open about your condition.
Theres no right or wrong time to tell someone you have bipolar disorder. Be open and honest as soon as youre ready. Consider sharing these facts to help your partner better understand the condition:
- when you were diagnosed
- what to expect during your depressive phases
- what to expect during your manic phases
- how you typically treat your moods
- how they can be helpful to you
One of the best ways to support and make a relationship successful is to stick with your treatment. Treatment helps you reduce symptoms and scale back the severity of your changes in mood. With these aspects of the disorder under control, you can focus more on your relationship.
Read Also: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Is Bipolar Disorder Treatment Different For Men And Women
In truth, the best bipolar treatment is different for each individual. Ideally, a treatment plan takes into account the persons history, symptoms, triggers, home and daily environment, available support, and personal goals and challenges. Those variables may be unique to each client.
Considering that there tend to be recognizable patterns of bipolar episodes that differ in men and women, this may inform the particulars of their clinical supervision. For example, because men tend to experience more frequent and severe episodes of mania, clinicians may place more emphasis on preparing male clients for the challenges related to mania. But, of course, this wouldnt make the depressive episodes any less serious. In fact, because men tend to be less likely to seek treatment, it is especially important that close attention is also paid to the lows that typically follow the highs.
On the other hand, women may experience more frequent depressive episodes and more rapid cycling of mania and depression. So, psychiatrists and therapists will aim to prepare female clients to cope with these personal challenges. They may also put in place treatment strategies to weather seasonal changes, as well as hormonal and phase-of-life changes that can affect bipolar women more intensely than men.
Who Experiences Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder usually begins in older teens and young adults, with at least half of all cases appearing before age 25. Children and adolescents, however, can develop this disease in more severe forms and often in combination with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder . Some studies have indicated that bipolar depression is genetically inherited, occurring more commonly within families.
While bipolar disorder occurs equally in women and men, women are more likely to meet criteria for bipolar II disorder. Women with bipolar disorder may switch moods more quickly this is called “rapid cycling.” Varying levels of sex hormones and activity of the thyroid gland in the neck, together with the tendency to be prescribed antidepressants, may contribute to the more rapid cycling seen in women. Women may also experience more periods of depression than men.
An estimated 60 percent of all people with bipolar disorder have drug or alcohol dependence. It has also been shown to occur frequently in people with seasonal depression and certain anxiety disorders, like post-traumatic stress disorder .
Recommended Reading: Psychotic Disorder Definition Psychology