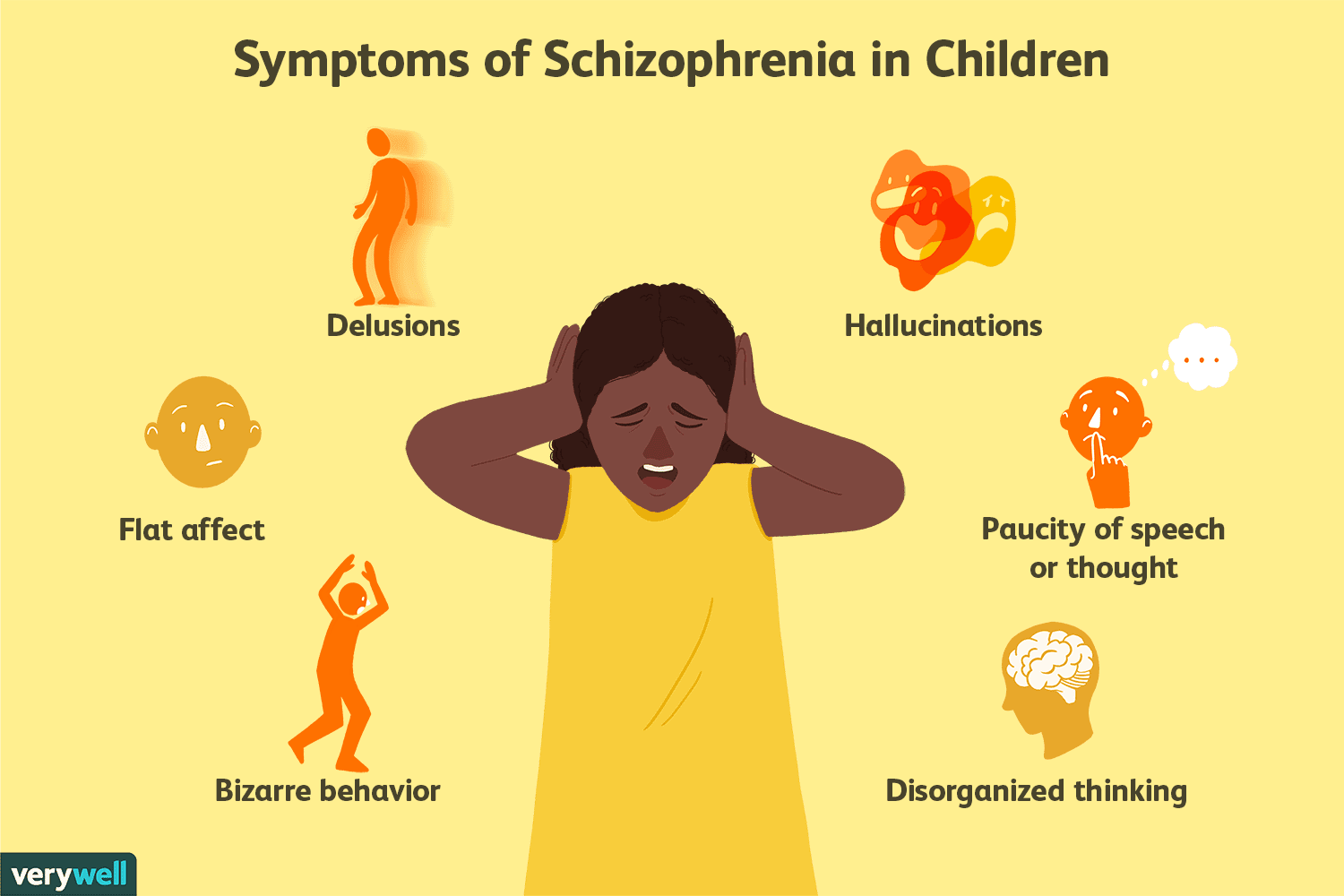
The Most Common Early Warning Signs Include:
While these warning signs can result from a number of problemsnot just schizophreniathey are cause for concern. When out-of-the-ordinary behavior is causing problems in your life or the life of a loved one, seek medical advice. If schizophrenia or another mental problem is the cause, getting treatment early will help.
Inflammation And Immune Function
Immune function is disturbed in schizophrenia. Overactivation of the immune system may result in overexpression of inflammatory cytokines and subsequent alteration of brain structure and function. For example, schizophrenic patients have elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines that activate the kynurenine pathway, by which tryptophan is metabolized into kynurenic and quinolinic acids these acids regulate NMDA receptor activity and may also be involved in dopamine regulation.
Insulin resistance and metabolic disturbances, which are common in the schizophrenic population, have also been linked to inflammation. Thus, inflammation might be related both to the psychopathology of schizophrenia and to metabolic disturbances seen in patients with schizophrenia.
Affective Symptoms In Fep And Suicide
Depressive symptoms in the prodromal phase of schizophrenia were frequently associated with suicidality during the following 12months of outcome . In particular, depressive symptoms are associated with lifetime as well as current risk for suicidal behaviors with higher rates of depression after the first episode and any relapse of psychosis .
Many authors point out that, in FEP patients, depression and suicidal behavior may be a reaction to the perceived persecutors and entrapment . Some other authors found that hopelessness was associated with suicidal ideation in FEP individuals and this symptom predicted suicidal ideation .
It has also been hypothesized that suicidality in FEP may be linked to patients altered basic self-awareness or sense of self, called self-disorders: there is a clear association between current suicidality and self-disorders, which appears to be connected by depressive states . Previously, Skodlar et al. and Skodlar and Parnas suggested that the effect of self-disorders on FEP was connected to specific feelings of inferiority and loneliness, and these feelings were different from usual feelings of low self-esteem or loneliness, since they are characterized by being profoundly dissimilar to other people.
Early intervention on depression in FEP is crucial to minimize suicidal ideation and attempts, particularly, in the first years of illness, which seem to be consistently characterized by high risk of suicide .
Read Also: A Person With Catatonic Schizophrenia Is Most Affected In
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often appear several years before somebody experiences their first acute schizophrenic episode.
These initial negative symptoms are often referred to as the prodromal period of schizophrenia.
Symptoms during the prodromal period usually appear gradually and slowly get worse.
They include the person becoming more socially withdrawn and increasingly not caring about their appearance and personal hygiene.
It can be difficult to tell whether the symptoms are part of the development of schizophrenia or caused by something else.
Negative symptoms experienced by people living with schizophrenia include:
- losing interest and motivation in life and activities, including relationships and sex
- lack of concentration, not wanting to leave the house, and changes in sleeping patterns
- being less likely to initiate conversations and feeling uncomfortable with people, or feeling there’s nothing to say
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often lead to relationship problems with friends and family as they can sometimes be mistaken for deliberate laziness or rudeness.
What To Do If You See Early Signs Of Schizophrenia In Someone
If you see someone else exhibiting early signs of schizophrenia, you may want to recommend that they get in for proper psychological evaluation. If they do have schizophrenia or some other condition, most professionals will be able to tell what is going on.
Treatment for the condition as soon as possible is associated with better functioning in society and a more favorable prognosis. If the individual has a family history of schizophrenia and they are showing the early warning signs and symptoms, it is likely that they are developing the same condition as there is a genetic link.
Most people with the early warning signs of schizophrenia are not aware of their condition. It typically takes outside intervention for someone to realize that what they are experiencing is in fact a mental illness. This is because all the symptoms that they are experiencing seem so real to them. Although the onset of these symptoms may be sudden or abrupt, the majority of people show a slow, gradual onset of these early signs.
Also Check: Schizophrenia Expected Findings
Early Signs Of Schizophrenia: The Warning Symptoms To Understand
The early signs of schizophrenia typically happen in the late teen years, and or in someones early adulthood. In many cases, they are pretty tough to spot unless you are very familiar with the illness. Another reason that it can be difficult to spot early warning signs of the illness has to do with the fact that teenagers experience a variety of mood swings and eccentric behavior.
In general, men tend to show warning signs of schizophrenia earlier than women, but theres really no set age for illness onset. The period before actual symptoms of schizophrenia symptoms appear is known as the prodromal phase. During this time a doctor or professional may diagnose someone as exhibiting signs of premorbid schizophrenia if they think that the condition may develop.
Sometimes an antipsychotic medication may be prescribed in order to delay the onset of symptoms. The prodromal phase typically lasts anywhere from 2 to 5 years before full blown schizophrenia develops. In men these signs typically appear from age 20 to 25 and in women from age 25 to 30. Unfortunately although we do not know what causes schizophrenia, there is documentation of many common early signs that someone may be developing this illness.
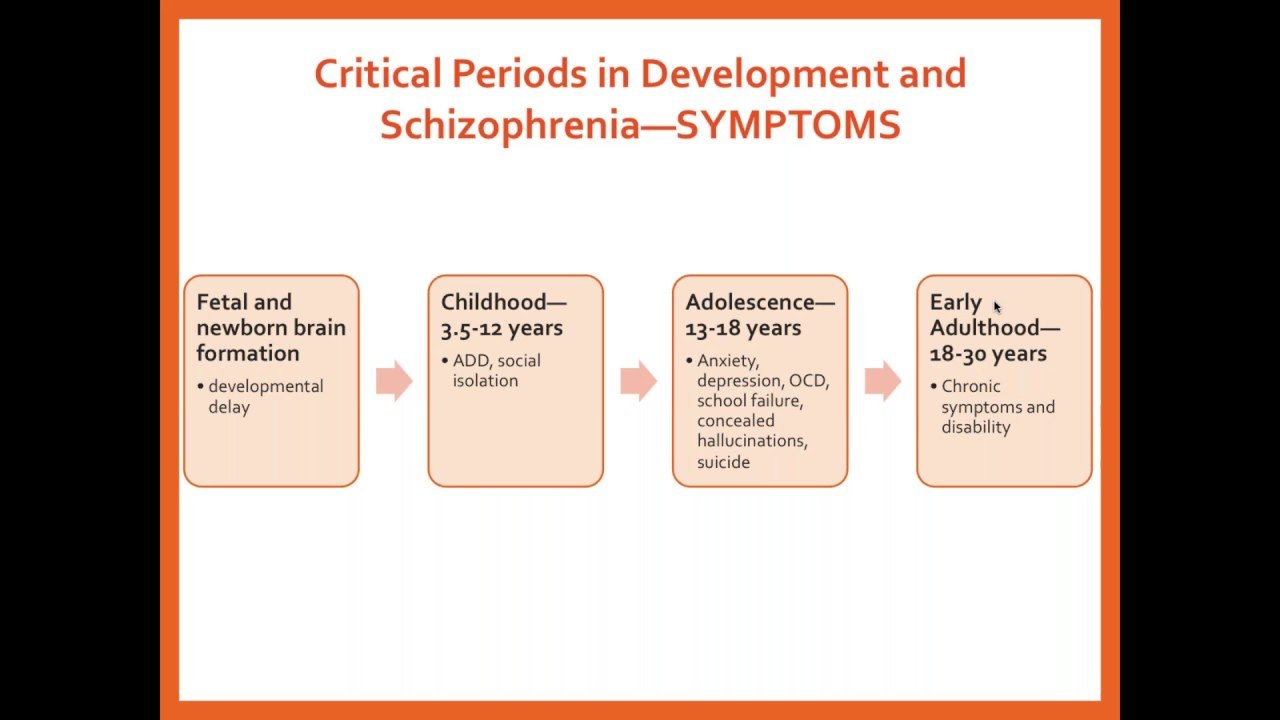
Phases Of Schizophrenia: Prodromal Active And Residual
People in the prodromal phases often isolate themselves, stay alone in their bedroom a lot and stop spending time with family or …
Schizophrenia – Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment – WebMD
The Schizophrenia are described in terms of the patient’s reaction to his symptoms and disabilities: anxiety, denial, ambivalence, depression and …
Stages of the clinical course of schizophrenia – Semantic Scholar
Both theories make a theoretical premise for creating the staging model for phases in the development of a schizo-.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Changes In Behaviour And Thoughts
A person’s behaviour may become more disorganised and unpredictable.
Some people describe their thoughts as being controlled by someone else, that their thoughts are not their own, or that thoughts have been planted in their mind by someone else.
Another feeling is that thoughts are disappearing, as though someone is removing them from their mind.
Some people feel their body is being taken over and someone else is directing their movements and actions.
Subthreshold Psychotic Experiences And Suicide In Schizophrenia
In the last decades, the research highlighted the importance of early intervention of FEP in order to reduce the DUP. Longer DUP, in fact, is associated with poor outcome in schizophrenia with higher prevalence of suicidal behaviors . A Norwegian study showed that, in the early phases of FEP, 38.8% of patients reported suicidal ideation and 25.9% attempted suicide before any treatment .
Authors from the Bonn School suggested the classification of basic symptoms of psychosis, which are subtle, subclinical, and detectable at an early stage such as distressing self-experienced disturbances in perception, thinking, memory, motility, mood, sense of awareness, and mastering . Authors underline the importance of detecting these symptoms in the early stage of psychosis to reduce the period of untreated illness .
A new psychopathological framework called attenuated psychosis disorder concerning subthreshold psychotic symptoms in youths was included in the Section 3 of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition, as a new putative disorder. The criteria specify that symptoms of APS are sufficiently distressing to call for clinical attention and very helpful to identify young people at risk for psychosis.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Diagnosis & Classification Of High
In an attempt to better categorize the prodromal period of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, and to elucidate the process of change or deterioration that represents a deviation from an individuals previous experience or behavior, researchers have proposed several diagnostic and classification systems for individuals at high risk of developing a psychotic disorder .
The Personal Assessment and Crisis Evaluation clinic in Melbourne, Australia, was the first to develop a standardized classification of prodromal syndromes, which they referred to as the ultra-high-risk states. Risk factors such as age, family history of psychosis and symptom scores were combined in a multifactorial index of risk . From this work came the creation of the CAARMS, which takes into account the intensity, frequency and duration of emerging positive symptoms, as well as declines in functioning. Help-seeking individuals between the ages of 14 and 29 years are categorized as UHR if they experienced APS during the past year, experience brief limited intermittent psychotic symptoms , and/or have schizotypal personality disorder or a family history of psychosis in concert with a significant decrease in functioning during the past year.
United States And International Statistics
The lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia has generally been estimated to be approximately 1% worldwide. However, a systematic review by Saha et al of 188 studies drawn from 46 countries found a lifetime risk of 4.0 per 1000 population prevalence estimates from countries considered least developed were significantly lower than those from countries classed as emerging or developed. Immigrants to developed countries show increased rates of schizophrenia, with the risk extending to the second generation.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
The Second Phase Is The Acute Phase
This is the stage when characteristic psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions and very odd or disorganized speech or behaviours emerge and are most noticeable. The experiences are often very distressing for the person. It is during this phase when appropriate treatment for psychosis needs to be started as soon as possible.
Development And Growth Of Ei
EI programs were first established in Melbourne, Australia and Buckinghamshire in the UK in mid-1980s and then extended to Birmingham , Germany, USA, Canada, Scandinavia in early 1990s, Switzerland in mid-1990s, Amsterdam and Australia in late 1990s. In 1999/2000, EI in UK received a major boost following extensive funding from NHS. By 2001, it had spread to Far East and South East Asia.
EI-EP service-models: There are three models of EI-EP service delivery.
Enhancing existing community mental health teams CMHT.
‘Hub and spoke’ model: The hub is a central specialist service which supports mainstream services by providing specialist input into individual cases.
Standalone early intervention service
The advantages and disadvantages of each are summarized in .
Don’t Miss: Schizophreniform Vs Brief Psychotic Disorder
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
Molecular PsychiatryDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth EditionDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text RevisionIndian Journal of PsychiatryPsychiatric ServicesClinical Child Psychology and PsychiatryPsychiatric TimesFrontiers in PsychiatryPsychiatry ResearchJournal of the American Medical AssociationBritish Journal of PsychiatryAmerican Academy of Social Work and Social WelfareScience DailyClinical NeuropsychiatryCurrent Antipsychotics, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 212Molecular PsychiatryPsychiatria DanubinaSchizophrenia BulletinBritish Journal of PsychiatryScienceSocial Studies of ScienceThe British Journal of PsychiatryAmerican Journal of PsychiatryPatient CareAm J PsychiatryMen and MasculinitiesHistory of PsychiatrySchizophrenia Research TreatmentGerman Journal of PsychiatryLancetPsychiatric ServicesCurrent Opinion in PsychiatryEpidemiologic ReviewsPsychiatric ServicesNeuropsychopharmacology: The Fifth Generation of Progress, Fifth EdClinical Schizophrenia and Related PsychosesPsychological BulletinSchizophrenia ResearchClinical TherapeuticsHarvard Mental Health LettAmerican Journal of PsychiatryAmerican Journal of PsychiatrySchizophrenia BulletinJournal of PsychopharmacologySchizophrenia BulletinAmerican Journal of PsychiatryPsychiatric TimesSchizophrenia BulletinAutismAmerican Journal of Psychiatry
Duration Of Untreated Psychosis
It is a topical and popular yet elusive concept. It denotes the time from manifestation of the first psychotic symptom to onset of antipsychotic treatment. However, it is limited by the absence of consensus about onset of psychosis or treatment and recall bias.
The interpretation of the term psychotic symptoms” may vary from any psychotic symptom to specified symptoms as measured by a scale while onset of treatment is defined variously as admission to a hospital, effective antipsychotic treatment or adequate period of treatment .
Several studies have reported association between longer DUP and worse outcome at 6 months in terms of total symptoms, overall functioning, positive symptoms, and quality of life in patients with schizophrenia. Patients with a long DUP were significantly less likely to achieve remission.
Given its relationship with outcome, DUP assumes significant public health importance as it is a potentially modifiable prognostic factor. It also has implications for understanding the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and may indicate toward a neurodegenerative process. However, the evidence in this regard is inconsistent.
Structured assessment of DUP can be done by diagnostic tools like interview for the retrospective assessment of the onset of schizophrenia , Royal Park multidiagnostic instrument for psychosis, and Nottingham onset schedule.
Read Also: What Does The Suffix Phobia Mean
Know The Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Most parents and families never imagine their child or loved one will develop a psychotic mental illness, so they dont know to look for early signs. All families should take unusual symptoms and behavioral changes seriously, but those with risk factors should be especially careful. Risk factors include:
- A family history of schizophrenia or another form of psychosis
- Major life stresses or trauma, such as homelessness, abuse, or assault
- Use of hallucinogenic drugs
- Certain pregnancy complications such as malnutrition or exposure to viruses, especially in the first and second trimesters
Schizophrenia does not have a single cause or a gene that triggers its onset, although it does tend to run in families. Most likely, schizophrenia occurs when there is a combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers that culminate in symptoms.
Incidence Of Suicide In Fep
A British 10-year follow-up study showed that subjects affected by FEP have died from unnatural causes more than general population . Suicide was recognized to be the cause of these deaths, and most of the suicides occurred in the first 2years . According to the available evidences on rates of suicide in first-admission psychotic patients, 23% of these have already attempted suicide, and 15% attempted it before the hospitalization . Recently, some authors aimed to test the progress in the field of suicide prevention and described the change in a 20-year period of suicide risk among FEP schizophrenia patients belonging to the same catchment area. It was found that suicide risk decreased over the two decades with a reduction of suicide rate from 11.0 to 2.4% . These data may suggest that early intervention and therapy improve the suicidality among FEP patients, even if they may attempt suicide before their contact with any mental health service: in fact, mortality rates may be underestimated because of complete suicides committed before seeking professional help . In addition, the prevalence of deliberate self-harm behaviors before psychosis is about 18.4% .
You May Like: How To Cure Schizophrenia Permanently
What If I Am Not Happy With My Treatment
If you are not happy with your treatment you can:
- talk to your doctor about your treatment options,
- ask for a second opinion,
- get an advocate to help you speak to your doctor,
- contact Patient Advice and Liaison Service and see whether they can help, or
- make a complaint.
There is more information about these options below.
Treatment options
You should first speak to your doctor about your treatment. Explain why you are not happy with it. You could ask what other treatments you could try.
Tell your doctor if there is a type of treatment that you would like to try. Doctors should listen to your preference. If you are not given this treatment, ask your doctor to explain why it is not suitable for you.
Second opinion
A second opinion means that you would like a different doctor to give their opinion about what treatment you should have. You can also ask for a second opinion if you disagree with your diagnosis.
You dont have a right to a second opinion. But your doctor should listen to your reason for wanting a second opinion.
Advocacy
An advocate is independent from the mental health service. They are free to use. They can be useful if you find it difficult to get your views heard.
There are different types of advocates available. Community advocates can support you to get a health professional to listen to your concerns. And help you to get the treatment that you would like.
The Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Complaints
You can find out more about:
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
Also Check: Feretrophobia Definition
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
A diagnosis for schizophrenia is often first made in the active stage. This is when symptoms become most obvious. Other people may recognize the disordered thoughts and behavior patterns for the first time.
At that point, a doctor may work with friends and family members to understand when early symptoms began. Symptoms of the first phase are often not recognized until a person is in the active phase.
Once a diagnosis is made, a doctor will also be able to determine when the active phase is over based on symptoms and behaviors.
Where to Find Help
Advocacy organizations can help you find immediate help. They can also connect you with local resources that can help you find sustained, long-term treatment. These mental health resources include:
Most people with schizophrenia arent diagnosed until the second phase, once symptoms worsen and become more obvious.
At this point, treatment options include:
Where to Seek Emergency Care
If you or a loved one is experiencing suicidal thoughts or dangerous behaviors, seek emergency care:
- Dial 911 or your local emergency number
- Visit a hospital or emergency department