Screening Tools For Different Ages
Different age ranges have unique needs regarding screening tools. For example, a young child might lack the vocabulary to describe their symptoms as fluently and accurately as an adult can. They need a screening test they can respond to.
Clinicians must consider how age influences each patients ability to express their feelings and experiences and choose screening tools accordingly. Here are recommendations for depression and anxiety screening two of the most common mental disorders for various age groups.
The Psychiatric Review Of Symptoms: A Screening Tool For Family Physicians
DANIEL J. CARLAT, M.D., Anna Jacques Hospital, Newburyport, Massachusetts
Am Fam Physician. 1998 Nov 1;58:1617-1624.
The psychiatric review of symptoms is a useful screening tool for identifying patients who have psychiatric disorders. The approach begins with a mnemonic encompassing the major psychiatric disorders: depression, personality disorders, substance abuse disorders, anxiety disorders, somatization disorder, eating disorders, cognitive disorders and psychotic disorders. For each category, an initial screening question is used, with a positive response leading to more detailed diagnostic questions. Useful interviewing techniques include transitioning from one subject to another rather than abruptly changing subjects, normalization and symptom assumption . The psychiatric review of symptoms is both rapid and thorough, and can be readily incorporated into the standard history and physical examination.
Family physicians frequently diagnose and treat psychiatric disorders, particularly in patients enrolled in managed care plans. One study revealed that 25 to 30 percent of patients presenting to primary care physicians have psychiatric disorders. Although estimates of missed psychiatric diagnoses are probably inflated and overemphasized, studies indicate that 30 to 80 percent of these cases are undetected by primary care physicians.
Depression and other mood disorders .
Personality disorders .
Substance abuse disorders.
Anxiety disorders .
Cognitive disorders .
Clinical And Research Implications
Our understanding of the psychosis continuum has expanded rapidly in the last decade. However, the rapid pace has resulted in inconsistencies with the terms used. A consensus for definitions regarding specific terms should have been established at the onset, yet this has not occurred. An approach to this issue is to firstly determine the terms required for these experiences and symptoms across the psychosis continuum. We have proposed a model in Figure which highlights the two dimensions which need to be considered: psychotic threshold level; and distress/help-seeking behaviors. Both dimensions range from low to high.
How Common Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is more common than most people think. About 1 in 200 of the people in the United States will develop schizophrenia over the course of their lives. It’s also important to know that schizophrenia has many different symptoms and can show up in many different ways.
Schizophrenia is not the same as a “split personality.” A split personality is another type of mental illness. Split personality is much less common than schizophrenia.
Mental Health Assessment Examples For Behavioral Health Practitioners

Mental and behavioral health assessments serve many purposes when working with a patient. Assessments can help you through the diagnosis and treatment-planning process, inform your decision-making and enable you to track patient progress. Unlike screenings, free mental health assessment tools come in various formats. Regardless of the method you choose, a behavioral assessment can help you understand, diagnose and treat your patients.
Here are six common behavioral assessment methods to consider using.
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
There are different types of treatment available. Medical professionals should work with you to find the right treatment for you. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends that you should be offered a combination of medication and talking therapies.
People who live with schizophrenia can respond to treatment differently.
For many treatment helps to reduce symptoms to help make daily life easier. You may find that you need to continue with treatment to keep well. For every 5 people with schizophrenia:
- 1 will get better within 5 years of their first obvious symptoms.
- 3 will get better but will have times when they get worse again.
- 1 will have troublesome symptoms for long periods of time.
What medication should I be offered?
Your doctor may offer you medication known as an antipsychotic. These reduce the symptoms of schizophrenia, but dont cure the illness. Your healthcare professionals should work with you to help choose a medication. If you want, your carer can also help you make the decision. Doctors should explain the benefits and side effects of each drug.
In the past, some antipsychotics had negative side effects. Some people find that the side effects of newer antipsychotic drugs are easier to manage.
Your medication should be reviewed at least once a year.
What type of psychosocial treatment will I be offered?
Family intervention is where you and your family work with mental health professionals to help to manage relationships.
What Are The Early Signs Of Schizophrenia
The most common early signs of schizophrenia may include social withdrawal, depression, hostility, oversleeping or insomnia, inability to cry or express joy, and deterioration of personal hygiene. The early stage of the schizophrenia is called the prodromal phase. It is difficult to diagnose schizophrenia during this early stage, as these symptoms could result from a number of other problems.
Advantage Of Mental Health Assessment And Screening
Mental health assessment tools are used throughout the therapeutic process to determine whether someone would benefit from seeking mental health treatment, describe and diagnose the problem, increase knowledge, insight, and understanding, and allow both client and professional to measure goals and progress during the treatment and at the end.
Mental health doctors and counselors are there to help people improve their mental health. Mental health assessment and screening tools allow professionals to collaborate with clients to shape the best personal healing process possible.
APA ReferencePeterson, T. . Mental Health Assessment and Screening Tools, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2021, August 27 from https://www.healthyplace.com/other-info/mental-illness-overview/mental-health-assessment-and-screening-tools
Schizophrenia Test And Early Psychosis Indicator
Dr Greg Mulhauser, Managing Editor
Test yourself for the early symptoms of the schizophrenia prodrome, which may appear before an individual becomes fully psychotic. This test takes account of both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
The Schizophrenia Test and Early Psychosis Indicator for Prodromal Syndromes and Psychosis is designed as a simple screening quiz to help identify symptoms of the schizophrenia prodrome before an individual becomes fully psychotic. Unlike other schizophrenia screening tests on the internet, the STEPI takes account of both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia while also testing for mitigating factors which can preclude a diagnosis of schizophrenia altogether.
What Can I Do To Manage Schizophrenia
People deal with their experience in different ways. You might need to try different things before finding something that works.
Support groups
You could join a support group. A support group is where people come together to share information, experiences and give each other support. Hearing about the experiences of others can help you feel understood. This may help you feel less alone and boost your self-confidence.
You might be able to find a local group by searching online. Rethink Mental Illness have support groups in some areas. You can find out what is available in your area, or get help to set up your own support group if you follow this link:
Or you can call our advice service on 0808 801 0525 for more information.
Recovery College
Recovery colleges are part of the NHS. They offer free courses about mental health to help you manage your experiences. They can help you to take control of your life and become an expert in your own wellbeing and recovery. You can usually self-refer to a recovery college. But the college may tell your care team.
Unfortunately, recovery colleges are not available in all areas. To see if there is a recovery college in your area you can use a search engine such as Google. Or you can call our advice service on 0808 801 0525 for more information.
Peer support through the NHS
- side effects,
- recognising and coping with symptoms,
- what to do in a crisis,
- meeting other people who can support you, and recovery.
Self-management techniques
Additional Information And Note On Validity
The Schizophrenia Test and Early Psychosis Indicator was developed by Dr Greg Mulhauser. Like most mental health screening tests you will find on the internet, this test has not been evaluated for validity in terms of sensitivity and specificity via comparison with a Structured Clinical Interview for the DSM . Therefore, this instrument should not be relied upon in any way as a diagnostic aid but should be used solely as a tool for increasing your own awareness of experiences which might, under the careful evaluation of a psychiatrist, be considered indicative of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders.
Dr Greg Mulhauser, an experienced counsellor and psychotherapist, has also developed:
Diagnostic Issues And Controversies
It has been argued that the diagnostic approach to schizophrenia is flawed, as it relies on an assumption of a clear dividing line between what is considered to be mental illness and mental health . Recently it has been argued, notably by psychiatrist Jim van Os and psychologist Richard Bentall, that this makes little sense, as studies have shown that psychotic symptoms are present in many people who never become ‘ill’ in the sense of feeling distressed, becoming disabled in some way or needing medical assistance.
Of particular concern is that the decision as to whether a symptom is present is a subjective decision by the person making the diagnosis or relies on an incoherent definition . More recently, it has been argued that psychotic symptoms are not a good basis for making a diagnosis of schizophrenia as “psychosis is the ‘fever’ of mental illness a serious but nonspecific indicator”.
Proponents have argued for a new approach that would use the presence of specific neurocognitive deficits to make a diagnosis. These often accompany schizophrenia and take the form of a reduction or impairment in basic psychological functions such as , , executive function and problem solving. It is these sorts of difficulties, rather than the psychotic symptoms , which seem to be the cause of most in schizophrenia. However, this argument is relatively new and it is unlikely that the method of diagnosing schizophrenia will change radically in the near future.
Laboratory And Imaging Tests

Your doctor may use diagnostic and laboratory tests to rule out other conditions. These may include:
- Blood test to rule out several conditions, including lead poisoning, thyroid issues, and syphilis.
- Imaging tests, such as an MRI to rule out brain tumors or brain injury.
- Electroencephalogram, to monitor brain activity, especially in the case of brain injury or .
+ Rating Scales And Assessment Tools For Adults And Children
Its nearly impossible to deny the impact of behavioral and mental health assessments on helping counselors understand patients in their care. However, clinicians may be hesitant to incorporate specific measures due to the possibility of accumulating excess papers and adding time-consuming tasks to their day. ICANotes electronic health record software for behavioral health allows you to use more than 75 well-known rating scales and assessment tools electronically. This paperless solution integrates assessment results into your patients health charts and treatment plans while keeping data accessible and secure.
Assessing Schizophrenia In Children And Adolescents
Dr. Ann Reitan | August 4, 2014
Childhood-onset differs from adult-onset schizophrenia and schizophrenia that is first manifested in individuals in adolescence. Adolescent-onset schizophrenia occurs before the age of 17 years, and childhood-onset schizophrenia is delineated as emerging prior to the age of 12 years. Schizophrenia, generally, is characterized by positive and negative symptoms. The symptoms that emerge with the onset of schizophrenia in childhood and adolescence are generally the same as those that appear with adult schizophrenia. Positive symptoms, specifically, include those that can be represented by behaviors that are added to the normal presentation of an individual, and negative symptoms comprise those behaviors that are deficits with regard to normal behavior. Positive symptoms include, but are not limited to, delusions and hallucinations, as well as symptoms of a formal thought disorder, including rapid or pressured speech. Negative symptoms include flat affect, or diminished emotional expression, poor hygiene, a lack of motivation and poverty of speech.
Children suspected as having schizophrenia may have difficulty in differentiating dreams from reality, and they may confuse television with reality. They may have vivid and bizarre thoughts and ideas. They may demonstrate severe moodiness, regression to earlier stages of development, and they may have difficult peer relationships.
Screening For Mental Health Problems
Mental health screenings are informal symptom checks. They’re typically checklists or questionnaires that ask people to consider their symptoms and either indicate that yes, they experience a given symptom, or no, they do not experience said symptom. Many prompt the test-taker to rate the degree of severity for each symptom he or she is experiencing.
Screening tests don’t diagnose mental disorders. Instead, they’re powerful tools for beginning to fully understand your mental health, to decide if you should see a mental health professional, and to figure out what you’d like to improve. Additionally, mental health screening tests allow people of all ages to identify and discuss problems before they spiral down and out of control.
Screening tools are sometimes available in places such as community health centers, clinics, and the offices of mental health organizations like the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance and the National Alliance on Mental Illness . Many times, these are free of charge. For the tech-savvy, screening apps are available for smartphones, and online psychological tests allow people to complete screenings on their own computer. Here are links to various screening tests on HealthyPlace.com:
- rating scales
- questionnaires
- standardized tests
General Interviewing Approaches To Psychiatric Symptoms
1. Schulberg HC, Burns BJ. Mental disorders in primary care: epidemiologic, diagnostic, and treatment research directions. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 1988;10:7987….
2. Coyne JC, Schwenk TL, Fechner-Bates S. Nondetection of depression by primary care physicians reconsidered. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 1995;17:312.
3. Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Kroenke K, Linzer M, deGruy FV 3d, Hahn SR, et al. Utility of a new procedure for diagnosing mental disorders in primary care. The PRIME-MD 1000 study. JAMA. 1994;272:174956.
4. Maurer K. PRIME-MD gets mixed reviews in the field. Clin Psychiatr News. 1996;24:23.
5. Shea SC. Psychiatric interviewing: the art of understanding. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1988.
6. Chochinov HM, Wilson KG, Enns M, Lander S.Are you depressed? Screening for depression in the terminally ill. Am J Psychiatry. 1997;154:6746.
7. Klein DN, Riso LP, Anderson RL. DSM-III-R dysthymia: antecedents and underlying assumptions. Prog Exp Pers Psychopathol Res. 1993;16:22253.
8. Wehr TA, Goodwin FK. Can antidepressants cause mania and worsen the course of affective illness? Am J Psychiatry. 1987;144:140311.
9. Lazare A. Personality. In: Lazare A, ed. Outpatient psychiatry: diagnosis and treatment. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1989.
10. Ewing JA. Detecting alcoholism. The CAGE questionnaire. JAMA. 1984;252:19057.
11. Steinweg DL, Worth H. Alcoholism: the keys to the CAGE. Am J Med. 1993;94:5203.
How Do Doctors Test For Schizophrenia
There are no laboratory tests to diagnose schizophrenia. Instead, a doctor will perform a physical evaluation, review your medical history, and may use various diagnostic tests, such as a blood test, MRI, or CT scan to rule out any other conditions. If there are no physical reasons for the symptoms, the individual is referred to a psychiatrist or psychologist, for further assessment. A diagnosis is made based on the symptoms the person is experienced and the psychiatrists observation of their behavior.
Who Is Schizophrenia This Quiz For
Below is a list of 10 questions designed for people who are concerned about schizophrenia. Read each question carefully, and indicate how often you have experienced the same or similar challenges.
If you have any been struggling for a month or more and those struggles have caused difficulties in functioning for the past six months, let your doctor know. This interactive quiz has been structured in a manner to allow for a short and simple self-assessment. The questions relate to life experiences common among people who have been diagnosed with schizophrenia and are based on criteria in the DSM-5.
To learn more about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of schizophrenia, read Psycoms comprehensive overview article.
Rating Scales And Assessment Tools For Adults
The following are the behavior assessment tools for adults ICANotes integrates with:
- RAPI: Rutgers Alcohol Problem Index
- RCADS-P: Revised Childrens Anxiety and Depression Scale Parent
- RCADS: Revised Childrens Anxiety and Depression Scale
- SCARED: Screen for Child Anxiety-Related Disorders
- TESI-C: Traumatic Events Screening Inventory for Children
Electronically storing your assessments saves you time and paper, allowing you to spend your sessions connecting with patients and providing quality treatment. Behavioral and mental health are already complex. Incorporating your screening and assessments into your EHR saves you from the hassle of paperwork and enables you to address your patients with the standard of care they deserve.
Negative Symptoms Assessment 4
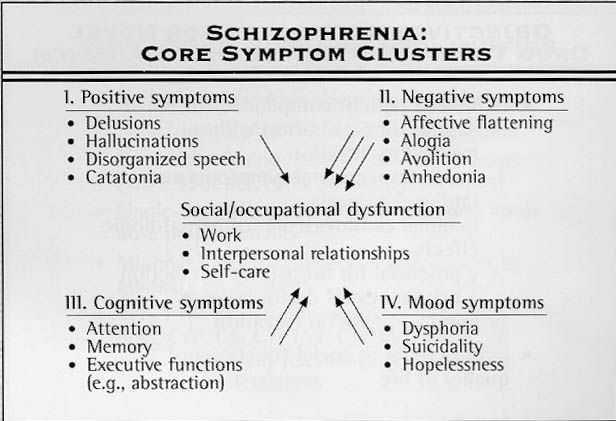
A study published in the Int. Journal of Psychiatry about the validation of a 4-item Negative Symptom Assessment . This study revealed NSA-4 is a short practical clinical tool for the assessment of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. The psychometric properties and predictive power of a four-item version were compared with the NSA-16 to determine predictive validity and construct validity. Both scales showed acceptable internal consistency and test retest reliability . This study demonstrates that NSA-4 ofters accuracy comparable to the NSA-16 in rating negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia .
Community Mental Health Team
If a diagnosis of schizophrenia is suspected, the GP should refer you to your local community mental health team .
CMHTs are made up of different mental health professionals who support people with complex mental health conditions.
A member of the CMHT team, usually a psychiatrist or a specialist nurse, will carry out a more detailed assessment of your symptoms. They’ll also want to know your personal history and current circumstances.
To make a diagnosis, most mental healthcare professionals use a diagnostic checklist.
Schizophrenia can usually be diagnosed if:
- you’ve experienced 1 or more of the following symptoms most of the time for a month: delusions, , hearing voices, incoherent speech, or negative symptoms, such as a flattening of emotions
- your symptoms have had a significant impact on your ability to work, study or perform daily tasks
- all other possible causes, such as recreational drug use or bipolar disorder, have been ruled out
Tools For Diagnosing Schizophrenia
Diagnosing schizophrenia is often difficult, especially in teens when it frequently shows up. Many of the symptoms of early schizophrenia resemble normal teenage behavior, such as changing friends, withdrawal from family, problems managing emotions, and difficulty making decisions. The diagnostic process should be thorough in order to insure an accurate diagnosis.
Schizophrenia: Old Wine In New Bottles And New Wine In Old Bottles
As commonly acknowledged, schizophrenia is characterized by an immense variability in individuals clinical expression and experiences. Further, it is clear that causal factors are complex and numerous. To address the problem of heterogeneity across patients, we further propose that generic sex and gender differences influence the clinical expression, risk, treatment, and outcome of schizophrenia . There are no sex differences unique to schizophrenia or explicitly pointing to other disorders. Men and women have the same core experience, namely disruption of the self, but express such experiences differently as they might be influenced by sex and gender roles that are transdiagnostic in their importance. The term transdiagnostic in this manuscript refers to research and theory that crosses traditional psychiatric diagnoses as represented in DSM-5 and focuses on common between diagnoses functions such as affect and cognition . To be clear, sex and gender are complex concepts encompassing a broad range of biopsychosocial processes, perhaps best characterized by the description of gender is the social meaning of sex embedded in social practices .
Emanuel Schwarz, … Sabine Bahn, in, 2011
The Positive And Negative Symptom Scale
PANSS provides objective measuring of clinical response to pharmacologic treatments and it is incredibly useful in clinical research, with some claiming it as the gold standard measure of treatment efficacy. Longitudinal data for individual patients can be pooled together to examine the effect covariates have on the treatment arm versus the control placebo group in therapy specific studies, hence, PANSS is a reliable means of assessing patients chronologically throughout the course of their illness. A study categorized patients into four mutually exclusive groups based upon results from the PANSS. These results showed that in a treatment group primarily seen in the outpatient setting, 19% of individuals were classified as having prominent negative symptoms, 20% as having prominent positive symptoms, and 21% as having both prominent positive and prominent negative symptoms . This study reinforced that those with negative symptoms have poorer overall outcomes as measured by remission rates and that those with both positive and negative symptoms have even worse outcomes, further demonstrating that the negative symptoms directly affect severity and chronicity of schizophrenia.
How Do You Assess Mental Health Status
Determining how you assess your patients mental health status will depend on the types of assessment and screening tools you use. Consider the following factors when selecting a tool:
- Reliability: Does the test have the reliability to produce consistent results?
- Validity: Does the test have the validity to differentiate between a patient with a problem and one without?
- Sensitivity: Does the test have the sensitivity to identify a problem accurately?
- Specificity: Does the test have the specificity to identify individuals who do not have a problem?
Selecting a test that conforms to the above factors will help make your results as accurate and helpful as possible. Disorder-specific assessments are valuable tools when working with patients, but how can you know which areas to test for? Screening tools can be the starting point that illuminates these risk areas.
The Scale For The Assessment Of Negative Symptoms And The Scale For The Assessment Of Positive Symptoms
The and were developed in 1980 to fill a conspicuous gap in tools that could effectively measure the severity of negative and positive symptoms . A standardized scale measuring either positive or negative symptoms did not exist at the time, and negative symptoms were often overlooked, in both clinical as well as in research settings, while positive symptoms were sometimes overemphasized. With Crow’s work on the importance of negative symptoms, new interest in screening patients with negative symptoms, as well as the inter-correlation of negative symptoms, arose . Partly in response to this paradigm shift, the Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms was developed . SAPS were subsequently released a year later, enabling the clinician to evaluate positive symptoms using a similar structure and format to SANS . Specific symptoms in both scales were chosen on the basis of both clinical experience and empirical statistical evaluation of data interrelationships and correlations .
Clinical Features And Diagnosis
The diagnosis of schizophrenia is made clinically, based on a typical combination of symptoms , in the absence of other psychiatric or medical conditions that would explain the symptoms . The exact number and combination of symptoms, as well as the required duration of symptoms to make a diagnosis of schizophrenia, differ depending on the classification system used . Making a diagnosis based on clinical symptomatology and course alone, without the help of genetic markers or biomarkers, can lead to different diagnoses over time .
Schizophrenia is a disorder with an onset in late adolescence or early adulthood. Most patients present with schizophrenia between 15 and 45 years of age. Onset during childhood or in late life is possible, but not common. Onset at the extremes of the age range show continuity with typical-onset schizophrenia, although the onset of psychosis after age 50 should raise suspicion for a secondary psychosis.
Delusions are false, nonculturally sanctioned beliefs that are held with great conviction, even in the face of overwhelming evidence to the contrary. Table 28-5 outlines common delusional themes. The delusional idea puts the patient at odds with his or her culture or subculture. The content of delusions can be nonbizarre or bizarre . By convention, bizarre delusions suggest schizophrenia and exclude delusional disorder.
Richard Lewine, Mara Hart, in, 2020
Tools To Assess Negative Symptoms In Schizophrenia

Although effective treatments for negative symptoms are currently limited, clinicians still need to assess and monitor them because of their impact on patient functioning. Further, documenting patients negative symptoms provides a complete clinical record that the clinician can use to make systematic and careful treatment decisions. Several tools for assessing negative symptoms in schizophrenia are available, including the Clinical Global Impression scale , the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale , the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale , the Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms , the 16-item Negative Symptoms Assessment , and the Schedule for Deficit Syndrome . Additionally, newer instruments are in developmentthe Clinical Assessment Interview for Negative Symptoms and the Brief Negative Symptoms Scale and are yielding promising results. This overview outlines these assessment tools so that clinicians can measure negative symptom severity and track treatment response for their patients with schizophrenia.