What Your Doctor Will Look For
The manic episodes of bipolar disorder often last a long time. Typically, your symptoms will be strong enough to seem unusual and disrupt your daily life.
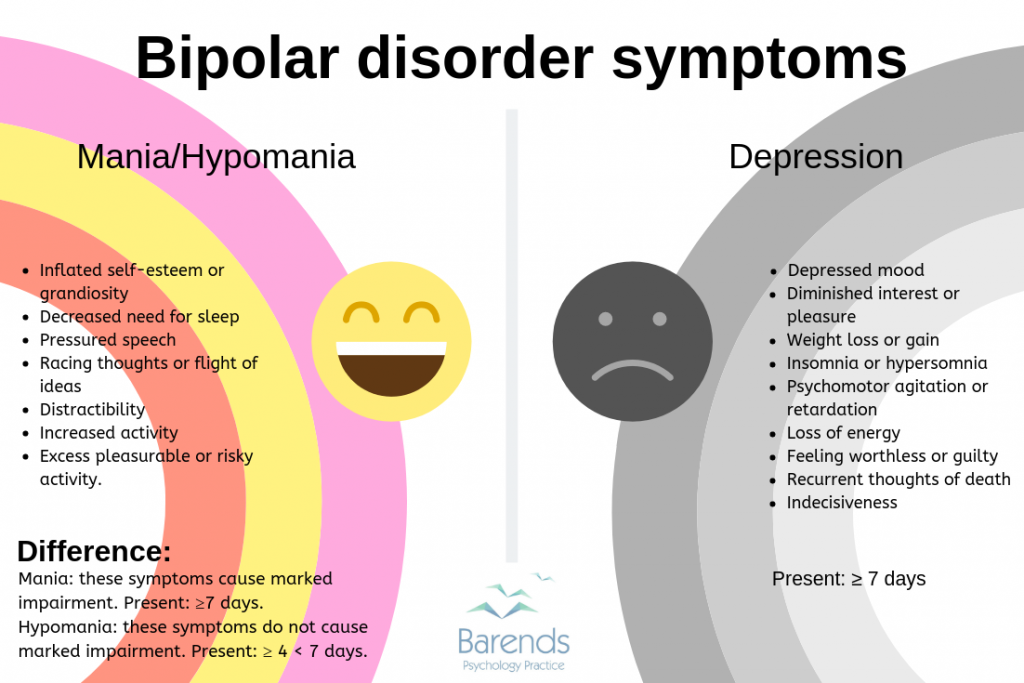
Symptoms of mania might include:
- Impulsive, high-risk behavior
- Unusually happy or outgoing mood
With bipolar disorder, you will also have depressive episodes. These symptoms are similar to depression:
- Change in eating habits, either not eating or overeating
- Change in sleep patterns
- Loss of interest in activities
- Thoughts of suicide or death
- Trouble concentrating
You can also have other symptoms. For instance, sometimes a person with bipolar disorder experiences a mixed state. This is when mania and depression are present at the same time. Someone with severe bipolar disorder may have psychotic symptoms. These include delusions or hallucinations.
What Is The Typical Age Of Onset For Bipolar Disorder
The average age of bipolar onset is around 25 years old, although it can vary.
Sometimes bipolar symptoms start in childhood or later in life. However, the most frequent range of onset is between the ages of 14 to 21 years.
Childhood bipolar is relatively rare, with only of children receiving this diagnosis.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health , about 4.4% of adults in the United States will experience bipolar disorder at some point in their lives. It affects men and women equally.
NIMH estimates that nearly 2.9% of adolescents those who are between 13 and 18 years old will experience bipolar disorder at some point, with the highest prevalence (
Despite common belief, bipolar disorder doesnt just occur in young people. In recent years, research has shown an increase in the diagnosis of late onset bipolar disorder .
According to a 2015 report from the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Task Force on Older-Age Bipolar Disorder , up to 25% of people with bipolar disorder are 60 years of age and older. Its estimated that between 5% and 10% of people start showing symptoms of bipolar disorder after the age of 50 years old.
People diagnosed with LOBD differ from those with early onset BD in several ways.
In addition, people with LOBD have vascular changes in their right brain hemispheres that have been
Who Is A Candidate For Diagnosis
Mood episodes are the main characteristic of bipolar disorder, and everyone experiences these a little differently. Most people who live with bipolar disorder experience manic episodes and depressive episodes .
These episodes can last for several days, weeks, or more. People with bipolar disorder tend to fluctuate rapidly between mania and depression. Some people with bipolar disorder have long periods of time with neutral moods as well.The way people experience manic episodes varies from one person to another, but the episodes are
Read Also: How To Recover From An Eating Disorder
Where Do I Go For Help
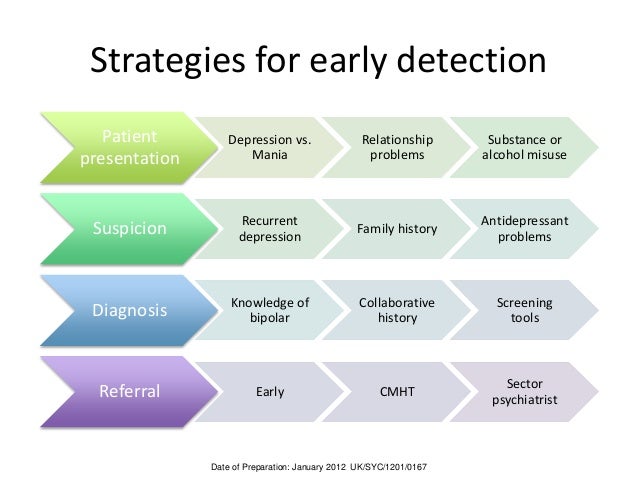
If youre not sure where to get help, your doctor, pediatrician, or other family health care provider is a good place to start. A health care provider can refer you to a qualified mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, who has experience treating bipolar disorder and can evaluate your childs symptoms.
You can learn more about getting help and finding a health care provider on the National Institute of Mental Health website. Hospital health care providers can help in an emergency. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has an online tool to help you find mental health services in your area.
Preparing For An Adult Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis
If you think you may have bipolar disorder, you can start by visiting a healthcare professional. They will likely do a physical examination, discuss your medical history, and ask you some basic questions about your symptoms, family history, and life experiences.
If your healthcare professional believes you may have bipolar disorder, they will probably refer you to a psychiatrist who will do a more detailed mental health evaluation. Some of the questions a psychiatrist may ask include:
- What symptoms are you experiencing?
- What are your thoughts and feelings like during a manic or depressive episode?
- Do you feel in control of your mania or how long an episode lasts?
- When did you first start experiencing these symptoms?
- Do you ever have suicidal thoughts or thoughts of self-harm?
- Do you have a history of substance misuse?
- Did anyone in your family have similar symptoms or a diagnosis of bipolar disorder?
They might also ask your permission to ask friends and family about your behavior.
The diagnosis for bipolar disorder requires at least one depressive and one manic or hypomanic episode. Any diagnosis will take into account other aspects of your medical history and the medications youve taken.
- emotional outbursts
- periods of sadness
- How often does your child have emotional outbursts?
- How many hours does your child sleep a day?
- How often does your child have periods of aggression and irritability?
Don’t Miss: What Is The Phobia Of Dogs Called
What Types Of Therapy Are Used To Treat Bipolar Disorder
Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, can be an effective part of the treatment plan for people with bipolar disorder.
Psychotherapy is a term for a variety of treatment techniques that aim to help you identify and change troubling emotions, thoughts and behaviors. Working with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, can provide support, education and guidance to you and your family.
Different types of therapy for bipolar disorder include:
Can Bipolar Disorder Go Away
Bipolar disorder tends to be seen as an ongoing condition that waxes and wanes throughout ones life, says Simon A. Rego, PsyD, Chief Psychologist at Montefiore Medical Center and Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City.
Fortunately, the symptoms can often be controlled and stabilized in most cases when proper treatment is in place, Rego says.
Don’t Miss: What Does Being Bipolar Mean
Information For Family Carers And Friends
How can I get support?
You can speak to your GP. You should be given your own assessment through NHS mental health services to work out what effect your caring role is having on your health. And what support you need. Such as practical support and emergency support.
These are some other options for you:
- Join a carers service
- Join a carers support group
- Ask your local authority for a carers assessment
- Read about the condition
- Apply for welfare benefits for carers
Rethink Mental Illness run carers support groups in some areas. You can also search for groups on the Carers Trust website:
- Rethink Mental Illness: www.rethink.org/about-us/our-support-groups
- Carers Trust: www.carers.org/search/network-partners
How can I support the person I care for?
You might find it easier to support someone with bipolar disorder if you understand their symptoms, treatment and self-management skills.
You should be aware of what you can do if you are worried about their mental state. It can be helpful to know contact information for their mental health team or GP.
You could find out from your relative if they have a crisis plan. You could help your relative to make a crisis plan if they dont have one.
As a carer you should be involved in decisions about care planning. But you dont have a legal right to this. The medical team should encourage the person that you care for to allow information to be shared with you.
You can find out more information about:
What Are Potential Results Of Screening For Bipolar
An estimated 2.8% of U.S. adults have been diagnosed with bipolar disorder. If left undiagnosed or untreated, the condition usually worsens, causing more problems with mood, energy and clear thinking.
If a diagnosis comes back as negative for bipolar, but you still experience symptoms, a health care professional may screen you for a similar condition such as schizophrenia or depression.
Getting a professional screening can start you on the path toward treatment, which can help improve your quality of life.
Also Check: What Is The Phobia Of Fire
What Happens After A Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis
You may experience a mix of emotions if you receive a bipolar disorder diagnosis, including shock and sadness, but also relief and hope. Bipolar disorder is considered a lifelong condition, but there are effective treatments available for you to live a full life.
Treatments for bipolar disorder include a combination of therapy and medication. Therapy options for bipolar disorder include:
What Is A Hypomanic Episode
A hypomanic episode is essentially a milder version of a manic episode. The mood and behavior changes seen in a hypomanic episode are not as extreme and they often do not last as long as a manic episode, although the emotional and behavioural changes are still definitely abnormal for the individual. Hypomanic episodes can feel more manageable than manic episodes and may not interfere so much with daily life, although other people may notice changes in the individuals behavior.
Also Check: What Kind Of Hallucinations Are Most Common In Schizophrenia
Whats The Difference Between Borderline Personality Disorder And Bipolar Disorder
While borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder have similar symptoms and are often confused for each other, theyre distinct conditions.
BPD involves a longstanding pattern of abrupt, moment-to-moment swings in moods, behavior and self-image that are often triggered by conflicts in interactions with other people. Nonsuicidal self-injury is also common in BPD but not in bipolar disorder.
Bipolar disorder is different from BPD because it involves distinct, longer-lasting episodes of mania/hypomania and/or depression. Several things can trigger manic or depressive episodes, such as sleep changes, stress, medications and substance use.
What If Im Not Happy With My Treatment
If you arent happy with your treatment you can:
- talk to your doctor about your treatment options,
- ask for a second opinion,
- get an advocate to help you speak to your doctor,
- contact Patient Advice and Liaison Service , or
- make a complaint.
There is more information about these options below.
How can I speak to my doctor about my treatment options?
You can speak to your doctor about your treatment. Explain why you arent happy with it. You could ask what other treatments you could try.
Tell your doctor if there is a type of treatment that you would like to try. Doctors should listen to your preference. If you arent given this treatment, ask your doctor to explain why it isnt suitable for you.
Whats a second opinion?
A second opinion means that you would like a different doctor to give their opinion about what treatment you should have. You can also ask for a second opinion if you disagree with your diagnosis.
You dont have a right to a second opinion. But your doctor should listen to your reason for wanting a second opinion.
What is advocacy?
An advocate is independent from the mental health service. They are free to use. They can be useful if you find it difficult to get your views heard.
There are different types of advocates available. Community advocates can support you to get a health professional to listen to your concerns. And help you to get the treatment that you would like. NHS complaints advocates can help you if you want to complain about the NHS.
Also Check: What Does Severe Depression Feel Like
Signs/symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
Individuals with this condition typically experience extremely intense emotional states that occur in what are referred to as mood episodes.
Each of these episodes is a drastic change from an individuals typical behavior and mood.
When an individual is overly excited or joyful, it is referred to as a manic episode. When an individual is extremely hopeless or sad, it is referred to as a depressive episode.
In some cases, a mood episode could include symptoms of depression and mania, this is referred to as a mixed episode. Individuals with this condition might also be very irritable and explosive during one of their episodes.
In addition, significant changes in activity, behavior, energy, and sleep accompany these mood changes.
Even in cases where the mood swings are not extreme, the individual could still have bipolar disorder.
In some cases, an individual with bipolar disorder experiences a condition known as hypomania, which is a form of mania.
During this period, the individual feels good, functions well, and is highly productive.
They dont feel that anything is wrong, but their loved ones might consider these moods as potential bipolar disorder.
Without getting the proper treatment, individuals with this condition are likely to develop more severe depression or mania.
This condition could also be present during a mixed state, where the individual experiences both mania and depression at the same time.
What Are The Side Effects Of Bipolar Disorder Medications
Side effects of bipolar disorder medications are common and vary by medication. Its important to talk with your healthcare provider about what you can expect when taking certain medications. Its also important to tell them if youre experiencing side effects.
Never stop taking your medication unless your healthcare provider tells you to do so. Abruptly stopping medication can cause severe side effects and trigger severe episodes.
The most common side effects of bipolar disorder medications include:
- Weight gain.
- Akathisia feelings of restlessness and agitation with a compelling need to move, rock or pace.
Also Check: What To Do When Someone With Ptsd Pushes You Away
Manic Symptoms In Children
Symptoms of mania in children can include:
- acting very silly and feeling overly happy
- talking fast and rapidly changing subjects
- having trouble focusing or concentrating
- doing risky things or experimenting with risky behaviors
- having a very short temper that leads quickly to outbursts of anger
- having trouble sleeping and not feeling tired after sleep loss
Diagnosing Bipolar Disorder In Adults
Bipolar disorder, also known as manicdepressive illness, is a medical condition that causes a person to experience intense mood swings that alternate between depression and mania. These mood swings can last for hours, days, or even weeks.
Mental health specialists at NYU Langone Psychiatry Associates, such as psychiatrists, psychologists, and licensed clinical social workers, can help determine if a person has bipolar disorder and, if so, how best to manage symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Can A Car Crash Cause Ptsd
Bipolar Disorder In Children And Teens
Diagnosing bipolar disorder in children is controversial, largely because children dont always display the same bipolar disorder symptoms as adults. Their moods and behaviors may also not follow the standards doctors use to diagnose the disorder in adults.
Many bipolar disorder symptoms that occur in children also overlap with symptoms of other conditions that commonly occur in children, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder .
However, in the last few decades, doctors and mental health professionals have come to recognize the condition in children. A diagnosis can help children get treatment, but reaching a diagnosis may take many weeks or months. It may be worth seeking care from a professional who specializes in treating children with mental health conditions.
Like adults, children with bipolar disorder experience extreme mood shifts. They can appear very happy and show signs of excitable behavior, or seem very tearful, low, and irritable.
All children experience mood changes, but bipolar disorder causes distinct and noticeable mood symptoms. Mood changes are also usually more extreme than a childs typical change in mood.
Diagnosing And Treating Bipolar Spectrum Disorders
Vol. 53 No. 1
Monitor on Psychology53
Learning objectives: After reading this article, CE candidates will be able to:
For more information on earning CE credit for this article, go to CE Corner.
In the 1990s, bipolar disorder was seen as a severe, rare, incurable condition found only in adults. Medication, primarily lithium, was the sole treatment offered to most patients. Today, experts are learning that the disorder is more commonaffecting about 4% of U.S. children and adultsand presents along a diverse continuum. More than half of patients have their first mood symptoms in childhood or adolescence, a full range of treatments exist, and people with the condition can survive and thrive .
The more we study bipolar disorder, the more we appreciate its complexity, especially around the onset of symptoms and in the underserved, said Manpreet K. Singh, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Stanford University. There isnt going to be a single genetic marker, research tool, or treatment plan that resolves this complexity.
Also Check: How Does Schizophrenia Affect Families
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
The defining sign of bipolar I disorder is a manic episode that lasts at least one week, while people with bipolar II disorder or cyclothymia experience hypomanic episodes.
But many people with bipolar disorder experience both hypomanic/manic and depressive episodes. These changing mood states dont always follow a set pattern, and depression doesnt always follow manic phases. A person may also experience the same mood state several times with periods of euthymia in between before experiencing the opposite mood.
Mood changes in bipolar disorder can happen over a period of weeks, months and sometimes even years.
An important aspect of the mood changes is that theyre a departure from your regular self and that the mood change is sustained for a long time. It may be many days or weeks in the case of mania and many weeks or months in the case of depression.
The severity of the depressive and manic phases can differ from person to person and in the same person at different times.
Signs and symptoms of manic episodes
Some people with bipolar disorder will have episodes of mania or hypomania many times throughout their life others may experience them only rarely.
Signs and symptoms of a manic episode include:
Most of the time, people experiencing a manic episode are unaware of the negative consequences of their actions. With bipolar disorder, suicide is an ever-present danger some people become suicidal in manic episodes, not just depressive episodes.