What Can Be Done About Anxiety
- Try to reduce the environmental demands and unnecessary stresses that may be causing anxiety.
- Provide reassurance to help calm the person and allow them to reduce their feelings of anxiety when they occur.
- Add structured activities into the daily routine, such as exercising, volunteering, church activities or self-help groups.
- Anxiety can be helped by certain medications, by psychotherapy from a mental health professional who is familiar with TBI, or a combination of medications and counseling.
A Case Report Of Mania And Psychosis Five Months After Traumatic Brain Injury Successfully Treated Using Olanzapine
Robert O. Cotes
1Faculty of Medicine, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul , Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
2Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
Abstract
Background. There are few published pharmacologic trials for the treatment of acute mania following traumatic brain injury . To our knowledge, we present the first case report of an individual being treated and stabilized with olanzapine monotherapy for this condition. Case Presentation. We describe the case of a 53-year-old African American male admitted to an inpatient psychiatric hospital with one month of behavioral changes including irritability, decreased need for sleep, hyperverbal speech, hypergraphia, and paranoia five months after TBI. Using Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition criteria, he was diagnosed with bipolar disorder due to traumatic brain injury, with manic features. He was serially evaluated with clinical rating scales to measure symptom severity. The Young Mania Rating Scale score upon admission was 31, and the Clinician-Rated Dimensions of Psychosis Symptom Severity score was initially 9. After eight days of milieu treatment and gradual titration of olanzapine to 15mg nightly, his symptoms completely abated, with YMRS and CRDPSS scores at zero on the day of discharge.. Olanzapine was effective and well tolerated for the treatment of mania following TBI.
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
The Link Between Brain Injury And Mental Health Issues
Brain injury significantly increases a persons risk of developing a mental health disorder. For example, a traumatic brain injury increases a persons risk of schizophrenia by 65 percent and depression by 59 percent, according to a large-scale study from the University of Copenhagen.
In addition, even a mild traumatic brain injury can increase a persons susceptibility to mental health symptoms. In fact, 20 percent of mild TBI patients can experience mental health disorders up to six months after their injury.
However, not all TBI patients with mental health symptoms will be diagnosed with a psychiatric condition. For a doctor to diagnose you with a specific mental health condition, you must display all the traits of that disorder set out in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Health Disorders .
For instance, many TBI patients suffer from extreme mood swings which also occur in bipolar disorder. But they may not receive a bipolar disorder diagnosis if they do not meet the other requirements.
Read Also: What Is The Phobia Of Puke Called
According To The National Alliance On Mental Illness 23 Million People In The United States Suffer From Bipolar Disorder
Every year, 2.9% of the U.S. population is diagnosed with bipolar disorder.1 But what is this condition? Bipolar disorder, or manic depression, is a serious brain disorder that causes extreme shifts in mood, energy, or functioning, and can range from episodes of mania to episodes of depression . These mood swings can range in severity and may last for hours, days, or months. But what causes these mood swings? How does bipolar disorder affect the brain?
Summary And Future Directions
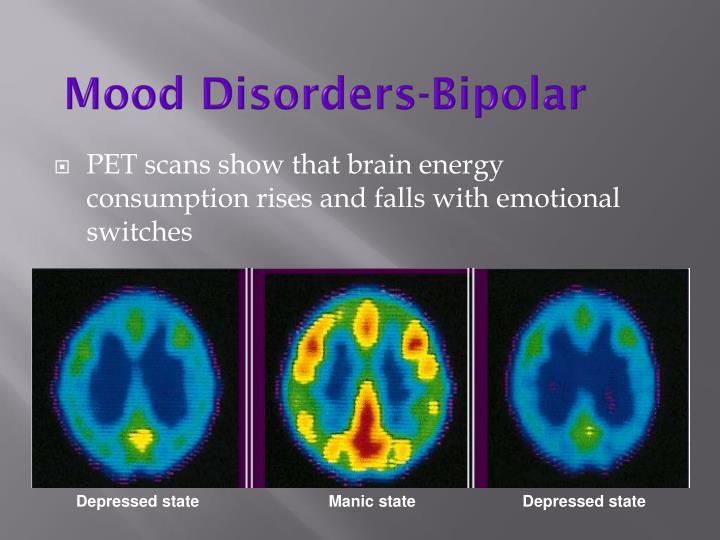
Mood disorders are frequent psychiatric complications of TBI that overlap with prominent anxiety, substance misuse, impulsivity and aggression. Furthermore, in a significant number of cases, they become chronic and resistant to treatment with the consequent deleterious impact on community reintegration and quality of life. Although the diagnosis of post-TBI mood disorders is still based on the DSM nomenclature, future nosology should incorporate the advances in neuroscience that are gradually allowing to parse the neural circuits whose disruption constitute the biological substrate of the behavioral alterations associated with these conditions. Current therapeutic strategies are based on current standards of practice rather that empirically-based controlled treatment trials. Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trials to establish the most effective treatments for the variety of mood disorders associated with TBI are needed.
You May Like: Topographic Depression Definition
Types Of Bipolar Disorder:
There are four basic types:
Diagnosed:
The mental health expert conducts several tests and assessments to diagnose the condition correctly and to rule out other underlying problems which could be causing these symptoms. To assess the severity of the symptoms, the expert may ask the person to maintain a daily record of their mood changes, sleep patterns, and details of daily activities that could help in prescribing the appropriate treatment.
A psychologist evaluates the persons thoughts, feelings, and emotions. The expert may also speak to the family members to collect more information about the persons condition. A psychological self-assessment may also be conducted to analyze the severity of the disorder.
Other Agents With More Limited Role
Beyond its potential role in early recovery in the acute/subacute post-TBI period, amantadine may also have a role in the treatment of chronic TBI-related irritability, agitation, and aggression, however data are mixed as to its benefits.,,, While its specific role in the management of such TBI-related symptoms remains to be elucidated, considerations for its use include the presence of additional target symptoms such as reduced alertness and cognitive deficits. Aside from their use to target TBI-related reduced alertness or cognitive deficits, stimulants may also improve frontal lobe function and have a role in reducing dysfunctional anger resulting from TBI.,,, Methylphenidate was shown to improve neurobehavioral symptoms, most notably anger, in patients with high levels of anger at baseline. It is unclear whether benefits are sustained beyond the short term as the only long-term study had a high attrition rate.,
Antidepressants have some evidence of benefit on agitation and aggression, but that is most often a secondary benefit in the course of their use for the treatment of depression. Buspirone may also represent another option for agitation and aggression, particularly if anxiety is associated with agitation. An ongoing trial will hopefully confirm the limited positive evidence available to date.
You May Like: Progression Of Schizophrenia
Does Bipolar Cause Memory Loss
People with bipolar disorder often report problems with memory and cognition. They have trouble with short- and long-term memory, think things through at subdued speeds, and have difficulty thinking outside that so-called box. These memory problems can pose considerable challenges for bipolar patients.
Should You Leave A Bipolar Person Alone
If your loved one with bipolar disorder is suicidal or violent, don’t try to handle the situation alone. If you’re worried that your loved one may hurt you, get to safety and then call the police. If your loved one is suicidal, don’t leave them alone. Call for an ambulance and stay with your loved one until it arrives.
Read Also: When Does Schizophrenia Develop In Females
How Do Bipolar People Stay Stable
Build structure into your life. Developing and sticking to a daily schedule can help stabilize the mood swings of bipolar disorder. Include set times for sleeping, eating, socializing, exercising, working, and relaxing. Try to maintain a regular pattern of activity even through emotional ups and downs.
Let Us Help You Manage & Treat Bipolar Disorder
As debilitating as bipolar disorder can be, it doesnt have to control your life. Here at StoneRidge Centers, we have programs that can help you manage the mood disorder and any other co-occurring disorders you may be living with. Were passionate and focused on restoring the brain to its optimal state of health. Thats why we have designed our programs to include the best of what brain science has to offer.
At the same time, we know that living with and managing a mood disorder can be challenging and overwhelming, so our approach to care is compassionate and comprehensive. Call us today at 928-583-7799 if you or a loved one are living with bipolar disorder and are ready to manage it in a healthy, wholesome way.
Categories
Contact Us
Read Also: Acrophobia Medical Definition
Traumatic Brain Injury Is Linked To Schizophrenia But Is It A Cause
A new study regarding Traumatic Brain Injury and schizophrenia has researchers taking a second look at the link between TBI and schizophrenia. The study shows that those who suffer a brain injury may also be at a higher risk for schizophrenia. The problem is worse in patients with a genetic risk for the mental disorder.
The Study
Past research on the link between TBI and schizophrenia has not been able to prove that TBI causes mental disease. This is because those diagnosed with schizophrenia are treated in the mental health system. They rarely arrive in clinics that treat head injuries.
This study group was made of 600 patients with a genetic risk for schizophrenia. These patients had at least two relatives diagnosed with the disease. Some patients were already schizophrenic. Researchers found that those already diagnosed with schizophrenia were three times more likely to have prior head injuries than the other patients.
A Link or Cause?
Some may wonder if schizophrenia made the head injury more likely and not the other way around. Researchers from this study disagree because the study looked at head injuries in both diagnosed and undiagnosed patients with a risk for schizophrenia. The group with the mental illness had a much higher number of prior head injuries. This leads to the belief that experiencing a head injury increases the risk of developing the mental disorder.
Another Theory
Contact Us
How Does Someone With Bipolar Act In A Relationship
They may become tearful or feel hopeless and pessimistic. Having low self-esteem may reduce a person’s sex drive, or they may feel less affectionate. It can be difficult for a person’s partner to know what to say or do to help. They may feel rejected, mistaking symptoms as a lack of interest in the relationship.
Also Check: What Is Apiphobia
What Mental Health Struggles Can A Concussion Or Severe Tbi Cause
The highest prevalence mental health struggles caused by a brain injury include depression, anxiety, PTSD, and a slew of emotional changes .
If you suffered from any of these emotional symptoms or mental illnesses before your injury, you have an increased risk of them coming back or worsening after the injury. Patients with a history of psychiatric disorders often need a combination of talk therapy and treatment for their brain injury in order to make the best recovery.
If you havent suffered from any of these issues before, you might make a faster recovery than if they were pre-existing issues, but each persons recovery journey is different. Taking longer to heal does not mean that there is something especially wrong with you.
What Is Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a problem with someones emotions and moods that has also been referred to as manic-depressive illness. In this disorder, problems with the wiring of the neurons in the brain lead to dramatic, rapid, and unusual shifts in mood. This makes it hard for people to carry out their tasks on a day to day basis.
While there are many different types of bipolar disorder, all of them involve fluctuations between extreme happiness, called mania , and times of sadness, called depression . Some people can have these oscillations over periods of several days. Other people might feel these swings in periods of a few hours. The degree to which people experience these ups and downs might also vary. Because of this, the disorder can present itself in a variety of ways.
Read Also: Eating Disorders Essay Outline
Treating Brain Injury And Mental Health Together
Treating a mental health disorder after brain injury will require support from a variety of professionals. If possible, its best to seek the help of a neuropsychologist: a trained clinical psychologist who specializes in the effects of brain injury.
Since they are intimately familiar with both brain injury and mental health, they will know the most effective ways to heal your mind.
Some methods they might suggest include:
- Talk therapy
- Medication
Your neuropsychologist may suggest a combination of these treatments to help you feel better.
If you cant find a neuropsychologist near you, other psychologists can also help. Just make sure they are familiar with the effects of brain injury on mental health.
What Causes Mental Illness After Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic brain injury can cause temporary or long-lasting mental illness or emotional symptoms. Often, these symptoms result from a combination of post-injury dysfunction in the way the brain communicates, post-injury stress on the autonomic nervous system, and the brains natural reaction to physical and emotional trauma.
Mental illnesses are conditions that affect a persons thinking, feeling, mood or behavior, such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia. Such conditions may be occasional or long-lasting and affect someones ability to relate to others and function each day.
So how does a head injury change how you feel and think? It starts with the physiological changes caused by brain injury. At the most basic level, even a mild traumatic brain injury can disrupt the relationship between neurons and the blood vessels that supply them with the right amount of nutrients at the right time, a process known as neurovascular coupling.
Dysfunctional neurovascular coupling results in hypoactive brain regions and hyperactive brain regions .
But this dysfunction isnt structural. Think of it like looking through the window of a business. The buildings intact, everyone has computers, and all the employees seem busy. All the physical components you need for the business are present, just like your brain is physically intact .
- Sensory sensitivity .
- Hormone dysregulation.
Read Also: Feretrephobia
If You Suffer A Head Trauma Your Risk Of Developing Certain Mental Disorders Increases Significantly In Some Cases By More Than 400 Percent New Study Reveals
Danish scientists have studied the link between head traumas such as concussion and skull fracture and the subsequent risk of developing mental disorders.They found that head injuries can increase the risk of developing certain mental disorders by up to 439 percent.
I am quite surprised by our findings. I had expected to see a correlation, but it is stronger than I had expected, says Sonja Orlovska, MD, of the Psychiatric Centre Copenhagen.
She is the lead author of the new study, published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Largest study to date
This is the largest study of its kind. It is a national register study based on all Danes born between 1977 and 2000 totalling 1.4 million people who were followed up to 2010.
In this period, 113,906 of them had been admitted to hospital with a head injury. Four percent of these were subsequently diagnosed with a mental disorder.The researchers looked at the following disorders: depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and so-called organic mental disorders .
- 65 percent more likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia.
- 59 percent more likely to develop a depression.
- 28 percent more likely to be diagnosed with bipolar disorder.
- 439 percent more likely to suffer from organic mental disorders.
What Does Untreated Bipolar Look Like
Periods of mania or depression that last for at least 7 days. Periods of mania or depression that are a major change from your normal behavior, most likely affecting your work and social life. Shifting back and forth between periods of feeling low, sad and helpless and feeling high, unstoppable and energetic.
Don’t Miss: What Does The Word Phobia Mean
Brain Injury And Mental Health: Understanding The Connection
Elizabeth Denslow, OTR/L Flint Rehab
Brain injury and mental health issues have a complicated relationship. Sometimes TBI is a separate condition from psychiatric disorders, while other times the two can exacerbate each other.
This page will explain the link between brain injury and various mental health problems. It will also look at some of the most frequent psychiatric conditions that can arise after a TBI.
Finally, we will show what treatments are available for those suffering from brain injury and mental health disorders and discuss how family members can offer support.
To jump ahead to certain sections, click on the relevant links:
Can A Head Injury Or Complications During Birth Cause Bipolar Disorder
Dr. Kiki Chang answers the question: ‘Can A Head Injury Increase Bipolar Risk?’
— Question: Can a head injury or complications during birth cause bipolar disorder?
Answer: There have been some studies that have found a higher incidence of obstetrical complications in adults who have bipolar disorder. In other words, when they were babies, there were some complications around their birth and during the pregnancy of their mother.
But it’s not clear exactly how these complications or difficulties lead to bipolar disorder. And it’s also not clear that head trauma or head injury early on definitively leads to bipolar disorder, but it can, just like it can lead to a whole host of other kinds of neurological or psychiatric disorders.
However, the biggest risk factor does appear to be genetics, and so again if there is a family history of bipolar disorder, perhaps combined with things like obstetrical complications or head injury, those two things could possibly worsen the outcome so that you are more likely to develop bipolar disorder.
Don’t Miss: How To Motivate Yourself To Workout When Depressed