Whats The Difference Between Grief And Depression
Given that the primary symptom associated with depression is sadness, it can be easy to think of grief or bereavement as depression. But grief is a natural response to specific experiences, such as the end of a relationship or the death of a loved one. While you might feel regret or remorse, and you might withdraw from usual activities if you are experiencing grief, youre unlikely to feel the overwhelming sense of worthlessness, thoughts of self-harm or suicide, and other symptoms of depression. Another important difference is that in grief, painful feelings usually come in waves and are often mixed with positive memories.
American Family Physician
Neuroimaging Modalities In Depression
Table 1 contains the 26 articles that were selected and are divided by the type of neuroimaging modality and by brain regions studied in the respective article. One article used positron emission tomography and sMRI modalities, and the other were developed using only one modality. The imaging technic more focused on was fMRI , followed by PET and sMRI .
Table 1 Neuroimaging modalities in depression.
Personal Factors That Can Lead To Depression
Personal factors that can lead to a risk of depression include:
- family history depression can run in families and some people will be at an increased genetic risk. However, this doesnt mean that a person will automatically experience depression if a parent or close relative has had the condition.
- personality some people may be more at risk because of their personality, particularly if they tend to worry a lot, have low self-esteem, are perfectionists, are sensitive to personal criticism, or are self-critical and negative
- serious medical conditions these can trigger depression in two ways. Serious conditions can bring about depression directly or can contribute to depression through the associated stress and worry, especially if it involves long-term management of a condition or chronic pain
- drug and alcohol use can both lead to and result from depression. Many people with depression also have drug and alcohol problems.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Motivated When Depressed
Why Does A Major Depressive Disorder Change Your Brain
When you suffer from depression, your brain is physically changed. Research by the National Institutes of Health shows that you lose gray matter volume when you suffer from depression. This loss is caused by parts of your brain shrinking due to the hormone cortisol impeding the growth of your brain cells.
The more serious depression a person suffers, the more GMV they lose. Since GMV contains most of your neurons or nerve cells, slowed growth means that your cognitive capabilities are at risk of impairment.
Depressed Brains Work Differently
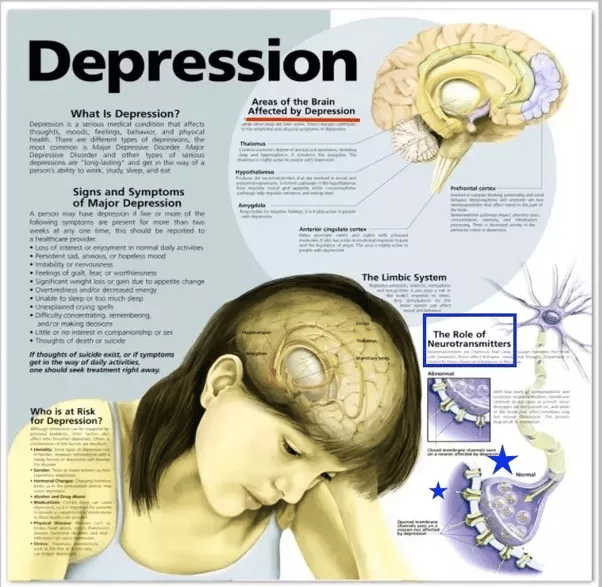
Brain imaging studies show that depression is not a character flaw or personal weakness. It is associated with biological changes in the brain. People with depression often have too much activity in the deep limbic systemthe brains emotional centers. But not everyone with depression has the same underlying brain patterns. Brain imaging has taught us is that there are 7 different brain patterns associated with depression, and knowing your type can be the key to getting the most effective treatment.
Read Also: What Kinds Of Depression Are There
Type : Cyclic Anxiety / Depression
Cyclic Anxiety/Depression is associated with extremely high activity in the brains basal ganglia and/or deep limbic system. These areas of excessive activity act like emotional seizures as the emotional centers hijack the brain for periods of time in a cyclical pattern. Cyclical disorders, such as bipolar disorder, cyclothymia, premenstrual tension syndrome, and panic attacks are part of this category because they are episodic and unpredictable.
Common symptoms of Cyclic Anxiety/Depression include 4 symptoms from Pure Anxiety and/or Pure Depression plus periods of time with at least 4 of the following:
- Abnormally elevated, depressed or anxious mood
- Grandiose notions, ideas or plans
- Increased talking or pressured speech
- Racing thoughts
- Delusional or psychotic thinking
Depression Is Different From Sadness Or Grief/bereavement
The death of a loved one, loss of a job or the ending of a relationship are difficult experiences for a person to endure. It is normal for feelings of sadness or grief to develop in response to such situations. Those experiencing loss often might describe themselves as being depressed.
But being sad is not the same as having depression. The grieving process is natural and unique to each individual and shares some of the same features of depression. Both grief and depression may involve intense sadness and withdrawal from usual activities. They are also different in important ways:
- In grief, painful feelings come in waves, often intermixed with positive memories of the deceased. In major depression, mood and/or interest are decreased for most of two weeks.
- In grief, self-esteem is usually maintained. In major depression, feelings of worthlessness and self-loathing are common.
- In grief, thoughts of death may surface when thinking of or fantasizing about joining the deceased loved one. In major depression, thoughts are focused on ending ones life due to feeling worthless or undeserving of living or being unable to cope with the pain of depression.
Grief and depression can co-exist For some people, the death of a loved one, losing a job or being a victim of a physical assault or a major disaster can lead to depression. When grief and depression co-occur, the grief is more severe and lasts longer than grief without depression.
You May Like: Can Anxiety Cause Tingling All Over Body
Type : Temporal Lobe Anxiety / Depression
Temporal Lobe Anxiety/Depression is related to too little or too much activity in the temporal lobes , in addition to overactivity in the basal ganglia and/or deep limbic system.
Common symptoms of Temporal Lobe Anxiety/Depression include 4 symptoms from Pure Anxiety and/or Pure Depression , plus at least 4 of the following:
- Short fuse or periods of extreme irritability
- Periods of rage with little provocation
- Often misinterpreting comments as negative when they are not
- Periods of spaciness or confusion
- Periods of panic and/or fear for no specific reason
- Visual or auditory changes, such as seeing shadows or hearing muffled sounds
- Frequent periods of déjà vu
- Sensitivity or mild paranoia
- Family history of violence or explosiveness
- Dark thoughts that may involve suicidal or homicidal thoughts
- Periods of forgetfulness or memory problems
Are The Changes Permanent
Scientists are still trying to answer that question. Ongoing depression likely causes long-term changes to the brain, especially in the hippocampus. That might be why depression is so hard to treat in some people. But researchers also found less gray matter volume in people who were diagnosed with lifelong major depressive disorder but hadnât had depression in years.
While more research is needed, thereâs hope that current or new treatments might help reverse or ward off some brain changes.
Hereâs what research says about two common depression treatments:
Antidepressants. These work on the chemicals in your brain that control stress and emotions. Thereâs evidence these drugs can help your brain form new connections and lower inflammation.
Cognitive behavior therapy . Experts think CBT promotes neuroplasticity. That means you can change your brain in a way that helps your depression.
Read Also: How Do You Tell If You Are Bipolar
What Are The Symptoms Of Dysthymia
Dysthymia is milder, yet more long lasting than major depression. Each person may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
- Lasting sad, anxious, or empty mood
- Less ability to concentrate, think, and/or make decisions
- Feeling hopeless
- Weight and/or appetite changes due to over- or under-eating
- Changes in sleep patterns, such as fitful sleep, inability to sleep, early morning awakening, or sleeping too much
- Low self-esteem
To diagnose this condition, an adult must have a depressed mood for at least 2 years , along with at least 2 of the above symptoms. The symptoms of this illness may look like other mental health conditions. Always talk with a healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Is There Such A Thing As A Depressed Brain
The brain is a magnificent organ about which we are still learning a lot. For example, scientists are still discovering how certain emotions affect the brain. Depression is one. The truth is that there will be times in your life when you will be depressed or sad, as well as personal events that will test you.
What happens to gray matter in the brain with depression?
There is growing evidence that several parts of the brain shrink in people with depression. Specifically, these areas lose gray matter volume . It is a tissue with many brain cells. GMV loss appears to be higher in people with regular or ongoing depression with severe symptoms.
What happens to the hippocampus in a depressed person?
The hippocampus is the part of the brain that regulates memory and emotions. The size of this structure has been found to decrease in people with chronic depression.
Also Check: How Likely Is Schizophrenia To Be Inherited
Treatments For Depression In The Brain
Below are the list of medications that can help with the imbalance of the chemicals in the brain due to depression:
· selective serotonin uptake inhibitor Alleviates depresseive symptoms by changing the levels of serotonin. e.g. citalopram , include fluoxetine , paroxetine ,
· tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-norepinephrine
reuptake inhibitors – Esed together, this will relieve depressive symptoms by changing the levels of norepinephrine and serotonin in the brain. These chemicals improved energy and mood. e.g., venlafaxine (Effexor
XR) and SNRIs include duloxetine and trimipramine and Imipramine
· norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake
inhibitors Increases levels of
the mood-boosting chemicals dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain of a person with major depressive disorder. e.g., Bupropion
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors Improves neuron communication and increases the amount of the brains serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.brain cell communication.
- atypical antidepressants this drug blocks communication between brain cell to calm the body. Some examples are mood stabilizers, antipsychotics and tranquilizers.
· Electroconvulsive Therapy Procedure used that boosts connection or communication between brain cells by passing electrical currents through the brain
· Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation A noninvasive treatment that regulates mood by sending electrical pulses sent through magnetic energy in certain regions of the brain responsible for mood control.
People With Depression Have A New Opportunity For Understanding Their Condition And Getting Helpful Treatments With The Technological Breakthrough Of Brain Scans
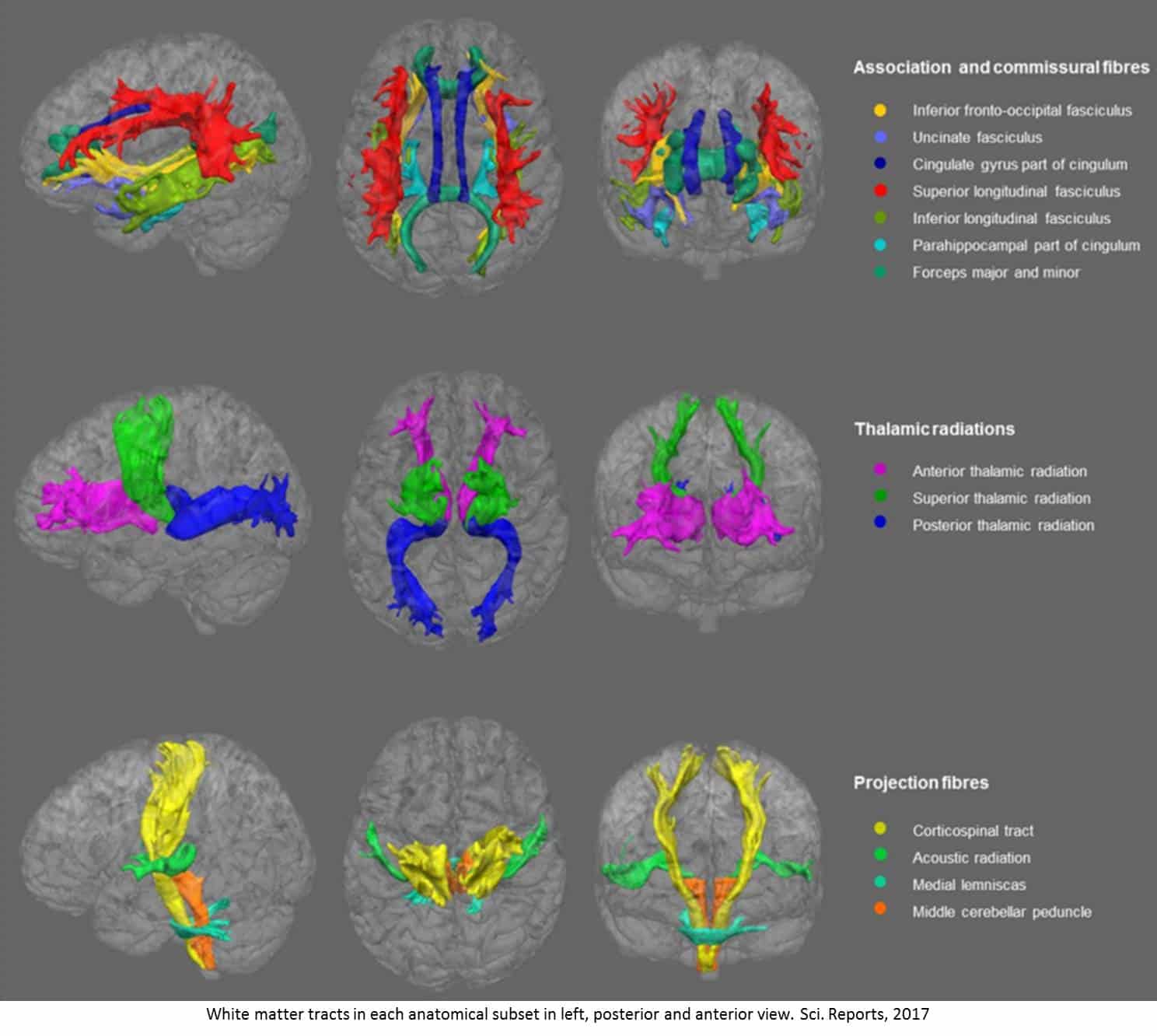
As experts look for new ways to better understand, diagnose and treat depression, they are increasingly turning to brain scans for guidance. Depression brain scans, including PET scans and MRIs for depression, can provide images of the brain of someone with depression or another mental health disorder.
You May Like: What’s The Phobia Of Heights
What Happens In The Brain With Depression
Depression causes the hippocampus to raise its cortisol levels, impeding the development of neurons in your brain. The shrinkage of brain circuits is closely connected to the reduction of the affected part’s function. While other cerebral areas shrink due to high levels of cortisol, the amygdala enlarges.
How Does A Brain Get Depressed
So, depression is attributed to a specific pattern of activated circuits in your brain and how theyre impacting each other, but how does this tendency take shape? There are many factors which contribute to forming depressive patterns:
Genetics Genes arent your destiny by any means, but they do guide the initial development of your brain circuitry. You can inherit a brain more thats more likely to become depressed. Research has determined that theres a genetic component to depression and that as much as 40% of people with depression have a genetic link. If a person has a parent or sibling that has had major depression, they are three times more likely to develop the condition which may be due to both hereditary and environment. Women have a 42 percent chance of hereditary depression, while men only have a 29 percent chance.
Early ChildhoodYour childhood experiences literally shape your brain. While genes supply the basic blueprint for brain development, experience tweaks brain circuitry, and young brains in a critical window of development are particularly sensitive. Stressful or traumatic events in childhood and adolescence dictate the development of neural circuitry and influence the levels of chemicals released in the brain having powerful and lasting effects. The prefrontal cortex of the brain doesnt finish maturing until a person is in their twenties and is susceptible to stress the whole time.
Luck Yes, randomness plays a part here. Korb writes:
Korb writes:
Recommended Reading: How To Deal With Bipolar Hypersexuality
What Does Loneliness Do To Someone
Loneliness can make a person feel alone, unwanted, empty, suicidal, helpless and worthless. Lack of self-esteem and self-care may also show due to the effects of depression. However, loneliness can make a person creative. There are a lot of brilliant people who suffer from depression who are successful in their career such as J.K. Rowling, Chester, Jim Carrey, Johnny Depp and Robin Williams.
Betterhelp: A Better Alternative
Those who are seeking therapy online may also be interested in BetterHelp. BetterHelp offers plenty of formats of therapy, ranging from live chats, live audio sessions and live video sessions. In addition, unlimited messaging through texting, audio messages and even video messages are available here.
BetterHelp also offers couples therapy and therapy for teenagers in its platform. Furthermore, group sessions can also be found in this platform, covering more than twenty different topics related to mental health and mental illness. The pricing of BetterHelp is also pretty cost-effective, especially considering the fact that the platform offers financial aid to most users.
Don’t Miss: How To Determine If You Have An Eating Disorder
How Does Depression Affect Brain Function
Reduced functionality of the hippocampus. This can cause memory problems. Reduced functionality of the prefrontal cortex. This can prevent the person from getting things done and affect their attention. Reduced functionality of the amygdala. It can directly affect mood and emotional regulation. develop.
What Does The Brain Look Like When Someone Is Depressed
Gray matter in the brain refers to brain tissue made up of cell bodies and nerve cells. People with depression have been shown to have thicker gray matter in parts of the brain involved in self-perception and emotions. This abnormality could contribute to a persons problems with depression in these areas.
Do you have brain damage from depression?
Depression not only makes a person sad and discouraged, but it can also permanently damage the brain so that the person has difficulty remembering and concentrating after the illness is over. Up to 20% of depressed patients never fully recover.
Can the brain repair itself after depression?
A depressed persons brain doesnt function normally, but it can recover, according to a study published in the Aug. 11 issue of Neurology, the scientific journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The researchers measured brain responsiveness using magnetic stimulation to the brain and targeted muscle movements.
What triggers depression in the brain?
Research suggests that depression doesnt simply stem from having too much or too little of certain brain chemicals. On the contrary, there are many possible causes of depression, including poor mood regulation by the brain, genetic vulnerability, stressful life events, medications, and medical conditions.
Read Also: Are People Born With Anxiety
Brain Imaging Identifies Different Types Of Depression
People may believe all cases of depression are the same, and that each person with depression has all the same symptoms and will respond similarly to all available treatments.
In reality, depression varies by symptoms displayed and symptom intensity. Treatment must be tailored to the type of depression for the best results.
Different types of depression may include:
- Depression with anxiety distress
- Depression with seasonal pattern
- Depression with melancholic features
According to Helen Mayberg, professor of psychiatry, neurology and radiology at Emory University School of Medicine,
All depressions are not equal and, like different types of cancer, different types of depression will require specific treatments. Using these scans, we may be able to match a patient to the treatment that is most likely to help them, while avoiding treatments unlikely to provide benefit.
To some extent, brain imaging can identify different types of depression according to the part of the brain affected. With the information compiled by numerous brain scans, researchers can find common themes in brain structure, brain function and mental health symptoms among people with depression.
Lifestyle Changes For Depression
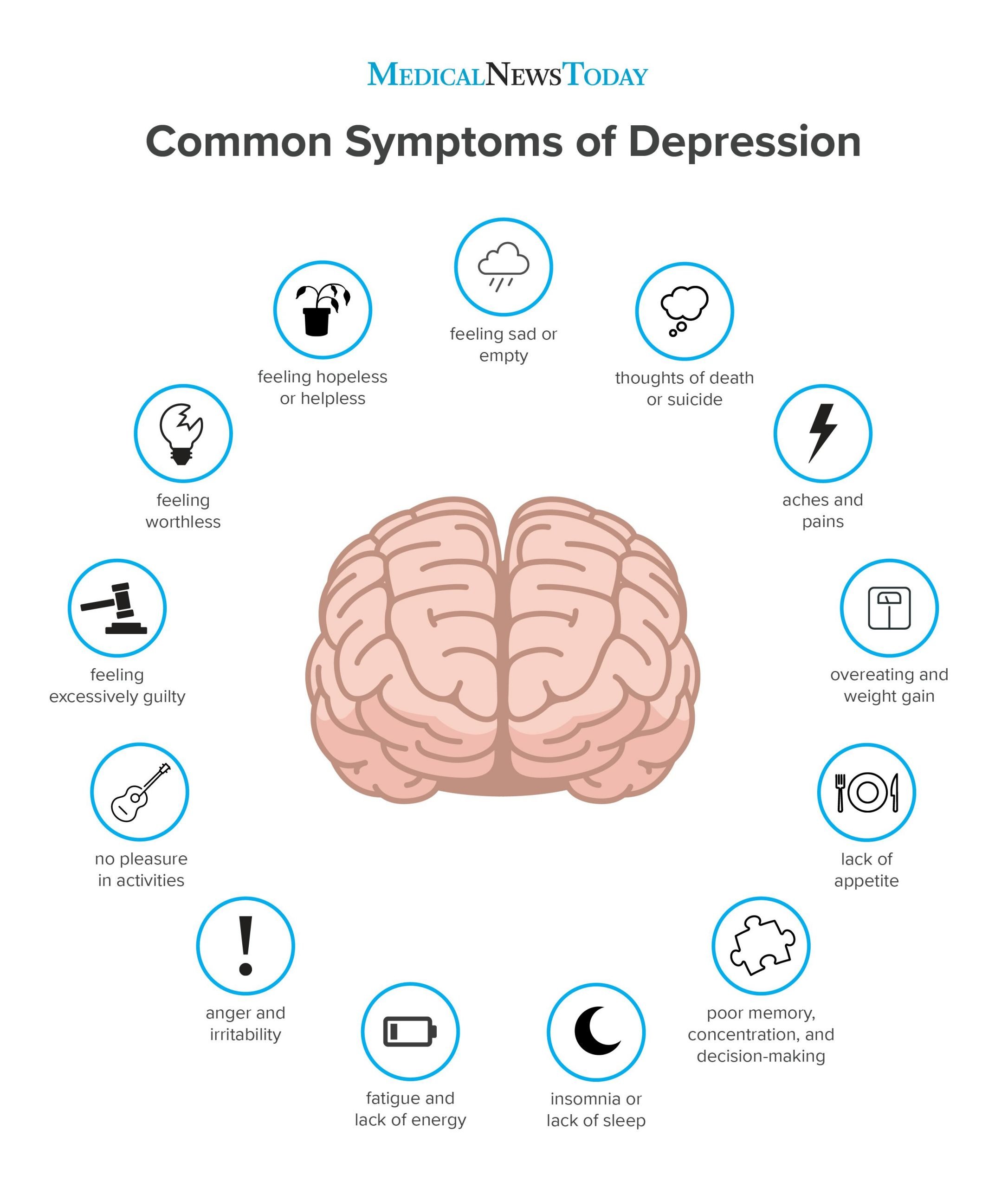
Lifestyle changes, such as making art, journaling, exercising more, and practicing yoga or mindfulness, can also alleviate depression and the stress that can heighten it. Alternative treatments like massage, acupuncture, and light therapy may also help.
Diet changes, too, can uplift your mood by reducing inflammation and helping to ensure your brain gets the nutrients it needs to function at its best.
PLoS One
You May Like: How Many Panic Attacks Is Normal
Signs And Symptoms: How To Identify Depression
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disordersdiagnosed with major depressive disorder
Do you:
- Constantly feel tearful, empty, or worthless?
- Have little interest or pleasure in your work, hobbies, friends, family, and other things you once enjoyed?
- Notice dramatic changes up or down in your appetite or your weight not related to dieting?
- Often feel listless or fatigued for no obvious reason?
- Have trouble concentrating or making decisions?
- Find yourself wringing your hands, pacing, or showing other signs of anxious restlessness or the opposite, moving or speaking more slowly than usual?
- Struggle with insomnia or sleep too much?
- Have recurrent thoughts of suicide or death?
To be diagnosed with MDD, one of your symptoms must be a persistent low mood or a loss of interest or pleasure, the DSM-5 states. Your symptoms must also not be due to substance abuse or a medical condition, such as thyroid problems, a brain tumor, or a nutritional deficiency.
Of course, its normal to have any or all of these symptoms temporarily from time to time. The difference with depression is that the symptoms persist and make it difficult to function normally.