What Are The Similarities
OCD and schizophrenia share many similarities as well. The most notable is that both disorders involve obsessions and compulsions.
People with OCD often recognize that their obsessions and compulsions are irrational, but they feel powerless to stop them. Schizophrenia sufferers also experience intrusive thoughts, images, or voices . These hallucinations can be very distressing and may cause the individual to act out to make them stop. Like OCD sufferers, people with schizophrenia often recognize that their hallucinations are not real, but they feel powerless to stop them.
Other similarities between OCD and schizophrenia include:
- Both disorders can be debilitating and significantly interfere with an individuals ability to function in everyday life.
- Both disorders can cause social isolation and withdrawal.
- Both disorders can be accompanied by depression, anxiety, and/or substance abuse.
The Specifics Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental illness that causes sufferers to misinterpret reality, affecting their ability to function in daily life. This misinterpretation causes problems with cognition, impulsive behaviors, and dysregulated emotions.
The symptoms of schizophrenia include the following:
Hallucinations: Sufferers may see things that are not there, smell things that arent there, or hear voices that dont exist. Hallucinations can affect any of the senses, but auditory hallucinations are the most common.
Delusions: Sufferers may experience paranoia brought on by delusional thinking. For example, someone with schizophrenia may assumed theyre being followed, harassed, spied on, or that something bad is about to occur. For example, someone with schizophrenia may see a fellow passenger smile at them on the subway and assume this means that person is in love with them or they may see a fellow passenger frown at them and take it as a sign that person is going to harm them in some way.
Compromised motor behavior: Sufferers may exhibit abnormal behavior, including acting like a child, unexplained agitation, a refusal to follow instructions, odd posture, extreme movement or restlessness, or unresponsiveness.
Symptoms can ebb and flow and psychotic episodes may come in phrases or appear only once or twice. At illness onset, symptoms are typically severe and sudden though sufferers may still understand distinct parts of reality.
The Types of Schizophrenia
Phenotypes Of Ocd Schizophrenia More Common Than Currently Acknowledged
Of the 16,231 individuals who developed schizophrenia, the researchers found that 447 had a prior OCD diagnosis. In addition, of the 30,556 people who developed a schizophrenia spectrum disorder defined as having one or more of the symptoms associated with schizophrenia 700 had a prior OCD diagnosis.
According to the researchers, their findings suggest that a previous diagnosis of OCD may be linked to an increased risk of developing schizophrenia late in life. Furthermore, the team found there was even an increased risk of schizophrenia among individuals whose parents were diagnosed with OCD.
These findings remained even after controlling for other factors that may influence schizophrenia risk, such as psychiatric history and family history of psychiatric disorders.
But despite the suggestion that OCD shares many etiological factors with schizophrenia and schizophrenia spectrum disorders, the team says this does not necessarily mean the conditions should be combined as one global diagnosis. They add:
However, given these findings and the fact that OCD and schizophrenia co-occur with one another at a higher rate than would be expected in the general population, the phenotypes of these disorders are potentially more similar than currently acknowledged.
Further research is needed to disentangle which genetic and environmental risk factors are truly common to OCD and schizophrenia or schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
Recommended Reading: How Many Mg Of Cbd For Anxiety
How Do You Stop An Ocd Loop
Tips for addressing ruminating thoughts Distract yourself. When you realize youre starting to ruminate, finding a distraction can break your thought cycle. Plan to take action. Take action. Question your thoughts. Readjust your lifes goals. Work on enhancing your self-esteem. Try meditation. Understand your triggers.
Clinical Presentation And Explanatory Concepts
Several heterogeneous subgroups of comorbid patients have been suggested depending on the diverse clinical course and phenotypic presentation. In order to unravel the specific interplay of genetic, psychosocial and pharmacological factors current research tries to focus on homogeneous subgroups. Subdivisions into such subgroups can for example be achieved according to the time point of first manifestation of comorbid OCS and the clinical course.
Recommended Reading: Is Bipolar More Common In Males Or Females
What Should You Not Say To Someone With Ocd
What Not to Say to Someone With Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Dont worry, Im kind of OCD sometimes, too. You dont look like you have OCD. Want to come over and clean my house? Youre being irrational. Why cant you just stop? Its all in your head. Its just a quirk/tic. It isnt serious. Just relax..
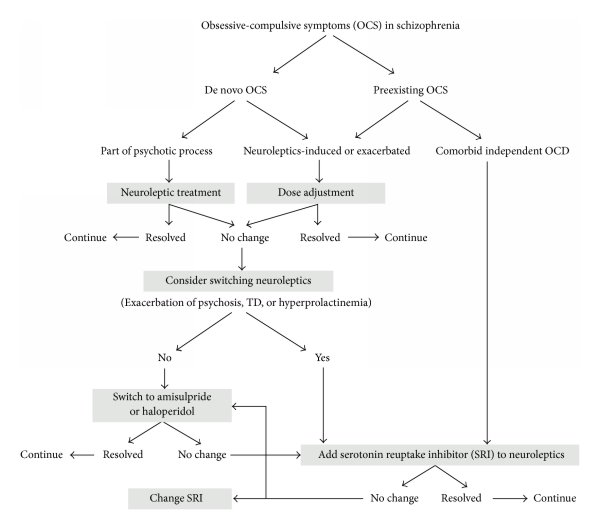
Management Of Obsessivecompulsive Symptoms/obsessivecompulsive Disorder In Schizophrenia
Although OCD is a common comorbidity in schizophrenia, there is limited literature on its treatment. There is some evidence that monotherapy with SGAs such as olanzapine and ziprasidone may help in alleviation of both psychotic and OCS in preexisting OCS in schizophrenia. Antipsychotics such as amisulpride and aripiprazole which have negligible serotonergic properties also appear to be somewhat useful in treating OCS in schizophrenia.
Because of the clinical similarity of OCS in schizophrenia and in primary OCD, attempts have been made to examine the efficacy of SSRIs and clomipramine. The APA guidelines recommend the use of SSRIs in combination with antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia with OCS/OCD. SSRIs seem to be beneficial, especially escitalopram at 20 mg/day, but not in all cases. Addition of fluvoxamine and clomipramine has been associated with worsening of psychosis. When adding an SSRI or clomipramine to an antipsychotic regimen, pharmacokinetic interactions, particularly between clozapine and certain SSRIs, need to be kept in mind to avoid side effects such as seizures and sudden elevation in clozapine levels.
Treatment of SGA-induced OCS/OCD involves reduction of antipsychotic dose , change to another antipsychotic with minimal influence on serotonergic systems such as aripiprazole, amisulpride, or haloperidol, addition of aripiprazole, and addition of SSRI and CBT.
Don’t Miss: Is Caffeine A Stimulant Or Depressant
Comorbidity: Schizophrenia With Obsessive
Alexandra Bottas, MDPsychiatric Times
The co-occurrence of obsessive-compulsive symptoms and psychotic illness has been a challenge for clinicians and investigators for more than a century. Over the past decade, interest in this area has burgeoned because of recognition of higher-than-chance comorbidity rates of schizophrenia and OCD.
The co-occurrence of obsessive-compulsive symptoms and psychotic illness has been a challenge for clinicians and investigators for more than a century.1 Over the past decade, interest in this area has burgeoned because of recognition of higher-than-chance comorbidity rates of schizophrenia and obsessive-compulsive disorder , and observations of appearance or exacerbation of OCS during treatment of schizophrenia with atypical antipsychotics.2-6 Emerging neurobiological and genetic evidence suggests that persons with comorbid OCD and schizophrenia may represent a special category of the schizophrenic population.
The evidence for a putative schizo-obsessive disorder is examined and practical treatment suggestions for this subgroup of patients are outlined in this article.7-9
Clinical and research challengesRecent studies have aimed to reduce bias and
Pedigree and genetic studiesPedigree and genetic studies have not found any familial relationship or shared etiology between OCD and schizophrenia in their pure forms. However, specific genotypes of polymorphisms of the same gene may differentially confer risk for the 2 disorders.
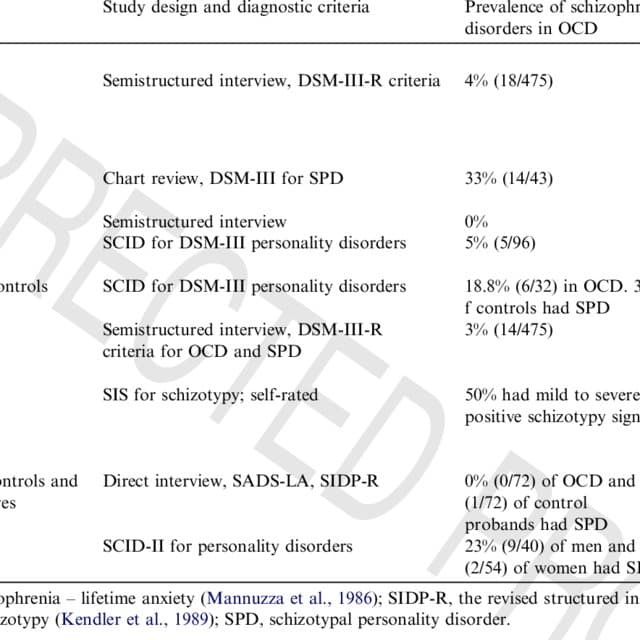
Validity Of International Classification Of Diseases Codes For Ocd
OCD probands were defined as individuals identified in the National Patient Register with at least one International Classification of Diseases -10 diagnosis of OCD . The ICD codes for OCD have been recently subject to validation . Briefly, we obtained a random sample of patient records from 3 Swedish counties . Each file was carefully reviewed and blindly rated by 2 independent clinicians specialized in OCD. The ICD-10 codes, which represent approximately 80% of the OCD cases in the Register, had excellent validity, with a positive predictive value of 91% and 98% . The inter-rater agreement between the 2 raters was outstanding . ICD-8 and ICD-9 patients were not included in this study because the validation study suggested relatively high rates of false positives.
Recommended Reading: Are Manic Depressive And Bipolar The Same
Gxei On A Second Level Of Complexity
GxEIs are core elements within current theories of schizophrenia , depression , anxiety disorders and OCD . High rates of bi-directional comorbidities lead to the obvious question, if these co-occurrences could also be explained by common GxEIs. One example of this experimental psychopathology has been illustrated by the described investigation of the risk to develop secondary OCS during treatment with SGAs. Here, the environmental factor is represented in the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia with pro-obsessive SGAs.
As stated in chapter 4, SGAs increase the risk for secondary OCS via a pharmacodynamic mechanism. Independently, a set of SNPs within the gene SLC1A1 seem to predispose to OCD. However, the initially reported high odds ratio by Kwon et al. could not be replicated in a similar study performed with European patients . Thus, the general genetic background of a patient might be of importance when a specific SGA is introduced as the treatment of choice. Furthermore, gene-x-gene interactions have been suggested as further influencing factors and should be considered in forthcoming studies. It is an important progress in recent neurobiological research to investigate how the interaction of these factors might influence the propensity of schizophrenia patients to suffer from comorbid OCS when being treated with SGAs.
Are Ocd And Schizophrenia Related
OCD is a common comorbid condition in those with schizophrenia and BD. There is some evidence that a diagnosis of OCD may be associated with a higher risk for later development of both schizophrenia and BD, but the nature of the relationship with these disorders is still unclear.
Read Also: How To Address Eating Disorders
Obsessivecompulsive Disorder As A Risk Factor For Schizophrenia
It is unclear if a diagnosis of OCD confers a risk for later development of psychosis, but there is some evidence to suggest that OCS may enhance the risk of psychosis. In a study based on Danish registers, prior diagnosis of OCD was associated with an increased risk of developing schizophrenia and schizophrenia spectrum disorders later in life. Similarly, children of parents with OCD had an increased risk of schizophrenia and schizophrenia spectrum disorders . The results were significant even after adjusting for family history of psychiatric disorders and the patient’s psychiatric history.
A Swedish registry-based longitudinal cohort and multi-generational family study found that patients with OCD had a 1213 times higher risk of having a comorbid diagnosis of schizophrenia, BD, and schizoaffective disorder compared with individuals without OCD. Longitudinal analyses showed that individuals first diagnosed with OCD had a 3-fold higher risk of receiving a later diagnosis of schizophrenia compared with individuals without OCD during the follow-up period. Similarly, when rates of OCD in primary psychotic disorders were studied, patients first diagnosed with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder had a 7 and a 5 times higher risk of receiving a later diagnosis of OCD, respectively, compared with individuals without schizophrenia. The risk of later development of OCD was only marginally reduced when the use of second-generation antipsychotics was corrected for.
When Does Anxiety Turn Into Ocd
Though distressing thoughts are a big part of both generalized anxiety disorder and ocd, the key difference is that ocd is characterized by obsessive thoughts and resultingcompulsive actions. A person with more general anxiety will not experience worries or take actions that are out of line.
Don’t Miss: Can Panic Attacks Last For Hours
What Causes Schizophrenia
Like with so many mental illnesses, there is no smoking gun that causes schizophrenia. Rather, it appears to manifest as a combination of several factors, including:
Genetics: Schizophrenia tends to run in families and those who have an immediate family member with the illness are at higher risk than members of the general public. If one identical twin has schizophrenia, the other has a 50/50 chance of developing it as well. This proves true even if the twins are raised in separate environments.
Still, no single gene has been identified as the main cause and, in those with or without inflicted family members, schizophrenia remains rare. Scientists believe that part of its rareness is likely due to the required involvement of numerous genes.
Brain development: Several people with schizophrenia demonstrate brain abnormalities. These include reduced grey matter in the medial temporal, prefrontal areas, and superior temporal. There may be impaired connectivity within the amygdala as well.
Interaction of neurotransmitters: Just as they are implicated in OCD, serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate play a role in schizophrenia. Those with schizophrenia are believed to have higher than normal levels of serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate as well as decreased levels of norepinephrine.
In addition to the above, there are several triggers that may lead to a schizophrenic episode. While these dont cause the disease, they can increase symptoms or awaken a dormant disorder.
What Are The Differences
There are some key differences between OCD and Schizophrenia.
OCD is characterized by obsessions, which are intrusive and unwanted thoughts, images, or impulses that cause anxiety or distress. Schizophrenia, on the other hand, is characterized by delusions, which are false beliefs that are not based on reality.
OCD can also cause compulsions, which are repetitive behaviors or mental rituals that a person feels they must do to reduce anxiety. Schizophrenia may also cause hallucinations, which are false perceptions that a person experiences.
OCD is typically treated with a combination of medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy, while schizophrenia is typically treated with medication and psychotherapy.
In OCD, the person is aware that their obsessions and compulsions are excessive and irrational, but they cannot control them. In schizophrenia, the person may not be aware that their delusions are false.
Also Check: What Can You Take For Panic Attacks
What Is Schizophrenia Ocd
- Losing your mind or becoming psychotic
- Not being able to live the life you want
- Not being able to take care of yourself
- Not being able to support yourself financially
- Not feeling able to identify real experiences
- Not being able to trust memories
- Living in a state of fear
- Engaging in behaviors that you might not normally do
- Not being able to function socially
- Not being able to have a relationship
Underlying Neurobiological Mechanisms And Environmental Factors
Neurobiology
While the described explanatory concepts mainly follow a clinical or psychopathological rationale, several investigations tried to improve the pathogenic understanding from a neurobiological perspective. So far, most emphasis has been given to a multimodal neurocognitive characterization. Preliminary investigations of neurological soft signs and neuroimaging techniques need replication.
For primary OCD recent reviews of published literature reported specific cognitive deficits especially in the areas of cognitive shifting abilities, inhibitory control and the application of effective planning strategies . Based on these findings, the question arose whether OCS in schizophrenia might also be linked to additional cognitive impairment in these OCD-related domains . Subsequently, several authors tried to differentiate schizophrenia samples with vs. without comorbid OCS on the basis of their neuropsychological performance. Findings have been contradicting. Whereas some investigations did not find any significant differences , others even suggested that OCS may be associated with better cognitive abilities , especially in the prodromal states of schizophrenia . Most results, however, showed more pronounced deficits in the described domains of executive functioning , cognitive flexibility , and also delayed visual memory .
Genetic disposition
Environmental factors
Also Check: How Do You Know If Your Bipolar Test
Is There A Link Between Anxiety And Paranoia
Yes, there is a link between anxiety and paranoia.
It is common for people with anxiety to constantly worry about someone or something. In some cases, the angst is grounded in reality, but in others, it is not. It is also common for these individuals to be paranoid or feel as if something ominous is going to happen to them or their loved ones.
Sometimes, the suspicions are warranted, however, most of the time, they are not. Also, understand that a person can be anxious and paranoid, but not be psychotic. In other words, a persons response to his or her anxiety and fear may be excessive and irrational, however, that does not automatically mean that he or she is delusional.
Listed below are examples of anxiety and paranoia:
- I cannot go grocery shopping because I am terrified, I will need to use the restroom and be forced to use a dirty and germ-filled public toilet. What if I catch something like Covid-19 from the bathroom stalls or toilet seat? Or, what if Covid-19 is in the air and I breathe it in, contract the virus, and die from it a few days later? To avoid this, I schedule curbside grocery pickup at my local grocery store.
- I am always scared that I will lose my keys while I am running errands, so I always carry multiple copies with me. If I lose my keys then someone will find them and break into my car or home and rob me. So, I rarely go out, but when I do, I always take all of my key copies with me.
“My OCD is finally manageable”
Jennifer S
The Spiraling Relationship Between Ocd And Schizophrenia
In the world of mental health, we know its common to find multiple disorders grouped together. For example, depression and anxiety are often found together, as well as OCD and Schizophrenia. It can be difficult to properly diagnose when sufferers are dealing with multiple issues at once. Does this person need help with their anxiety, that could, as a result, help their depression? Or is it the depression that needs attention to ease the anxiety? Can we treat OCD and Schizophrenia at the same time?
In this article, were going to take a look at the link between OCD and Schizophrenia, the differences and similarities between these two disorders along with the warning signs.
Also Check: How To Deal With Someone With Paranoid Schizophrenia