Does My Child Have Schizophrenia
Early signs of schizophrenia can be hard to detect because they often overlap with common adolescent behavior. Moreover, these symptoms in people of any age group do not necessarily mean that a person will develop schizophrenia.
These symptoms can be disruptive though, and they may indicate something worrisome is going on, even if it isn’t schizophrenia. If you or your child are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should make an appointment with a healthcare provider.
When A Loved One Has It
Relationships can be rocky for people with schizophrenia. Their unusual thoughts and behaviors may keep friends, co-workers, and family members away. Treatment can help. One form of therapy focuses on forming and nurturing relationships. If you are close to someone who has schizophrenia, you may want to join a support group or get counseling yourself, so you can get support and learn more about what they are going through.
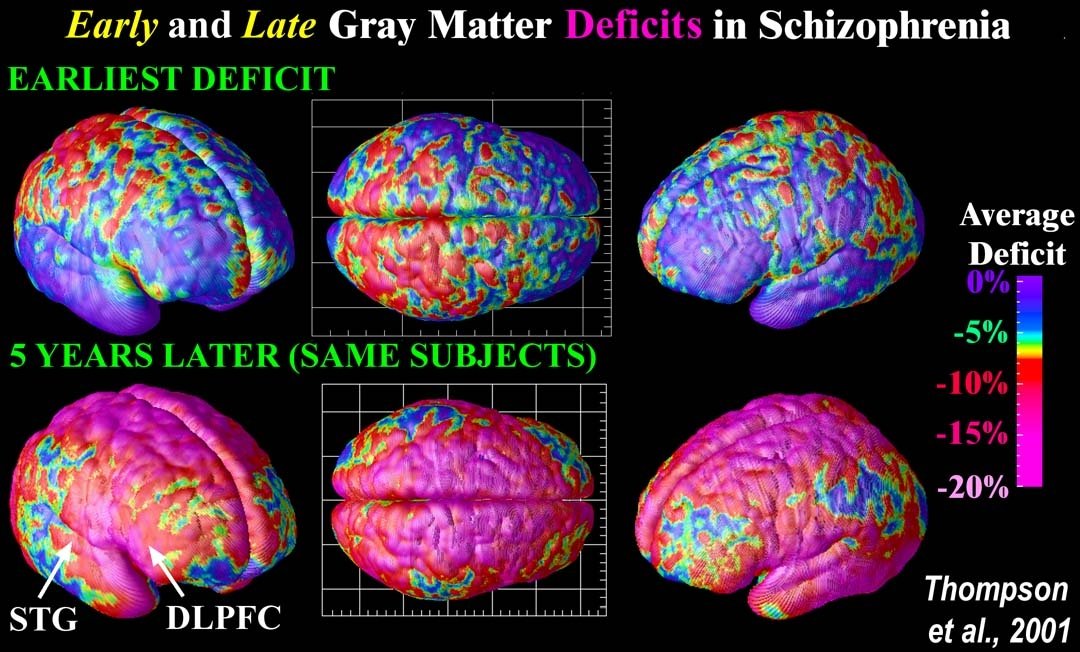
Lack Of Brain Tissue Found In Schizophrenic Patients
Scans from the patients first episode revealed that they had less brain tissue, compared with healthy individuals without the disorder.
The researchers say this finding suggests that something is affecting the brains of those with schizophrenia before they demonstrate obvious symptoms of the conditions.
Prof. Andreasen explains:
There are several studies, mine included, that show people with schizophrenia have smaller-than-average cranial size.
Since cranial development is completed within the first few years of life, there may be some aspect of earliest development perhaps things such as pregnancy complications or exposure to viruses that on average, affected people with schizophrenia.
The brain scans also showed that those who suffer from schizophrenia demonstrated the highest tissue loss in the first 2 years after their first episode, after which point it slowed down significantly.
Prof. Andreasen says that this finding may help doctors to identify the most effective time periods to prevent tissue loss in schizophrenic patients, as well as other effects caused by the disorder.
Also Check: Aphobic Definition
Also Check: What Is A Depression Contour
What Happens After You Get The Results From A Schizophrenia Brain Scan
If brain scans are ordered for a person who is showing schizophrenia symptoms, it is usually to rule out or confirm other conditions that could be causing the symptoms.
Whether the scan shows a different condition or plays a part in confirming a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the healthcare provider will discuss treatment options.
Additional Consultation Needed For Diagnosis
Following any scans or tests, a healthcare professional may make a referral to a mental health expert who has more specialized knowledge on the subject. It is also common for healthcare professionals to speak with the friends and/or family of a person who is showing signs of schizophrenia.
If schizophrenia is diagnosed, then the person with schizophrenia and their support team will work on a treatment plan together.
You May Like: Late Onset Schizophrenia
Data Recorded In The Database
The following data were extracted from the chosen studies: number of subjects and percentage of males in the study sample age of the patient at first MRI measurement duration of illness at the time of the first MRI interval between the two MRI scans type of antipsychotic medications taken during the MRI scan interval Tesla value of the MRI scanner MRI slice thickness year of publication of the study percentage change in brain tissue volume /volume at baseline) × 100) in patients with schizophrenia and in healthy comparison group or volume of a given cerebral structure analyzed at baseline and at follow-up scans in patients with schizophrenia and controls. The percent change in volume was selected to estimate the ES. If this measure was not reported, the percent change in volume over time in each study was calculated by the authors using the following formula: /volume at baseline) × 100.
Dont Miss: Can Anxiety Cause Burning Skin
Risk Factors Likely Interact Synergistically To Increase Odds For Developing Scz
Here, we have highlighted the diverse risk factors for SCZ and how they impact the CNS by altering immune signaling. Likely, these risk factors act additively on certain signaling pathways to push vulnerable individuals past a certain threshold into a disease state. This field would benefit from future studies that aim to elucidate how the immune system regulates specific circuits and neuromodulatory systems to drive the diverse phenotypes observed in SCZ. Additionally, an in-depth understanding of the specific signaling networks compromised in SCZ may enable the restoration of typical immune-driven neurodevelopment after exposure to the various genetic and environmental risk factors described in this review.
You May Like: Pristiq Depression
Schizophrenia And The Brain
- Schizophrenia is a disease that affects the brain. It alters brain chemistry and brain form to produce the different behavior in those afflicted with the problem. It appears that these alterations change the inherent I-function in each individual
- The scans of patients with schizophrenia revealed various abnormalities in portions of the corpus callosum, a bundle of fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain and is considered critical to neural communication
- Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It can cause hallucinations, delusions, and other mental problems that make it seem like a person has lost touch with reality. It affects about 1 in 100 people. Several factors likely contribute to the risk of developing schizophrenia
- e and regulates coordinated movement, motivation and the reward pathway. This complex pathway reinforces patterns of behavior that make a person feel good
- The brain scans also showed that those who suffer from schizophrenia demonstrated the highest tissue loss in the first 2 years after their first episode, after which point it slowed down..
- Brain scans and microscopic tissue studies indicate a number of abnormalities common to the schizophrenic brain. The most common structural abnormality involves the lateral brain ventricles. These fluid-filled sacs surround the brain and appear enlarged in images of the brains of those with schizophrenia
Hope From Scans Of Schizophrenia In The Brain
Imaging scans of schizophrenia in the brain have helped researchers locate a small area of the brain that may help them predict whether people will develop schizophrenia with 71 percent accuracy for high-risk patients. The study results, which appear in the September 2009 issue of Archives of General Psychiatry, pinpoint the exact area of a part of the brain that shows hyperactivity in schizophrenics.
The researchers used high-resolution MRI equipment to show what areas of the brain are affected by schizophrenia. The scientists discovered three areas of the schizophrenic brain that differed from normal brains two areas in the frontal lobes and one very small area of the hippocampus, known as CA1. Weve always known that schizophrenics have a more active hippocampus, the area used for memory and learning, but this study pinpoints the exact spot of hyperactivity in patients with the illness.
This discovery brings new hope and promise to those at risk for developing a schizophrenic brain and for those already suffering from it. Doctors hope that once researchers further develop the findings, that they can use this as a diagnostic marker to predict whether certain high-risk patients will go on to develop full-blown psychosis after prodrome. They also hope to use the CA1 subfield marker in the hippocampus to indicate the efficacy of treatments. For example, a decreased amount of activity in the area could indicate the success of treatment strategies.
Don’t Miss: Dikigorosophobia
Role Of Amygdala And Entorhinal
Amygdala
Entorhinal-hippocampal system
Bilateral hippocampal size reduction in SZ, has been described as early as the first psychotic episode . Morphometric neuroimaging, magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and functional neuroimaging, have provided evidence for abnormal hippocampal structure and functionality in SZ. Hippocampal volume reduction is now one of the most consistent structural abnormalities found in SZ it can be found at onset of the illness and to a lesser degree in first-degree relatives of SZ patients. Decreased levels of N-acetyl-aspartate imply a cellular or axonal basis for the volume changes. Functional neuroimaging studies have demonstrated enhanced levels of hippocampal activity at rest, during the experience of auditory verbal hallucinations , and during the performance of memory retrieval tasks. These neuroimaging study results complete the evidence of post-mortem and behavioural studies, which have found specific regional hippocampal abnormalities and of memory function in SZ .
Patients with SZ undergoing fMRI during visual tasks showed reduced habituation of the hippocampus and visual cortex, and a lack of neural discrimination between old and new images in the hippocampus. Hippocampal discrimination correlated with memory performance, suggesting reduced habituation may contribute to the memory deficits commonly observed in SZ patients .
How Schizophrenia Affects The Body Not Just The Brain
- Toby Pillinger, Kings College London
- Read Time: 5 mins
Schizophrenia is considered a disorder of the mind, influencing the way a person thinks, feels and behaves. But our latest research shows that organs, other than the brain, also change at the onset of the disease.Scientists have known for a long time that people with schizophrenia have much higher rates of physical illness compared with the general population, and this contributes to startlingly high rates of premature death. People with the disorder die 15 to 20 years earlier than the average person.
This poor physical health has often been seen as a secondary effect of illness. Antipsychotic drugs, for example, are associated with an increased risk of weight gain and type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle factors have been thought to play a part, too. A person with debilitating mental symptoms is more likely to forgo exercise and have a poor diet.
However, in recent years, scientists have observed that people who have recently been diagnosed with schizophrenia and who arent on any medication yet show evidence of physiological changes, such as an overactive immune system. Could it be that schizophrenia is in fact a body-wide disorder?
Read Also: Can Anxiety Cause High Blood Sugar
Analyzing Brain Structure In Schizophrenia
The study used software that generates automated segmentations of the brain from MRI scans to measure brain structures.
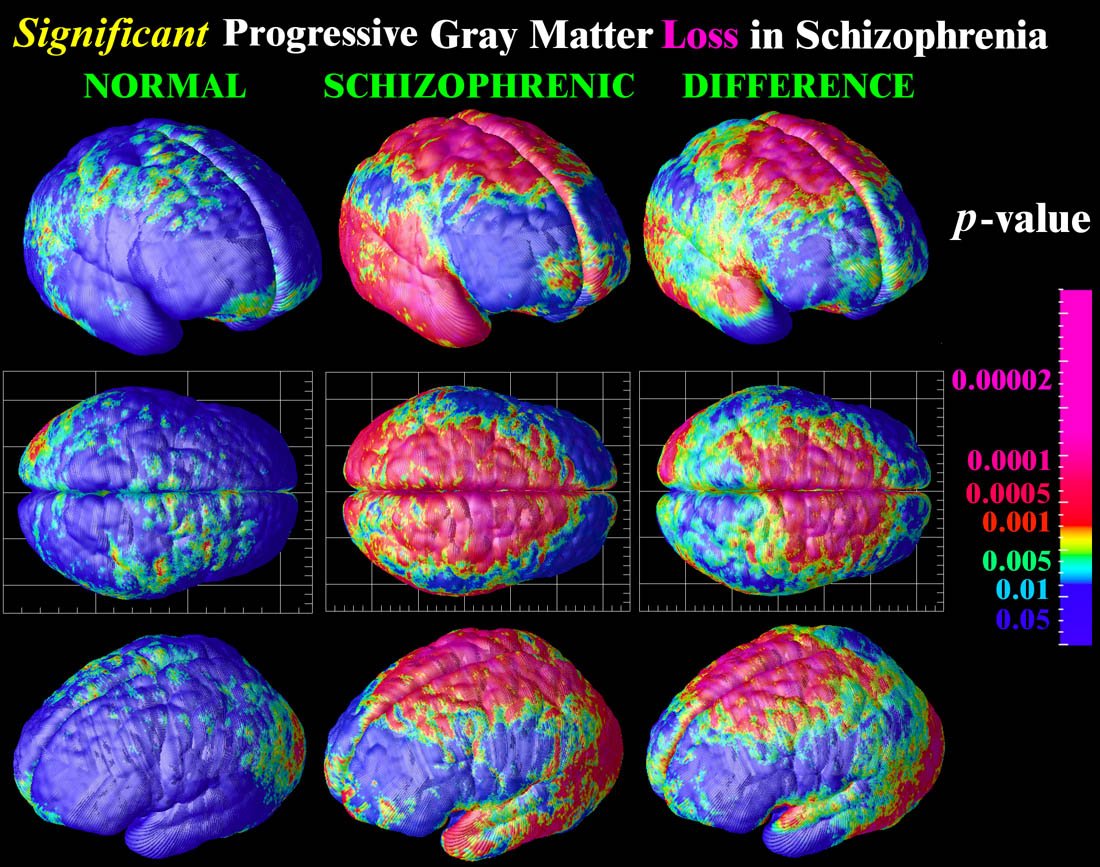
A collaborative study that included Northwestern Medicine scientists has identified structural brain abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia.
Scientists analyzed neuroimaging data gathered from 15 different study populations worldwide that included a total of 2,028 schizophrenia patients and 2,540 healthy controls. The findings, in Molecular Psychiatry, help further the understanding of the mental disorder.
We conducted a meta-analysis across the 15 studies to look for an aggregate effect of schizophrenia on brain volumes, said coauthor Lei Wang, PhD, assistant professor in Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Radiology.
Joining to form the ENIGMA Schizophrenia Working Group, scientists in locations across the United States, Europe and in Japan calculated brain volumes for their samples. They shared group data including averages and standard deviations of subcortical brain volumes as well as demographic information such as age, illness duration and medication usage.
Lei Wang, PhD, assistant professor in Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Radiology, was coauthor of a paper that looked at the effect of schizophrenia on subcortical brain volumes.
Smaller intracranial volumes in schizophrenia could imply problems during development at a young age, Wang said.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
To diagnose this disease, your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. You may also have a physical exam. You may also have lab tests to rule out other conditions.
Mental health care professionals diagnose and treat this illness. They often interview family members. This helps the healthcare team get a complete picture of the symptoms.
Also Check: Define Aerophobia
Schizophrenia Changes Brain Structure: A Review Of Studies Of Individuals With Schizophrenia Never Treated With Antipsychotic Medications
Summary
A review of 56 studies of individuals with schizophrenia who had never been treated with antipsychotic medications indicates significant abnormalities in brain structure and function. Neurological and neuropsychological measures show the most consistent and largest group differences between those affected and normal controls. Measures of structural differences and cerebral metabolic function are significant but less impressive. Electrophysiological differences also are found, but most such studies are older and have methodological problems. The brain abnormalities implicate a variety of interrelated brain regions, primarily the medial temporal, prefrontal, thalamic, and basal ganglia areas. It is concluded that schizophrenia is a brain disease in the same sense that Parkinsons disease and multiple sclerosis are, and that the brain abnormalities in schizophrenia are inherent in the disease process and not medication-related. The challenge for the future is to use the new molecular techniques to study these brain areas and elevate our understanding of schizophrenias etiology to the next level.
Introduction
Alcohol Drugs Are A Risk
People with schizophrenia are much more likely than other people to abuse alcohol or illicit drugs. Some substances, including marijuana and cocaine, can make symptoms worse. Drug abuse also interferes with treatments for schizophrenia. If you know someone whoâs dealing with that, look for substance abuse programs designed for people with schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: Can Low Blood Sugar Cause Anxiety
Neuropathology And Aberrant Functional Connectivity
Bleuler, who coined the term schizophrenia, stated `the thousands of associations guiding our thought are interrupted by this disease . . . The thought processes, as a result, become strange and illogical, and the associations find new paths . His view that the key symptoms of schizophrenia were those of `psychic splitting now have their counterparts in neuropsychological models and in imaging studies which have implicated aberrant functional connectivity between different brain regions as the pathophysiological mechanism of psychosis . Although the evidence in favour of altered connectivity in schizophrenia remains circumstantial and its details poorly specified, the concept has been widely promulgated. Examples are shown in Table 6.
Much remains to be done before the hypothesized association between structure and function can be confirmed and shown to be causal. It will not be easy to falsify or to clarify its detail, and the overriding need at present is still to improve the robustness of the contributory data. Nevertheless, the goal should be kept firmly in mind when designing neuropathological investigations into schizophrenia.
Which Part Of Brain Is Affected In Schizophrenia
brainaffectedschizophreniabrainschizophrenia
In respect to this, what happens in the brain during schizophrenia?
In a brain with schizophrenia, far more neurotransmitters are released between neurons , than are in a normal brain . Dopamine is further implicated by the fact that a schizophrenia-like psychosis can be induced by abusing amphetamines, which act on dopamine pathways.
Subsequently, question is, which of the following brain abnormalities is associated with schizophrenia? The patients with schizophrenia tended to have smaller volume in brain regions that included the hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, nucleus accumbens and intracranial space than their healthy peers, the researchers reported in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
One may also ask, what part of the brain does psychosis affect?
But knowledge of what is happening in the brain in a psychosis might be more helpful in reducing stigma. It is suggested that psychosis is due to an affection of the supplementary motor area , located at the centre of the Medial Frontal Lobe network.
Does Schizophrenia damage the brain?
This is crucial for schizophrenia as it is believed that with every psychotic episode, increased damage is done to the brain. While no cure exists for schizophrenia, it is treatable and manageable with medication and behavioral therapy, especially if diagnosed early and treated continuously.
Also Check: Why Is Liam Afraid Of Spoons
Is Scz An Inflammatory Disease
There is growing evidence from both human and animal studies that many of the risk factors for SCZ converge on their ability to promote neuroinflammation, and that these effects are mediated in part by microglia. However, is there a pro-inflammatory phenotype in SCZ? Post-mortem and clinical studies show an increase in pro-inflammatory markers in people with SCZ compared to controls . Moreover, there is evidence for elevated levels of cytokines in blood samples from people with SCZ, whether they are medication-naive or receiving antipsychotic treatment, during episodes of psychosis . Thus, such studies suggest that inflammation might contribute to the development of SCZ and also drive its progression and cyclic nature.
Indeed, there are multiple disease-associated microglial subtypes such as those seen in neurodegenerative disorders and dark microglia which were recently observed in SCZ post-mortem brain samples . More work is needed to fully understand microglial subtypes that are more prevalent in disease states and how they contribute together to pathology, however data suggest they partially contribute to disease by enhancing synaptic pruning . Future studies should also aim to develop more translational animal models so that in vivo studies can be performed to gain greater understanding into how microglia functionally impact synaptic development and circuit function in pathological states.
Work Still To Be Done
We need to do more work to figure out whether changes around the body are a cause or a consequence of schizophrenia. One approach is to look at those people who are at risk of developing schizophrenia to see how changes around the body evolve in the ones who develop schizophrenia compared with those who dont. More work is also needed to see how changes around the body respond to changes in the severity of symptoms of schizophrenia.
Finally, most premature deaths seen in schizophrenia are due to cardiovascular disease. Life expectancy in schizophrenia has failed to improve over recent decades. Studies are needed to determine if addressing physical health early on will reduce mortality in schizophrenia.
Also Check: Does Dehydration Cause Anxiety
How Schizophrenia Affects The Brain
Its hard to fully understand a mental disease like schizophrenia without peering into the human brain. Now, a study by University of Iowa psychiatry professor Nancy Andreasen uses brain scans to document how schizophrenia impacts brain tissue as well as the effects of anti-psychotic drugs on those who have relapses.
Andreasens study, published in the American Journal of Psychiatry, documented brain changes seen in MRI scans from more than 200 patients beginning with their first episode and continuing with scans at regular intervals for up to 15 years. The study is considered the largest longitudinal, brain-scan data set ever compiled, Andreasen says.
Schizophrenia affects roughly 3.5 million people, or about one percent of the U.S. population, according to the National Institutes of Health. Globally, some 24 million are affected, according to the World Health Organization.
The scans showed that people at their first episode had less brain tissue than healthy individuals. The findings suggest that those who have schizophrenia are being affected by something before they show outward signs of the disease.
The researchers also analyzed the effect of medication on the brain tissue. Although results were not the same for every patient, the group found that in general, the higher the anti-psychotic medication doses, the greater the loss of brain tissue.
This story appeared originally on the Department of Psychiatry website and has been re-purposed for Iowa Now.