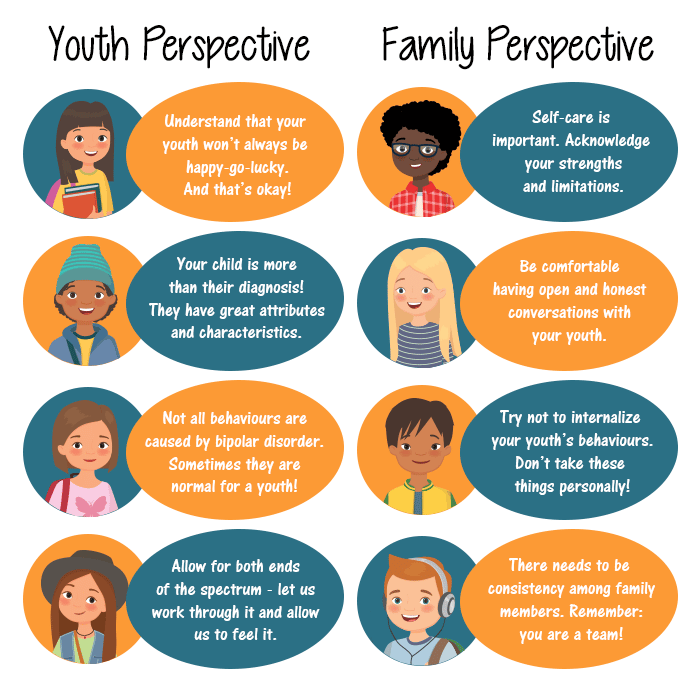
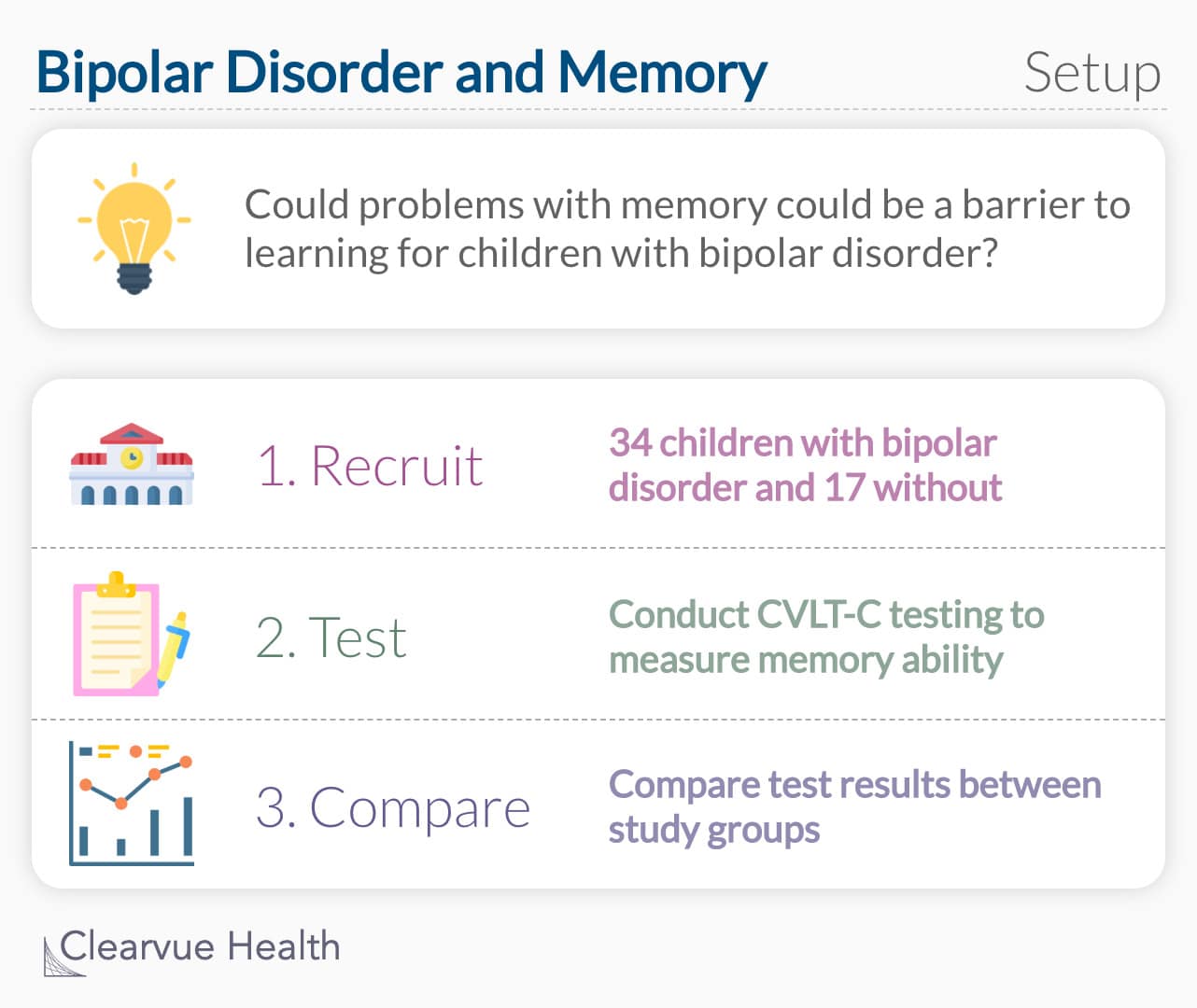
Whats The Screening Test For Bipolar Disorder Like
Current screening tests for bipolar disorder dont perform well. The most common report is the Mood Disorder Questionnaire .
In a 2019 study, results indicated that people who scored positive on the MDQ were as likely to have borderline personality disorder as they were to have bipolar disorder.
You can try some online screening tests if you suspect you have bipolar disorder. These screening tests will ask you a variety of questions to determine if youre experiencing symptoms of manic or depressive episodes. However, many of these screening instruments are home grown and may not be valid measures of bipolar disorder.
Symptoms for shifts in mood include:
| Mania, or hypomania | Depression |
When getting a diagnosis for bipolar disorder, the usual method is to first rule out other medical conditions or disorders.
Your healthcare provider will:
- order tests to check your blood and urine
- ask about your moods and behaviors for a psychological evaluation
If your healthcare provider doesnt find a medical cause, they may refer you to a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist. A mental health professional may prescribe medication to treat the condition.
You may also be referred to a psychologist who can teach you techniques to help recognize and manage shifts in your mood.
Even in the case of rapid cycling or mixed episodes, a bipolar diagnosis requires someone to experience:
| Type |
Bipolar Disorder And Relationships
When it comes to managing a relationship while you live with bipolar disorder, honesty is the best policy. Bipolar disorder can have an impact on any relationship in your life, perhaps especially on a romantic relationship. So, its important to be open about your condition.
Theres no right or wrong time to tell someone you have bipolar disorder. Be open and honest as soon as youre ready. Consider sharing these facts to help your partner better understand the condition:
- when you were diagnosed
- what to expect during your depressive phases
- what to expect during your manic phases
- how you typically treat your moods
- how they can be helpful to you
One of the best ways to support and make a relationship successful is to stick with your treatment. Treatment helps you reduce symptoms and scale back the severity of your changes in mood. With these aspects of the disorder under control, you can focus more on your relationship.
What Will My Doctor Ask Me
To make a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, your doctor will ask you about:
- How many symptoms you experience
- Which types of mood episodes you experience
- How long your mood episodes last for
- How many mood episodes you’ve had
- How often your mood episodes occur
- How your symptoms impact your life
- Your family history
They may also:
- Ask you to keep a diary of your moods to help you both identify patterns and triggers.
- Check up on your physical health. For example, some conditions like thyroid problems can cause mania-like symptoms.
Only a mental health professional like a psychiatrist can give you a bipolar disorder diagnosis not your GP.
However, if you’re experiencing bipolar moods and symptoms, discussing it with your GP can be a good first step. They can refer you to a psychiatrist, who will be able to assess you.
For more information see our pages on seeking help for a mental health problem.
Once properly diagnosed, I knew the cause. I understood that I was someone with an illness. I was not a failure, not a bad person.
Don’t Miss: How To Relax During A Panic Attack
Nature Of Bipolar Disorder
Several types of bipolar disorder are recognized by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders of the American Psychiatric Association , differentiated by the severity and duration of manic symptoms. A diagnosis of bipolar I disorder is made based on a single lifetime episode of mania, which is in turn defined by euphoric or irritable mood, along with at least three additional symptoms that result in marked social or vocational impairment. The duration criterion for mania specifies that symptoms must last one week or require hospitalization. Bipolar II disorder, in contrast, is defined by a history of at least one hypomanic episode and at least one major depressive episode. Criteria for hypomania are similar to those of mania, but in milder form: instead of impairment, a hypomanic episode is marked by a distinct change in functioning. Cyclothymic disorder is an even milder subtype of bipolar disorder, and is diagnosed based on a period of at least two years of recurrent mood swings. By definition, these mood swings must be in both the up and the down directions, but do not meet full criteria for mania, hypomania, or depression. In addition, the symptomatic two-year period cannot include any two-month span that is free of mood swings.
Challenges With Getting A Diagnosis
The symptoms of bipolar disorder can overlap with other mental health problems. Different people may experience or express their symptoms in different ways. And professionals do not always get it right.
Because of this, you might:
- Not get a diagnosis of bipolar disorder when you feel you should have one.
- Get a diagnosis of a different mental health problem, which you don’t agree with.
- Get a diagnosis of bipolar disorder that you think is incorrect.
Even if you think your diagnosis is correct, you may still feel that it doesn’t completely fit your experiences.
If you are unhappy or concerned about your diagnosis, it’s important to discuss this with your doctor.
You can make sure your voice is heard, seek a second opinion and take steps if you’re not happy with your doctor. For more information, see our pages on:
Don’t Miss: How Much Vitamin D For Depression
What Is The Treatment For Mania Hypomania And Depression
You can check what treatment and care is recommended for bipolar disorders on the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence website.
NICE produce guidelines for how health professionals should treat certain conditions. You can download these from their website at:
The NHS doesnt have to follow these recommendations. But they should have a good reason for not following them.
What medications are recommended?
Mood stabilisers are usually used to manage mania, hypomania and depressive symptoms.
The mood stabilisers we talk about in this factsheet are:
- Certain benzodiazepine medication
Mania and hypomaniaYou should be offered a mood stabiliser to help manage your mania or hypomania. Your doctor may refer to your medication as antimanic medication.
If you are taking antidepressants your doctor may advise you to withdraw from taking them.
You will usually be offered an antipsychotic first. The common antipsychotics used for the treatment of bipolar disorder are:
If the first antipsychotic you are given doesnt work, then you should be offered a different antipsychotic medication from the list above.
If a different antipsychotic doesnt work, then you may be offered lithium to take alongside it. If the lithium doesnt work you may be offered sodium valproate to take with an antipsychotic. Sodium valproate is an anticonvulsive medication.
Sodium Valproate shouldnt be given to girls or young women who might want to get pregnant.
- Fluoxetine with Olanzapine
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
The defining sign of bipolar I disorder is a manic episode that lasts at least one week, while people with bipolar II disorder or cyclothymia experience hypomanic episodes.
But many people with bipolar disorder experience both hypomanic/manic and depressive episodes. These changing mood states dont always follow a set pattern, and depression doesnt always follow manic phases. A person may also experience the same mood state several times with periods of euthymia in between before experiencing the opposite mood.
Mood changes in bipolar disorder can happen over a period of weeks, months and sometimes even years.
An important aspect of the mood changes is that theyre a departure from your regular self and that the mood change is sustained for a long time. It may be many days or weeks in the case of mania and many weeks or months in the case of depression.
The severity of the depressive and manic phases can differ from person to person and in the same person at different times.
Signs and symptoms of manic episodes
Some people with bipolar disorder will have episodes of mania or hypomania many times throughout their life others may experience them only rarely.
Signs and symptoms of a manic episode include:
Most of the time, people experiencing a manic episode are unaware of the negative consequences of their actions. With bipolar disorder, suicide is an ever-present danger some people become suicidal in manic episodes, not just depressive episodes.
Recommended Reading: How To Control A Bipolar Person
Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
During a depressive episode, a person may experience irritability, persistent sadness, or frequent crying. He or she may have thoughts of death or suicide and lose interest in activities that were previously enjoyable. Other signs include a low energy level, fatigue, poor concentration, and a change in eating or sleeping habits.
During a manic episode, a person may seem unusually happy or excited. He or she may also talk too much and too fast or appear distracted or overly confident and ambitious.
Mania may also involve psychosis, or being out of touch with reality. This symptom can be characterized by hallucinations, which involve hearing or seeing things that arent there, or delusions, which involve believing things that arent supported by evidence.
Other symptoms of mania include experiencing increased energy despite a lack of sleep, driving recklessly, being sexually promiscuous, and engaging in risky behavior, such as abusing drugs or alcohol.
How Do I Get Help If I Think I Have Bipolar Disorder
The usual first step to getting help is to speak to your GP.
It can help to keep a record of your moods. This can help you and your GP to understand your mood swings. Bipolar UK have a mood diary and a mood scale on their website. You can find their details in the Useful contacts section at the bottom of this page.
Your GP cant diagnose bipolar disorder. Only a psychiatrist can make a formal diagnosis. Your GP may arrange an appointment with a psychiatrist if you have:
- depression, and
- ever felt very excited or not in control of your mood or behaviour for at least 4 days in a row.
They might refer you to a psychiatrist at your local NHS community mental health team .
Your GP should make an urgent referral to the CMHT if they think that you might have mania or severe depression. Or there is a chance that you are a danger to yourself or someone else.
Your GP should refer you to your local NHS early intervention team if you have an episode of psychosis and its your first one.
Bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose because it affects everyone differently. Also, the symptoms of bipolar disorder can be experienced by people who have other mental illness diagnoses. It can take a long time to get a diagnosis of bipolar disorder.
You can find more information about:
- NHS mental health teams by clicking here.
You May Like: Can People With Schizophrenia Drive
Do Other Illnesses Mimic Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
Mood swings and impulsive behavior can sometimes reflect psychiatric problems other than bipolar disorder, including:
- Substance use disorders
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- Certain anxiety disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder
Psychosis can occur not only in bipolar disorder but other conditions such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. In addition, people with bipolar disorder often have additional psychiatric problems such as anxiety disorders , and social anxiety disorder), substance use disorders, or personality disorders that may complicate an illness presentation and require independent treatment.
Some non-psychiatric illnesses, such as thyroid disease, lupus, HIV, syphilis, and other infections, may have signs and symptoms that mimic those of bipolar disorder. This can pose further challenges in making a diagnosis and determining the treatment.
Other problems often resemble mania but reflect causes other than bipolar disorder. An example is mood or behavior changes caused by steroidmedications like prednisone . .
What Is Bipolar Disorder
A person with bipolar disorder has fluctuations in their mood . They have rapid changes in energy levels . There are significant shifts in their thinking. The other name of variations is mood episodes. There are some bipolar disorder test to diagnose this disorder.
Mood episodes can range from a few hours to weeks in duration. People with bipolar disorder may go through great swings in behavior or activities. These may appear dangerous during these mood episodes. These are overspending, engaging in unsafe sexual practices, taking drugs or alcohol excessively. Its important for family and friends of those who have this condition to be aware of this. The foregoing symptoms are not limited to feelings. Ones thoughts may also shift during an episode, for example, from being terrible to being incredibly wonderful.
Don’t Miss: When Does Bipolar Typically Start
What Are The 3 Types Of Bipolar Disorder
There are three types of bipolar disorder:
Brain Structure And Function
Research shows that the brain structure and function of people with bipolar disorder may differ from those of people who do not have bipolar disorder or other mental disorders. Learning about the nature of these brain changes helps researchers better understand bipolar disorder and, in the future, may help predict which types of treatment will work best for a person with bipolar disorder.
Also Check: What To Do If Your Girlfriend Is Depressed
The Difference Between Bipolar And Depression
Once you know the symptoms, its easier to see the difference between bipolar disorders and depression. Depression is characterized by frequent low moods which can last for sustained periods, and when youre not feeling depressed you will return to a normal state.
Bipolar fluctuates a lot more. People with bipolar can dip very low and very high, swinging between the two frequently. Depression can be a part of bipolar, but it isnt the be-all and end-all of the disorder.
What Are The Different Types Of Bipolar Disorder
There are different types of bipolar disorder.
What is bipolar disorder I disorder?
A diagnosis of bipolar I disorder means you will have had at least 1 episode of mania that lasts longer than 1 week. You may also have periods of depression. Manic episodes will generally last 3-6 months if left untreated. Depressive episodes will generally last 6-12 months without treatment.
What is bipolar II disorder?
A diagnosis of bipolar II disorder means it is common to have symptoms of depression. You will have had at least 1 period of major depression. And at least 1 period of hypomania instead of mania.
What is bipolar I or II disorder with mixed features?
You will experience symptoms of mania or hypomania and depression at the same time. You may hear this being called mixed bipolar state. You may feel very sad and hopeless at the same time as feeling restlessness and being overactive.
What is bipolar I or II disorder with rapid cycling?
Rapid cycling means you have had 4 or more depressive, manic or hypomanic episodes in a 12-month period.
What is bipolar I or II with seasonal pattern?
Seasonal pattern means that either your depression, mania or hypomania is regularly affected in the same way by the seasons. For example, you may find that each winter you have a depressive episode, but your mania doesnt regularly follow a pattern.
There can be some similarities between bipolar I or II with seasonal pattern and another conditional called seasonal affective disorder.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Phobias In Outer Worlds
What Should You Know Before Seeing A Doctor About Bipolar Disorder
Before seeing a doctor for bipolar disorder, take note of your symptoms, along with criteria such as:
- whether the episodes have been manic or depressive
- what has happened during the episodes
- how severe episodes have been
- how long an episode has lasted
- how long you have experienced such symptoms and episodes
- your moods and feelings throughout
Also be prepared to talk with your doctor about:
- changes in your sleep
- changes in your energy levels
- changes in your speech
- family history regarding mental illness
- your own medical history, including medications you take
- lifestyle habits
- stress in your personal life, such as in employment or relationships
Sometimes, taking a family member along with you can help. They may be more aware of behavioral changes.
What Is Bipolar Disorder Test
To diagnose bipolar disorder, the first step is for a doctor to conduct an examination. Before making this diagnosis, doctors get more accurate information. This is on whats causing your symptoms and indications by eliminating other diseases with similar indicators before doing so.
The patients health status may be critical in diagnosing Bipolar Disorder, as stated in this passage. Because those illnesses affect many regions at the same time. One condition such as diabetes or high blood pressure might only appear in some parts of our bodies. The other will continue to suffer without appropriate therapy. This is due to the fact that these problems affect numerous areas simultaneously.
Recommended Reading: Is Apathy A Symptom Of Depression
Assessment Of Symptom Severity
The most common approach to measuring the severity of manic symptoms has been clinician-rated interviews. The Young Mania Rating Scale and Bech-Rafaelsen Mania Rating Scale are two of the most widely used clinician-rated scales for assessing symptom severity. These scales have been commonly used to track changes in symptoms over time as treatment progresses. We briefly review these two scales, as well as the Schedule for Affective Disorders and SchizophreniaChange version mania subscale. There has been growing recognition, though, of the need to track both clinician and patient perspectives on the course of treatment, and so we discuss available symptom severity measures that rely on self-report. Some research has focused on measures useful for case conceptualization and treatment planning, but this literature is not covered in detail here: interested readers are referred to other reviews . Table 2 summarizes some of the well-supported measures for assessing symptom severity in bipolar disorder.