How Does Serotonin Cause Schizophrenia
4.5/5schizophreniaschizophreniaSEROTONINread here
Compared with healthy subjects, schizophrenic patients may also have increased levels of serotonin and levels of norepinephrine in the brain. Conventional antipsychotic drugs nonselectively block dopamine D2 receptors throughout the central nervous system.
Likewise, what is the chemical imbalance that causes schizophrenia? Chemistry: Scientists believe that people with schizophrenia have an imbalance of the brain chemicals or neurotransmitters: dopamine, glutamate and serotonin. These neurotransmitters allow nerve cells in the brain to send messages to each other.
Subsequently, question is, does serotonin help with schizophrenia?
Introduction. Clozapine, which has a high affinity for serotonin receptors, has been shown to be more effective in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Then, there is increased interest in the role of serotonin in pathogenesis and treatment of schizophrenia.
Which neurotransmitter imbalance occurs in a patient with schizophrenia?
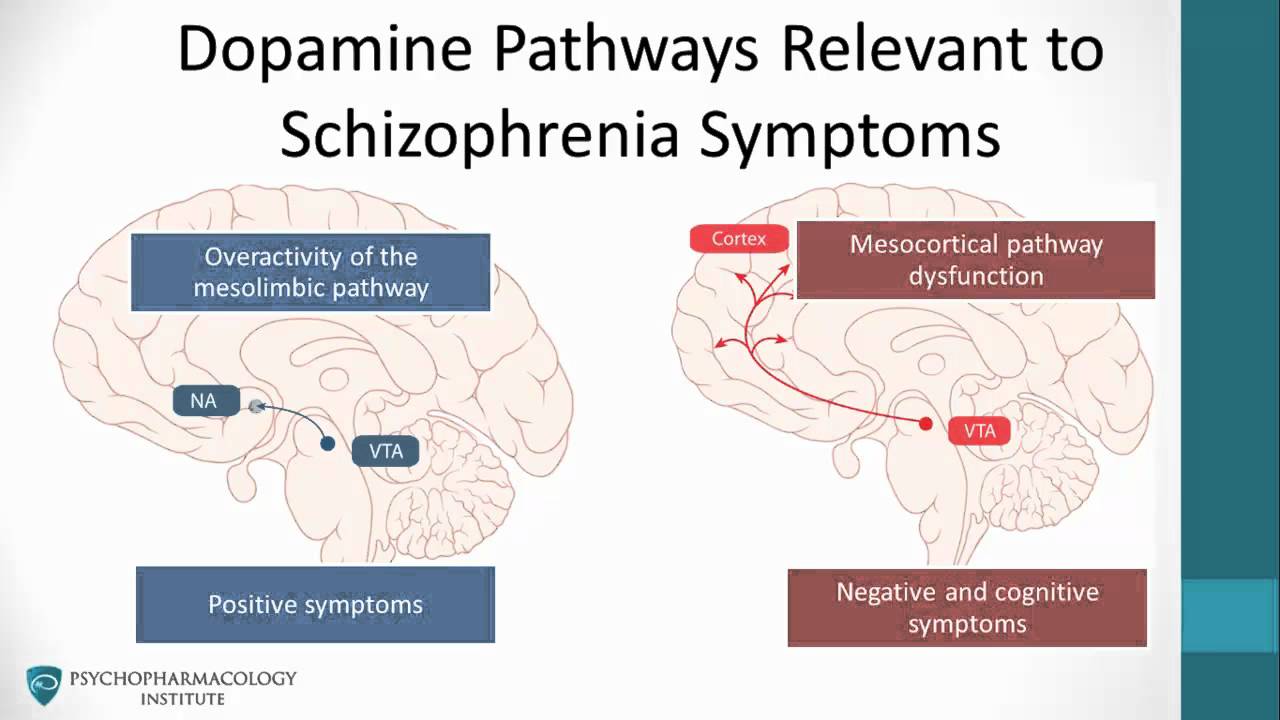
Dopamine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in the pathology of schizophrenia. The revised dopamine hypothesis states that dopamine abnormalities in the mesolimbic and prefrontal brain regions exist in schizophrenia.
How Does Dopamine Cause Schizophrenia
dopamineschizophreniaschizophreniacauseddopamineDopamineSchizophreniadopamineschizophrenicdopamine
People Also Asked, How does dopamine work in schizophrenia?
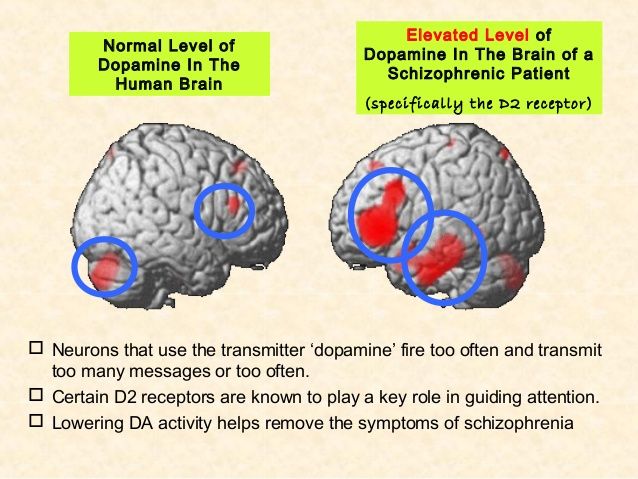
Simply so, how does dopamine work in schizophrenia?In schizophrenia, dopamine is tied to hallucinations and delusions. Thats because brain areas that run on dopamine may become overactive. Antipsychotic drugs stop this. National Institute of Mental Health: Schizophrenia.
Also know, do people with schizophrenia have more dopamine? It is thought that the brains of people with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders produce too much dopamine. Secondly, drugs that increase levels of dopamine, like amphetamines, often cause psychotic symptoms and a schizophrenic-like paranoid state. However, several factors challenge the dopamine hypothesis.
Contents
Biochemical Factors Controlling The D2high State
The rate of interconversion between the high- and low-affinity states of a G protein-linked receptor may be minutes or seconds. There are many factors that increase the prevalence of the high-affinity state and, therefore, the sensitivity of the tissue to the agonist.
RGS9 co-localizes with D2 in the striatum and accelerates the termination of D2-triggered events. A reduction in RGS9, as occurs in RGS9 knockout mice, leads to behavioral dopamine supersensitivity and a marked increase in the proportions of D2High receptors in the striatum .
The reduced expression of RGS9-2 in schizophrenia hippocampus is consistent with supersensitivity and increased D2High levels.
Because D2High receptors are consistently elevated in all the animal models of the various human psychoses, and because the majority of psychotic episodes respond to D2 blockade, D2High may be a common target for the convergence of the various psychosis pathways. Consistent with this hypothesis of D2High is the fact that most psychoses respond to treatment with D2 antagonists, including phencyclidine psychosis . The treatment of phencyclidine psychosis by haloperidol is significant, because haloperidol does not block NMDA receptors, indicating that the D2 target is critically active in phencyclidine psychosis .
The negative aspects of psychosis, especially cognition, which is impaired in schizophrenia, may arise from overexpression of D2 in the striatum .
You May Like: Prodromal Stage Of Schizophrenia
How Do You Calm Down A Schizophrenic
Schizophrenia: Helping Someone Who Is Paranoid
Indirect Evidence For Glutamatergic Dysfunction In Schizophrenia
Animal models
The administration of NMDA antagonists to nonhuman primates and rodents has been shown to induce a variety of schizophrenialike behaviours, such as sensorimotor gating impairments, increased locomotion, abnormal repetitive movements, and cognitive and social deficits. NMDA antagonism has also been shown to lead to hippocampal hypermetabolism, similar to that which has been observed in schizophrenia, .
A genetic animal model that reduced levels of the NMDA coagonist Dserine was associated with neurobiological changes similar to those observed in schizophrenia, such as reduced dendritic spine density and hippocampal volume. Several other genetic mice models, such as those involving inactivation of Damino oxidase and reduction of the synaptic protein dysbindin, also show NMDA receptor hypofunction accompanied by behavioural and neurobiological changes analogous to those observed in schizophrenia.
CSF and postmortem studies
Initial small studies of CSF found reduced glutamate levels in patients, but these findings were not replicated, . However, CSF and postmortem brain levels of kynurenic acid, an NMDA receptor antagonist, have consistently found to be raised, although not plasma levels.
Postmortem studies investigating structural alterations of glutamate neurons have generally found reductions in dendrite arborization, spine density, and synaptophysin expression across frontal and temporal regions.
Psychopharmacology of NMDA antagonists
Also Check: What Is The Fear Of Spoons Called
What Does Psychosis Look Like
Psychosis is characterized as disruptions to a person’s thoughts and perceptions that make it difficult for them to recognize what is real and what isn’t. These disruptions are often experienced as seeing, hearing and believing things that aren’t real or having strange, persistent thoughts, behaviors and emotions.
Behavioural Flexibility: Serial Reversal Learning
One limitation of outcome-specific devaluation is that it does not allow for the delineation of functional deficits in the PFC vs. associative striatum. Thus, pairing this task with another that relies on the associative striatum, but not the PFC, is required. The basal ganglia is also involved in flexible decision-making and specifically reversal learning which can be tested similarly in humans and rodents . Extensive work in rodents, primates and humans have demonstrated that specific forms of behavioural flexibility are dependent on differing neurocircuitry,, . For example, the orbitofrontal cortex and associative striatum are critical for reversal learning when re-exposed to previous contingencies . In contrast, the PFC is critical for shifting from one rule or strategy to another . Thus, deficits in serial reversal learning are particularly sensitive to orbitofrontal cortex and associative striatal dysfunction but not PFC dysfunction. Persons with schizophrenia exhibit deficits in both attentional set-shifting and reversal learning. Deficits in reversal learning are independent of working memory deficits and have also been associated with disorganised thought.
Don’t Miss: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
What Occurs In The Brain
| The picture below showsmagnetic resonance image brain scans of a pair of twins:one with schizophrenia, one without schizophrenia. Notice that theventricles are larger in the twin withschizophrenia. |
A reduced size of the hippocampus, increased size of the basal ganglia,and abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex are seen in some people withschizophrenia. However, these changes are not seen in all people withschizophrenia and they may occur in people without this disorder.
Challenging Longstanding Assumptions And Moving Forward
Clozapine, discovered in the 1960s, remains the most effective antipsychotic medication, although its use is restricted due to its side effect profile. This stagnation in drug development for schizophrenia highlights a key weakness in schizophrenia research a lack of effective bi-directional translation between basic and clinical research. The fact that the current methods of testing for psychotic symptoms in rodents are now misaligned with recent clinical evidence indicates a need to advance how positive symptoms are examined in animal models. We have proposed a combination of behavioural tests in rodents that are sensitive to dysfunction at the primary site of dopaminergic neurobiology observed in schizophrenia. There will never be a perfect model for psychosis in rodents, but it is critical that we acknowledge the limitations of current methods so that an active dialogue is established.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Of Puke
Implications For The Dopamine Hypothesis Of Schizophrenia
It is important to distinguish between the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia and the dopamine hypothesis of antipsychotic drug action. The latter proposes that reduction of dopaminergic function via either blockade of postsynaptic receptors or attenuation of presynaptic neuronal activity underlays the therapeutic effect of most known antipsychotic agents. Conversely, the former takes this concept a stage further and from it proposes that dopaminergic hyperfunction, via either supersensitivity of postsynaptic receptors or elevated activity of presynaptic neuronal activity, is an important element in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia .
Though it remains important not to overlook the possible role of non-dopaminergic systems in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and in antipsychotic drug action , it should be emphasized that clarification of whether selective D1 antagonists do or do not show therapeutic efficacy in this disorder will be a watershed in the evolution of these concepts . Furthermore, the putative roles of individual, molecular biologically defined members of the D1-like and of the D2-like families of dopamine receptor in mediating antipsychotic activity remain enigmatic, but may in the future challenge further our present perspectives.
David L. Atkinson, Jeff K. Abbott, in, 2018
The Dopamine Theory Of Schizophrenia
Pharmacological treatments support the idea that an overactive dopamine system may result in schizophrenia: Medications that block dopamine receptors, specifically D2 receptors, reduce schizophrenia symptoms.
The brain regions known as the thalamus and the striatum are affected by dopaminergic activity. Manzano et al. explain that schizophrenia results in altered levels of D2 binding potential in those two regions of the brain. For example, the authors note that schizophrenia patients who do not take antipsychotic medications have a lower thalamic D2 binding potential. In addition, untreated schizophrenia patients have a higher number of D2 receptors in the striatum.
Recommended Reading: Eating Disorders Psychology Articles
Does Estrogen Change Your Face
The first changes you will probably notice are that your skin will become a bit drier and thinner. Your pores will become smaller and there will be less oil production. You may become more prone to bruising or cuts and in the first few weeks youll notice that the odors of your sweat and urine will change.
Link Between Hallucinations And Dopamine Not Such A Mystery Finds Study
- Date:
- Columbia University Medical Center
- Summary:
- Researchers have found that people with schizophrenia who experience auditory hallucinations tend to hear what they expect, an exaggerated version of a perceptual distortion that is common among other people without hallucinations. The researchers found that elevated dopamine could make some patients rely more on expectations, which could then result in hallucinations.
Researchers at Columbia University Irving Medical Center and New York State Psychiatric Institute found that people with schizophrenia who experience auditory hallucinations tend to hear what they expect, an exaggerated version of a perceptual distortion that is common among other people without hallucinations. Those with hallucinations and other psychotic symptoms are known to have elevated dopamine, the main area of focus for available treatments for psychosis, but it was unclear how this could lead to hallucinations. The researchers found that elevated dopamine could make some patients rely more on expectations, which could then result in hallucinations.
The findings, published recently in Current Biology, explain why treatments targeting the production of dopamine could help alleviate this condition.
The study is titled “A perceptual inference mechanism for hallucinations linked to striatal dopamine.”
Story Source:
Don’t Miss: Schizoaffective Disorder Has Symptoms Typical Of Both Schizophrenia And Which Type Of Disorder
Data Processing And Analysis
Image processing and PET data analysis were performed as described in the preclinical study with the following exceptions. Ratio data from five consecutive scans 3050 min after injection and immediately before amphetamine administration and five consecutive scans 75100 min post-raclopride bolus injection were averaged . Individual group comparisons were conducted with paired and unpaired t tests where appropriate. Behavioral data were analyzed with a repeated-measures ANOVA with time and group as factors. Change in behavior were correlated with change in percent raclopride striatal binding ratios using a Pearsons correlation coefficient. All comparisons were two-tailed and group data were presented as mean ± SEM.
The Default Mode Network
When weâre just hanging out — the dishes are done, weâve finished our homework, or we’ve completed a tough project at work — our thoughts are free to roam. This âdefault modeâ allows us time to daydream, reflect, and plan. It helps us to process our thoughts and memories. Scientists call this the default mode network. When weâre not focused on a given task, it âlights up.”
If you have schizophrenia, your default mode network seems to be in overdrive. You may not be able to pay attention or remember information in this mode, one study shows.
You May Like: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Which Of The Three D2
The D3 receptor has been extensively investigated for linkage and association to schizophrenia , but the results remain controversial. The only D3-selective drug that has been tested against schizophrenia is BP897 at 10 mg per day for 4 weeks, a dose that did not attain a significant antipsychotic effect.
Likewise, the D4 receptor, although earlier thought to be elevated in schizophrenia, has not been found to be a main target for schizophrenia treatment.
An example of D2 occupancy is given in Figure 15, where the % of D2 receptors occupied by risperidone is approximately 70% at the average therapeutic daily dose of 2 to 6 mg. The data in Figure 14 and Figure 15 are consistent with the point of Figure 1 that the main target for antipsychotic action is the D2 receptor.
Neural Circuits And Dopamineglutamate Interactions
The evidence discussed above suggests that, while the dopamine hypothesis can account for the positive symptoms of psychosis, it is less clear whether it can fully account for negative and cognitive symptoms. Similarly, while glutamatergic models of psychosis are able to replicate a wide range of symptoms of psychosis, they do not directly account for the finding of increased presynaptic striatal dopamine function, nor the clinical effectiveness of dopamine antagonists. This suggests that dysfunction in both systems contributes to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, and highlights the need to understand how these two systems may interact.
Much research has investigated dopamineglutamate relationships in humans using pharmacological challenges. Amphetamine administration has been shown to increase cortical glutamate levels, as measured using 1HMRS, but dopamine antagonists do not have consistent effects on glutamate levels as measured using 1HMRS. Several, but not all, PET studies have found that ketamine administration is associated with striatal dopamine release. While glutamatergic dysfunction may encourage dopaminergic disinhibition, it is clear that this is not the only route to symptoms, given that dopamine antagonists do not entirely ameliorate the effects of NMDA antagonists.
Don’t Miss: Is Pristiq A Good Antidepressant
Indirect Evidence For Dopamine Dysfunction In Schizophrenia
Animal models
Rodent models of schizophrenia are useful for investigating molecular mechanisms that may be of pathophysiological relevance, and for testing novel therapeutic interventions.
One well characterized model of dopaminergic hyperactivity involves administering repeated doses of amphetamine. This has been shown to induce events that are also observed in individuals with schizophrenia, such as reduced prepulse inhibition, stereotyped behaviours, and impaired cognitive flexibility and attention. Given that amphetamine results in dopamine release, and that the above effects can be ameliorated with the administration of dopamine antagonists, this provides indirect evidence for a role of dopamine in behaviour thought to be a proxy for psychotic symptoms.
Another example is that of mice genetically modified to overexpress dopamine D2 receptors in the striatum, which also display a wide range of schizophrenialike behaviours. Similarly, transgenic insertion of tyrosine hydroxylase and guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrase 1 into the substantia nigra in early adolescence increases dopamine synthesis capacity, and has been associated with a schizophrenialike behavioural phenotype.
In summary, multiple methods have been used to induce increased striatal dopamine signalling in animal models, and these consistently produce behaviours analogous to those observed in individuals with schizophrenia.
Cerebrospinal fluid and postmortem studies
Summary of indirect findings
Does Coffee Increase Dopamine
Coffee also releases dopamine, the feel-good chemical in the brain which is released when you have an orgasm, win the lottery and shoot heroin. A similar addiction cycle with dopamine leads to depression and fatigue when you arent hitting the beans. Finally, caffeine takes about six hours to leave your system. ,
Also Check: Is Sex Good For Depression
Are There Other Neurotransmitters Involved
While dopamine receives a large amount of attention when looking at schizophrenia symptoms, its not the only neurotransmitter researchers are eyeing with this disorder.
Of the over 40 different neurotransmitters studied by researchers today, there are four others that are believed to play a role in schizophrenia — glutamate, GABA, serotonin, and acetylcholine.
Lets take a closer look at these neurotransmitters and what theyre responsible for:
The Dopamine Hypothesis Of Schizophrenia
The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia, simply stated, postulates that certain dopaminergic pathways are overactive in schizophrenia and so cause the symptoms of an acute schizophrenic episode. Clinical studies indicate that drugs like L-dopa or amphetamine, which potentiate dopaminergic activity, may induce or exacerbate schizophrenic symptoms.
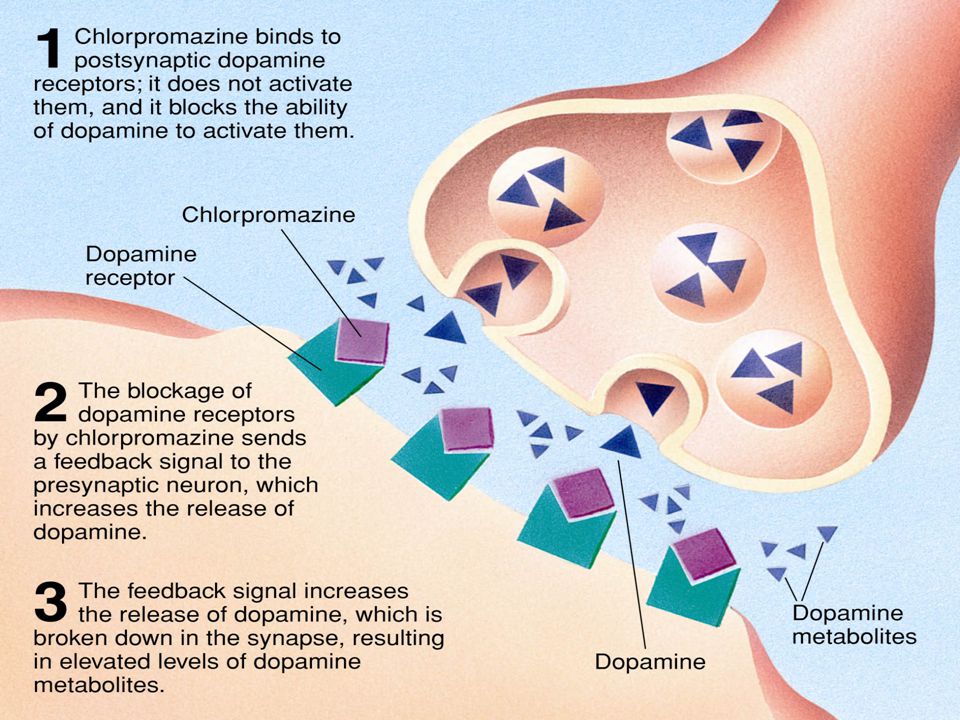
When the antipsychotic drugs were first introduced, their mode of action was unknown. At first, studies in the peripheral nervous system suggested that the anti-adrenergic effects of chlorpromazine probably explained its antipsychotic action, perhaps by reducing arousal. However, the fact that potent anti-adrenergic agents had no antipsychotic benefit did not support this hypothesis. Carlsson & Lindqvist first suggested that DA receptor blockade was the basis of antipsychotic effects. The low activity of butyrophenone antipsychotics at DA receptor sites linked to adenylate cyclase stimulation was seen as evidence against this idea. It was supported, however, by the recognition of two types of DA receptor. One was linked to adenylate cyclase stimulation, and another, higher affinity one was sometimes associated with adenylate cyclase inhibition and exhibited preferential binding of butyrophenones.
Agata Faron-Górecka, … Marta Dziedzicka-Wasylewska, in, 2020
Also Check: Which Organization Sets The Standards For Diagnosing Eating Disorders