What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
There are at least three stages to the progression of schizophrenia: prodrome, initial episode, and chronic phase.
The prodrome, the initial episode, and the long-term chronic phase are all stages of the disease. Its also true that theres a pre-morbid period before the prodrome, during which delays in early neurodevelopmental indicators, such as early paediatric milestones, might indicate a higher chance of schizophrenia in the future.
Is It Possible To Recover From Schizophrenia
Many people who live with schizophrenia have recovery journeys that lead them to live meaningful lives.
Recovery can be thought of in terms of:
- clinical recovery, and
- personal recovery.
What is clinical recovery?
Your doctor might have talked to you about recovery. Some doctors and health professionals think of recovery as:
- no longer having mental illness symptoms, or
- where your symptoms are controlled by treatment to such a degree that they are not significantly a problem.
Sometimes this is called clinical recovery.
Everyones experience of clinical recovery is different.
- Some people completely recover from schizophrenia and go on to be symptom free.
- Some who live with schizophrenia can improve a great deal with ongoing treatment.
- Some improve with treatment but need ongoing support from mental health and social services.
What is personal recovery?
Dealing with symptoms is important to a lot of people. But some people think that recovery is wider than this. We call this personal recovery.
Personal recovery means that you can live a meaningful life.
What you think of as being a meaningful life might be different to how other people see it. You can think about what you would like to do to live a meaningful life and work towards that goal.
Below are some ways you can think of recovery.
What can help me recover?
You may want to think about the following questions.
The following things can be important in recovery.
Why The Difference In Schizophrenia Symptoms In Men And Women
While researchers continue to study this important question, one thing is known: Males and females have different schizophrenia symptoms and experiences because of differences in the brain. Multiple areas within the brain have been implicated in schizophrenia .
The areas of damageincluding, but not limited to, the inferior parietal lobe in the cerebral cortexthat are associated with this mental illness are different in men and women. Schizophrenia damages male brains differently than female brains.
Men and women can have different symptoms of schizophrenia, and those symptoms affect lives uniquely. One isnt better or worse, because schizophrenia is a mental illness that is challenging for everyone who lives with it. Also, while there is no cure for schizophrenia, people of both genders can work to minimize symptoms and live a quality life. When someone with schizophrenia is viewed as an individual with symptoms and strengths, the gender differences dont seem as big.
Recommended Reading: Does Celine Dion Have An Eating Disorder
When To See A Healthcare Provider
As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
Symptoms may intensify in the run-up to an acute episode of psychosis in schizophrenia. The warning signs include:
- A worrying drop in grades or job performance
- New difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating
- Suspiciousness of or uneasiness with others
- Withdrawing socially, spending a lot more time alone than usual
- Unusual, overly intense new ideas, strange feelings, or having no feelings at all
- Difficulty telling reality from fantasy
- Confused speech or trouble communicating
While these changes might not be concerning by themselves, if you or a loved one are experiencing a number of these symptoms, you should contact a mental health professional. It can be difficult for those with schizophrenia to want to get help, especially if they are experiencing symptoms such as paranoia.
If you or your loved one is thinking of or talking about harming themselves, contact someone who can help right away. You can call the toll-free, 24-hour National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-237-8255.
If you require immediate emergency care, call 911 for emergency services or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
You May Like: Bipolar Binge Eating
What Is The Typical Age Of Onset For Schizophrenia
Men and women are equally likely to get this brain disorder, but guys tend to get it slightly earlier. On average, men are diagnosed in their late teens to early 20s. Women tend to get diagnosed in their late 20s to early 30s. People rarely develop schizophrenia before they’re 12 or after they’re 40.
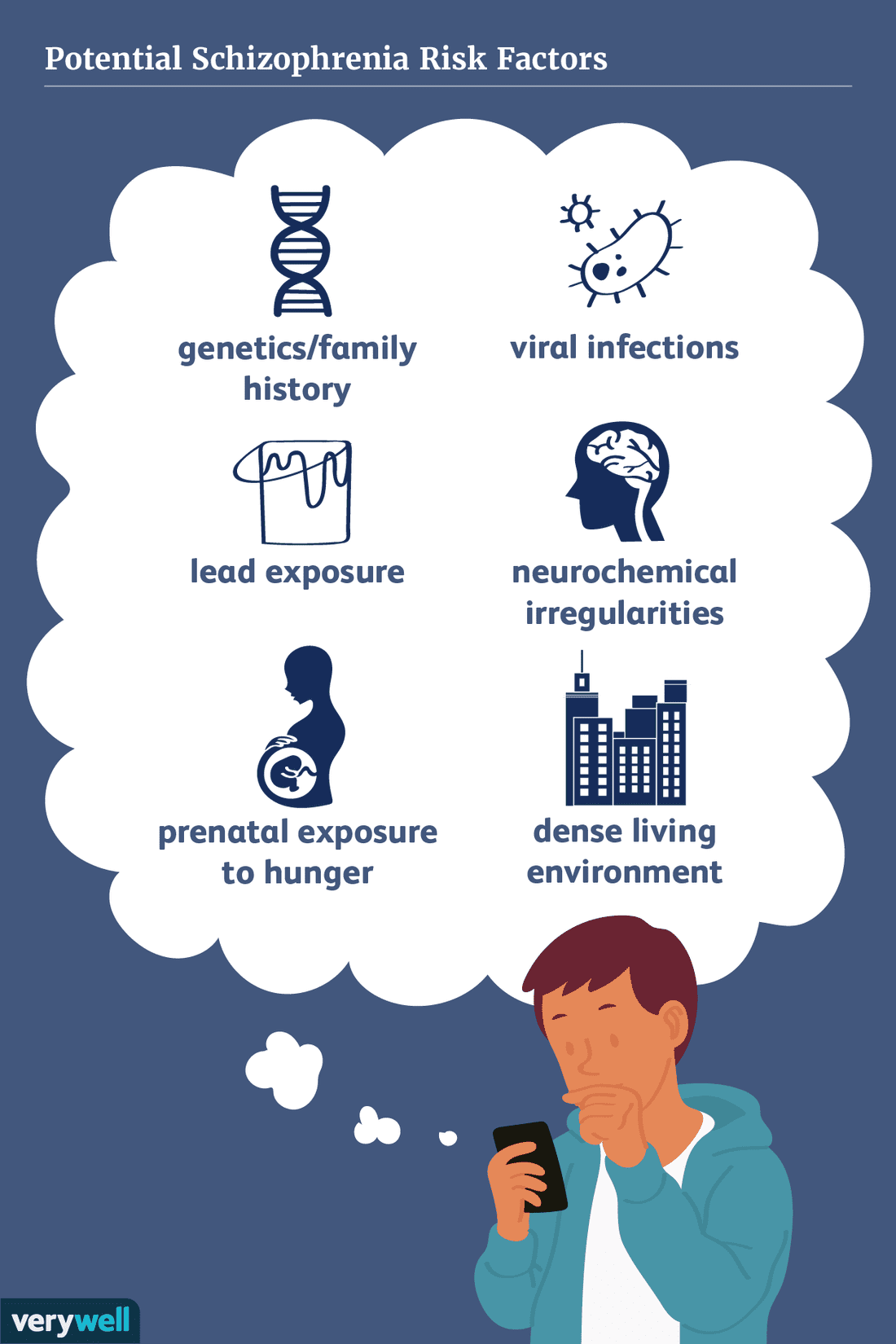
Brain And Body Risk Factors
Developmental theories of schizophrenia suggest that something goes wrong when the brain is developing. Brain development, from the earliest stage of fetal development, the early years of life and through adolescence, is an extremely complicated process. Millions of neurons are formed, migrate to different regions of the forming brain, and specialize to perform different functions.
The something that goes wrong might be a viral infection, a hormonal imbalance, an error in genetic encoding, a nutritional stress, or something else. The common element in all developmental theories is that the causal event occurs during the brains development.
Even though these potential causes may be rooted in very early development, symptoms of schizophrenia typically emerge in late adolescence or early adulthood.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Meaning
What Is The Treatment
Even though schizophrenia is a serious mental illness it is also treatable, especially when the signs are caught early. Many people with schizophrenia live satisfying lives when they get good treatment. As with other mental illnesses, there are a few approaches to treatment that, when used all together, work the best. One approach is taking medicine prescribed by a psychiatrist or psychiatric nurse practitioner. Another approach is through individual or group therapy. There are also community programs that can help with daily living and job goals. Its helpful for family members to become educated so the person dealing with this illness is never alone in the journey.
Differences Between Schizophrenia In Men And Schizophrenia In Women
Delusions and hallucinations are the most well-known and generally prominent schizophrenia symptoms but other more subtle symptoms, like cognitive deficits, exist as well. Cognitive deficits represent any problem with the way a person is able to think.
In the case with schizophrenia in men, they tend to suffer more with the following symptoms:
- Lack of will and directed energy a tremendous sense of inertia
- Inability to plan and complete things
- Making decisions
Men with schizophrenia may also react less positively to medication.
Because the symptoms of schizophrenia in women are less severe, women are more likely to:
- Hold down a job
Men tend to have more trouble with joblessness and homelessness.
Schizophrenia is more likely in women who have been born to mothers who have been exposed to a viral infection, whereas men with schizophrenia are more likely to be born where birth trauma is involved. Why there is a gender difference among these risk factors is unknown.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Anxiety Symptoms
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
If symptoms of schizophrenia are present, the doctor will perform a complete medical history and sometimes a physical exam. While there are no laboratory tests to specifically diagnose schizophrenia, the doctor may use various tests, and possibly blood tests or brain imaging studies, to rule out another physical illness or intoxication as the cause of the symptoms.
If the doctor finds no other physical reason for the schizophrenia symptoms, they may refer the person to a psychiatrist or psychologist, mental health professionals trained to diagnose and treat mental illnesses. Psychiatrists and psychologists use specially designed interviews and assessment tools to evaluate a person for a psychotic disorder. The therapist bases their diagnosis on the person’s and family’s report of symptoms and their observation of the person’s attitude and behavior.
A person is diagnosed with schizophrenia if they have at least two of these symptoms for at least 6 months:
- Delusions
One of the symptoms has to be
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- Disorganized speech
During the 6 months, the person must have a month of active symptoms. Symptoms should negatively affect them socially or at work, and canât be caused by any other condition.
Identifying Environmental Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
The degree of risk of schizophrenia in members of families with one or more patients with schizophrenia correlates with the degree of biological relatedness between the relative and the patient: the closer the relationship, the higher the level of risk. Yet even if an individual has an identical twin with schizophrenia, or two affected parents, the risk is nowhere near 100%. In the case of identical twins with one affected member, the genetic predisposition is present in both individuals, but is expressed only in the twin who has undergone certain environmental experiences as well. Consistent with this view, Gottesman & Bertelsen showed that the offspring of identical twins who were discordant for schizophrenia showed similar rates of developing the disorder, regardless of whether their parent was the affected or the unaffected twin.
Recommended Reading: Three Phases Of Schizophrenia
Late Onset Schizophrenia And Dementia
Many researchers have wondered whether late onset of schizophrenia is somehow related to dementia. Brain studies have suggested that although tempting, this theory is not strong enough given that proof of brain degenerative causes for late onset of schizophrenia have not yet been confirmed.
Certain psychotic symptoms are the main symptoms of both and schizophrenia and this is the primary reason these two are linked. Etiologically, the disorders are different and only related to each other symptomatically.
Tips For Living With Someone With Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a debilitating mental disorder that typically first hits adults in their 20s and early 30s. When someone is diagnosed with schizophrenia, they must remain on antipsychotic medications for the rest of their lives to control symptoms. One of the reasons why schizophrenia does not go away is the fact that genetics and physical abnormalities of the brain play key roles in its development.
Before learning how to live with someone with schizophrenia, it helps to understand how this mental illness develops and why people with schizophrenia think and behave the way they do. No one chooses to live with schizophrenia, just like nobody chooses to have personality disorders, PTSD, or major depression. Loving someone with schizophrenia means recognizing they have no control over what they believe, what they say or how they treat you. It is up to caregivers to provide the stability and unconditional love that people with schizophrenia want and need.
Recommended Reading: Feretrephobia
What Can Be Done
If you suspect that your child might have schizophrenia, talk to a doctor or psychiatrist right away. Getting help as early as possible is important. Studies have shown that the earlier schizophrenia is diagnosed and symptoms managed, the more likely the person with schizophrenia will be able to manage their illness and the better their future outcomes. Most areas in BC have Early Psychosis Intervention programs to help young people who have psychosis . EPI programs are a very good place to start if you think your child might have schizophrenia.
Treatment and Strategies
Medication is very important in treating schizophrenia. Everyone’s brain is a bit different, and it may take awhile for doctors to find the right medication to help your child. Your child may need to be in the hospital for a while to help with this. Early intervention and diagnosis leads to the potential to find treatments that work earlier, resulting in a better likelihood of the person with schizophrenia being able to manage their symptoms and develop strategies for school, work and life.
An imbalance in brain chemistry causes symptoms of schizophrenia, therefore medication is key in schizophrenia treatments. Other treatments work best in conjunction with the use of medication.
Selfmanagement strategies
What To Look For
Symptoms in teens can come on gradually over days, weeks, several months or more. This is called the prodromal period. The early symptoms of schizophrenia can sometimes look like those of other problems such as or .
Especially at first, symptoms may look like the stuff of typical teen years: bad grades, changing friends, , or irritability.
But there are some early warning signs in teens that show up as changes in thinking, emotions, and behavior.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Liam Afraid Of Spoons
Schizophrenia At A Glance
Reviewed By :
Schizophrenia Genetics: Is Schizophrenia Hereditary
Schizophrenia genetics is an interesting subject. When someone is diagnosed with schizophrenia, one of the first things people want to know is how they got it did they get it from their parents is schizophrenia hereditary?
Its natural to ask these questions, but the answers may be unsettling. Scientists believe that schizophrenia involves genes and the environment but no single gene, or even known combination of genes, causes schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: Can Low Blood Sugar Cause Panic Attacks
How Do Physicians Ensure That The Person Has The Correct Diagnosis
Diagnosing both schizophrenia and dementia can be challenging. The challenges increase when a person already has one of the two conditions.
There is no single definitive test for dementia. While tests can show that a person has declined in cognitive function, these tests cannot conclusively prove that dementia is the cause, or determine which type of dementia a person has. That said, the testing can help to determine which diagnosis is more or less likely.
Instead, doctors use a combination of tests , such as bloodwork and brain scans, to look for dementia markers, including signs of plaques in the brain. However, not all people with dementia develop brain signs of the disease, and some people with plaques or other symptoms do not have dementia.
Similarly, no single test can prove that a person has schizophrenia, and doctors do not use brain scans or blood tests to diagnose this condition. Rather, such as delusions, hallucinations, socially unacceptable behavior, and a disconnection from reality.
Some of these symptoms are similar to dementia.
Certain types of dementia, especially frontotemporal dementia, are easy to confuse with schizophrenia. Frontotemporal dementia affects behavior and mental health, potentially causing aggression, impulse control, and hallucinations. It also tends to appear earlier in life than Alzheimers, making it even easier to mistake for schizophrenia.
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
You May Like: Schizophrenic Disorders Usually Emerge During
Physical Health And Schizophrenia
Physical Health in People with Schizophrenia
Without a doubt physical health is a problem for people with schizophrenia and whilst the focus of health professionals traditionally has been to minister to the mental health needs, the cost of physical illnesses to those living with schizophrenia and the wider society in premature death, serious illness and poor quality of life has long been under-rated.
The average life expectancy of people living with schizophrenia is about 10 to 20 years less than that of the general population2 and research has shown quite conclusively that people with schizophrenia have increased rates of physical illnesses in fact over 75% of people with a diagnosis of schizophrenia have at least one chronic physical condition running alongside their schizophrenia and the more severe the schizophrenia is the more severe their physical problems are also likely to be3.
Thus it is clear that, even allowing for suicide , the mortality rate for people with schizophrenia is higher.
The range of illnesses that afflict people with schizophrenia disproportionately is very wide and includes the more obvious candidates like heart disease, stroke and diabetes but also high blood pressure, some cancers, sexual dysfunction, osteoporosis and infectious diseases like HIV, TB and hepatitis3,12.
Caring for the Physical Health of People with Schizophrenia
Many GPs are not particularly good at monitoring the physical health of their schizophrenia patients.
Obesity
Diabetes