The Realities Of Childhood Schizophrenia
Although the diagnostic criteria used in children are the same as adults, there are some key differences in clinical presentation of psychotic features. More in this podcast about childhood schizophrenia.
PSYCHPEARLS PODCAST
Child and adolescent psychiatrist Abhijit Ramanujam, MD, discusses clinically relevant issues in childhood schizophrenia. Dr Ramanujam is Regional Director of Community Psychiatry, Sacramento, CA.
Transcript edited for clarity. -Ed
Laurie Martin : How common is schizophrenia in children under the age of 18?
Abhijit Ramanujam, MD: The worldwide prevalence of early onset schizophrenia,that is symptoms prior to the age of 18yrs is estimated to be about 0.5% of the population,whereas childhood onset or very early onset schizophrenia which begins prior to the age of 13, has been estimated to be around 0.04% in the United States.Much less is known about the prevalence of childhood onset schizophrenia internationally.
LEM: Is there an age in which a child is too young to consider a diagnosis of schizophrenia? What do we know about early detection of schizophrenia and how soon can it be diagnosed?
Abhijit Ramanujam, MD: Although there is no official age considered too young for a diagnosis of schizophrenia, we have to keep in mind that childhood-onset schizophrenia that starts before aged 13 years is extremely rare.
Although the diagnostic criteria used in children are the same as those for adults, there are some key differences in clinical presentation:
Ruling Out Other Conditions
The DSM-5 also requires a mental health practitioner to rule out schizoaffective disorder and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features before making a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
If there is a history of autism spectrum disorder or a communication disorder of childhood onset, schizophrenia can be diagnosed only if there are prominent delusions or hallucinations in addition to the other required symptoms of schizophrenia. These symptoms must have been present for at least one month .
How Is Childhood Schizophrenia Treated
Treatment for early schizophrenia depends on the child and the type and severity of symptoms. Treatment usually includes therapy and education for both patient and family. Depending on the childs age, the doctor may prescribe antipsychotic medications to help control symptoms.
In addition to medications, doctors often recommend social skills training and counseling for the child and family. Ongoing individual therapy helps children with schizophrenia learn coping skills. This support can help them maintain relationships and do well in school.
Recommended Reading: Celine Dion Anorexic
Optimism Surrounds New Approach To Schizophrenia In Youth; More Research Is Needed
We dont have any longitudinal studies yet, Duckworth says. These clinics havent been going on long enough. Most mental health conditions, the earlier you get at them the better the outcome is. That has been shown over and over.
Says Gogtay: The duration of untreated psychosis if the psychosis goes untreated for a longer time that is detrimental to mental health outcomes. may not be able to cure the illness, but what the studies indicate is we might be able to influence the outcome in a more favorable direction.
Blunted And Flat Affect

Blunted affect is a lack of affect more severe than restricted or constricted affect, but less severe than flat or flattened affect. “The difference between flat and blunted affect is in degree. A person with flat affect has no or nearly no emotional expression. He or she may not react at all to circumstances that usually evoke strong emotions in others. A person with blunted affect, on the other hand, has a significantly reduced intensity in emotional expression”.
Recommended Reading: Can Depression Make You Lose Your Appetite
Possible Early Symptoms In Adolescents And Teens
- Blank affect
- Awkward, contorted, or unusual movements of the face, limbs, or body
- Suspicions of threats, plots, or conspiracies
- Dwelling excessively on failures, perceived slights, or past disappointments
- Unprovoked or disproportionate irritability or angry outbursts that are extreme
- Unwarranted resentment and accusations against others that is extreme
- Difficulty following a single train of thought
- Inability to read and respond appropriately to other people’s nonverbal cues
- Inappropriate behavior and responses to social situations
- Incoherent speech
- Visual or auditory hallucinations
- Sudden, painful sensitivity to light and noise
- Sudden, significant changes in sleep patterns, such as the inability to fall or stay asleep , or excessive sleepiness and listlessness
- Talking aloud to themselves, often repeating or rehearsing conversations with others
- Tendency to rapidly shift topics during a single conversation
- Using nonsense or made-up words
- Withdrawal from friendships, family, and activities
Adolescents and teens with childhood schizophrenia may also experience irrational thinking, including:
- Assigning a special meaning to events and objects with no personal significance
- Assumption of extravagant religious, political or other authority
- Believing that another person or entity is controlling their body, thoughts, or movements
- Believing that an evil force, spirit or entity has possessed their body or mind
Life Expectancy And The Risk Of Suicide
Depressed individuals have a shorter than those without depression, in part because people who are depressed are at risk of dying of suicide. They also have a higher from other causes, being more susceptible to medical conditions such as heart disease. Up to 60% of people who die of suicide have a mood disorder such as major depression, and the risk is especially high if a person has a marked sense of hopelessness or has both depression and . About 2â8% of adults with major depression die by , and about 50% of people who die by suicide had depression or another . The lifetime risk of suicide associated with a diagnosis of major depression in the US is estimated at 3.4%, which averages two highly disparate figures of almost 7% for men and 1% for women . The estimate is substantially lower than a previously accepted figure of 15%, which had been derived from older studies of people who were hospitalized.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Def
What Is Schizophrenia Or Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a challenging brain disorder that often makes it difficult to distinguish between what is real and unreal, to think clearly, manage emotions, relate to others, and function normally. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, and sees the world.
The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia, or schizophrenia with paranoia as its often called. People with paranoid schizophrenia have an altered perception of reality. They may see or hear things that dont exist, speak in confusing ways, believe that others are trying to harm them, or feel like theyre being constantly watched. This can cause relationship problems, disrupt normal daily activities like bathing, eating, or running errands, and lead to alcohol and drug abuse in an attempt to self-medicate.
Many people with schizophrenia withdraw from the outside world, act out in confusion and fear, and are at an increased risk of attempting suicide, especially during psychotic episodes, periods of depression, and in the first six months after starting treatment.
Take any suicidal thoughts or talk very seriously
If you or someone you care about is suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-TALK, visit IASP;or;Suicide.org;to find a helpline in your country, or read;Suicide Prevention.
Assessing Schizophrenia In Children And Adolescents
Dr. Ann Reitan | August 4, 2014
Childhood-onset schizophrenia differs from adult-onset schizophrenia and schizophrenia that is first manifested in individuals in adolescence. Adolescent-onset schizophrenia occurs before the age of 17 years, and childhood-onset schizophrenia is delineated as emerging prior to the age of 12 years. Schizophrenia, generally, is characterized by positive and negative symptoms.; The symptoms that emerge with the onset of schizophrenia in childhood and adolescence are generally the same as those that appear with adult schizophrenia.; Positive symptoms, specifically, include those that can be represented by behaviors that are added to the normal presentation of an individual, and negative symptoms comprise those behaviors that are deficits with regard to normal behavior.; Positive symptoms include, but are not limited to, delusions and hallucinations, as well as symptoms of a formal thought disorder, including rapid or pressured speech.; Negative symptoms include flat affect, or diminished emotional expression, poor hygiene, a lack of motivation and poverty of speech.
Children suspected as having schizophrenia may have difficulty in differentiating dreams from reality, and they may confuse television with reality.; They may have vivid and bizarre thoughts and ideas.; They may demonstrate severe moodiness, regression to earlier stages of development, and they may have difficult peer relationships.
Also Check: The Fear Of Spoons
Childhood Schizophrenia Signs And Symptoms
Some children who develop schizophrenia first go through a period called the prodrome or the prodromal phase. They might withdraw from daily life, with more anxiety and less interest in school or friends. Not all children who show these signs will have a psychotic disorder, so itâs important to talk to your doctor if you notice any issues.
Early childhood schizophrenia symptoms
A baby or toddler may have signs of schizophrenia that are different from those in older children, teens, and adults.
The disorder affects how your child develops. You may notice things like:
- Long periods in which theyâre sluggish or not active
- Floppy arms or legs
- Delays in crawling, walking, or talking
- Odd movements such as rocking or flapping their arms
- A limp or slumped posture
Some of these symptoms show up in children with other problems besides schizophrenia. And some happen in kids without any mental health conditions. Only your child’s doctor can figure out what’s really going on.
Later childhood schizophrenia symptoms
In older kids, you might notice the behavior changes of schizophrenia over time or suddenly, as if out of nowhere. Your child may act withdrawn and clingy, or they may talk about strange and disturbed ideas and fears.
Tell your doctor as soon as you see symptoms of schizophrenia. It’s important to get a diagnosis and start treatment before your youngster shows signs of a break from reality, called psychosis.
Symptoms in older children include:
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
In children with schizophrenia, behavior changes may occur slowly, over time, or have a sudden onset. The child may gradually become more shy and withdrawn. He or she may begin to talk about bizarre ideas or fears and begin to cling more to parents. One of the most disturbing and puzzling characteristics of schizophrenia is the sudden onset of its psychotic symptoms. “Psychotic” refers to ideas, perceptions, or feelings that are grossly distorted from reality. The following are the most common symptoms of schizophrenia. However, each child may experience symptoms differently.
Early warning signs of schizophrenia in children may include:
-
Distorted perception of reality
-
Confused thinking
-
Detailed and bizarre thoughts and ideas
-
Suspiciousness and/or paranoia
-
Hallucinations
-
Delusions
-
Extreme moodiness
-
Flat affect
-
Difficulty in performing schoolwork;and/or a decline in previous levels of academic achievement;
-
Social withdrawal
-
Disorganized or catatonic behavior
-
Odd behaviors
Read Also: What Is Phobia Mean
Preparing For An Appointment
You’re likely to start by first having your child see his or her pediatrician or family doctor. In some cases, you may be referred immediately to a specialist, such as a pediatric psychiatrist or other mental health professional who’s an expert in schizophrenia.
In rare cases where safety is an issue, your child may require an emergency evaluation in the emergency room and possibly a hospital specializing in child and adolescent psychiatry.
How And When Does Schizophrenia Start
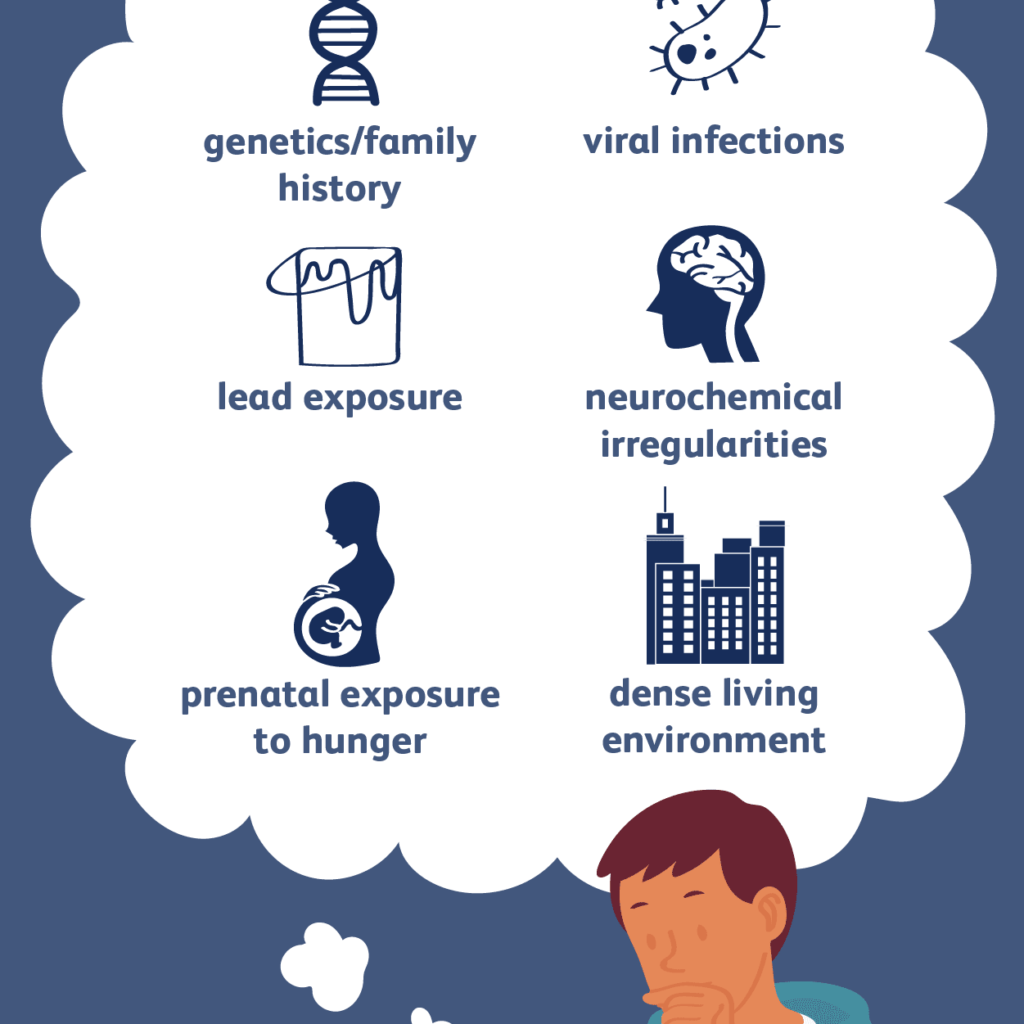
The onset of schizophrenia is usually during the teen years or early adulthood, according to the National Institute of Mental Health . The disorder is extremely rare in childhood, however, experts are homing in on early warning signs of the disease in an effort to diagnosis schizophrenia early and launch treatment.
Related: Can Marijuana Cause Schizophrenia?
Read Also: Pronounce Hippopotomonstrosesquipedaliophobia
Social And Clinical Implications
Implications from avolition often result in social deficits. Not being able to initiate and perform purposeful activities can have many implications for a person with avolition. By disrupting interactions with both familiar and unfamiliar people, it jeopardizes the patient’s social relations. When part of a severe , avolition has been reported, in first person accounts, to lead to physical and mental inability to both initiate and maintain relationships, as well as work, eat, drink or even sleep.
Clinically, it may be difficult to engage an individual experiencing avolition in active participation of . Patients are also faced with the stresses of coping with and accepting a mental illness and the stigma that often accompanies such a diagnosis and its symptoms. Regarding schizophrenia, the reported in 2013 that there currently are “no treatments with proven efficacy for primary negative symptoms” . Together with schizophrenia’s chronic nature, such facts added to the outlook of never getting well, might further implicate feelings of hopelessness and similar in patients as well as their friends and family.
Schizophrenia: The 7 Keys To Self
Seek social support. Friends and family vital to helping you get the right treatment and keeping your symptoms under control. Regularly connecting with others face-to-face is also the most effective way to calm your nervous system and relieve stress. Stay involved with others by continuing your work or education. If thats not possible, consider volunteering, joining a schizophrenia support group, or taking a class or joining a club to spend time with people who have common interests. As well as keeping you socially connected, it can help you feel good about yourself.
Manage stress. High levels of stress are believed to trigger schizophrenic episodes by increasing the bodys production of the hormone cortisol. As well as staying socially connected, there are plenty of steps you can take to reduce your stress levels. Try adopting a regular relaxation practice such as; yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
Get regular exercise. As well as all the;emotional and physical benefits, exercise may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, improve your focus and energy, and help you feel calmer. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days, or if its easier, three 10-minute sessions. Try rhythmic exercise that engages both your arms and legs, such as walking, running, swimming, or dancing.
You May Like: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Research That May Inform Diagnostic Testing In The Future
Genetics
Evidence from twin, family, and adoption studies indicate genetic factors play an etiological role in schizophrenia. A possible susceptibility gene for schizophrenia is localized in the region 8p22-8p21. Studies of children with velocardiofacial syndrome suggest that chromosomal region 22qll.2 may have a role in development of schizophrenia because the autoso mal dominant syndrome sometimes leads to chronic paranoid schizophrenia. An ongoing study at the NIMH in 47 subjects with COS demonstrated that 5 patients had cytogenetic abnormalities: 3 patients had VCFS, 1 had Turner’s syndrome , and 1 had a balanced translocation of chromosomes 1 and 7.
Biological markers
Disorganized Or Catatonic Behaviors
This refers to impaired behaviors that drastically impact a person’s daily functions and activities.
For example:
- Engaging in inappropriate activities or speech
- Extreme moodiness and irritability
- Wearing clothing that is inappropriate for the weathersuch as a winter coat in summer heat
- Lack of or inappropriate habits personal hygiene habits, such as not bathing or not brushing their teeth
- Catatonic state
Don’t Miss: How Does Schizophrenia Affect Families
The Timing Of Schizophrenia Disease Onset
Schizophrenia is particularly devastating because it often occurs at a key time of life when adolescents or young adults are honing their identities and making decisions about careers, education, and relationships, Dr.;Duckworth says.
That is one of the great challenges. Schizophrenia attacks cognition, emotion, and behavior while they are trying to establish their own identity, he says.
Related: Myths and Facts About Schizophrenia
Watch For Drug Interactions
Medications used to treat childhood schizophrenia can interact negatively with other drugs. Make sure to tell your child’s healthcare provider about any prescription or over-the-counter medication they are taking, along with any vitamins, supplements, or herbal/natural products. Street drugs and alcohol can also have an effect on this medication. Encourage your child or teen to be honest with their healthcare provider about their drug and alcohol use.
Read Also: What Is The Phobia For Bees
How Is Schizophrenia Treated In A Child
Antipsychotic medications are the treatment of choice, Dr. Fornari says. If a child were to be diagnosed with COS, second-generation antipsychotic medications would be used, he says. But early identification of the disorder is important, as are psychosocial treatment such as social support groups. For a child with schizophrenia, both academic and social support is key.
Finding ways to keep the person motivated and engaged is important, too, Dr. Houston says. Now people are really recognizing the value of these psychosocial interventions, he says.
Concerned Your Child May Have Schizophrenia

Take our 2-minute Schizophrenia quiz to see if he or she may benefit from further diagnosis and treatment.
Naturally, there is typically a high level of parental distress and confusion when a young child demonstrates what appear to be the symptoms of schizophrenia, says Peter L. Klinger, MD, assistant professor in the Departments of Psychiatry and Pediatrics at the University of Arizona in Tucson and psychiatrist for the Early Psychosis Intervention Center at Banner University Medical Group.
Read Also: What Phobia Is Weather Related
What Are The Symptoms Of Childhood Schizophrenia
Childhood schizophrenia causes symptoms similar to schizophrenia in adults. In many cases, children who have schizophrenia first show social and developmental delays that occur with other conditions, including:
- Disorganized behaviors, including inappropriate outbursts
- Motor skill delays, including a delay in learning to walk
- Poor attention span
- Speech delays or other problems, such as echolalia
Risk Factors May Offer Early Clues To Severe Mental Illness
Experts are trying to find better ways to recognize the early signs of schizophrenia, Duckworth says. A major study funded by NIMH, called North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study , is underway to try to identify youth at risk for developing psychosis and understand the risk factors and symptoms that may precipitate psychosis.
Read Also: How To Cure Schizophrenia Permanently