Treatment Of Schizophrenia In Children
As a treatment for this medical condition, you need to take the child to the psychiatrist and psychologist and they will be giving the right treatment. They will also suggest what the family members need to do with the child when the kid is not happy. There are even social workers and psychiatric nurses who are ready to look over them.
Diagnosis Of Schizophrenia In Children
The diagnosis of childhood schizophrenia always starts with ruling out other mental health diseases associated with similar symptoms, like autism spectrum disorder and determining that the symptoms arent due to substance abuse or medication. The diagnosis process may involve
- Physical exam: This may be done to rule out other problems causing the symptoms and to check for any related complications.
- Tests and screenings: These include tests to rule out other medical disorders and tests to screen for drugs and alcohol. The doctor may also ask to get an MRI or CT scan done.
- Psychological evaluation: This involves doing a complete psyche analysis observing the childs appearance, asking about thoughts feelings and behaviour patterns , evaluating the ability to think and function at the age-specific level, noting anxiety and psychotic symptoms, and discussing family history.
- Diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia: The doctor may use the criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistic Manual of Mental Health Disorders , published by the American Psychiatric Association to diagnose the schizophrenia in the child.
Chemical Changes In The Brain
A series of complex interrelated chemicals in the brain, called neurotransmitters, are responsible for sending signals between brain cells.
Low levels or imbalances of these chemicals are believed to play a role in the development of schizophrenia and other mental health conditions.
Dopamine, in particular, seems to play a role in the development of schizophrenia.
Researchers have found evidence that dopamine causes an overstimulation of the brain in people with schizophrenia. It may account for some of the symptoms of the condition.
Glutamate is another chemical thats been linked to schizophrenia. Evidence has pointed toward its involvement. However, there are a number of limitations to this research.
Complications before and during birth may increase the likelihood a person will develop mental health disorders, including schizophrenia.
These complications include:
Because of the ethics involved in studying pregnant women, many of the studies that have looked at the connection between prenatal complications and schizophrenia have been on animals.
Women with schizophrenia are at an increased risk for complications during pregnancy.
Its unclear if their children are at an increased likelihood for developing the condition because of genetics, pregnancy complications, or a combination of the two.
Read Also: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Your child’s doctor is likely to ask you and your child a number of questions. Anticipating some of these questions will help make the discussion productive. Your doctor may ask:
- When did symptoms first start?
- Have symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- How severe are the symptoms?
- What, if anything, seems to improve the symptoms?
- What, if anything, appears to worsen the symptoms?
- How do the symptoms affect your child’s daily life?
- Have any relatives been diagnosed with schizophrenia or another mental illness?
- Has your child experienced any physical or emotional trauma?
- Do symptoms seem to be related to major changes or stressors within the family or social environment?
- Have any other medical symptoms, such as headaches, nausea, tremors or fevers, occurred around the same time that the symptoms started?
The doctor will ask additional questions based on responses, symptoms and needs.
©1998-2021 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research . All rights reserved. Terms of Use
What Caused This Disease To Develop At This Time

The cause of schizophrenia is not known, but research is ongoing to elucidate the relative roles of genetics, environment, and neurodevelopmental as well as psychosocial stressors.There is a 10%-15% risk of schizophrenia developing if one parent has it, compared with a 1% risk in the general population.The prevalence of childhood-onset schizophrenia, defined as onset before age 13 years, is 0.1% or less.There is evidence that schizophrenia in childhood has frequently been misdiagnosed and with careful follow-up, these children will end up with another diagnosis .
The prevalence increases during adolescence until it reaches adult levels of 1% during late adolescence.The peak ages of onset for the disorder are from 15-30 years of age.There is evidence that supports an interaction between a neurodevelopmental and a genetic/environmental component that leads to the development of childhood-onset schizophrenia.
The majority of patients with early-onset schizophrenia have been found to have premorbid abnormalities, including social withdrawal and isolation, speech and language problems, academic and disruptive behavioral problems, as well as developmental delays. It has been found that the premorbid functioning of patients with bipolar disorder can be a way to differentiate that group from patients with schizophrenia, for they do not tend to have premorbid abnormalities as listed above.
Also Check: Can Dehydration Cause Panic Attacks
What Are The Possible Outcomes Of Childhood Psychosis
Increasing evidence indicates that compared with later-onset schizophrenia, childhood-onset schizophrenia is associated with worse outcomes that may have to do with the negative impact of the illness on the rapidly developing brain. Onset before the age of 10 years is associated with a poor outcome. Outcome is best predicted by premorbid functioning and the severity of positive and negative symptoms during the acute phase.
There is a percentage of patients who have only one cycle of the illness: prodrome, acute phase, recovery phase. Twenty percent of patients may have complete remission. Insidious onset and onset before age 12 years have been associated with a poorer outcome and incomplete remission. Misdiagnosis of children and adolescents is a significant problem in the patient group referred for the treatment of schizophrenia. Hallucinations in childhood are not necessarily a sign of schizophrenia. Diagnostic clarification comes over time with careful follow-up.
What Complications Might You Expect From The Disease Or Treatment Of The Disease
See above regarding possible side effects secondary to antipsychotic medication. The risk of suicide or accidental death resulting from behaviors caused by psychotic thinking appears to be at least 5%. Adults with schizophrenia have a suicide rate as high as 10%. They are also at increased risk for medical illness and mortality.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Of Puke
How Is Schizophrenia Treated In A Child
Antipsychotic medications are the treatment of choice, Dr. Fornari says. If a child were to be diagnosed with COS, second-generation antipsychotic medications would be used, he says. But early identification of the disorder is important, as are psychosocial treatment such as social support groups. For a child with schizophrenia, both academic and social support is key.
Finding ways to keep the person motivated and engaged is important, too, Dr. Houston says. Now people are really recognizing the value of these psychosocial interventions, he says.
Types Of Childhood Schizophrenia
There are several forms of schizophrenia that are visible among children. Maatai et al. is of the view that forms of schizophrenia among children are similar to those among adults. Three major forms of this condition have been recorded to date. Different major symptoms are used to classify schizophrenia into several forms. The three major forms of this condition are as analyzed below:
You May Like: Phobia In A Sentence
Treatment For Childhood Schizophrenia
Treatment options for children with schizophrenia have improved considerably in recent years. Physicians and mental health experts take a multi-faceted approach to treat schizophrenia in children and teens. A combination of medications, individual and family therapy, and specialized school programs result in better recovery outcomes for children and adolescents.
The medications used in the treatment of schizophrenia in children and teens belong to a class of drugs called antipsychotics or neuroleptics. Depending on your childs medical history, the severity of symptoms, age of onset and many other factors, the attending physician will determine whether to go with traditional varieties of these drugs or use the newer, atypical antipsychotics. A psychiatrist who specializes in children and adolescents will prescribe the medications he or she believes will work best for your child. The doctor will closely monitor how these powerful medications affect your child.
The newer antipsychotic drugs seem to manage symptoms better than traditional medications and carry a lower risk of the common severe side effects associated with the first-generation antipsychotic medications. The most common side effect associated with these newer medications is relatively significant weight gain. Because of this, the medical staff will watch for signs of insulin resistance. If unchecked, insulin resistance can worsen and result in the patient developing diabetes.
Does Child Abuse Lead To Schizophrenia
The amount of research on whether child abuse results in the development of schizophrenia in the child is not conclusive. However, it cannot be ruled out that child abuse may be one of the causes, as serious trauma during childhood can lead to schizophrenia.
Although discovering that your child has schizophrenia is devastating, an early diagnosis and treatment will improve prognosis and the childs outlook towards life. You can also join a support group to empower yourself to be better prepared to cope with the situation and help your child to lead a normal life.
You May Like: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
What Is Child Schizophrenia
It is a mental disorder occurring in the children. This starts early and in between from 7 to 13 years of age. When compared to severity, it is like the adult schizophrenia. The problems of these children include behavior and emotional problems. Also, they have different hallucinations, delusions, and many other extreme disorders. All these severely impact the ability of the children.
When Should You Consult A Doctor
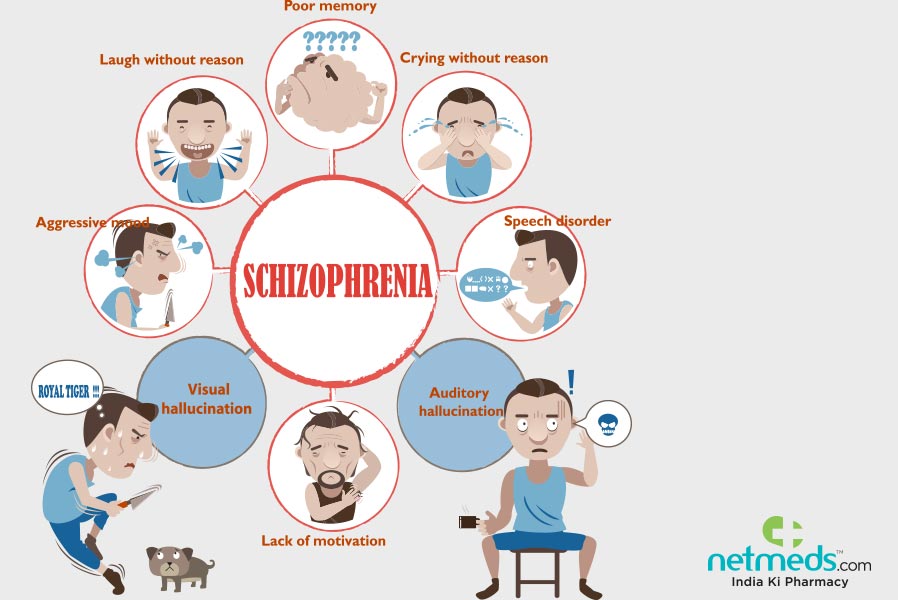
Seek medical help if you notice a change in your childs behaviour and the appearance of symptoms of childhood schizophrenia, such as
- Has stopped doing daily tasks such as bathing or dressing
- No longer wants to socialize
- Is slipping in academic performance
- Has strange eating rituals
- Shows excessive suspicion towards others
- Has strange ideas and fears
- Confuses dreams or television for reality
- Has violent or aggressive behaviour
- Has developmental delays compared with other siblings or peers
- Shows a lack of emotion
- Has bizarre ideas, behaviour or speech
Also Check: Brief Psychotic Disorder Vs Schizophreniform
The Causes Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a very serious mental illness where individuals are unable to differentiate between reality and imagination. It is the most common type of psychotic illness and is thought to affect up to 1 in 100 people in the UK during their lifetime.
Schizophrenia results in a disturbance of thoughts and feelings and can lead to odd and troubling behaviours. It is often mistaken for, and incorrectly labelled as, split personality, which makes the perception of it inaccurate and therefore more difficult to understand.
Are You Sure Your Patient Has Childhood Psychosis What Are The Typical Findings For This Disease
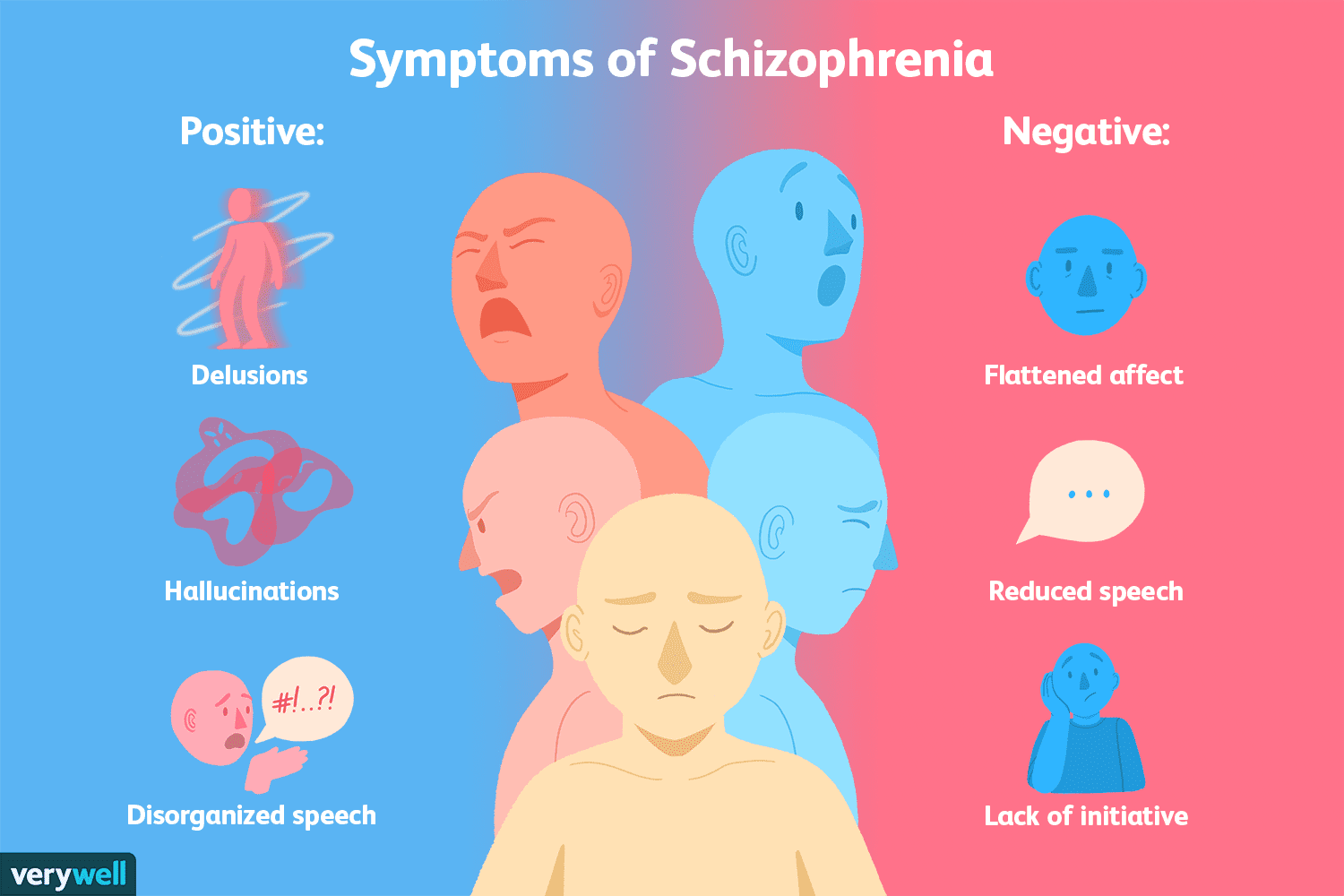
The term childhood psychosis actually could refer to any one of a group of disorders that have common symptoms. It is important to differentiate between these disorders, however, because of differences in treatment, course, and prognosis.The common symptoms shared by these disorders can be hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking or formal thought disorder, affective disturbances, and impaired reality testing. After ruling out other causes for psychotic symptoms, the diagnosis of schizophrenia can be made if the symptoms have lasted longer than 6 months, and schizophreniform disorder can be diagnosed if symptoms have lasted less than 6 months. During that time there is a least a 1-month period of 2 or more or the following:
Criterion A:
Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
Negative symptoms: affective flattening, alogia, or avolition.
The clinical presentation of childhood/adolescent schizophrenia is on a continuum with adult-onset schizophrenia, taking into account the childs developmental stage. Negative symptoms, including affective flattening, anhedonia, alogia, and avolition often occur but can be more difficult to recognize in children and adolescents..Disorganized thinking or formal thought disorder can be part of the acute presentation of schizophrenia and can be associated with disorganized and bizarre behavior.
Also Check: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Following Treatment Is Essential
Whether it begins in childhood or adulthood, schizophrenia is a life-long condition. Management is on-going and needs to be followed closely to help ensure success, even if the person feels better or the symptoms subside. Always check with your child’s healthcare provider before changing their treatment plan.
Environmental Factors During Pregnancy
The following environmental factors during pregnancy are believed to be associated with schizophrenia in children .
- Exposure to certain chemicals and hormones
- Illicit drug use
Other factors that may increase the risk for schizophrenia in children may include
- Immune system activation due to inflammation.
- Increased paternal age.
Although the factors mentioned above are linked to schizophrenia in children, how they cause or trigger the disorder is unclear.
Also Check: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
The Multi Dimensionally Impaired Group
To-date 33 children have been given the provisional diagnosis of MDI after the medication washout period and have been followed prospectively along with the COS children. This heterogeneous group of children, in general, has severe functional impairment associated with transient psychotic symptoms, multiple developmental abnormalities, abnormal neuropsychological test profiles, eye movement abnormalities, and familial risk factors that are not adequately characterized by existing DSM-IV categories . Despite the presence of overlapping symptoms with childhood and early onset schizophrenia, there are distinct features which have been used as the operational diagnostic criteria by the NIMH group to distinguish these individuals. :
Brief, transient episodes of psychosis and perceptual disturbance, typically in response to stress.
Nearly daily periods of emotional lability disproportionate to precipitants.
Impaired interpersonal skills despite the desire to initiate peer friendships .
Cognitive deficits as indicated by multiple deficits in information processing.
No clear thought disorder .
**ADHD is highly comorbid in the MDI group.
Children Suffering From Schizophrenia Are Dangerous
It is a fact beyond doubt that children with schizophrenia tend to be more violent and boisterous than other children their age. This is as a result of the delusions and hallucinations that these children experience. However, to claim that these children are dangerous than their counterparts who are normal is erroneous. The fact is that the children are not any more violent than the average child or a danger to other people around them .
Don’t Miss: What Is A Fear Of Bees Called
Possible Early Onset Schizophrenia Risk Factors
- History of first or second-degree genetic relatives with schizophrenia
- Mother became pregnant at an older age
- Stressful living environment
- Exposed to viruses while in the womb
- Mother with severe malnourishment during pregnancy
- Taking psychoactive drugs, such as LSD, psilocybin , or MDMA during the pre-teen and early teen years
Treatment For Schizophrenia In Children
There is no specific cure for schizophrenia but early diagnosis will lead to early interventions. The existing treatment strategies aim to reduce symptoms and improve the childs quality of life. A combination of therapies is often needed for the effective management of schizophrenia. Some children may require lifelong treatment. Parents need to be supportive and understand need of therapies and medications. The child with schizophrenia can lead a productive life if treatment is given with patience and love.
Hospitalization is often recommended for children with severe symptoms. This can ensure a childs safety, nutrition, hygiene, and sleep. However, some children may receive partial hospitalization and residential care if the symptoms are not too severe .
The following treatment methods are often recommended by pediatric psychiatrists .
- Medications
Medications are necessary to treat schizophrenia. Neuroleptics or antipsychotic medications are commonly prescribed to reduce schizophrenic symptoms in children. Taking medications as per the prescription can help reduce the severity of hallucinations, delusions, etc.
Follow-ups are required to adjust the dosage and type of medication over time to maintain their effectiveness. Haloperidol , Loxapac , Thorazine , etc., are examples of neuroleptics used to treat the symptoms of schizophrenia.
- Psychotherapy
Psychotherapies can also help the child deal with the stigma of mental illness and cope with daily challenges.
Read Also: Why Are Aquarius So Depressed
What Are The Adverse Effects Associated With Each Treatment Option
Children and adolescents treated with atypical antipsychotic agents are at higher risk than most adults for the development of multiple adverse effects. They include sedation, extrapyramidal symptoms , withdrawal dyskinesia, prolactin-related adverse effects , weight gain, dyslipidemia, and suicidal ideation and behaviors.
There should be baseline blood work done as well as baseline height, weight, and body mass index measurement. These indices should then be followed over time, as long as the patient is taking medication. The recommended assessments and frequency are as follows:
Personal and family history: at baseline and annually
Lifestyle monitoring: at every visit
Height, weight, BMI percentile/z score:at every visit
Somnolence/sedation: at every visit
Sexual symptoms/signs: at baseline, titration, then every 3 months
Blood pressure, pulse baseline: at titration, and every 6 months
Fasting glucose, lipids ± insulin determinations: at baseline, 3 months, then every 6 months
Liver function tests: at baseline, 3 months, then every 6 months
Extrapyramidal symptoms, akathisia: at baseline, titration, 3 months, then annually
Dyskinesia/tardive dyskinesia: at baseline, 3 months, then annually
Electrolyte determination, blood count, renal function: at baseline and annually
Prolactin levels: only when symptomatic
Electrocardiogram: if taking ziprasidone, during titration and at maximum dose
What Is Schizophrenia In Children
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness. Its a long-lasting and disabling problem of the brain. It can be treated, but right now there is no cure. A child with this disorder has unusual behavior and strange feelings. They may suddenly start to have psychotic symptoms. Experiencing psychosis means having strange ideas, thoughts, or feelings that are not based in reality.
Schizophrenia is not often found in children younger than age 12. Its also hard to spot in the early stages. Often, the psychotic symptoms start in the middle to late teen years. Slightly more boys develop it in childhood. But by the teen years it affects both boys and girls equally.
Also Check: Panic Attack Blurry Vision