Write Down What Youre Feeling And Experiencing
It can be so easy to forget details or even entire events when it feels like everything is spinning out of control. There have been numerous times where Ill experience symptoms, intend to tell my doctor, and completely forget about them at my appointment. But the more detail your mental health professional has, the better they will be able to understand what youre going through. When possible, keep notes about what youre experiencing and not just what you think are symptoms. Adding more detail can also potentially help you and your doctor identify any symptoms you may not have caught and any potential triggers to your symptoms.
Common Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
You may be diagnosed with schizophrenia if you experience 2 or more of the following symptoms for at least 1 month:
- delusions
- hallucinations
- incoherent speech, or speech that quickly switches from topic to topic with no thread between them
- severely disorganized or catatonic behavior
- any of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia has two main types of symptoms: positive and negative.
Delusions and hallucinations are the main characteristics of schizophrenia. These are positive symptoms.
A delusion is a fixed belief that doesnt change, even when a person is given evidence the belief isnt based in reality. An example of a delusion is that everyone is out to get me.
Hallucinations involve seeing, hearing, or feeling things that arent there. Examples include hearing voices that arent your own, or seeing people that arent actually in the room.
Hallucinations and delusions are called positive symptoms because they represent additional behaviors not generally seen in people without the condition. Negative symptoms can be seen as behaviors that are missing or underdeveloped.
Negative symptoms include:
Frequently Asked Questions About Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality. Although schizophrenia is not as common as other mental disorders, the symptoms can be very disabling.
Schizophrenia is a severe and debilitating brain and behavior disorder affecting how one thinks, feels and acts. People with schizophrenia can have trouble distinguishing reality from fantasy, expressing and managing normal emotions and making decisions. Thought processes may also be disorganized and the motivation to engage in lifes activities may be blunted. Those with the condition may hear imaginary voices and believe others are reading their minds, controlling their thoughts or plotting to harm them.
While schizophrenia is a chronic disorder, it can be treated with medication, psychological and social treatments, substantially improving the lives of people with the condition.
A moving presentation by Dr. Kafui Dzirasa on Schizophrenia
View Webinar on Identifying Risk Factors and Protective Pathways for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia affects men and women equally. It occurs at similar rates in all ethnic groups around the world. Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30.
Learn more about childhood-onset schizophrenia from this expert researcher:
Find answers to more questions about Schizophrenia in our Ask the Expert section.
Don’t Miss: Can You Be Bipolar And Have Bpd
Schizophrenia And The Americans With Disabilities Act
The ADA does not contain a list of medical conditions that constitute disabilities. Instead, the ADA has a general definition of disability that each person must meet. A person has a disability if he/she has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, a record of such an impairment, or is regarded as having an impairment. For more information about how to determine whether a person has a disability under the ADA, see How to Determine Whether a Person Has a Disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act Amendments Act .
When A Loved One Has Schizophrenia

The love and support of family and friends plays an important role in schizophrenia treatment and recovery. If you have a loved one with schizophrenia, you may be struggling with any number of difficult emotions, including fear, guilt, anger, and frustration. You may feel helpless in the face of your loved ones symptoms, worried about the stigma of schizophrenia, or confused and embarrassed by their strange behaviors. You may even be tempted to hide your loved ones illness from others.
But its important to remember that a diagnosis of schizophrenia is not a life-sentence. Recovery is possible, especially with your love and support. To help someone with schizophrenia, its crucial you:
- Accept the illness and its difficulties.
- Not buy into the myth that someone with schizophrenia cant get better or live a full and meaningful life.
- Do your best to help your loved one feel better and enjoy life.
- Pay attention to your own needs.
- Maintain your sense of humor and remain hopeful.
While dealing with a loved ones schizophrenia can be challenging, the following strategies can help you guide your loved one on the road to recovery without losing sight of your own hopes and dreams.
Tips for helping a loved one with schizophrenia
You May Like: Antidepressant-induced Hypomania
Can Someone With Schizophrenia Live A Normal Life
While schizophrenia cannot be cured, with the right treatment plan many people with schizophrenia can live relatively normal lives outside of a healthcare setting. The treatment must be ongoing for the person with schizophrenia to continue to live a productive, fulfilling life, including maintaining a job or socializing with friends and family.
Is Schizophrenia Classified As A Disability
People with schizophrenia experience a range of impairments affecting various aspects of daily functioning, including the ability to work. In the U.S., the principal sources of public disability insurance are the Social Security Disability Insurance and Supplemental Security Income programs. People with schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders fall under the category Schizophrenia/Paranoid Functional Disorders. For all mental disorders, claimants must submit evidence supporting a medical cause of disability and meet specific criteria relating to impairment in at least two out of four domains of functioning. For schizophrenia, claimants may meet an additional set of criteria related to chronic disorder-related impairment, instead of or in addition to the second disability criteria. The SSDI allowance rate typically exceeds 80% in applicants with schizophrenia. Many unsuccessful applicants are not denied, rather they are simply unable to manage the appeals process after an initial denial. Advocates suggest applicants work with a Social Security disability attorney with experience dealing with clients with mental disorders. Although living with schizophrenia presents significant challenges, comprehensive treatment including medication management can help many people work, drive and be productive members of society.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Vocational And Social Services
While treatment and support can help successfully manage symptoms of schizophrenia, patients still may be left with deficits in function. For instance, they may struggle with holding down a job or finding housing and managing money. To really live an independent and normal life with schizophrenia requires a range of services and assistance. Vocational training can help someone get and keep a job, while housing services can help find a recovering patient an affordable place to live. Other services may include transportation, academic support, or social groups.
What Risks And Complications Can Schizophrenia Cause
Physical health
Research suggests that people with serious mental illness , such as schizophrenia, have a shorter life expectancy. People with mental illness may die 15 to 20 years earlier than the general population. This may because people who live with SMI are at higher risk of having a range of health issues. Such as being overweight, having heart disease, smoking and diabetes.
Because of these issues, NICE recommends that when you start taking antipsychotic medication, your doctor should do a full range of physical health checks. This should include weight, blood pressure and other blood tests. These checks should be repeated regularly.
Mental health professionals are responsible for doing these checks for the first year of treatment. Responsibility may then pass to your GP. Your doctor or mental health team should offer you a programme which combines healthy eating and physical health checks. You should be supported by a healthcare professional to help stop smoking.
Suicide
The risk of suicide is increased for people with schizophrenia. Research indicates that around 513% of people who live with with schizophrenia die by suicide.
Research has found that the increased risk is not usually because of positive symptoms. The risk of suicide is associated more to affective symptoms, such as low mood.
Key risk factors for suicide include:
- previous suicide attempts,
Recommended Reading: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Meeting A Disability Listing For Schizophrenia
The Social Security Administration will automatically approve you for disability benefits for schizophrenia if you meet the requirements of Listing 12.03, Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, in its Listing of Impairments. disorder, and substance/medication-induced psychotic disorder.)
To be eligible for benefits under this disability listing, you must have medical evidence showing that you have one or more of the following symptoms on a persistent basis, despite taking medication:
- hallucinations or delusions
- illogical thoughts and other disorganized thinking as evidenced by speech, or
- a catatonic state or grossly disorganized behavior.
In addition to these signs and symptoms, Social Security will need proof of how your disorder limits you. You don’t need to prove specific limitations if your disorder has persisted for at least two years and you have either been receiving intensive medical treatment and mental health therapy or have been living in a highly structured setting that diminishes your symptoms. You will need to prove that you have minimal capacity to adapt to changes in your environment or to demands that are not already part of your daily life.
If this doesn’t apply to you, you must show that you have an extreme limitation in at least one of the following areas, or a “marked” limitation in at least two of the following areas:
Note that Social Security defines “marked” as less than extreme, but worse than moderate.
Avoiding Drugs And Alcohol
While alcohol and drugs may provide short-term relief from your symptoms, they’re likely to make your symptoms worse in the long run.
Alcohol can cause depression and psychosis, while illegal drugs may make your schizophrenia worse. Drugs and alcohol can also react badly with antipsychotic medicines.
If you’re currently using drugs or alcohol and finding it hard to stop, ask your care co-ordinator or GP for help.
You May Like: Pristiq For Social Anxiety
Helping A Suicidal Friend Or Relative
If you see any of these warning signs:
- get professional help for the person, such as from a crisis resolution team or the duty psychiatrist at your local A& E department
- let them know they’re not alone and you care about them
- offer your support in finding other solutions to their problems
If you feel there’s an immediate danger of the person attempting to end their life , stay with them or have someone else stay with them. Remove all available means of suicide, such as sharp objects and medication.
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
You May Like: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
How Can Schizophrenia Impact Your Ability To Work
Schizophrenia can severely limit a persons ability to perform daily activities. This is especially true for people who experience visual and auditory hallucinations, since these can make carrying out tasks impractical or even dangerous for themselves and others in the workspace. In addition, adapting to a work environment can be especially challenging since the disorder can cause disordered thinking and inability to concentrate or interact with others.
However, when symptoms are controlled through medications and therapy, its possible for people with schizophrenia to hold gainful employment. For some, working can help in the healing process and build a sense of independence and well-being.
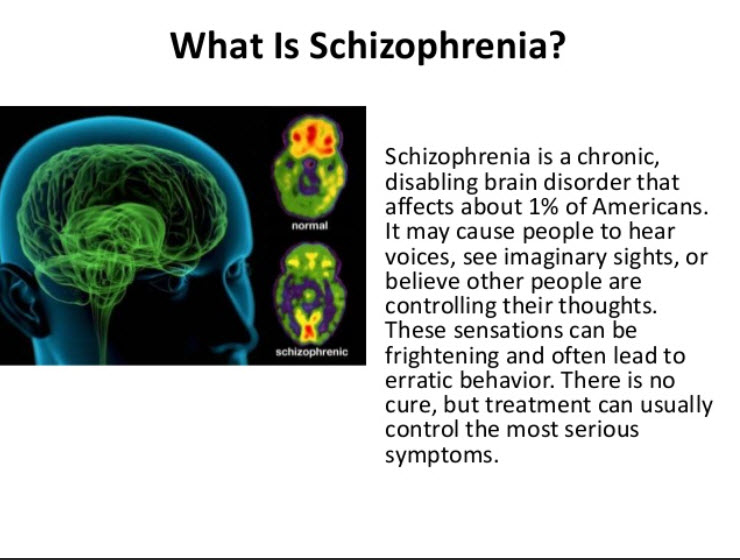
What Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia most often appears in the late teens to early twenties and may have an earlier onset in men than women. When not controlled, schizophrenia can cause hallucinations, delusions, voices in the head, lack of motivation, and trouble concentrating.
Currently, there’s no cure for schizophrenia, but research is leading to newer, safer, and more successful treatments. Treatment of schizophrenia is mainly offered through the use of antipsychotic medications and therapies such as talk therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy , and family intervention.
Don’t Miss: Can Dehydration Cause Panic Attacks
How Is It Treated
Medicines help your symptoms, and counselling and therapy help you change how you think about things and deal with the illness. Treatment may last a long time.
When you have your symptoms under control, you are in recovery. Recovery usually is a lifelong process. In the recovery process, you learn to cope with your symptoms and challenges, find and meet your goals, and get the support you need. Your recovery depends upon a partnership between you, your doctors, and others who are important in your life.
People who have schizophrenia often stop treatment. This may be because they don’t understand that they have an illness or because the medicines cause side effects. When treatment stops, symptoms usually come back or get worse. A relapse might happen right after treatment is stopped or months later. A later relapse makes it hard to see that stopping the medicine was the cause. During a relapse, some people who have schizophrenia may need to spend time in a hospital.
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of schizophrenia include:
- Negative symptoms. “Negative” doesn’t mean “bad.” Negative symptoms are things that are “lost” from your personality or how you experience life. You may:
- Not care about things.
- Have no interest or drive to do things.
- Not take care of yourself, such as not bathing or not eating regularly.
- Find it hard to say how you feel.
- Become angry with strangers for no reason and react to others in other harmful ways.
Symptoms usually start when you are a teen or a young adult, but they may start later in life. They may appear suddenly or may develop slowly. You may not be aware of your symptoms.
Negative symptoms usually appear first. They may be hard to recognize as schizophrenia, because they are similar to symptoms of other problems, such as depression. Positive symptoms can start days, months, or years after the negative symptoms.
These signs don’t mean you have schizophrenia. But if you notice these signs, see a doctor.
Don’t Miss: Which Of The Following Represents A Negative Symptom Of Schizophrenia
Dont Take It Personally
Schizophrenia can be a difficult illnessfor everyone. During episodes of psychosis, your loved one may experience frightening sensations that you cant understand. They may act in ways that you dont understand. Other symptoms of schizophrenia can make it hard for people to express emotions or feelings, communicate clearly, or seem interested in others. Its important to know that these are symptoms of an illness. They are no ones fault, but they can still be hard to cope with. Consider reaching out to a family and friends support group for your own support. The BC Schizophrenia Society has a directory of groups around BC at www.bcss.org/monthly-meetings-calendar/.
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia And How Is It Diagnosed
How is schizophrenia diagnosed?
Only a psychiatrist can diagnose you with schizophrenia after a full psychiatric assessment. You may have to see the psychiatrist a few times before they diagnose you. This is because they need to see how often you are experiencing symptoms.
There are currently no blood tests or scans that can prove if you have schizophrenia. So, psychiatrists use manuals to diagnose schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.
The 2 main manuals used by medical professionals are the:
- International Classification of Diseases which is produced by the World Health Organisation , or
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual which is produced by the American Psychiatric Association .
NHS doctors use the ICD-10.
The manuals explain which symptoms should be present, and for how long for you to receive a diagnosis. For example, according to the NHS you need to be hearing voices for at least 1 month before you can be diagnosed. Mental health professionals may say you have psychosis before they diagnose you with schizophrenia.
What is the future of diagnosis in schizophrenia?There are many research studies being conducted across the world on how to better diagnose schizophrenia. For example, a recent study found through looking at images of the brain, there may be different sub-types of schizophrenia.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
The symptoms of schizophrenia are commonly described as positive symptoms or negative symptoms. This doesnt mean that they are good or bad.
You May Like: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
The Importance Of Residential Treatment For Schizophrenia
Symptoms of schizophrenia can be very troubling and disruptive. They can also be severe and cause significant impairment in a persons life. In some cases an episode of symptoms may even be severe enough to require temporary hospitalization. For anyone diagnosed with this mental health condition, residential treatment is strongly recommended.
Residential care gives patients the opportunity to focus on and engage with treatment without worrying about home, family, work, and other responsibilities. Inpatient care is also more intensive and helps patients jump-start recovery, guiding them through strategies and exercises that will help them manage their illness once back at home. Treatment in a residential facility gives patients all the tools they need to be successful once they leave, while also providing a safe environment in which to go through therapy.