What Are The Dsm
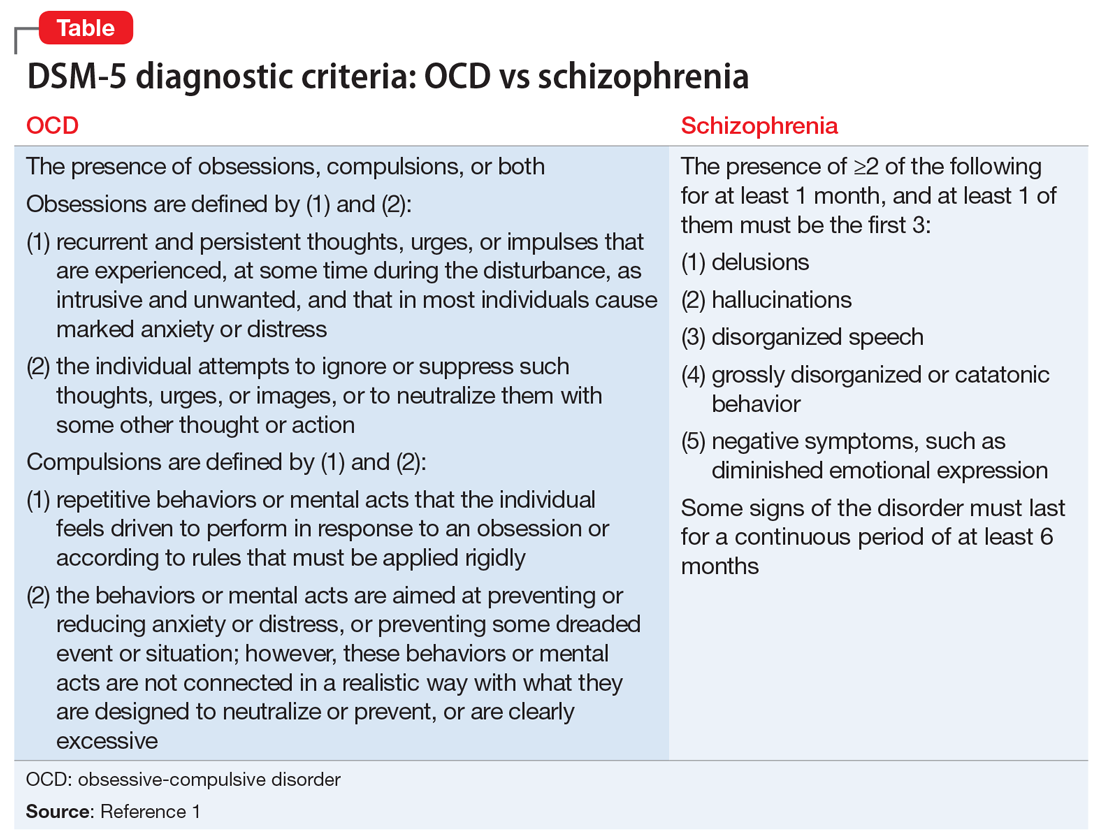
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual-V is the manual most mental health professionals use to diagnose disorders such as schizophrenia. The DSM-V specifies six diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia :
- Delusions
- Catatonic behavior or grossly disorganized behavior
- Negative symptoms, which include avolition, or a lack of motivation
- Significant behavioral disturbance such that a person does not work or interact with others well over the course of six months
A person must have at least two of the first five symptoms over the course of one month for a mental health professional to diagnose a person with schizophrenia.
How Schizophrenia Is Diagnosed
Schizophrenia is diagnosed on the basis of a consultation with the affected person. Specific diagnostic tools, in the form of a series of structured questions, will be used during the consultation to facilitate an accurate diagnosis.
Other relevant information about the patient may be also be taken into account, often from relatives or people who are very close to the patient.1
Paranoia And Delusional Disorderdsm
summarizes the symptomatic diagnostic criteria for paranoia/delusional disorder in the 4 major US operationalized systems that contained criteria for this syndrome. Two technical issues arose in describing these criteria. First, all of the DSM criteria sets contained one criterion that read something like Criterion A for schizophrenia has never been met. So that meant we had 2 levels of criterionthose specifically written for paranoia/delusional disorder and the rule outs that derived from the schizophrenia criteria. To differentiate these, we put the latter in italics. Second, only in DSM-III were there separate criteria for a broader non-schizophrenic paranoid syndrome and a narrower syndrome . We focus on the latter.
Diagnostic Criteria for Paranoia and Delusional Disorder from DSM-III Through DSM-5 and The Relationship of These Criteria to Symptoms and Signs Noted by Our Textbook Authors
| . |
|---|
Second, of the 3 symptoms/signs reported by 7 or 8 of the authors, one of themlack of affective deteriorationwas present from DSM-III to DSM-5 as a result of criterion Criteria A for schizophrenia has never been met that is present in modified form in all these editions. A second onelack of insightwas missing from all the relevant DSM manuals. The thirdnon-bizarre delusionswas present in DSM-III, III-R and IV, but not DSM-5.
Recommended Reading: Can You Be Bipolar And Not Take Medication
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
There arent any diagnostic tests for schizophrenia-spectrum conditions. But healthcare providers will likely run tests to rule out other conditions before diagnosing schizophrenia. The most likely types of tests include:
- Imaging tests. Healthcare providers will often use computerized tomography , magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging tests to rule out problems like stroke, brain injuries, tumors and other changes to your brain structure.
- Blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid tests. These tests look for chemical changes in bodily fluids that might explain changes in your behavior. They can rule out heavy metal toxicity or other causes of poisoning, infections and more.
- Brain activity testing. An electroencephalogram detects and records the electrical activity in your brain. This test can help rule out conditions like epilepsy.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed Dsm
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that deeply affects people. Because a correct schizophrenia diagnosis can improve someones quality of life, its important that it be made as soon as possible after the symptoms of schizophrenia appear.
Currently, no tests can provide a schizophrenia diagnosis. To determine whether someone has the disorder, doctors follow established criteria for a schizophrenia diagnosis.
You May Like: Is Anxiety A Chronic Illness
Why Did The Dsm Eliminate Types Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a rare mental illness that impacts an individuals interpretation of reality. This disease affects less than 1% of people. Those who suffer from this condition experience hallucinations, delusions, and behavior that stunts their day-to-day functioning, thus distorting how they experience the world.
This isnt only disturbing for the impacted individualit can also create distress for concerned family and friends. Without treatment, it isnt uncommon for this disorder to become debilitating. However, medical professionals can treat this illness, and daily functioning can be restored with proper treatment.
In 2013, our understanding of schizophrenia was forever changed due to shifts in the DSM-5. The DSM-5 is a tool used to diagnose mental health disorders, outlining the criteria for hundreds of illnesses.
Revisions to diagnostic information for a mental health disorder significantly impact research and treatment. It also affects how those experiencing the disorder understand their condition. The criteria to receive a diagnosis of schizophrenia changed when previously existing schizophrenia subtypes were eliminated.
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Schizophrenia is a condition that has severe effects on a persons physical and mental well-being. This is because it disrupts how your brain works, interfering with your thinking ability, memory, how your senses work and more.
Because your brain isnt working correctly, having schizophrenia often causes you to struggle in many parts of your day-to-day life. Schizophrenia often disrupts your relationships . It can also cause you to have trouble organizing your thoughts, and you might behave in ways that put you at risk for injuries or other illnesses.
Read Also: What Is The Worst Phobia
How Can I Support A Person Suffering From Schizophrenia
If you know someone or have a friend with schizophrenia, it is important to show your support.
Encourage that person to seek professional help and tell them that this is something it will be able to overcome.
Find information about the disorder so you can know more about the symptoms and help at the time of its manifestation.
Keep a positive attitude all the time and let that person know that he can count on you.
International Classification Of Diseases Diagnostic Criteria For Schizophrenia34
ICD-10 general criteria for the diagnosis of schizophrenia
The general criteria listed in the ICD-10 for the diagnosis of schizophrenia are listed below.
Either at least one of the syndromes, symptoms, and signs listed under below, or at least two of the symptoms and signs listed under should be present for most of the time during an episode of psychotic illness lasting for at least 1 month .
Recommended Reading: Can Ptsd Cause Shortness Of Breath
Schizophrenia Diagnosis: Rule Out Other Conditions
A diagnosis involves what someone is experiencing as well as what he is not. Some disorders have some features or symptoms that are shared with schizophrenia therefore, doctors check to see if something else fits better than schizophrenia. Some of the conditions that, according to criteria in the DSM-5, have some similarities with schizophrenia are
- Mood disorders with psychotic features
- Schizophreniform
The Decision To Eliminate Types Of Schizophrenia
Mental health professionals found the schizophrenia subtypes unreliable in the diagnostic process. Aside from being inconsistent, clinicians found them ultimately unhelpful.
Most subtypes went unused, aside from paranoid and undifferentiated. While developing reliable diagnostic criteria was crucial in these changes, the highest priority was developing a more substantial clinical assessment and treatment system.
Another effort made to facilitate efficient treatment was clarifying the diagnostic criteria of schizoaffective disorder. Schizoaffective disorder is a condition that has schizophrenic features alongside mood disorder symptoms. The schizoaffective disorder criteria shifted to include that indicators of a manic or depressive episode are consistently present for the duration of the illness.
People looking to learn more about schizophrenia may appreciate learning about the subtypes. While they are no longer used, they can provide deeper insight into how this illness has presented throughout the years.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Phobia Of Snakes
Or At Least Two Of The Following:
-
Persistent hallucinations in any modality, when occurring every day for at least 1 month, whenaccompanied by delusions without clear affective content, orwhen accompanied by persistent overvalued ideas
-
Neologisms, breaks, or interpolations in the train of thought, resulting in incoherence or irrelevantspeech
-
Catatonic behaviour, such as excitement, posturing or waxy flexibility, negativism, mutism, andstupor
-
Negative symptoms, such as marked apathy, paucity of speech, and blunting or incongruity ofemotional responses
The most common exclusion clauses are:
-
If the patient also meets criteria for manic episode or depressive episode, the criteria listed undersection and above must have been met before the disturbance of mood developed.
-
The disorder is not attributable to organic brain disease or to alcohol- or drug-related intoxication,dependence, or withdrawal.
Dsm 5 Schizophrenia Subtypes

The DSM 5 Schizophrenia does not contemplate the subtypes, which were eliminated when version 5 of the manual was published.
In the previous version, DSM 4, the following were contemplated:
- Paranoid type: there is the presence of delusions and hallucinations, but the thought disorder, disorganized behaviour or affective flattening are not.
- Disorganized type: in this type, the disorder of thought and flat affection are present together.
- Catatonic type: the subject can be almost motionless or exhibit agitated and purposeless movements.
- Undifferentiated type: Psychotic symptoms are present, but the criteria for paranoid, disorganized or catatonic types are not met.
- Residual type: positive symptoms are present only at low intensity.
You May Like: What Age Does Bipolar Disorder Develop
What Medications Or Treatments Are Used
Treating schizophrenia and related conditions typically involves multiple methods. Those methods can happen in combinations or steps.
Medications
There are two main types of medications that treat schizophrenia.
- Typical antipsychotics. Also known as first-generation antipsychotics, these medications block how your brain uses dopamine, a chemical your brain uses for cell-to-cell communication.
- Atypical antipsychotics. These medications, also called second-generation antipsychotics, work differently from first-generation antipsychotics. These block both dopamine and serotonin, two key communication chemicals in your brain. Clozapine is a particularly effective medication that can treat symptoms of schizophrenia when other drugs dont work. However, it has a rare serious side effect that requires frequent blood monitoring to keep people safe, which is why healthcare providers usually recommend other antipsychotics first.
There are other medications your healthcare provider might also prescribe to treat other symptoms that happen alongside or because of your schizophrenia symptoms. They might also prescribe medications to help reduce side effects of antipsychotic medications such as tremors.
In general, your healthcare provider is the best person to talk to about the medications they might prescribe. They can give you more specific information related to your specific situation, including your life circumstances, medical history and personal preferences.
Psychotherapy
Criteria For Schizophrenia Diagnosis In Dsm
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition is the authority on mental illness. Created and published by the American Psychiatric Association, this comprehensive manual describes all known mental disorders, among them schizophrenia.
Mental health professionals use the DSM-5 when determining what someone is experiencing. Doctors use the information and analyze:
- diagnostic features and symptoms
- duration of symptoms
- other conditions that share symptoms
They also look at age. While its not part of the diagnostic criteria, they do consider someones age. The typical age of schizophrenia diagnosis is between late adolescence and the mid-30s. This varies, though, with peak ages ranging from the early- to mid-20s for males and late-20s for females . Further, while its rare, schizophrenia can be diagnosed as early as childhood and as late as the 40s .
Age provides a general idea of the likelihood that someone has schizophrenia. Schizophrenia wont be the first consideration for a man in his 40s, for example. Beyond this, age isnt a diagnostic criterion. Just what are the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia?
Also Check: Can Untreated Anxiety Lead To Schizophrenia
Treatment For Schizophrenia Dsm
Even in cases where symptoms have lessened or subsided, schizophrenia requires lifelong treatment. Treatment may include therapy, medication, or a combination of the twothis is determined on a case-by-case basis.
Why The Subtypes Were Removed
With the release of the DSM-5, these subtypes were removed for
- They werent very reliable descriptions.
- People living with schizophrenia didnt always experience the same symptoms or subtype.
- There was no difference in brain functioning between the subtypes.
- The subtypes didnt help predict how the condition would play out over time.
- Some people couldnt be assigned a subtype based on their symptoms.
- They didnt help with treatment decisions.
- Scientists had stopped using the subtypes in their reports.
Instead, the APA believed it was more accurate to describe the symptoms of schizophrenia as a spectrum.
This means that people with schizophrenia may experience different symptoms at different times. It also means that not everyone with a schizophrenia diagnosis experiences the same symptoms.
This is why the condition is now called Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Disorders in the DSM-5, compared with just Schizophrenia and Other Disorders in the DSM-4.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Help For Bipolar Disorder
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
People with schizophrenia should do the following to help care for themselves and manage their condition:
- Take medications as prescribed. One of the most critical things a person with schizophrenia can do to help themselves is to take their medications. If you have schizophrenia, you should not stop your medication without talking to your healthcare provider. Sudden stopping of medication often speeds up the return of psychosis symptoms. Side effects are common with antipsychotics. However, there are many antipsychotic medications, so its often possible to work with your healthcare provider to find one that both works well for you and has minimal or no side effects.
- See your healthcare provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your condition.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Schizophrenia is more likely to respond and have a good outcome with early diagnosis and treatment.
- Avoid alcohol and recreational drug use. Alcohol and drug use can make schizophrenia symptoms worse and can lead to other issues. This includes using prescription medications in a way other than prescribed.
- Consider seeking support. Organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness can offer resources and information that can help.
Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Criteria What Is The Dsm 5 Code For Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria. Here are a number of highest rated Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria pictures on internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by doling out in the best field. We give a positive response this kind of Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria graphic could possibly be the most trending subject later than we part it in google plus or facebook.
Diagnostic Categories Covered In K Sads Pl Dsm 5 Download Table, What Is Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Schizophrenia Definition Symptoms, Pin By Angela Tomecko On Psychology Dsm Iv Delusional Psychology, Clinical Characteristics Of Schizophrenia Essay College Paper Directory,
Crumbtrail.org is an open platform for users to share their favorite wallpapers, By downloading this wallpaper, you agree to our Terms Of Use and Privacy Policy. This image is for personal desktop wallpaper use only, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, DMCA report please Contact Us
Recommended Reading: What Does Schizophrenia Literally Mean
Diagnosing Schizophrenia Using Symptoms And Features
Professionals use specific diagnostic features in the DSM-5 to help determine whether someone meets the criteria for schizophrenia. The DSM-5 delineates five main criteria. Paraphrased:
A. Two or more of
B. Level of functioning has declinedC. The symptoms in Criterion A have persisted for at least 6 monthsD. Schizoaffective disorder, major depression, and bipolar disorder have been ruled outE. Substance use/abuse has been ruled out as a cause
In order for someone to be diagnosed with schizophrenia, he must experience a group of these symptoms and features. One or two are not enough.
To receive a schizophrenia diagnosis, someone can have any of the symptoms and features, but he must have the following:
- At least two symptoms from Criteria A
- One of those two must be delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech.
- These must have been present for at least one month.
The symptoms must impair ones life and get in the way of her ability to work , have positive relationships , and practice self-care. The problems in these areas must be new, a decline in the previous status.
Duration of the symptoms is also important for a schizophrenia diagnosis. Someone must have been experiencing steady symptoms for at least one month. Symptoms must be present some of the time for six consecutive months.
How Common Is This Condition

Here are some statistics about how common schizophrenia is worldwide:
- New cases: There are about 2.77 million new schizophrenia diagnoses every year worldwide.
- Average number of worldwide cases: There are about 22.1 million cases globally at any time .
- Odds of developing it at some point in your lifetime: About 0.85% of the global population will experience schizophrenia at some point in their life.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Diagnose Schizophrenia
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
Schizophrenia is a condition that is dependent upon treatment. Traditional schizophrenia treatment plans include a combination of psychotherapy and medication.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is the preferred psychotherapy treatment. It challenges negative thought patterns, creates tactics for managing emotional responses, and can help facilitate healthy relationships.
Antipsychotic medications help manage symptoms. It is important to remember that medication in conjunction with psychotherapy is critical for optimal treatment. By dropping the schizophrenia subtypes, doctors were able to clarify symptoms, leading to more efficient medication management.