How To Know If You Might Have Bipolar Disorder
It can feel overwhelming to find an answer to the question: How do I know if I have bipolar disorder? While many consider it daunting, this is not the case. You may be seeking answers to understand the issue better if you suspect you or someone you love suffers from it.
When navigating a bipolar diagnosis, knowledge is power, which is incredibly accurate. By understanding your mental health condition, you will be able to improve your quality of life and cope better.
In this article we will discuss how to know if you have bipolar disorder, what treatment options are available, and more as we discuss the signs and symptoms of the condition.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Bipolar Disorder
While the self-test above can be an informative tool, a diagnosis needs to be made by a professional mental health expert.
Therapy and medication can be effective treatment options for Bipolar Disorder.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can help people better control both their manic and depressive behaviors. Psychoeducation can help people understand themselves and their condition better. Interpersonal and Social Rhythm helps people focus on developing regular daily habits to add stability to ones life.
Medications such as antidepressants can help prevent depressive episodes. Antipsychotics may help people with severe manic episodes avoid breaks from reality. Mood stabilizers can help a person better keep a consistent mood. Anti-anxiety medications can be a short-term treatment to help treat anxiety and sleep disturbances.
Unfortunately, finding the right medication regime is difficult in people with bipolar disorder. Oftentimes different medications, or combination of medications, needed to be tested and managed by a highly skilled doctor.
If you happen to be reading this and looking for help in the Southern California area, Solara Mental Health can be an option for you. Our San Diego Mental Health Center treats disorders such as bipolar disorders. Our skilled psychiatrists and therapists may be able to provide the help youve been looking for.
Contact us today if you are looking for a proper diagnosis and treatment for your disorder.
Whats The Difference Between Feeling Good Vs Hypomania
It takes time to know the difference. Everyone enjoys being happy and feeling good. But feeling good doesnt always mean you are good. Over time, youll start to understand yourself and learn the warning signs that you may be starting to have an elevated mood that is different than just feeling good.
Ask family and close friends who you trust, and have frequent contact with, to give you feedback. Ask them to tell you when they see beyond normal changes in your mood or behaviors.
Read Also: Phobia Definition Medical
What Are Manic Episodes
There are two different types of manic episodes: mania and hypomania. They share the same symptoms but differ in severity mania being more severe.
Both manic and hypomanic episodes will include three or more of the following:
- Uncontrollable energy
- Sense of worthlessness or guilt
- Shortened attention span and problems remembering things
- Thoughts that bounce from one idea to the next
- Lack of interest in activities that usually bring joy
- Thoughts of, or plans of committing suicide
What Causes Bipolar Disorder

The cause of bipolar disorder isnt clear. Research suggests that a combination of different things can make it more likely that you will develop bipolar disorder.
Genetic factors
There is a 13% chance you will develop bipolar disorder if someone in your immediate family, like a parent, brother or sister has bipolar disorder.
This risk is higher if both of your parents have the condition or if your twin has the condition.
Researchers havent found the exact genes that cause bipolar disorder. But different genes have been linked to the development of bipolar disorder.
Brain chemical imbalance
Different chemicals in your brain affect your mood and behaviour. Too much or too little of these chemicals could lead to you developing mania or depression.
Environmental factors
Stressful life events can trigger symptoms of bipolar disorder. Such as childhood abuse or the loss of a loved one. They can increase your chances of developing depressive episodes.
You can find more information about Does mental illness run in families? by clicking here.
You May Like: Progression Of Schizophrenia
Understanding Different Forms Of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar I And Bipolar Ii Are The Most Common Types With Two Main Differentiators:
- Bipolar I: A person may experience a manic episode of extreme highs lasting around seven days or requiring hospitalization. This may or may not be followed by an extremely depressed period lasting around two weeks.
- Bipolar II: A person may experience a less-intense version of mania called hypomania, which is not as severe as bipolar I. A depressive episode may occur before or after the hypomania. This depressive state can be severe and one condition of bipolar is not more or less serious than another.
- Cyclothymic disorder. This type of disorder can occur when the mania or depression episode lasts longer than two years.
- Other: This type of disorder could be rooted in substance use disorder affecting mood or other health concerns.
Read Also: Does Depression Make You Hungry
Clear Signs Of Sadness
The single most prominent sign of a depressive episode is extreme feelings of sadness. Like feelings of happiness, they may appear suddenly.
This sadness can be overwhelming. A person may not find humor in things that they used to laugh at. They may withdraw from important activities and social gatherings.
Other negative feelings may accompany sadness. A person may feel empty. They may feel like they dont have anything important to say.
Despite knowing that they are in a depressive episode, they may feel like their sadness will never go away. They may notice that their feelings are making other people sad.
This can cause their feelings to get worse. They may remain unconvinced of their worth, even when shown examples of it.
What Is The Treatment For Bipolar Disorder
If your doctor thinks you have bipolar disorder, they may refer you to a psychologist or psychiatrist.With help and support from family and friends, most people learn to manage their bipolar disorder and get on with life. You are likely to have times when you are well and times when you are unwell. The treatment with medication offered by your doctor or psychiatrist is tailored to your needs to help you recover from periods of illness so you get back to your normal moods and behaviours. They then adjust your treatment to help you remain well. Medical treatment is usually accompanied by psychological support to learn about the triggers and identify the early warning signs of your symptoms, and to teach you effective and healthy coping strategies.Most people return to their usual level of functioning after times of illness, although about 1 in 5 will have some ongoing difficulties.
Recommended Reading: Hippopotomonstrosesquipedaliophobes.
Caveats When Diagnosing The Type
There are two important caveats that may further complicate the process of distinguishing the two types of bipolar disorder.
One is that although the presence of psychotic symptoms are one of the things that differentiate bipolar I mania from bipolar II hypomania, someone with bipolar II may experience hallucinations or delusions during depressive episodes without the diagnosis changing to bipolar I.
The second is that someone with bipolar I disorder may also have hypomanic episodes. In fact, they commonly do. But, someone with bipolar II does not ever have a manic episode. If a manic episode occurs in someone with bipolar II, the diagnosis will be changed.
What Is Bipolar Ii Disorder
Bipolar II disorder is a type of bipolar disorder in which people experience depressive episodes as well as hypomanic episodes , but never mania. People with bipolar II disorder tend to have longer and more frequent depressed episodes than people with bipolar I disorder.
If the severity of your symptoms never rises to the level of mania, you have bipolar II disorder. If you have even a single episode of what is considered mania or one psychotic event during a hypomanic episode, your diagnosis would change to bipolar I disorder.
Also Check: Pristiq For Ptsd
How Is Bipolar Disorder Diagnosed
Bipolar disorder is diagnosed through a clinical interview with a licensed mental health professional, explains Simon A. Rego, PsyD, Chief Psychologist at Montefiore Medical Center and Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City.
Sometimes, the mental health professional will also ask the person to complete some assessment measures to aid in the diagnosis, Rego says. They may also ask to speak with a family member or partner, or other significant person in the persons life, in order to get additional information about the impact the disorder has had on the person and their relationships.
What Is Bipolar Disorder
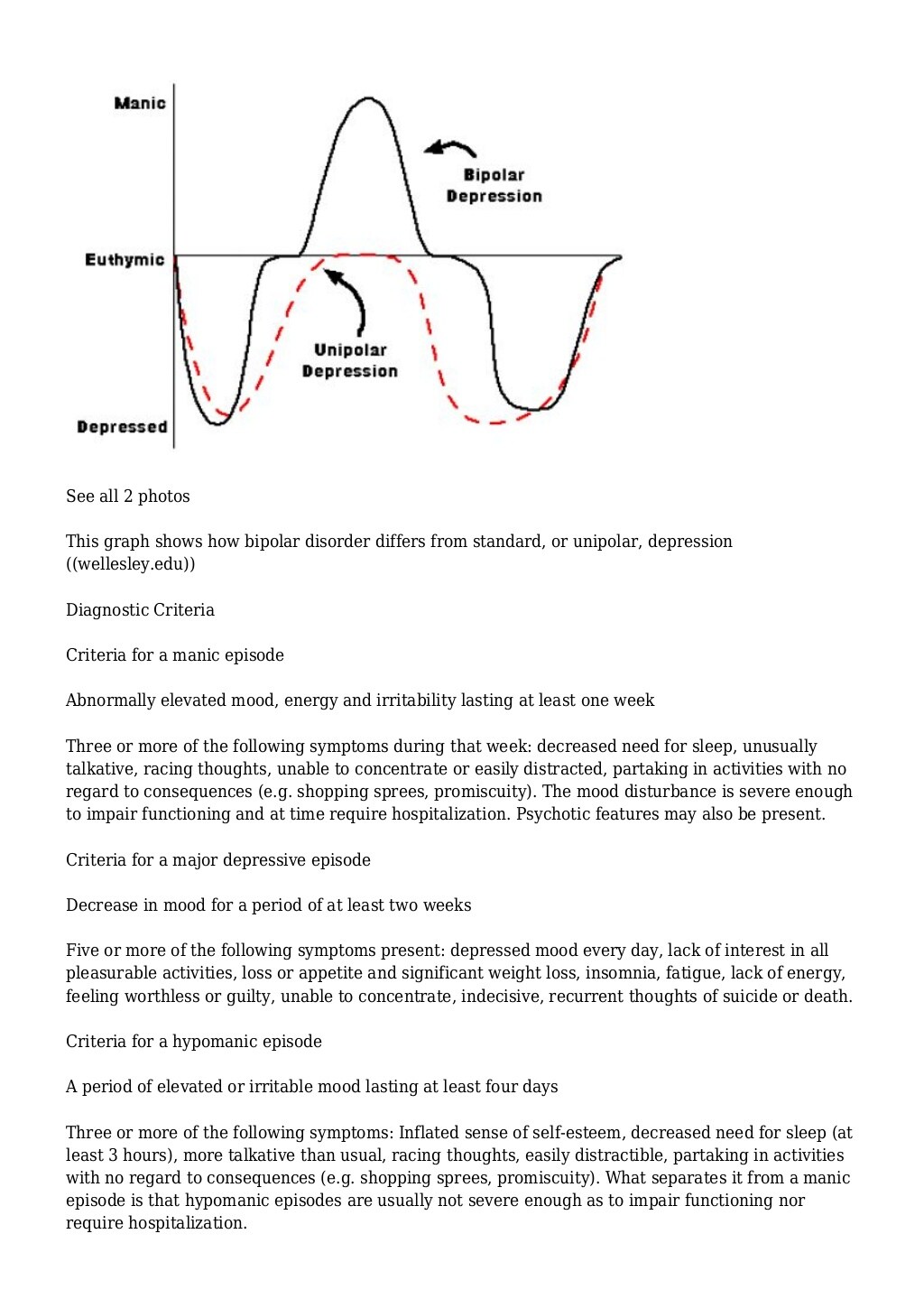
Bipolar disorder can be a life-long mental health problem that mainly affects your mood. It affects how you feel, and your mood can change massively. You can experience episodes of:
- mania, and
- depression.
You may feel well between these times. When your mood changes, you might see changes in your energy levels or how you act.
Symptoms of bipolar disorder can be severe. They can affect areas of your life, such as work, school and relationships.
You usually develop bipolar disorder before you are 20. It can develop in later life, but it rarely develops after the age of 40.
You could have symptoms of bipolar disorder for some time before a doctor diagnoses you. A doctor might say you have something else such as depression before you get a bipolar disorder diagnosis. This is because diagnosing mental illnesses can be sometimes difficult for doctors. They usually cant do things like blood tests and scans to help them.
Bipolar disorder used to be called manic depression.
You May Like: Can Being Dehydrated Cause Anxiety
How Do Doctors Treat It
Although there’s no cure for bipolar disorder, treatment can help stabilize moods and help the person manage and control symptoms. Like other teens with long-lasting medical conditions , teens with bipolar disorder need to work closely with their doctors and other medical professionals to treat it.
This team of medical professionals, together with the teen and family, develop what is called a treatment plan. Teens with bipolar disorder will probably receive medication, such as a mood stabilizer, from a psychiatrist or other medical doctor. A psychologist or other type of counselor will provide counseling or psychotherapy for the teen and his or her family. Doctors will watch the symptoms closely and offer additional treatment advice if necessary.
What Causes Depression In Men
Depression is one of the most common mental disorders in the U.S. Current research suggests that depression is caused by a combination of risk factors including:
- Genetic factorsmen with a family history of depression may be more likely to develop it than those whose family members do not have the illness.
- Environmental Stressfinancial problems, loss of a loved one, a difficult relationship, major life changes, work problems, or any stressful situation may trigger depression in some men.
- Illnessdepression can occur with other serious medical illnesses, such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, or Parkinsons disease. Depression can make these conditions worse and vice versa. Sometimes, medications taken for these illnesses may cause side effects that trigger or worsen depression.
Also Check: How Is A Depression Shown On A Contour Map
What Causes Hypomania
Scientists arent completely sure what causes hypomania. However, there are several factors that are thought to contribute. Causes differ from person to person.
Causes may include:
- Family history. If you have a family member with bipolar illness, you have an increased chance of developing mania. This is not definite though. You may never develop mania even if other family members have.
- Chemical imbalance in your brain.
- Side effect of a medication , alcohol or recreational drugs.
- A significant change in your life, such as a divorce, house move or death of a loved one.
- Difficult life situations, such as trauma or abuse, or problems with housing, money or loneliness.
- High stress level and inability to manage it.
- Lack of sleep or changes in sleep pattern.
- As a symptom of mental health problems including cyclothymia, seasonal affective disorder, postpartum psychosis, schizoaffective disorder or other physical or neurologic condition such as brain injury, brain tumors, stroke, dementia, lupus or encephalitis.
How Accurate Is It
This quiz is NOT a diagnostic tool. Mental health disorders can only be diagnosed by a licensed mental health professional or doctor.
Psycom believes assessments can be a valuable first step toward getting treatment. All too often people stop short of seeking help out of fear their concerns arent legitimate or severe enough to warrant professional intervention.
Read Also: Schizophrenia Progression
Types And Causes Of Bipolar Disorder
There are two different types of bipolar disorder. People with bipolar disorder I have severe manic episodes, whereas those with bipolar disorder II experience milder episodes.
Bipolar disorder tends to run in families, and research suggests that certain genes may increase the risk. The condition is usually diagnosed before age 25, although some people experience symptoms for the first time later in life.
Some people with bipolar disorder also have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, which usually develops before bipolar disorder. Other psychological conditions, including anxiety disorders, may accompany bipolar disorder.
It can be difficult to distinguish between depressive episodes that occur due to regular, or unipolar, depression, and those that occur due to bipolar disorder. NYU Langone is home to nationally renowned psychiatrists who specialize in identifying bipolar disorder. A correct diagnosis is essential to the appropriate management of bipolar disorder. Medications to ease symptoms of unipolar depression can actually trigger manic episodes in people with bipolar disorder.
To diagnose bipolar disorder, a doctor performs a physical exam, asks about your symptoms, and recommends blood testing to determine if another condition, such as hypothyroidism, is causing your symptoms.
If the doctor does not find an underlying cause of your symptoms, he or she performs a psychological evaluation.
Find What Works For You
King finds relief through self-reflection, frequent exercise, multiple hobbies, and having creative outlets. For Ayetoro, journaling and deep breathing practices help to bring her peace. Most people we interviewed are thankful for taking medication.
But what works for one person may not work for the next.
Howard encourages folks to try different things and not be afraid to fail. Every failed coping skill attempt gets you closer to what will work.
Consider combining these approaches for a more holistic treatment plan. Speak with a mental health professional to figure out what might work best for you.
Don’t Miss: Pristiq What Is It Used For
How To Know If You Have Bipolar Disorder Adhd Or Borderline Personality Disorder
An estimated 46 million people around the world are affected by bipolar disorder. In the U.S. alone, around 2.3% of the adult population has this condition. Unfortunately, many patients with bipolar disorder are still misdiagnosed.
Bipolar patients may be mistakenly diagnosed with depression or with other severe conditions, like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or borderline personality disorder . Such misdiagnoses can significantly affect treatment effectiveness and overall quality of life.
While there may be alternative treatments for bipolar disorder that also work well for individuals with ADHD and BPD, it is still best to get correctly diagnosed for a more targeted treatment plan.
Identifying Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a mental illness primarily characterized by extreme ups and downs in mood and energy levels.
The extreme mood swings and energy shifts can make it more challenging to make decisions and manage everyday tasks.
Bipolar disorder was also once called manic-depressive disorder. People with the illness fluctuate between very high or euphoric episodes called mania and extremely low and depressive periods.
The two periods of extremes manifest different symptoms entirely.
Extreme highs or manic episodes can last up to one week. Symptoms of a bipolar patient experiencing a manic episode may include:
- Sleeping too much
- Increase in appetite and weight
- Low, hopeless, or dejected mood
- Suicidal thoughts
Can Bipolar Disorder Go Away

Bipolar disorder tends to be seen as an ongoing condition that waxes and wanes throughout ones life, says Simon A. Rego, PsyD, Chief Psychologist at Montefiore Medical Center and Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City.
Fortunately, the symptoms can often be controlled and stabilized in most cases when proper treatment is in place, Rego says.
Recommended Reading: Is Phobia A Disease