Helping A Suicidal Friend Or Relative
If you see any of these warning signs:
- get professional help for the person, such as from a crisis resolution team or the duty psychiatrist at your local A&E department
- let them know they are not alone and you care about them
- offer your support in finding other solutions to their problems
If you feel there is an immediate danger of the person committing suicide, stay with them or have someone else stay with them. Remove all available means of suicide, such as sharp objects and medication.
Want to know more?
Psychosocial Interventions For Alcohol And Substance Use Disorders
Many individuals with schizophrenia also struggle with an alcohol or substance use disorder. Co-occurring disorders are best treated concurrently, meaning that treatment for schizophrenia should be integrated with the treatment for the alcohol or drug problem. Integrated treatment includes motivational enhancement and cognitive-behavioral interventions. Integrated treatments are effective at reducing substance use, preventing relapse, and keeping individuals in treatment longer. These interventions can be delivered one-on-one or in a group format.
Getting Treatment For Schizophrenia And Disordered Eating
A good residential treatment facility will give your loved one the best possible differential diagnosis. This will be the first step in planning treatment, because it informs what comes next. For patients with schizophrenia and secondary anorexia or another eating disorder, treatment must focus on the psychotic condition with an emphasis on disordered eating.
Its not easy to get this integrated care outside of a residential setting. Schizophrenia alone is a serious condition that requires long-term care in a safe and supervised place. The most effective treatment will address all mental health issues at the same time, especially when they are so interconnected.
Your loved one will get an individualized plan for treatment, but the center of care will be therapy and medical treatment. Both of these are essential for symptom management. Antipsychotic drugs can help reduce symptoms and psychotic episodes, but therapy will help your loved one learn to manage their illness over the long-term.
Therapy for schizophrenia may include behavioral interventions that help your loved one change their thought patterns and behaviors. It may also involve social skills training, relationship and family counseling, and group support. In a residential setting, your loved one will also have access to a wide variety of other types of supplemental care like alternative therapies, holistic medicine, vocational training, and life skills training.
Begin Your Recovery Journey Today.
When A Loved One Has Schizophrenia
The love and support of family and friends plays an important role in schizophrenia treatment and recovery. If you have a loved one with schizophrenia, you may be struggling with any number of difficult emotions, including fear, guilt, anger, and frustration. You may feel helpless in the face of your loved ones symptoms, worried about the stigma of schizophrenia, or confused and embarrassed by their strange behaviors. You may even be tempted to hide your loved ones illness from others.
But its important to remember that a diagnosis of schizophrenia is not a life-sentence. Recovery is possible, especially with your love and support. To help someone with schizophrenia, its crucial you:
- Accept the illness and its difficulties.
- Not buy into the myth that someone with schizophrenia cant get better or live a full and meaningful life.
- Do your best to help your loved one feel better and enjoy life.
- Pay attention to your own needs.
- Maintain your sense of humor and remain hopeful.
While dealing with a loved ones schizophrenia can be challenging, the following strategies can help you guide your loved one on the road to recovery without losing sight of your own hopes and dreams.
Tips for helping a loved one with schizophrenia
Effective Treatment Is Long
Research indicates that treatment of substance use disorders is most effective and results in the best outcomes when it lasts for at least three months. This is one reason why residential treatment is ideal for patients with this particular co-occurrence.
A stay in a residential facility gives a patient a chance to leave behind the stress of daily life, of work, school, housing problems, legal troubles and others, and to focus on treatment. Long-term care in a facility provides patients with the time, the tools, and the expertise from a large staff in order to learn to stop drinking and manage symptoms of schizophrenia in healthier ways.
Specialized Educational And/or Structured Activity Programs
Children and adolescents with schizophrenia may reap significant benefits from specialized programs offered at schools, in medical centers, or in the community. Examples of these programs might include:
- customized, smaller classroom settings, with educators who have specialized training in teaching children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders
- social skills training to:
- develop healthy personal interaction techniques
- create a checklist for good hygiene
- learn how to manage everyday tasks like balancing a checkbook or preparing a meal
Your clinician can refer you to the educational and activity programs in your area that are best suited to address your child’s needs.
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
Voluntary And Compulsory Detention
More serious acute schizophrenic episodes may require admission to a psychiatric ward at a hospital or clinic. You can admit yourself voluntarily to hospital if your psychiatrist agrees it’s necessary.
People can also be compulsorily detained at a hospital under the Mental Health Act , but this is rare.
It’s only possible for someone to be compulsorily detained at a hospital if they have a severe mental disorder and if detention is necessary:
- in the interests of the person’s own health and safety
- to protect others
People with schizophrenia who are compulsorily detained may need to be kept in locked wards.
All people being treated in hospital will stay only as long as is absolutely necessary for them to receive appropriate treatment and arrange aftercare.
An independent panel will regularly review your case and progress. Once they feel you’re no longer a danger to yourself and others, you’ll be discharged from hospital. However, your care team may recommend you remain in hospital voluntarily.
The Side Effects Of Risperidone
As we mentioned above, the side effects associated with risperidone are lower than those linked to the classic antipsychotic drugs. For example, haloperidol. Especially noteworthy is the decrease in extrapyramidal symptoms. These symptoms are more prevalent with the use of traditional drugs.
One of the main side effects of risperidone is hypotension. Its more marked at the beginning of treatment. Its also more common in elderly and weaker patients. In addition, some patients treated with it experience neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
The most common side effects of this drug are:
- Insomnia.
- Drowsiness and decreased attention.
- Parkinsonism. This includes symptoms like slow movements, muscle stiffness, tremor at rest, or loss of facial expression.
- Headache.
However, other side effects may also occur. These include:
- Weight gain.
Types Of Psychosocial Therapy
If a person with schizophrenia sees improvement during psychotherapy sessions, itâs likely theyâll need more help learning how to become part of a community. Thatâs where psychosocial therapy comes in.
Social skills training. This type of instruction focuses on improving communication and social interactions.
Rehabilitation. Schizophrenia usually develops during the years we are building our careers. So rehabilitation may include job counseling, problem-solving support, and education in money management.
Family education. Your knowledge of psychosis and schizophrenia can help a friend or family member who has it. Research shows that people with schizophrenia who have a strong support system do better than those without the encouragement of friends and family.
Self-help groups. You should encourage your loved one to participate in community care and outreach programs to continue working on their social skills. The National Alliance on Mental Illness is an outreach organization that offers a free peer-to-peer program, for instance. It includes 10 sessions for adults with mental illness who want to learn more about their condition from people who have experienced it themselves or been through it with a loved one.
Assertive community treatment . This offers highly personalized services to help people with schizophrenia meet lifeâs daily challenges, like taking medications. ACT professionals also help them handle problems proactively and work to prevent crises.
How To Help Someone Who Refuses Treatment
Some of the symptoms of schizophrenia can include hallucinations, delusions, and other disturbances in thinking and perception. Additionally, the medications prescribed to treat the condition can often cause unpleasant side effects.
Because of these factors, some individuals may refuse treatment. However, oftentimes not seeking treatment is associated with a poorer prognosis and quality of life.
Follow the tips below to help a loved one thats refusing treatment:
How To Help Manage Symptoms
1. Dietary Alterations
Like all conditions, schizophrenia onset is affected, in part, by what a person eats. There is evidence, for instance, that celiac disease may be a precipitating factor for the illness. Having excessive free radical damage and not enough antioxidants circulating is also connected to a higher risk of schizophrenia.
Another dietary risk factor for symptoms of schizophrenia is poor metabolism of essential fatty acids . Two fatty acids, arachidonic acid and DHA, are much lower in patients suffering from schizophrenia and may be increased by some antipsychotics, one possible reason these drugs decrease symptoms.
However, a diet for schizophrenia mirroring what we already know about treating food as medicine will be beneficial for maintaining lower weights and overall health but it may not help to treat the condition.
For example, a 1999 clinical trial observed participants with schizophrenia eating and supplementing their diet based on food sensitivities and nutrient deficiencies. After five months, patients had improved the blood levels of their nutrients, but no direct symptoms of schizophrenia.
There are some impressive case studies that suggest keto might be a revolutionary natural treatment for schizophrenia. Among the most popular are cases of two women and one man with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder who experienced a drastic reduction in all symptoms of schizophrenia while following the diet. 30063-4/abstract” rel=”nofollow”>35, , )
Schizophrenia Symptoms And Behaviors

People with schizophrenia can have intense behavioral symptoms, most often confusion and disorientation, making it difficult for them to distinguish between reality and their delusions or hallucinations. Its important to note that the symptoms of schizophrenia vary dramatically from person to person, both in pattern and severity. Some might have their symptoms worsen or improve unpredictably, and others might have consistent symptoms.
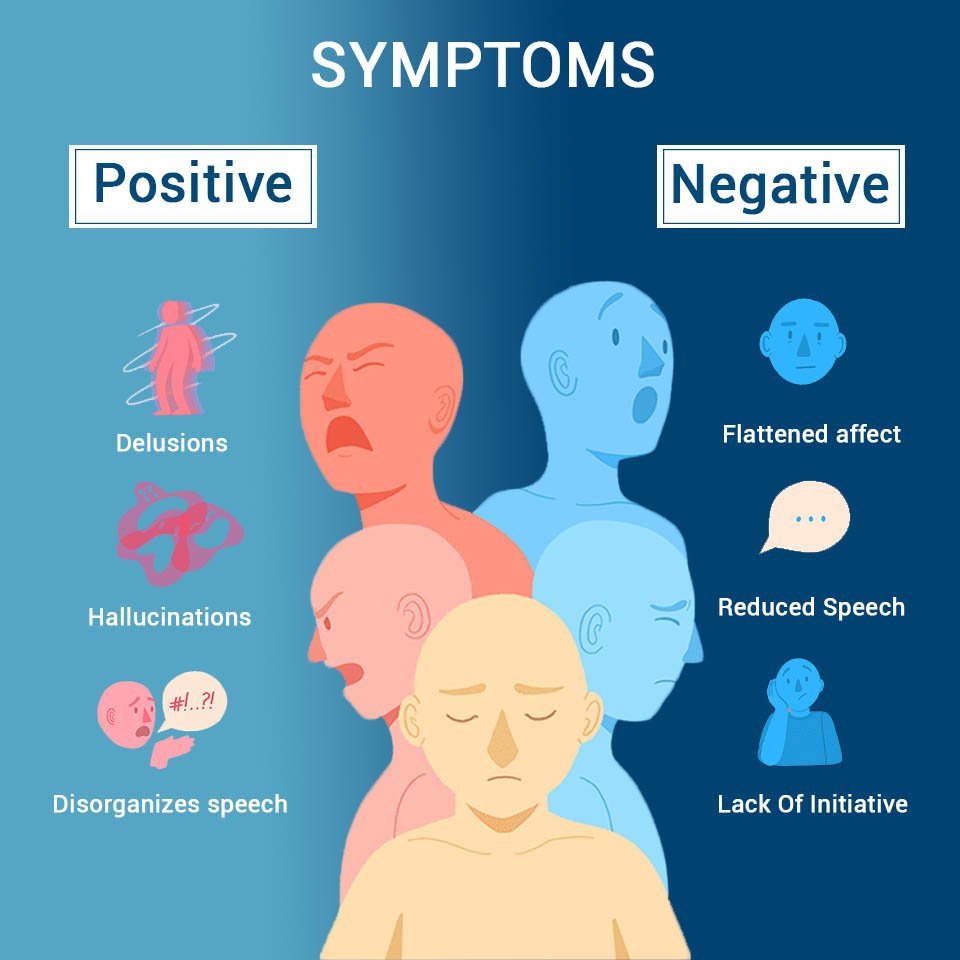
Schizophrenia symptoms are considered to be either positive or negative, not because they are good or bad, but based on whether or not they mark the presence or absence of symptoms. Positive symptoms, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thoughts and speech represent increased activation of certain areas of the brain. The positive symptoms tend to respond well to drug therapy. Negative symptoms, on the other hand, include symptoms that halt normal functioning and dont respond as well to drug therapy, such as a lack of desire for any social connections and lack of emotional affect.
There are five main types of schizophrenia symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, disorganized behavior, and the aforementioned negative symptoms.
Delusions: Broadly, a delusion is a firmly-held belief that a person has despite clear and obvious evidence to the contrary.
Negative symptoms: Negative symptoms can include lack of emotional expression, lack of enthusiasm, social withdrawal, and lack of awareness of ones environment.
Social Skills Training And Vocational Rehabilitation
Schizophrenia can impact every aspect of a persons life, including their ability to develop and maintain relationships and get and keep a job. Community support services can help patients work, shop, and care for themselves, as well as manage a household, build meaningful relationships, and follow through with treatment.
Examples include cognitive remediation therapy, which is designed to improve attention, working memory, and executive functioning required to learn or relearn task completion techniques, and supported employment, where a patient is provided with onsite support from a job coach to promote integration and adaptation.
Why Does Schizophrenia Happen
The exact cause of schizophrenia is unknown. However, most experts believe the condition is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
It is thought certain things make you more vulnerable to developing schizophrenia, and certain situations can trigger the condition.
Read more about the causes of schizophrenia.
What Kind Of Symptoms Might People With Schizophrenia Have
People with schizophrenia may have a number of psychotic symptoms. These symptoms can come and go in phases, or they can happen only once or twice in a lifetime. When the illness begins, psychotic symptoms are usually sudden and severe.
During psychotic phases, the person may still understand parts of reality. He or she may lead a somewhat normal life, doing basic activities such as eating, working and getting around. In other cases, the person may be unable to function. Symptoms during psychotic phases include:
- Seeing, hearing, feeling or smelling things that are not real .
- Having strange beliefs that are not based on facts . For example, the person may believe that people can hear his or her thoughts, that he or she is God or the devil, or that people are putting thoughts into his or her head.
- Thinking in a confused way, being unable to make order out of the world, shifting quickly from one thought to the next.
- Having emotions, thoughts and moods that do not fit with events.
People with schizophrenia also may:
- Have a lot of energy or be overly active, or become “catatonic,” a state in which the body becomes rigid and cannot be moved.
- Talk in sentences that do not make sense.
- Not wash or groom.
- Cut themselves off from family, friends and the outside world.
- Be unable to function in school, work, or other activities.
- Lose interest in life.
- Be very sad or have mood swings.
- Have dulled emotions.
Therapeutic Approaches To Treatment
The most recent treatment guidelines for schizophrenia state that medication is not enough to effectively treat the condition and that it must be combined with psychosocial strategies. These include various types of therapy. One of the most effective types of therapy for all kinds of mental health patients is cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT. It uses mindfulness, goals, and active steps to help patients recognize and normalize abnormal thoughts and behaviors, to practice healthy coping mechanisms, and to have healthier relationships. CBT can be used in individual or group therapy.
Other types of therapy that may help patients with schizophrenia include motivational interviewing, which helps a patient commit to making positive changes, solution-focused therapy, which includes setting and working toward specific goals, and experiential or creative therapies like art, music, or drama therapy, animal therapy, or adventure therapy.
How Long Does Treatment Take
Treatment for schizophrenia is complex and multi-faceted. How long it takes to help a patient stabilize and maintain minimal symptoms and good overall function depends on individual factors, like commitment to treatment, severity of the illness, and others. Most patients benefit from a long-term stay in a residential facility and from receiving several weeks to months of intensive inpatient care. Even after this treatment, maintenance requires ongoing outpatient care, often for the rest of a persons life.
The most effective treatment for schizophrenia is the combination of strategies that provides each individual with the greatest symptom relief, maximum restored function, and minimal side effects. This almost always includes medications and therapy, but good treatment can also include other treatments, support, and education.
What Causes Schizophrenia
There’s no one cause for schizophrenia. It does not happen because of poor parenting or a bad upbringing. Although stress can trigger or worsen symptoms, stress does not cause schizophrenia. Schizophrenia is a disorder of the brain. It most likely develops from a mix of factors that may include:
- A defect in certain chemicals in the brain that control thinking and understanding.
- The person’s genetic make-up
- A defect in how the brain forms a person’s personality.
Where To Find Treatment
If you experience symptoms of schizophrenia it is best to speak with your doctor. They may want to do blood work and run tests to make sure the symptoms are not being caused by another medical condition. From there you can meet with a psychiatrist or other qualified mental health practitioner to discuss what you are experiencing.
Keep in mind that you may need to be evaluated extensively to make sure that the diagnosis is accurate. This evaluation process involves meeting with you to talk about your experiences, as well as meeting with a spouse or other family members to gather collateral information.
Schizophrenia And Treatment With Antipsychotic Medication

The main choice in antipsychotic schizophrenia treatment is whether to use a first or second generation antipsychotic. Most often, the doctor will select a second-generation antipsychotic medication called an atypical antipsychotic. First generation antipsychotics are not normally the first choice to treat schizophrenia due to side effects that can severely affect body movements; however, those who do not respond to second-generation antipsychotics may respond to first-generation antipsychotics.
First generation antipsychotics are known to induce movement disorders in more than 1-in-3 patients and some of these movement disorders may be permanent, even after the medication is stopped. Movement side effects can include:
- Inner restlessness
- Tremor
- Involuntary and repetitive movements
First generation antipsychotics are also known to be related to high levels of prolactin in the blood, as well as a severe neurological side effect known as neuroleptic malignant syndrome . Blood tests are often required to check for possible problems with this type of schizophrenia treatment.
Atypical antipsychotic schizophrenia treatment is associated with weight gain as well as blood sugar and cholesterol issues. People on these medications can develop type 2 diabetes. Movement disorders can also occur with this type of schizophrenia treatment but they are far less prevalent.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
Schizophrenia is often diagnosed in a persons late teens through early 30s. Males tend to show signs of the disease a little earlier than females. Someone with schizophrenia may show some early signs of schizophrenia, such as cognitive troubles or difficulties with social interactions, years before a diagnosis is made.
While the symptoms of schizophrenia can sometimes be quite obvious and life-changing, diagnosing schizophrenia can often be difficult. The use of certain mind-altering drugs, such as LSD, can produce schizophrenia-like symptoms, for example.
Even more challenging is that many people with schizophrenia dont believe they have it or any other mental disorder. This not only means many people never get diagnosed in the first place, but that those who do begin treatment often stop taking medications or attending therapy because they insist they dont need it.
Diagnosing schizophrenia relies largely on the observation of symptoms over a period of months, while eliminating other potential causes of such symptoms such as a brain tumor, a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, or other separate mental disorder.
To be formally diagnosed with schizophrenia, a person must have at least two of the following symptoms, and they must persist regularly:
- delusions
- disorganized or catatonic behavior
- negative symptoms
Schizophrenia is sometimes divided into phases characterized by the presence and intensity of certain symptoms. The phases include:
What Can Family Friends And Partners Do To Help
Friends, relatives and partners have a vital role in helping people with schizophrenia recover and make a relapse less likely.
It is very important not to blame the person with schizophrenia or tell them to “pull themselves together”, or to blame other people. It is important to stay positive and supportive when dealing with a friend or loved one’s mental illness.
As well as supporting the person with schizophrenia, you may want to get support to cope with your own feelings. Several voluntary organisations provide help and support for carers.
Friends and family should try to understand what schizophrenia is, how it affects people, and how they can help. You can provide emotional and practical support, and encourage people to seek appropriate support and treatment.
As part of someone’s treatment, you may be offered family therapy. This can provide information and support for the person with schizophrenia and their family.
Friends and family can play a major role by monitoring the person’s mental state, watching out for any signs of relapse, and encouraging them to take their medication and attend medical appointments.
If you are the nearest relative of a person who has schizophrenia, you have certain rights that can be used to protect the patient’s interests. These include requesting that the local social services authority ask an approved mental health professional to consider whether the person with schizophrenia should be detained in hospital.
Want to know more?
Can Schizophrenia Be Prevented In Autistic Children
In short, there is no way to prevent schizophrenia.
People with autism do have a greater risk for developing the disorder. There is likely an environmental link for schizophrenia, however. As a result, there are some things that parents can do for autistic children to potentially decrease the odds for the second disorder occurring.
Early intervention for autism is vital to managing the symptoms of the disorder, improving functionality and quality of life, and minimizing the risk of a co-occurring mood or anxiety disorder, such as schizophrenia. Its important to keep stress levels low and emotions regulated.
Early intervention techniques teach children how to cope with stressors and keep themselves calm. This can prevent increased stress from becoming a risk factor for schizophrenia. If a child has undiagnosed autism, their symptoms may worsen, and they may experience added stress from not seeing a reason behind their symptoms.
The best thing to do is to be aware of your childs moods and habits. Alert your childs pediatrician immediately if you notice changes and suspect an issue.
Continue to be an advocate for your child to ensure the right diagnosis is made and treatments are provided. Remember that the earlier you get an accurate diagnosis, the better the long-term prognosis for your child.
What About Hospital Care
Sometimes, visiting the hospital is the best option for helping you feel stable and recover from an episode of psychosis.
Staying in a hospital is common for many peoples first episode of psychosis. If your symptoms are severe, the hospital might become a familiar place where you can get help and start feeling better.
This might help when youre having severe delusions or hallucinations, are unable to care for yourself, or if theres a risk of harm to yourself or others.
If youve had a hospital visit, your doctor or therapist might change or adjust your medication and help you work out a crisis plan for the future. The hospital generally provides a medical evaluation and therapeutic interventions.
According to a 2019 study, having another condition such as a substance use disorder, bipolar disorder, or depression can make hospital visits more likely.
If youre not aware that your symptoms have become severe, which is relatively common during an episode of psychosis, a loved one or therapist might request that you get taken to hospital. Different U.S. states have different laws about involuntary hospital stays.
Most hospital stays are short term, from several days to several weeks. It depends on the severity of symptoms and your access to treatment outside the hospital.
Here are some ways you can help:
Looking for more? Check out these ways you can help a loved one with schizophrenia.
Start your search for a local support group at NAMI.