History Of Manic Depression
The term manic depression has Greek and Roman origins. They used the words mania and melancholia for people living with mental illness, which translates to our words manic and depressive. During the 19th century, two French doctors, Jules Baillarger and Jean-Pierre Falret, both separately described the condition to the Académie de Médicine in Paris.
Manic depression was coined by the early 20th-century German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin. He distinguished manic depression from schizophrenia because of the symptom-free periods that people with untreated manic depression experience.
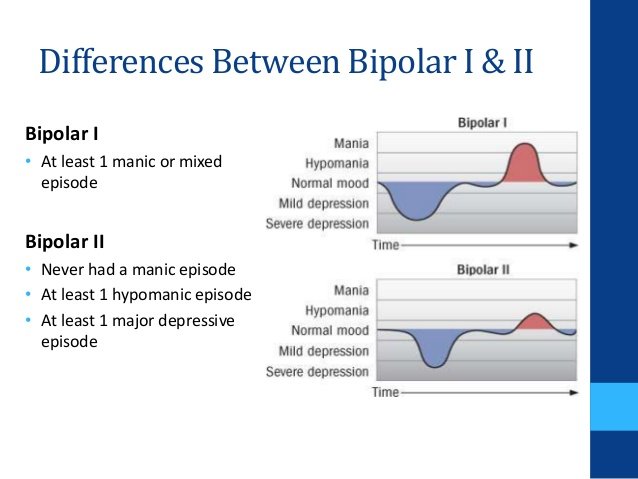
Symptoms Specific To Bipolar I
Where bipolar I and II differ is the length and intensity of the high and the presence of major depression. Bipolar I requires one experience of mania, but does not require an episode of major depression .
The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders classifies mania to be a period of abnormality, featuring an elevated, persistent or irritable mood, severe enough to impair functioning, with three or more symptoms of:
- Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
- Increased goal-directed activity
- Excessive involvement in activities that have high potential for painful consequences.
For an episode to be defined as manic it must last at least one week. Someone experiencing mania may not know they are ill or in need of treatment, and occasionally an episode will include an experience of psychosis or delusional thoughts.
Many people who experience mania describe their actions as euphoric, a feeling of invincibility, where no idea is too big or too optimistic.
Dov is a SANE Speaker who was diagnosed with bipolar disorder while completing his medical degree. Dov describes mania as a highly traumatic roller coaster ride.
What Is The Outlook
Bipolar disorder isnt curable. But with proper treatment and support from family and friends, you can manage your symptoms and maintain your quality of life.
Its important that you follow your doctors instructions regarding medications and other lifestyle choices. This includes:
Including your friends and family members in your care can be especially helpful.
Its also helpful to learn as much as you can about bipolar disorder. The more you know about the condition, the more in control you may feel as you adjust to life after diagnosis.
You may be able to repair strained relationships. Educating others about bipolar disorder may make them more understanding of hurtful events from the past.
Read Also: Do You Have Social Phobia
Learn The Differences Between These Two Disorders How To Spot The Signs Of Each And How To Treat Them
Life is turbulent, and changing moods can often be a natural response to stressful situations.
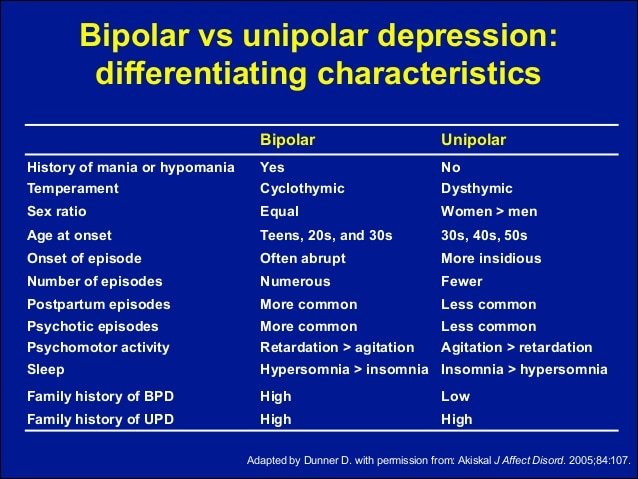
But for some, mood shifts are so extreme that they could be a sign of more serious conditions such as borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder, both of which are characterized in part by major mood swings, according to Frank Yeomans, M.D., Ph.D., director of training at the NewYork-Presbyterian Borderline Personality Disorder Resource Center, an internationally recognized center for the study of personality disorders, and a clinical associate professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine Department of Psychiatry.
This partial similarity in mood shifts, going from an extremely high mood to a very low mood, causes many people, including some clinicians, to confuse the two disorders, says Dr. Yeomans, who is also an adjunct associate professor of psychiatry at the Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons Center for Psychoanalytic Training and Research. Yet they are two distinct and serious diagnoses with different symptoms that require different methods of treatment.
Both illnesses affect millions of Americans. Bipolar disorder is estimated to affect 2.8 percent, or roughly 6.5 million adults, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. The prevalence of borderline personality disorder is estimated to range from 1.6 to 5.9 percent of the American adult population.
Many People With Bipolar Disorder Are Misdiagnosed As Depressed
Up to 25 percent of people with bipolar disorder are wrongly diagnosed with depression initially, which may have to do with the fact that they only seek treatment when they’re trapped in the desperate pit of clinical depression. Later on, when the medical professional learns of the episodes of mania or hypomania in the patient’s life, they are more often able to correctly identify bipolar disorder.
There’s another side to the misdiagnosis, though. “Many people think of bipolar as a way to describe extreme mood swings and it tends to be overdiagnosed, especially in teenage populations,” Aman tells Bustle. But the phases of mania or hypomania differ distinctly from mood swings, both in their duration and how they interfere with people’s everyday lives. Individuals with bipolar disorder, versus those with severe mood swings or clinical depression, are more likely to suffer from substance abuse, eating disorders, and metabolic issues.
This also means treatment will vary for each person. Aman says she cannot prescribe a single way of helping someone through a manic stage, as everyone responds differently. She does point out, though, that every person with bipolar disorder, no matter what “type” they have or how often they fall into a clinical depression, “needs loads of support from friends and family.” They often forget the fact that they’re loved, so keep encouraging them, even if you feel like you don’t quite get what they’re going through.
Images: Fotolia ; Unsplash
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Symptoms Of An Eating Disorder
How To Get A Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis
Health providers diagnose bipolar disorder through patient interviews, typically following a questionnaire on mood disorders.
However, it’s a difficult diagnosis to make. Some symptoms develop and reveal themselves over time, or they look similar to other mental health problems. When symptoms are less severe, like those of hypomania, they are usually not debilitating, and may appear to be personality traits, like being an extreme extrovert or overachiever.
In fact, there is an average seven year delay from the time a person first visits a health professional with symptoms to receiving a bipolar diagnosis from a mental health professional.;
“Most often people are presenting with symptoms to their health provider when they are depressed, and it looks very similar to major depressive disorder. With hypomania, when people have high levels of energy, and need to sleep less, and are maybe goal oriented or productive, they are like, ‘Well, that’s great,'” Clark says.;
Mania may also be misdiagnosed as borderline personality disorder, or confused with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder . Bipolar is often misdiagnosed as ADHD because manic symptoms resemble hyperactivity and the lack of motivation associated with depression can seem like inattention.;
Bipolar Disorder And Suicide
The depressive phase of bipolar disorder is often very severe, and suicide is a major risk factor. In fact, people suffering from bipolar disorder are more likely to attempt suicide than those suffering from regular depression. Furthermore, their suicide attempts tend to be more lethal.
The risk of suicide is even higher in people with bipolar disorder who have frequent depressive episodes, mixed episodes, a history of alcohol or drug abuse, a family history of suicide, or an early onset of the disease.
Suicide warning signs include:
- Talking about death, self-harm, or suicide.
- Feeling hopeless or helpless.
Read Also: What Phobia Is Fear Of Snakes
Bipolar Disorder & Manic Depression Are Actually The Same Thing
Bustle spoke with Jodi Aman, a psychotherapist with over 20 years of experience working with mentally ill patients and the author of You 1 Anxiety 0, who says the two terms clinically have no difference. “The name of changed from manic depressive to bipolar,” she says. Technically, the term manic depressive is no longer used in the medical community. It was removed as an official label several years ago in order to distinctly separate it from depression, yet people will still use it in conversation, which is why you still hear it.
Clinical Depression Is Part Of The Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis
In order to gain a better understanding of bipolar disorder, it’s important to understand why manic depression was ever used as a name for the disease in the first place. A person with bipolar disorder will suffer from bouts of clinical depression, along with the phases of mania or hypomania. That’s precisely why the term manic depression was assigned to bipolar disorder a long time ago, because it referred to both the mania and the depression in one neat package.
However, this use of manic depressive has led to a lot of confusion, and some have to come to think that it just means someone is wrestling with depression for an extended period of time before they bounce back to normal. Aman reminds us that bipolar disorder is so much more than that. “The manic or depressive episodes last longer than a few hours or days,” she says, which distinguishes it clearly from clinical depression.
Read Also: What Phobia Is Weather Related
Now We Know The Difference Where To Now
For people living with bipolar recovery is possible. Combining medication with a healthy lifestyle and support from community services and health professionals is an effective way to manage and respond to symptoms.
Charlotte is a SANE Speaker who was diagnosed with bipolar disorder ten years ago. She says shes made mistakes, but has learnt and continues to refine the management of her symptoms.
After the confusion, relief, blaming and identity crisis, I knew I had to sort myself out with help from doctors, medication, therapy, and family understanding, she says.
I kept going and Ive become a better human being. I know my own vulnerabilities and accept them. I know my stress triggers, how to step back, take a breath, regroup my feelings and then I can deal with it.
Yes, Ive stuffed up occasionally, but Ive learnt. Having bipolar disorder doesnt define me, but its helped me to teach my mind to be clearer.
For information about mental illness, including bipolar disorder, visit SANE Facts & Guides, or contact the SANE Help Centre on 1800 18 7263 .
Bipolar 2 Diagnostic Criteria
Bipolar 2 affects 0.4% of all people, according to a 2018 study published in Therapeutic Advancements in Psychopharmacology.
Women are more likely than men to have bipolar 2, and to experience more episodes of depression, says Crystal Clark, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and OB/GYN at Northwestern University.;
Criteria for a diagnosis of bipolar 2 include:;
- At least one lifetime hypomanic episode;
- At least one lifetime major depressive episode;
- Neither of these episodes were the result of medication, substances, or another medical illness;
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Relationship Anxiety
What Is The Difference Between Bipolar 1 And Bipolar 2
The main difference between bipolar 1 and 2 is the intensity of manic episodes. Bipolar 1 involves periods of severe mania whereas bipolar 2 involves periods of less severe hypomania.;
A manic episode lasts for at least one week, and its effects are intense and debilitating, affecting someone’s personal life and ability to work.
Symptoms include erratic behavior like talking too rapidly and loudly, breaking the law, and driving or spending money recklessly. A manic episode may also cause someone to have overblown feelings of self-importance or to experience hallucinations and delusions. There must be at least one episode of mania for a diagnosis of bipolar 1.
Meanwhile, those with bipolar 2 experience similar, but less intense symptoms in a hypomanic episode. They may feel euphoric and excited for a few days. They may be extremely physically active, appear agitated, and have difficulty sleeping.
Not everyone who has hypomanic episodes has bipolar disorder. It is possible for someone to be diagnosed as having bipolar 2, and then to have an episode of mania that changes their diagnosis to bipolar 1.
Prevalence of depressive episodes is another difference between bipolar 1 and 2. A bipolar 2 diagnosis requires a patient to experience one or more depressive episodes. Although those with bipolar 1 may also experience a major depressive episode, it is not a diagnostic requirement.;
Treatment For Bipolar Disorder
While there is no difference between bipolar and manic depression labeling, both the mania and the depression must be managed. Once the particular type of bipolar disorder is diagnosed, a treatment protocol will be created for the individual. In most cases, a combination of medication and psychotherapy is the first line of treatment. For those who have bipolar I, admission into a residential treatment program or hospitalization is the appropriate level of care.
Medication: Psychotropic medications are prescribed according to the predominant features of the bipolar disorder. These may include antidepressants, benzodiazepines, and anti-psychotic medication.
Psychotherapy: Talk therapy and group therapy helps individuals process the disruption that their bipolar disorder causes in daily life and find solutions for managing relationships and other stressors better. CBT can assist the individual with shifting pessimistic thoughts that drives irrational behaviors to more optimistic thinking.
Family-focused therapy: Stress that is a common feature within families when a member has bipolar disorder can undermine recovery. This involves helping family members learn to communicate better, practice better problem solving skills, and manage anger and conflicts more effectively.
Stress-management: Teaching individuals with bipolar disorder to better manage their stress level is intrinsic to a positive outcome. These methods include deep breathing, yoga, and mindfulness training.
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of Anxiety And Panic Attacks
What Is Bipolar 2 Disorder
Bipolar 2 disorder involves a major depressive episode lasting at least two weeks and at least one hypomanic episode . People with bipolar 2 typically dont experience manic episodes intense enough to require hospitalization.
Bipolar 2 is sometimes misdiagnosed as depression, as depressive symptoms may be the major symptom at the time the person seeks medical attention. When there are no manic episodes to suggest bipolar disorder, the depressive symptoms become the focus.
As mentioned above, bipolar 1 disorder causes mania and may cause depression, while bipolar 2 disorder causes hypomania and depression. Lets learn more about what these symptoms mean.
Risk Factors For Bipolar Disorder And Schizophrenia
No one knows what causes bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. However, genetics are probably a risk factor, as both conditions likely run in families. This doesnt mean that youll definitely inherit the disorder if your parent or sibling has it. Your risk increases, however, if multiple family members have the disorder. But knowing theres a risk increases the chance of early detection and treatment.
Environmental factors may also contribute to your risk, but this connection isnt entirely understood yet.
Also Check: How To Get Motivated To Exercise When Depressed
Coping With Bipolar Disorder
Living with bipolar disorder can be challenging, but there are ways to help make it easier for yourself, a friend, or a loved one.
- Get treatment and stick with itrecovery takes time and its not easy. But treatment is the best way to start feeling better.
- Keep medical and therapy appointments and talk with the provider about treatment options.
- Take all medicines as directed.
- Structure activities: keep a routine for eating and sleeping, and make sure to get enough sleep and exercise.
- Learn to recognize your mood swings and warning signs, such as decreased sleep.
- Ask for help when trying to stick with your treatment.
- Be patient; improvement takes time. Social support helps.
- Avoid misuse of alcohol and drugs.
Remember: Bipolar disorder is a lifelong illness, but long-term, ongoing treatment can help control symptoms and enable you to live a healthy life.
What Are The Treatments For Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a long-term illness that requires management throughout a person’s life. People who have numerous episodes of mood changes in a year can be much more difficult to treat. Medication is the primary form of treatment, but the additional use of psychotherapy or “talk” therapy is sometimes recommended to help prevent future episodes.
There are many drugs available to treat bipolar disorder. Proposed guidelines for treatment options are based on the three main phases of bipolar disorder, which include the acutemanic/mixed mood states, acute major depressive episodes, and finally the continuation/maintenance phase. As a general rule, avoiding antidepressants and taking two mood stabilizers has proven to be an effective strategy for most patients.
Mood-stabilizing drugs
Lithium is a mood-stabilizing drug. It has proven helpful in controlling mania and depression and preventing depression and manic episodes. Lithium will reduce symptoms of mania within two weeks of starting therapy, but it may take weeks to months before the condition is completely controlled. Thus other drugs like antipsychotic drugs or antidepressant drugs may also be used to help control symptoms.
Common side effects of lithium include:
- Frequent need to urinate
- Nausea
The following are signs of a lithium overdose. Call your doctor immediately or go to the nearest emergency room if you experience:
- Blurred vision
- Weight gain
- Slight trembling of hands
Atypical neuroleptics
Also Check: Did Diana Have An Eating Disorder
What Is Depression
Clinical depression is a serious illness that affects every aspect of an individuals life, including their personal and family relationships, work or school life, sleeping and eating habits, and general health. The symptoms of depression include:
- Loss of energy
- Change in appetite
- Change in sleep patterns
What You Can Do
People can often manage the symptoms of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia with medication and therapy. Having a support system in place will increase your chances of successfully managing your symptoms. A support system may include family, friends, and the people in your workplace.
If you have either bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, you have an increased risk of suicide. See your doctor if you have thoughts of suicide. They can provide treatment. Support groups can help to reduce the risk of suicide. You should also avoid alcohol and drugs to further reduce your risk.
If you have bipolar disorder, you should do the following:
- Follow a relatively stable lifestyle.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep.
- Maintain a healthy diet.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Help With Binge Eating Disorder