What Is A Personality Disorder
A personality disorder is a mental health condition that involves long-lasting, all-encompassing, disruptive patterns of thinking, behavior, mood and relating to others. These patterns cause a person significant distress and/or impair their ability to function.
There are 10 types of personality disorders, each with different characteristics and symptoms.
Personality is vital to defining who we are as individuals. It involves a unique blend of traits including attitudes, thoughts and behaviors as well as how we express these traits in our interactions with others and with the world around us.
Personality disorders may cause distorted perceptions of reality, abnormal behaviors and distress across various aspects of life, including work, relationships and social functioning. Additionally, people with a personality disorder may not recognize their troubling behaviors or the negative effect they have on others.
Explorative Analysis Of Change Of Bpd Symptoms
The total score of observer-rated BPD symptoms significantly decreased after 10 weeks with significant reductions in the subscales abandonment, impulsivity, affective instability, and a trend for emptiness . There was a statistical trend for a reduction of self-reported BPD symptoms after 10 weeks of CBASP . When controlling for change of MADRS, the reduction of impulsivity remained significant .
Thirty-nine out of 50 patients participated in at least one session of DBT skills training that may have contributed to a reduction of BPD symptoms. Patients that attended DBT skills training did not differ from patients without DBT skills training regarding MADRS, BDI-II, or BSL-23 at baseline . However, there was a trend that patients that participated in DBT skills training reported more BPD symptoms at baseline in the clinician-based interview . Furthermore, there was a trend that patients with DBT skills training showed a stronger BPDSI-IV reduction than patients without skills training .
Effective Treatment For Depressive Personality Traits
Major depressive disorder is a mental health condition characterized by the presence of several different symptoms that leave affected individuals in chronically depressed or melancholy moods. The presence of depressive personality traits can seriously diminish a persons sense of well-being, especially when these traits appear in combination with diagnosable major depression.
Many people who struggle with depression respond well to treatment with forms of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy and psychodynamic therapy. While CBT aims to address factors like harmful thought processes and assumptions that contribute to the issue, psychodynamic therapy works towards building a more total understanding of ones own thoughts and emotions. At Promises Behavioral Health, we offer both types of therapy as part of our depression treatment program. Contact us at today to find what combination of therapies best suits you and tackle depression on your own terms.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Phobia Of Snakes
What Are The Types Of Personality Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , which is the standard reference publication for recognized mental illnesses, organizes the 10 types of personality disorders into three main clusters . Each cluster has different symptoms in common.
Cluster A personality disorders
Cluster A personality disorders involve unusual and eccentric thinking or behaviors. These include:
- Paranoid personality disorder: The main feature of this condition is paranoia, which is a relentless mistrust and suspicion of others without adequate reason for suspicion. People with paranoid personality disorder often believe others are trying to demean, harm or threaten them.
- Schizoid personality disorder: This condition is marked by a consistent pattern of detachment from and general disinterest in interpersonal relationships. People with schizoid personality disorder have a limited range of emotions when interacting with others.
- Schizotypal personality disorder: People with this condition display a consistent pattern of intense discomfort with and limited need for close relationships. Relationships may be hindered by their distorted views of reality, superstitions and unusual behaviors.
Cluster B personality disorders
Cluster B personality disorders involve dramatic and erratic behaviors. People with these types of conditions display intense, unstable emotions and impulsive behaviors. Cluster B personality disorders include:
Cluster C personality disorders
Personality Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
Everybody is individual and behaves in unique ways, so it is only natural to not fit neatly into the categories described above.
If you experience some personality disorder traits but not enough to fully meet the criteria of a specific type, you may receive a diagnosis of personality disorder not otherwise specified .
This diagnosis may also be known as personality disorder trait specified . These names can sound like opposites, but they both focus on the fact that you have some personality disorder traits but not enough of one type.
Also Check: Which Of The Following Elevates The Risk For Developing Ptsd
How Do You Know If Someone Has A Personality Disorder
You cant know for sure if someone has a personality disorder unless they receive a professional, medical diagnosis.
Its important to understand the difference between personality types and personality disorders. A person who is shy or likes to spend time alone doesnt necessarily have an avoidant or schizoid personality disorder.
The difference between personality style and a personality disorder can often be determined by assessing how the persons personality affects different parts of their life, including:
- Behavior and impulse control.
Some general signs of people with a personality disorder include:
- Their behavior is inconsistent, frustrating and confusing to loved ones and other people they interact with.
- They may have issues understanding realistic and acceptable ways to treat others and behave around them.
- They may be unaware of how their behaviors cause problems for themselves and/or others.
- If theyre a parent, their parenting style may be detached, overemotional, abusive or irresponsible. This can sometimes lead to physical, emotional or mental issues in their children.
The Construct Of Personality
Before addressing the relation between personality and depression, several conceptual issues regarding the construct of personality should be considered. First, personality has traditionally been conceptualized as having two components: temperament, which refers to biologically based, early-emerging, stable individual differences in emotion and its regulation, and character, which refers to individual differences due to socialization. However, the distinctions between these constructs are questionable, as a large body of evidence has accumulated indicating that personality traits have all the characteristics of temperament, including strong genetic and biological bases and substantial stability over the lifespan . Hence, the terms personality and temperament are now often used interchangeably . As most research on personality in childhood has been conducted under the temperament rubric, in this review we refer to this work using the term temperament and reserve the term personality for discussing the literature on adolescents and adults. However, this is intended to reflect traditional usage rather than a conceptually meaningful distinction.
Don’t Miss: What Percentage Of The World Has Depression
Treatment: Cbasp Inpatient Program
All participants underwent 10 weeks of multimodal CBASP treatment following the CBASP manual , modified for an inpatient setting . The CBASP program included two individual sessions per week , two group sessions per week , mindfulness training , group physical therapy and occupational therapy . In addition, patients had regular medical rounds by the attending physician as well as the senior physician and a weekly nurse-patient encounter . The whole team received regular CBASP trainings and supervision . One psychotherapist was a certified CBASP therapist , the rest of the team were at an advanced psychotherapy and CBASP training stage with weekly supervision.
Patients received algorithm-based psychopharmacological treatment following national guidelines for depression . Table 1 presents medication rates on admission and discharge.
Table 1. Frequency and percentage of prescribed drugs on admission and discharge and mean number of prescribed psychotropics for CBASP dropouts medication at the date of dropout is reported.
Furthermore, a specifically trained nurses’ team offered an optional weekly group skills training based on the Dialectical Behavioral Therapy manual by Bohus and Wolf-Arehult . The DBT skills training included sessions on mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation and interpersonal effectiveness. For each patient, the number of participated group sessions was assessed. Skills group dosage ranged from 0 to 10 sessions.
Variations On A Theme: The Ten Personality Disorders
The APA currently cites ten distinct personality disorders, listing them into three clusters:
- Cluster A: The odd cluster, includes three personality disorders that evoke strikingly or eccentric behavior:
- Paranoid Personality Disorder: Distrustful of others and tends to believe those around them want to take advantage of them.
- Schizoid Personality Disorder: Limited emotional expression and social interaction.
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder: Extremely eccentric and struggles to navigate relationships. At times also experiences reality distortions.
- Cluster B: The dramatic cluster, includes four personality disorders that induce unpleasant emotionality and erratic behavior:
- Antisocial Personality Disorder: Tends to disregard rules and others safety, while feeling comfortable carrying out deceitful behavior.
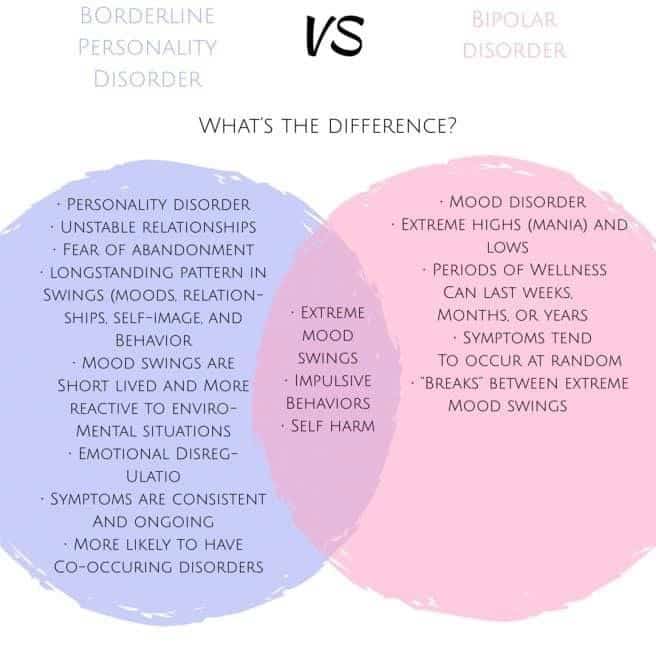
- Borderline Personality Disorder: Defined by impulsivity, unstable relationships, and significant insecurity. Women compose 75% of those with this condition.
- Histrionic Personality Disorder: Defined by extreme attention-seeking, emotionality, and being impressionable.
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder: Marked by a great deal of loneliness. a lack of empathy, and self-involvement, with a constant need for admiration.
Read Also: What Part Of Brain Does Schizophrenia Affect
What Types Of Personality Disorder Are There
Currently psychiatrists tend to use a system of diagnosis which identifies ten types of personality disorder. These are grouped into three categories.
Suspicious:
Each personality disorder has its own set of diagnostic criteria. To get a specific diagnosis you must meet some of these criteria. The minimum amount you need to meet is different for different types, but it should always be more than one or two. If you meet criteria for more than one type this may be called mixed personality disorder.
It is also possible to get a diagnosis without meeting the full criteria for a specific type. This is known as personality disorder not otherwise specified or personality disorder trait specified.
A wide range of people may get the same diagnosis, despite having very different personalities and different individual experiences. Your experience of living with a personality disorder will be unique to you.
When And Why Personality Disorders Occur
Personality disorders typically emerge in adolescence and continue into adulthood.
They may be mild, moderate or severe, and people may have periods of “remission” where they function well.
Personality disorders may be associated with genetic and family factors. Experiences of distress or fear during childhood, such as neglect or abuse, are common.
Don’t Miss: How To Help A Dog With Severe Separation Anxiety
Cluster A Personality Disorders
A person with a cluster A personality disorder tends to have difficulty relating to others and usually shows patterns of behaviour most people would regard as odd and eccentric. Others may describe them as living in a fantasy world of their own.
An example is paranoid personality disorder, where the person is extremely distrustful and suspicious.
How Effective Is Depressive Personality Treatment
The researchers at Lund University examined the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy and psychodynamic therapy as treatment options for people with depressive personality traits. They concluded that these two forms of psychotherapy produce significant treatment benefits, even in cases that combine depressive personality characteristics with the symptoms of diagnosable major depression, minor depression, or dysthymia. In fact, in contrast to the researchers expectations at the beginning of their examination, people with depressive traits benefit from CBT and psychodynamic therapy just as much as people with various mental health problems who do not have depressive personalities.
Recommended Reading: Does Bipolar Skip A Generation
The Case Of The Depressive Personality Disorder Category
The APAs 1968 edition of its mental health guidebook, the DSM-II, included a diagnosis of depressive personality disorder. The disorder has gone through a rather volatile recognition process of its own: after being removed from the DSM-III in 1980, it was included in 2000 in one of the DSM-IVs appendixes, which stated its validity should be further discussed. The current DSM-V has once again removed the depressive personality disorder from its pages, demonstrating the fluctuating dynamics that shape each generations perception of mental health. Rather than discard the diagnosis completely, it can contribute to a richer understanding of cases where the individuals mental health status seems to be built around a deep moroseness that defines their very character.
Depressive personality disorder was defined through its pervasiveness. For the diagnosis to had been considered, feelings of gloom, guilt, and worry, as well as beliefs of inadequacy and worthlessness, had to have appeared at different periods of the individuals life, starting from early adulthood.
The persistence of such depressive features had caused mental health professionals to state that in essence, the definition of depressive personality disorder is not significantly different than that ofpersistent depressive disorder, otherwise known as dysthymia. Over time, this claim gained a good amount of traction, until in 2013, the diagnosis was indeed removed from the APAs manual.
Pdd And Comorbidity Assessment
On admission, a trained and supervised psychological research assistant assessed PDD and comorbid diagnoses with the German version of the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV . In addition to SCID-I, diagnostic criteria for PDD were assessed according to DSM-5, as the German version of the DSM-5 preceded the publication of SCID-5-CV and was already available at the beginning of the study. Since its publication in 2019, the respective German interviews for DSM-5 were used. BPD criteria were rated for each participant even in the absence of BPD symptoms in the screening questionnaire.
Alongside the categorial assessment of a BPD diagnosis, SCID-II already allowed to calculate a dimensional score by summing up the scores of the nine BPD criteria . SCID-5-PD also offers the possibility to take subthreshold criteria into account and to characterize BPD features in more detail. However, answers are rated differently . As the diagnostic criteria for BPD have not changed from DSM-IV to DSM-5, we transformed SCID-II ratings to match SCID-5-PD scores. Consequently, the reported dimensional BPD score ranges between 0 and 18.
Don’t Miss: Why Is Schizophrenia More Common In Urban Areas
Dynamic Models Of Personality
Similarly, the predisposition model can be expanded to recognize personality change. This dynamic predisposition model acknowledges transactions between personality and the environment and integrates them with the environmental moderation and mediation mechanisms of the classic predisposition model. In the environmental moderation version of this account, negative life experiences influence not only depression onset but also levels of trait vulnerability . This increase in personality liability may then lead to additional life stress. If this vicious cycle is perpetuated unchecked, personality liability would continue to increase, and at some point, a negative life event could overwhelm coping capabilities and elicit a depressive disorder. Importantly, and in contrast to the dynamic precursor model, in this account maladaptive traits alone are not sufficient to cause depression, and an environmental trigger is necessary.
The vicious cycle of increasing trait vulnerability and stress exposure does not necessarily indicate that personality per se influences depression onset. Indeed, certain traits may increase stress exposure but have no effect on depression otherwise , consistent with the environmental-mediation pathway.
Depressive Personality History In Dsm
The DSM system has undergone substantial changes in the way that it has addressed the depressive personality construct in its history. Prior to the multiaxial system introduced in DSM-III, DSM-I and DSM-II considered any depressive reaction as a type of neurosis or one of the symptoms of a personality disturbance. In DSM-I, depressive personality disorder per se was not listed. Rather, any pattern of depression
Recommended Reading: What Is The Phobia Of Throwing Up
Cluster B: Emotional And Impulsive
- Antisocial personality disorder. People with antisocial personality disorder tend to manipulate or treat others without expressing remorse for their actions. They may engage in dishonest behavior like lying and stealing, and they may be prone to heavy alcohol and drug use.
- Borderline personality disorder. People with borderline personality disorder often feel empty and abandoned, regardless of family or community support. They may have difficulty dealing with stressful events and have episodes of paranoia. They also tend to engage in risky and impulsive behavior, such as binge drinking and gambling.
- Histrionic personality disorder. People with histrionic personality disorder frequently try to gain more attention by being dramatic or provocative. They may be easily influenced by other people and are sensitive to criticism or disapproval.
- Narcissistic personality disorder. People with narcissistic personality disorder often believe that theyre more important than others. They tend to exaggerate their achievements and may brag about their attractiveness or success. Other symptoms include a deep need for admiration but lack empathy for other people.
The Types Of Treatment For Depression
There are several types of treatment for depression. An experienced mental health professional can determine the treatment option that best suits your needs. The following are just a few examples of the therapy options that may be included in your treatment plan:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy Participants in cognitive-behavioral therapy learn how to identify false, damaging, or dysfunctional mental reactions that adversely affect their judgment during moments of everyday or extraordinary stress. They also learn how to replace those harmful reactions with alternatives that increase their sense of well-informed judgment and secure well-being. Depending on the individual, a psychotherapist can conduct CBT in a group, one-on-one, or family-centered setting. Whatever the setting, the therapy is usually conducted for anywhere from 10 to 20 separate sessions.
- Psychodynamic therapy Participants in psychodynamic therapy learn how to identify past relationships, behaviors, or conflicts that contribute to current poor decision-making during moments of everyday or extraordinary stress. According to the tenets of the therapy, this kind of self-investigation frees the individual from the need to react in ways that produce mental harm. The theories underlying the psychodynamic approach go all the way back to some of the original ideas of psychoanalysis, first established in the early 20th century.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get A Waiver For Depression In The Military
How Are Personality Disorders Treated
Personality disorders are usually treated with psychological treatments or talking therapies. Below we explain more about the different types of therapies.
Treatment can help you to be able to have a meaningful life or cope better with your condition.
The options for treating personality disorders are continuously developing.
You and your doctor or healthcare team should agree on a treatment plan that works best for you.
If your GP feels you have a complex personality disorder, they may refer you to a:
- an NHS community mental health team, or
- a specialist NHS personality disorder service if there is one locally.
You can search on the internet to see if theres a specialist NHS personality disorder service locally. Use a search term like NHS personality disorder service .
These services are made up of professionals such as psychologists, psychiatrists, and therapists. They will have experience in helping people with personality disorders. Sometimes you can contact these services yourself to get help.
Its always worth asking why a certain treatment is being offered. And if there are other things that could help you to get better.
When thinking about what treatment to offer you professionals should consult guidelines NICE guidelines, if relevant. NICE stands for The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. The NICE guidelines recommend treatment for conditions.
For personality disorders NICE only have guidelines for:
You can find these online, at the links below: