Are All Panic Attacks The Same
Not all panic attacks are experienced in the same way. The following describes one way panic attacks are categorized:
- Expected panic attacks: These attacks occur when a person is subjected to or is anticipating a particular trigger. For example, a person with a fear of heights may have a panic attack when inside of a tall building.
- Situational predisposed panic attacks: These attacks are similar to cued panic attacks, but do not always occur after subjection to a feared situation. These attacks also dont always occur at the time the person is exposed to the trigger. For instance, a person who has a fear of flying may not always have a panic attack while on a plane or may have one after being on a flight.
- Unexpected panic attacks: These attacks occur suddenly without any internal or external cues.
How To Stop A Panic Attack
You could try any of these ways to calm a panic attack:
- Cooldown anxious thoughts: Thoughts like this is awful will trigger attacks. Try to change what is possible and accept what you cant change.
- Stay Positive: Have a positive mindset about yourself. Keep reminding yourself that you are a fighter.
- Exercise: Soothe your system with some yoga stretches or a gentle rub on your back.
- Get Some Perspective: In most cases, attacks arise because you worry about many things. Filter out unimportant stuff, including small details that will not help you in the long run.
- Dont Ignore Panic Disorder: Panic attacks are an indicator that something needs attention. Get professional help to get your life back on track.
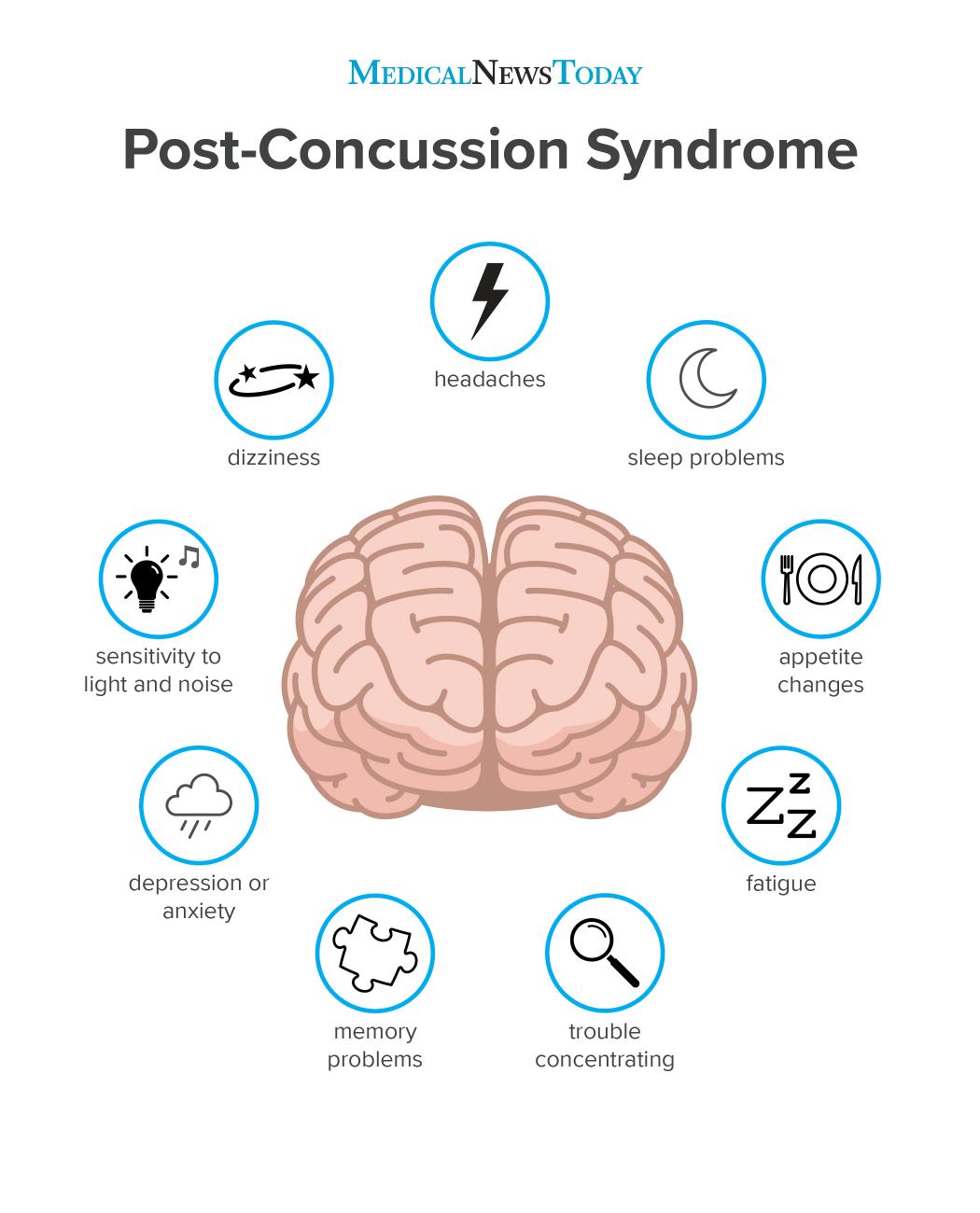
Childhood Brain Injury Tied To Adult Anxiety Depression
By Madeline Kennedy, Reuters Health
5 Min Read
– Children who sustained traumatic brain injuries may experience psychological effects like anxiety, phobias and depression more than a decade later, researchers say.
The study suggests that brain injury is in some way related to longer-term anxiety symptoms, while previously it was thought that brain injury only leads to short-term effects, said lead author Michelle Albicini in an email.
The anxiety may have many causes, including actual brain damage or the experience of living in an anxious family environment after the injury, said Albicini, a researcher at Monash University School of Psychological Sciences in Melbourne, Australia.
Albicinis team reports in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation that children with moderately severe brain injuries and females in general were at the greatest risk for long-term psychological effects compared with boys and children who had milder brain injuries.
Traumatic brain injury occurs when an outside force, usually a blow to the head, causes some kind of brain dysfunction, such as loss of consciousness, amnesia or damage to brain tissue thats visible on a scan.
But more research is needed to fully understand the long-term psychological effects faced by people who experience TBIs during childhood, the researchers write.
This revealed that compared to people with no brain injuries, those with any type of TBI were five times more likely to have an anxiety disorder.
Read Also: Can Seroquel Cause Panic Attacks
History Of Trauma Or Abuse
Traumatic events, such as car accidents or childhood abuse, can increase the risk of developing panic disorder. This is because trauma can lead to changes in the brain that make it more difficult to cope with stress. Trauma also results in feelings of fear, helplessness, and anxiety, which contribute to the occurrence of panic attacks. This also happens because these events can be stressful enough that they cause changes in the brain that make it difficult to cope with stress.
Some People May Develop Panic Disorders
For many people, the feelings of panic occur only occasionally during periods of stress or illness. A person who experiences recurring panic attacks is said to have panic disorder, which is a type of anxiety disorder. They generally have recurring and unexpected panic attacks and persistent fears of repeated attacks.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get A Waiver For Depression In The Military
Neck Treatment Can Play A Valuable Role In Peoples Recovery From A Post
A paper from the School of Physiotherapy, Division of Health Sciences, University of Otago in New Zealand was published in November 2021 in The Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy. The question the study authors were seeking to answer was: Can the neck contribute to persistent symptoms post-concussion? What the authors did to answer this question was to assess individual long-term outcomes of people with persistent symptoms following a concussion who received neck treatment as part of multidisciplinary concussion care. The authors then noted that a secondary objective they wanted to help answer was how participants described the outcomes of neck treatment.
To do this they followed 11 patients long-term . They had the patients at the initial start of the study, at the completion of their neck manipulation treatments, and at six and 6, and 12 months assess their neck disability, dizziness, headache, and neck pain. Ten of the 11 participants reported neck treatment as a beneficial part of their care and described the effects on the neck, multiple symptoms, and their overall recovery. However, seven participants experienced recurrent headaches, neck pain, or dizziness at 6- or 12-month follow-up. Long-term follow-up of individuals receiving neck treatment shows improvement across a range of patient-reported outcomes, yet highlights frequent recurrence of symptoms. Neck treatment can play a valuable role in peoples recovery that extends beyond local effects on the neck.
Cervical Afferent Dysfunction: A Distortion Of Time And Space In Post
In some patients with post-concussion syndrome, they report symptoms of out of body, or a sensation of exaggerated movement, like they are moving at a high rate of speed. Things around them have become accelerated.
Cervical afferent dysfunction in simple terms means something is not working correctly within the nerves of the neck. This dysfunction can be caused by a traumatic injury to the neck such as in sports or whiplash.
In her study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, Dr. Julia Treleaven of the University of Queensland wrote:
- There is considerable evidence to support the importance of cervical afferent dysfunction in the development of dizziness, unsteadiness, visual disturbances, altered balance, and altered eye and head movement control following neck trauma, especially in those with persistent symptoms.
- However, there are other possible causes for these symptoms beyond cervical afferent dysfunction
- Understanding the nature of these symptoms and differential diagnosis of their potential origin is important for rehabilitation.
- In addition to symptoms, the evaluation of potential impairments should become an essential part of the routine assessment of those with traumatic neck pain, including those with concomitant injuries such as concussion and vestibular or visual pathology or deficits.
Recommended Reading: When Is The Best Time To Take Magnesium For Anxiety
Can You Go To One Doctor And Be Told You Have Post
Can you go to one doctor and be told you have Post-concussion syndrome and go to another one and be told you dont have Post-concussion syndrome? The answer is yes. One doctor may be using one set of criteria to diagnosis post-concussion syndrome and another doctor may be using another set of criteria to diagnosis post-concussion syndrome.
This article is filled with possible symptoms because criteria and diagnosis are matched to symptoms. Above we showed that mild traumatic brain injury and whiplash-related disorders can share post-concussion syndrome symptoms but can be considered separated non-related entities, or as demonstrated below, they can be considered related, concurrent entities.
There is research that can be somewhat alarming to patients and their families where post-concussion syndrome is present. Published in the medical journal Brain Injury doctors of the American College of Sports Medicine say a standard definition of Post-Concussion Syndrome does not exist.
- Symptoms vary from patient to patient but can include
- anxiety and depression.
These symptoms can range in severity from being slightly annoying to becoming an overwhelming disability.
When the doctors in the study asked what would be the minimum number of symptoms required to diagnose PCS, responses varied:
- and four or more symptoms .
When asked how long these symptoms should persist before a diagnosis of Post Concussion Syndrome is made, the doctors of the studies responded:
When Can I Stop Worrying About A Head Injury
Seek immediate emergency medical care if you have danger signs. In rare cases, a dangerous blood clot that crowds the brain against the skull can develop. The people checking on you should call 9-1-1 or take you to an emergency department right away if you: Have a headache that gets worse and does not go away.
Don’t Miss: Is Binge Eating An Eating Disorder
Mood And Anxiety Concussion Symptoms
You may be experiencing this type of concussion if you are:
- Having a hard time turning off your thoughts
- Ruminating excessively
- Suffering from extreme worry or concern and this is interfering with your life
- Experiencing unusual sleep patterns due to the above issues delaying your ability to fall asleep
What Are Vestibular Impairments
We are going to move away from this research for some brief understanding notes and then we will return:
- The vestibular system is the bodys sensory system that regulates balance and spatial orientation .
- It sits in the inner ear and works by adjusting fluid levels that act as the balance mechanism.
- As human beings, we set our awareness of our place in space by using the ground as the constant place of orientation. We can keep our balance when we walk because we understand the ground is the constant and our vestibular system makes constant involuntary adjustments to keep things steady, to prevent motion from creating dizziness or sway.
Recommended Reading: Are Manic Depressive And Bipolar The Same
What Causes Depression After A Concussion
The physical symptoms of a concussion can be debilitating. This change can affect a persons ability to enjoy life, which can cause depression. In a 2018 study, 1 in 5 participants met the criteria for a major depressive episode within 6 months of sustaining a traumatic brain injury.
It isnt common to be depressed after a concussion, but it does happen, says Gail Saltz, MD, associate professor of psychiatry at the NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Weill-Cornell Medical College and host of How Can I Help? from iHeartRadio.
Depression doesnt usually occur right away after a concussion, Saltz continues. Depression from a concussion, she says, usually occurs later as the symptoms of a concussion disrupt a persons usual routine.
This loss alone can cause some people to develop depression.
Concussions can also alter hormones. In rare circumstances, changes in hormone levels caused by a concussion can result in depression. Additionally, people who have had depression in the past may have a reoccurrence of depression after a concussion, Saltz adds.
Lack of sleep from a concussion can increase depression, hormonal changes in the thyroid or other hormones can cause depression and emotional responses to ongoing pain like headache can increase depression, Saltz explains.
When severe physical symptoms persist, theres a chance it will have a negative effect on your mood and overall mental health.
Signs of depression can include:
Types Of Anxiety Disorders:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is characterized by chronic and exaggerated worry and tension, much more than the typical anxiety that most people experience in their daily lives. People may have trembling, twitching, muscle tension, nausea, irritability, poor concentration, depression, fatigue, headaches, light-headedness, breathlessness or hot flashes.
Panic Disorder: People with panic disorder have panic attacks with feelings of terror that strike suddenly and repeatedly with no warning. During the attacks, individuals may feel like they cant breathe, have lost control, are having a heart attack or even that they are dying. Physical symptoms may include chest pain, dizziness, nausea, sweating, tingling or numbness, and a racing heartbeat. Some people will have one isolated attack, while others will develop a long term panic disorder either way, there is often high anxiety between attacks because there is no way of knowing when the next one will occur. Panic disorders often begin early in adulthood. Many people with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia . See more on Panic Attacks.
Phobias are irrational fears. Individuals with phobias realize their fears are irrational, but thinking about or facing the feared object or situation can bring on a panic attck or severe anxiety.
Read Also: What’s My Phobia Called
Family History Of Anxiety
If you have primary anxiety symptoms, your family history and your personal medical history should be considered. There may be an underlying issue that can increase anxiety after a concussion.Highly functional individuals suffer the most.
Though not an absolute, the more highly functional an individual typically is, the more likely they are to be the most anxious. Theyre used to performing at a high level, so the symptoms caused by having a concussion affect them more.
Understanding Blood Flow To The Brain In Patients
Most patients know the exact head position that gives them the symptoms of dizziness, lack of oxygen to the brain, and related problems. I can tell you that head position is almost always when they are standing or sitting upright, not when they are lying down or standing upright with a stiff postural position. Their head does not move.
The cervical spine is intertwined with nerves and blood vessels. Cervical spine instability can compress or pinch the nerves and arteries causing a myriad of symptoms depending on how the patient moves his/her head.
Don’t Miss: What To Do After Your First Panic Attack
Transcranial Doppler & Extracranial Doppler Ultrasound
For this and other reasons, we offer testing with Transcranial Doppler & Extracranial Doppler Ultrasound. For the full article on this testing please visit our page: Using Transcranial Doppler & Extracranial Doppler Ultrasound Testing at the Hauser Neck Center.
Here is a summary of that article and how this type of testing can show disruptions in blood flow to the brain and may help explain to patients why they feel that they are not getting enough oxygen.
- Transcranial doppler can track real-time, moment-to-moment changes in blood flow to the brain. This allows for an assessment of blood flow changes to the brain and their impact on patient symptoms when the patient moves their head and creates changes in neck positioning. This includes monitoring the blood flow even while the patient walks into the office.
Understanding that blood flow may only be suppressed in certain positions of the neck
- If the blood flow is intermittently compromised, such as only when the neck is in certain positions, it will be difficult to catch and diagnose. To assess proper blood flow to the bodys most important nerves and nervous tissue , especially with head and neck motions, we perform transcranial doppler and extracranial Doppler ultrasound examinations.
- It is through dynamic transcranial doppler and extracranial Doppler ultrasound analysis that this decrease in blood supply can be documented with its root cause being compression of the arteries as they run through the cervical spine.
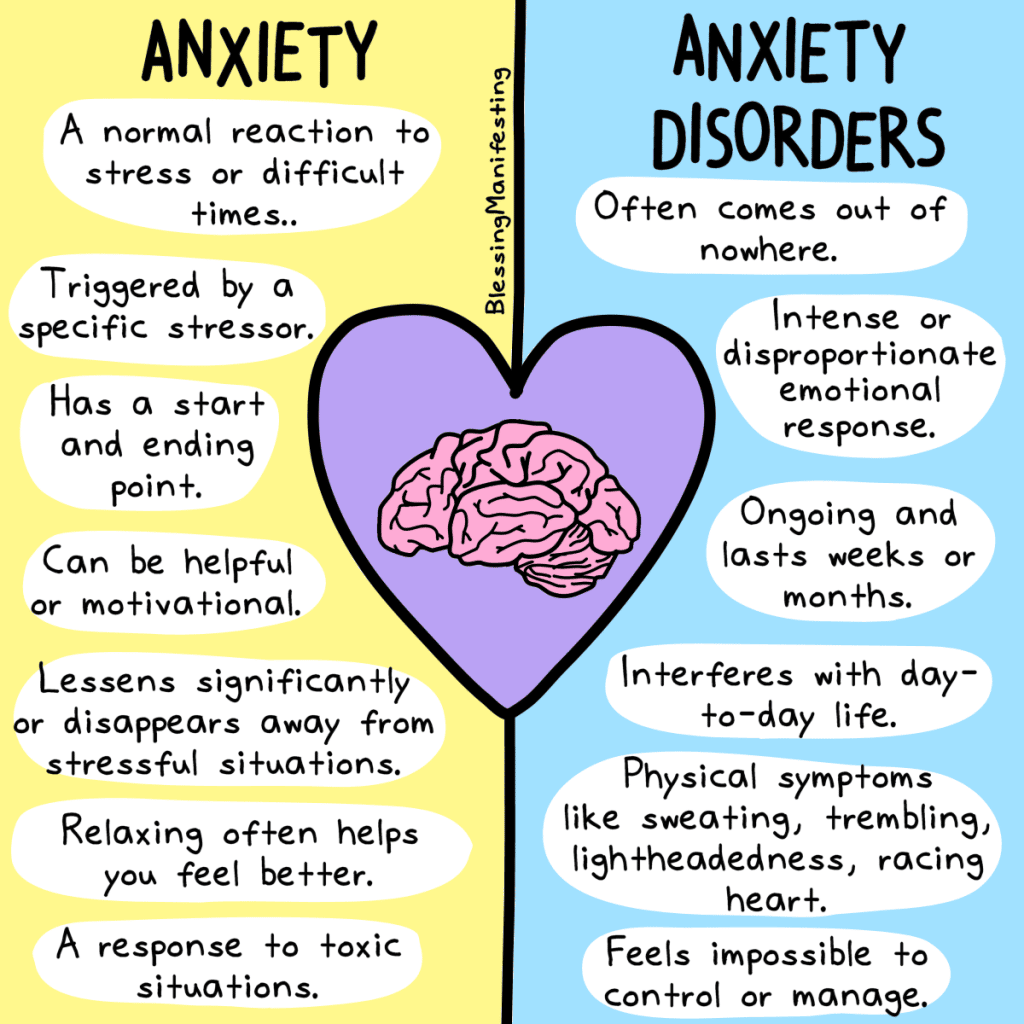
What Are Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety is a normal emotion. Itâs your brainâs way of reacting to stress and alerting you of potential danger ahead.
Everyone feels anxious now and then. For example, you may worry when faced with a problem at work, before taking a test, or before making an important decision.
Occasional anxiety is OK. But anxiety disorders are different. Theyâre a group of mental illnesses that cause constant and overwhelming anxiety and fear. The excessive anxiety can make you avoid work, school, family get-togethers, and other social situations that might trigger or worsen your symptoms.
With treatment, many people with anxiety disorders can manage their feelings.
Also Check: What Percentage Of The Population Suffer From Schizophrenia
Unexpected Neurological And Other Somatic Symptoms After Concussion Should Not Be Dismissed As An Exaggeration
A December 2021 study in the Journal of Psychosomatic Research looked at people reporting unexpected symptoms after a concussion. In some of these people, the researchers noted it may reflect a Functional Neurological Disorder , Somatic Symptom Disorder , or exaggeration . In this study, the researchers aimed to determine whether reporting unexpected symptoms after concussion was associated with risk factors for Functional Neurological Disorder / Somatic Symptom Disorder, exaggeration, or both.
How was the study done?
- Seventy-seven adults with persistent symptoms following concussion rated the presence and severity of unexpected neurological symptoms and somatic symptoms that did not overlap with post-concussion symptom scale items. The independent variables were risk factors for exaggeration and predisposing and perpetuating factors for developing Functional Neurological Disorder and/or Somatic Symptom Disorder .
Results:
- Fear-avoidance behavior was most strongly related to unexpected neurological symptoms
- Current anxiety scores were most strongly related to unexpected somatic symptoms.
Conclusion: Unexpected neurological and other somatic symptoms after concussion should not be dismissed as an exaggeration. Psychological factors thought to perpetuate Functional Neurological Disorder and Somatic Symptom Disorder may contribute to unexpected symptoms following concussion.
Concussions And Anxiety: Whats The Connection
R.J. Elbin, PhD, is a researchanalyst with the Inova Sports Medicine Concussion Program. He is also thedirector of the Office for Sport Concussion Research in the Department ofHealth, Human Performance and Recreation at the University of Arkansas.
Concussionscan cause all sorts of symptoms: Physical problems like headaches and nausea.Cognitive problems that affect thinking and memory. Sleep troubles. Andemotional problems, including irritability, depression and anxiety.
Recently,our research team decided to take a deeper look at anxiety. Its not surprisingthat someone would feel anxious after a brain injury. But after treating lots of patients, our concussion management team suspected there was moreto the story.
Along with other members of the Inova Sports Medicine Concussion Program, I shared the results of this research at the Big Sky Athletic Training Sports Medicine Conference in February 2019.
Anxiety Increases Concussion Symptoms
When we talk about anxiety, there are two types: trait anxiety andstate anxiety. Trait anxiety describes someones general levels of anxiety. State anxiety, meanwhile, refers to the situationsand moments when any person might feel anxious .
We looked at both types of anxiety in concussion patients. As you mightexpect, we found that patients who were more trait anxious were more likely to havehigher states of anxiety after experiencing a concussion.
AnxietyCan Affect Concussion Recovery
Dont Ignore Anxiety
Also Check: Can You Have Bipolar Disorder And Schizophrenia