What Causes Bipolar Disorder
Experts have yet to discover the exact causes of bipolar disorder, but they have identified several risk factors for the condition. As you saw above, having one or more family members with bipolar disorder increases the risk. So does a history of emotional trauma, high stress, or substance abuse. In addition, bipolar disorder is associated with changes in the structure and function of the brain .
Left untreated, bipolar disorder can cause major problems in life, including:
- Self-esteem issues
- 39% hospitalization rate
- A decrease of over 9 years in life expectancy
- 15 times more likely to attempt suicide than general population
Medications For Bipolar Disorders
Once the bipolar diagnosis is established or suspected, mood stabilizers often are very helpful for both moods and headaches. Divalproex sodium is effective for mania, hypomania, depression associated with bipolar disorder, and for headache prevention. It has been extremely well studied for these conditions and has become one of the primary migraine and chronic daily headache preventives. Lithium carbonate is underutilized it should be used more often. One or more of the newer antiepileptics may prove to be helpful for bipolar disorders and migraine. Carbamazepine has some utility as a mood stabilizer, but not for migraine prophylaxis. Oxcarbazepine is a milder form of carbamazepine, and may be useful.
Lamotrigine is becoming one of the most commonly used mood stabilizers. It is one of the few effective medications for bipolar depression.15 Doses must be slowly titrated due to the 1 out of 2,000-5,000 occurrences of toxic epidermal necrolysis, or Stevens Johnson Syndrome.
The atypical antipsychotics are also used for bipolar symptoms.16 When a mood stabilizer is effective, the underlying agitation, anger, or depression improves. Quetiapine has reasonable efficacy data. As a class, the atypicals do carry the risk of metabolic syndrome.
Implications And Future Directions
Little is currently understood of the molecular mechanisms underlying bipolar disorder, and current treatments are far from maximally effective. Part of the value of research in this area is to better understand the genetic pathways contributing to risk. The low signal produced by genome-wide studies, with individual allelic effect sizes on the order of 0.5-1%, suggests that a large portion of the variance operates in clinically unaffected individuals . This also suggests that the phenotype is poorly understood, implicating the need to define better measures to detect the common alleles contributing to 25% of the risk for bipolar disorder and operating in the general population. Through the assessment of positive traits, we broaden the concept of bipolar disorder into a fully dimensional spectrum and presumably capture specific portions of the variance, which will facilitate the detection of the underlying genes and pathways contributing to risk. Understanding the relationship between positive traits and bipolar disorder may thus provide insight into the mechanisms of illness, which may someday lead to novel therapeutic targets.
Recommended Reading: Lamictal Borderline Personality Disorder
How To Recognize Mania In An Autistic Person
If you think you or a loved one may have both bipolar disorder and autism, its important to understand how the conditions appear together. The symptoms of comorbid bipolar disorder and autism are different than if either condition appeared by itself.
Depression is often obvious and easy to identify, while mania is less clear. Thats why recognizing mania in an autistic person can be difficult.
If the behaviors have been a constant since symptoms associated with autism appeared, theyre unlikely to be the result of mania. However, if you noticed a sudden shift or change, these behaviors may be the result of mania.
Recombination And Genetic Linkage
The diploid nature of chromosomes allows for genes on different chromosomes to or be separated from their homologous pair during sexual reproduction wherein haploid gametes are formed. In this way new combinations of genes can occur in the offspring of a mating pair. Genes on the same chromosome would theoretically never recombine. However, they do, via the cellular process of . During crossover, chromosomes exchange stretches of DNA, effectively shuffling the gene alleles between the chromosomes. This process of chromosomal crossover generally occurs during , a series of cell divisions that creates haploid cells. , particularly in microbial , appears to serve the adaptive function of repair of DNA damages.
The first cytological demonstration of crossing over was performed by Harriet Creighton and in 1931. Their research and experiments on corn provided cytological evidence for the genetic theory that linked genes on paired chromosomes do in fact exchange places from one homolog to the other.
Genes generally their functional effect through the production of , which are complex molecules responsible for most functions in the cell. Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptide chains, each of which is composed of a sequence of , and the DNA sequence of a gene is used to produce a specific . This process begins with the production of an molecule with a sequence matching the gene’s DNA sequence, a process called .
Don’t Miss: Which Phobia Means You Have An Intense Fear Of Halloween
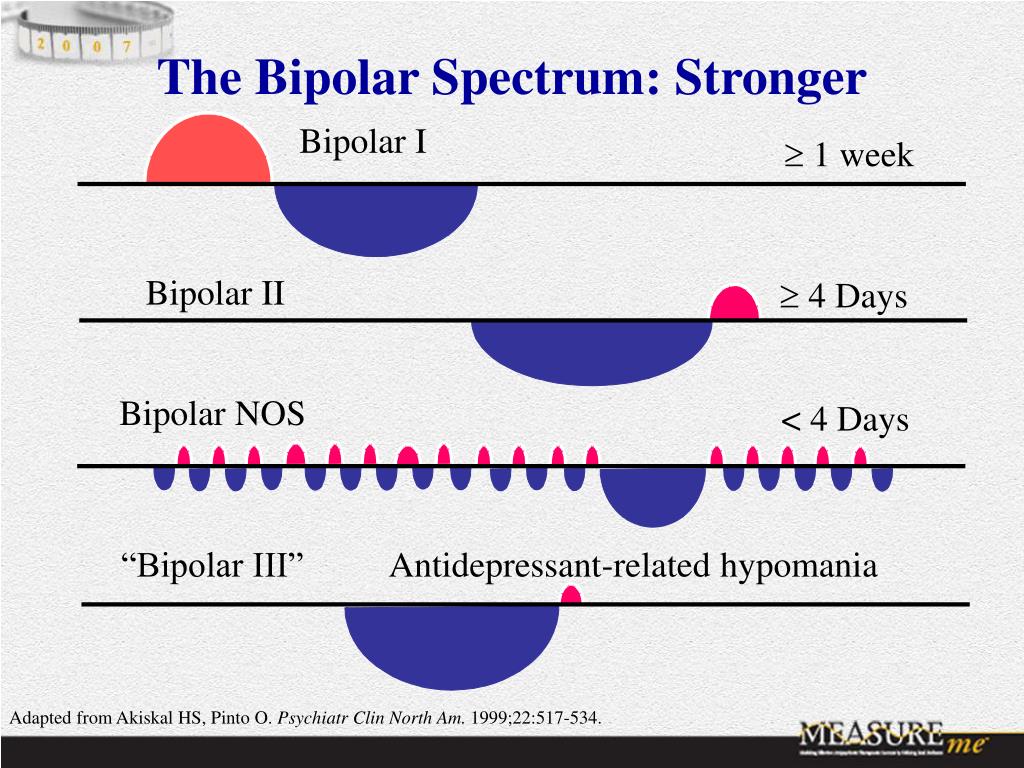
The Bipolar Spectrum: Bipolar I
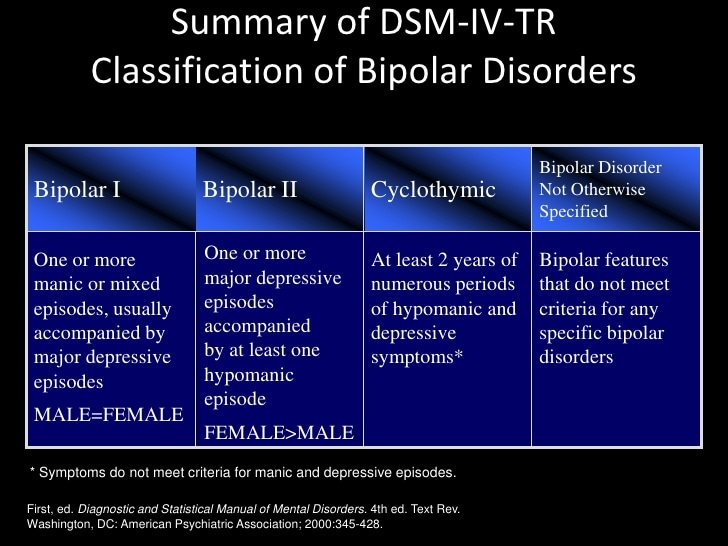
Bipolar disorder is traditionally defined by four main forms:
- In bipolar I disorder, a person has at least one manic episode lasting at least a week. They also has multiple episodes of major depression. Without treatment, the episodes of depression and mania usually repeat over time. Time spent with depressive symptoms, may outnumber time spent with mania symptoms by about 3 to 1.
- In bipolar II disorder, a person has a milder form of mania, called hypomania, lasting several days or longer. Periods of depression, though, outnumber the time spent with symptoms of hypomania by almost 40 to 1 in many people with this form of the disorder. Because hypomania can be mistaken for ordinary happiness or even normal functioning, bipolar II may often be misdiagnosed as depression alone .
- In bipolar disorder not otherwise specified , people have symptoms of mania or hypomania that are too few in number or too short in duration to meet currently accepted definitions of a manic or hypomanic syndrome or episode.
- In cyclothymic disorder , a person has hypomanias that alternate frequently with brief periods of depression. When present, though, the symptoms of depression do not last long enough and involve enough symptoms to define major depression as a full syndrome.
The concept of a bipolar spectrum may include additional subtypes of bipolar disorder that were proposed in the 1980s. Those subtypes include:
Autism And Bipolar Disorder
May 22, 2014
This weeks Got Questions? answer comes from psychiatrist Jessica Hellings, MD, and psychologist Andrea Witwer, PhD, program directors at Ohio State Universitys Nisonger Center, which is part of Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network.
For those of you not familiar with bipolar disorder, its a mood disorder once known as manic depression. Persons with bipolar disorder alternate between a frenzied state known as mania and episodes of depression. While some individuals experience only the manic episodes, many affected individuals rapidly alternate between these two states and experience great irritability.
As with other psychiatric disorders, studies suggest that bipolar disorder may be relatively common among children and adults with autism. Some studies have found that as many as 27 percent of those with autism also have symptoms of bipolar disorder. By contrast, its prevalence in the general population is around 4 percent.
However, we believe that bipolar disorder is mistakenly over-diagnosed in those with autism. In part this is because some of their symptoms can overlap.
For these reasons, traditional methods of assessing psychiatric disorders can be inappropriate for many of those with autism. Its particularly important for the doctor to get to know the individual and his or her family and environment before attempting such a diagnosis.
The point is that all these behaviors could be considered symptoms of bipolar disorder!
Read Also: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Natural Selection And Evolution
Mutations alter an organism’s genotype and occasionally this causes different phenotypes to appear. Most mutations have little effect on an organism’s phenotype, health, or reproductive . Mutations that do have an effect are usually detrimental, but occasionally some can be beneficial. Studies in the fly suggest that if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, about 70 percent of these mutations will be harmful with the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial.
studies the distribution of genetic differences within populations and how these distributions change over time. Changes in the in a population are mainly influenced by , where a given allele provides a selective or reproductive advantage to the organism, as well as other factors such as , , , and .
Over many generations, the genomes of organisms can change significantly, resulting in . In the process called , selection for beneficial mutations can cause a species to evolve into forms better able to survive in their environment. New species are formed through the process of , often caused by geographical separations that prevent populations from exchanging genes with each other.
Organisms were chosen, in part, for convenienceâshort generation times and easy made some organisms popular genetics research tools. Widely used model organisms include the gut bacterium , the plant , baker’s yeast , the nematode , the common fruit fly , and the common house mouse .
A Depressive Period May Include:
- A low mood
- Prolonged sadness or unexpected, unexplained crying
- Significant changes in appetite and sleep patterns
- Irritability, anger, worry, agitation, and anxiety
- Loss of energy
- Feelings of guilt or worthlessness
- Inability to concentrate
- Recurring thoughts of death or suicide
- A sense of doom or fear of having done something terrible
- Psychosis, in some cases
You May Like: Phobia Definition Medical
Subthreshold Bipolar Disorder Not Ready For Prime Time
Posted May 9, 2011
About 1% of our population suffers from “no doubt about it” bipolar affective disorder . Persons with this disorder experience serious episodes of both depression and mania that can last for weeks to years. Manic symptoms are dramatic and disruptive, and typically include elevated or irritable mood, inappropriate self-esteem , markedly decreased need for sleep, excessive energy, hypertalkativeness , and extremely bad judgment, often involving sexual behaviors or financial decisions. Psychotic symptoms, including auditory and visual hallucinations, and delusional thinking , are common and disruptive. Untreated, this illness severely impairs function and can lead to disability and death. Many, but not all, patients with bipolar I disorder respond well to currently available treatments. Patients are usually treated with medications along with education and rehabilitative therapies.
So, what’s the problem?
Treatments for bipolar disorder include mood stabilizers such as lithium, mood stabilizing anticonvulsants, and antipsychotic medications. These are powerful drugs with significant and sometimes dangerous side effects. When used for bipolar I disorder, the benefits of these treatments usually outweigh the risks.
Alternative Options For Classifying Bipolar Disorder
The proper classification of mood disorders in general, and in particular, bipolar disorder has been a longstanding conundrum. As is currently the case, in the absence of the basic scientific data that would allow a more biologically based classification system, interested observers can only suggest improvements on our current, somewhat arbitrary system. With that caveat, there may be other methods of classifying bipolar disorder.
An example of an alternate method of classifying bipolar disorder utilizes predominant polarity as the central factor, initially described by Angst and revisited and updated more recently by others . Predominant polarity reflects the relative number and severity of manic vs. depressive episodes within individual patients, defined by at least twice as many episodes of one pole vs. the other . Patients may be mania predominant, depression predominant or neither, when neither pole dominates the clinical course. Rates of PP differ markedly across different populations but, in general, depressive PP patients outnumber manic PP patients .
Also Check: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Dna Sequencing And Genomics
, one of the most fundamental technologies developed to study genetics, allows researchers to determine the sequence of nucleotides in DNA fragments. The technique of , developed in 1977 by a team led by , is still routinely used to sequence DNA fragments. Using this technology, researchers have been able to study the molecular sequences associated with many human diseases.
As sequencing has become less expensive, researchers have of many organisms using a process called , which utilizes computational tools to stitch together sequences from many different fragments. These technologies were used to sequence the in the completed in 2003. New technologies are dramatically lowering the cost of DNA sequencing, with many researchers hoping to bring the cost of resequencing a human genome down to a thousand dollars.
came about due to the ever-increasing demand for low-cost sequencing. These sequencing technologies allow the production of potentially millions of sequences concurrently. The large amount of sequence data available has created the subfield of , research that uses computational tools to search for and analyze patterns in the full genomes of organisms. Genomics can also be considered a subfield of , which uses computational approaches to analyze large sets of . A common problem to these fields of research is how to manage and share data that deals with human subject and .
What Problem Do We Need Tosolve Right Now When Shouldantidepressants Be Used
As we consider revisions to the currentdiagnostic system, we should rememberthe problem we are trying to solve.At present, the DSM system workswell at the extremes of diagnosis:mania identifies BD well when recognizedas such. Conversely, anadult with a single episode of majordepression following severe psychosocialstress with no family history ofBD will be widely recognized as havingMDD. These fully expressed, recognizablecases–shown in the Figure aspoints E and A–will be treated withmood stabilizers and antidepressants,respectively.
Point D in the Figure representsidentifiable BD II, with fully expressedhypomania. The DSM system of diagnosisworks reasonably well for such apatient. Our problem comes with intermediateforms. Point C represents subthresholdcases per the NCS-R. Somepsychiatrists would call this BD nototherwise specified .However, others would regard this as aform of depression, perhaps atypical butnot bipolar because DSM criteria forhypomania are not met.
The same disagreement arises–andperhaps with more strength–at pointB, where only a few bipolar-minded cliniciansmight persist in calling this BDNOS, and most psychiatrists would callit MDD. Obviously, from a spectrumviewpoint there are almost an infinite variety of other intermediate cases .
You May Like: Pheritriphobia
Bipolar Spectrum: A Model For Research And Clinical Practice
The development of a validated bipolar spectrum concept can provide a moredifferentiated research and treatment model for affective disorders and mayhelp reduce the underrecognition of bipolarity.
A dimensional concept was proposed by Kretschmerin 1921 for schizophrenia and foraffective disorders as well as by Bleuler . The term spectrum was first used in psychiatry in1968 for the schizophrenia spectrum, which integrated schizoid personalities. In 1977 Akiskal proposed a cyclothymicbipolar spectrum and in1981 Klerman suggested a mania spectrum .
Today the term bipolar spectrum is mainly used in two complementary senses:
Fig. 1 Two-dimensional mood/affective spectrum . The precise relationship of personality disorders to thedisease spectra is uncertain and an unsolved general problem ofpsychiatric classification. BP-I , bipolar-I disorder type I D, major depression, d, minor depression M, mania m,hypomania MDD, major depressive disorder RBD, recurrent briefdepression sx, symptoms
a spectrum of severity, which embraces psychotic and non-psychoticmajor and minor bipolar disorders , cyclothymic disorders,hypomania and, at its broadest, even borderline disorders andcyclothymic temperament
Bipolar Disorder And Creativity: A Shared Vulnerability
Fig. 1
Positive traits within the bipolar spectrum and a shared vulnerability. According to the inverted-U model, creativity and other positive traits would be expected to increase with genetic loading up to a threshold, beyond which they would start to diminish with the increasing impairment of illness . Polygenic risk indicates genetic vulnerability due to common variation in aggregate, which is maintained in the population by clinically unaffected individuals, who benefit from the positive traits. BD, bipolar disorder.
Also Check: What Is A Phobia Of Spoons Called
Bipolar Disorder And Other Conditions
Some bipolar disorder symptoms are similar to those of other illnesses, which can make it challenging for a health care provider to make a diagnosis. In addition, many people may have bipolar disorder along with another mental disorder or condition, such as an anxiety disorder, substance use disorder, or an eating disorder. People with bipolar disorder have an increased chance of having thyroid disease, migraine headaches, heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and other physical illnesses.
Psychosis: Sometimes, a person with severe episodes of mania or depression may experience psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations or delusions. The psychotic symptoms tend to match the persons extreme mood. For example:
- People having psychotic symptoms during a manic episode may have the unrealistic belief that they are famous, have a lot of money, or have special powers.
- People having psychotic symptoms during a depressive episode may falsely believe they are financially ruined and penniless, have committed a crime, or have an unrecognized serious illness.
As a result, people with bipolar disorder who also have psychotic symptoms are sometimes incorrectly diagnosed with schizophrenia. When people have symptoms of bipolar disorder and also experience periods of psychosis that are separate from mood episodes, the appropriate diagnosis may be schizoaffective disorder.
Anxiety: It is common for people with bipolar disorder to also have an anxiety disorder.
Major Depressive Episode Symptoms
The third symptom of bipolar disorder is depression, which can severely impact a persons daily life. A person is experiencing a major depressive episode if they are experiencing five or more of the following symptoms:
- Severe loss of interest or feeling no pleasure in normal activities
- Noticeable weight loss when not trying to lose weight, weight gain, or changes in appetite
- Feeling sad, empty, hopeless, or teary all the time. In children/teens, this depressed mood can present as irritability
- Sleeping too much or not being able to sleep, as with insomnia
- Having less energy or always feeling tired
- Feeling worthless or overly guilty
- Struggling to concentrate or make decisions
- Feeling suicidal or having suicidal thoughts
Are you in a crisis?
While bipolar disorder can cause a person to feel depressed, this condition is not the same as getting diagnosed with depression. Bipolar disorder is marked by periods of two extremes: Mania or hypomania, the up, and major depressive episodes, the down. In contrast, depression causes moods and emotions that are always down without any moments of high energy.
You May Like: What Is The Fear Of Spoons Called