Gender Differences In Schizophrenia And First
Susana Ochoa
1Research and Developmental Unit of Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu, CIBERSAM. GTRDSM, Sant Boi de Llobregat, 08330 Barcelona, Spain
2Department of Mental Health, Corporació Parc Sanitari Taulí, GTRDSM, Sabadell, 08830 Barcelona, Spain
3Department of Mental Health, Institut de Psiquiatria Pere Mata, GTRDSM, Reus, Tarragona, Spain
4Monash Alfred Psychiatry Research Centre , We Mend Minds, Old Baker Building, The Alfred Commercial Road, Melbourne, VIC 3004, Australia
Academic Editor:
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prevalence and Incidence of Schizophrenia
No gender differences have been found in prevalence of schizophrenia in epidemiological studies however, it seems that more new cases of schizophrenia have been detected in men.
3. Age of Onset
Some authors have suggested that differences in age of onset appear to depend on the presence or absence of family history, with no differences being found between men and women if they had a family history .
Besides, the findings of early age of onset in men have been replicated in first-episode psychosis , indicating a consistency with the results found in schizophrenia.
Gender differences have been found in most of the studies done in age of onset in schizophrenia and first-episode psychosis, showing a different profile of onset of illness between women and men.
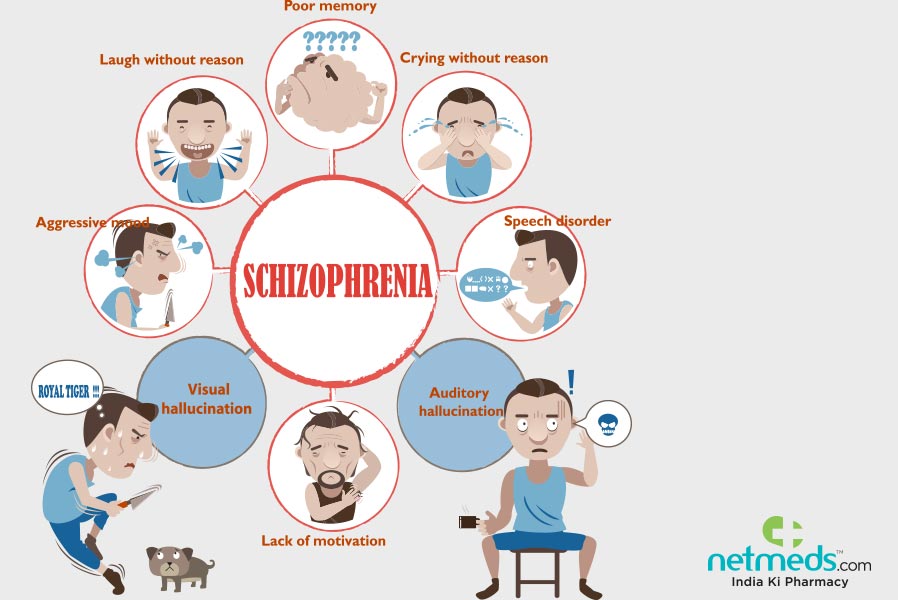
4. Symptoms
Nevertheless, most of the studies found no significant clinical differences in symptoms, which is in line with our teams findings .
12. Conclusions
The Incidence Of Schizophrenia Has Prominent Variation By Sex
Two independent systematic reviews, using different summary methods, have concluded that the incidence of schizophrenia is significantly higher in men than in women. Both studies found the overall male:female risk ratio to be 1.4 and that this difference could not be accounted for by methodological factors related to age range or diagnostic criteria.
Schizophrenia Has Variations According To Month Of Birth
Individuals born in winter and spring have a small but significantly increased risk of developing schizophrenia. This finding, one of the most consistently replicated findings in schizophrenia epidemiology, was confirmed in a systematic review of studies based on the Northern Hemisphere sites. This same meta-analysis found that the size of the winter/spring excess was positively associated with latitude. A well-designed study from Denmark estimated that while the odds ratio for schizophrenia associated with winter/spring birth was very small , because birth in winter/spring is such a common exposure, the population-attributable fraction associated with season of birth was sizable .
Don’t Miss: Pristiq Irritability
Life Challenges For Women With Schizophrenia
Typically, women with schizophrenia function better socially than men, often because a later age of onset indicates a less severe form of mental illness. Women with schizophrenia are likely to experience fewer hospitalizations and shorter visits while in the hospital compared to men. Some researchers believe that this later onset is because hormones like estrogen have a protective effect.4 However, this disparity in the age of onset is not present in all ethnic groups. For example, multiple studies in the country of India have found no difference in the mean age of onset between men and women.5
What Are The Different Types Of Schizophrenia
Prior to 2013, schizophrenia was divided into five subtypes as separate diagnostic categories. Schizophrenia is now one diagnosis.
Although the subtypes are no longer used in clinical diagnosis, the names of the subtypes may be known for people diagnosed prior to the DSM-5 . These classic subtypes included:
- paranoid, with symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized speech
- hebephrenic or disorganized, with symptoms such as flat affect, speech disturbances, and disorganized thinking
- undifferentiated, with symptoms displaying behaviors applicable to more than one type
- residual, with symptoms that have lessened in intensity since a previous diagnosis
- catatonic, with symptoms of immobility, mutism, or stupor
According to the DSM-5, to be diagnosed with schizophrenia, two or more of the following must be present during a 1-month period.
At least one must be numbers 1, 2, or 3 on the list:
Read Also: In Which Of The Following Phases Of Schizophrenia Are The Psychotic Symptoms Most Prominent
Living With Schizophrenia Statistics
Only about 15 percent of people diagnosed with schizophrenia are able to work full time. This means that they are likely to struggle with paying rent or a mortgage. They are likely to struggle to pay for healthcare insurance. These are some of the reasons why so many individuals with schizophrenia are homeless. Yet, with ongoing treatment and a comprehensive array of support, people with schizophrenia can lead happy, productive lives. When their symptoms are in check, people with schizophrenia can function well in society.
The key to managing schizophrenia optimally is to obtain medical care at a facility that specializes in mental and behavioral health conditions. Like many mental health disorders, schizophrenia typically requires multiple types of support that include therapy, medication, and holistic support. Given this multi-tiered support, schizophrenia patients can expect to enjoy excellent disease management, allowing them to lead fulfilling lives.
What We Get Wrong About Schizophrenia
Technically, the word schizophrenia translates into split mind. First coined in 1911 by Swiss psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler, schizophrenia was used to describe a disorder of thought and feeling, a split in the mental process between the intellect and the external realityemotion and cognition.8
The result of this split, he thought, was a fragmented mental process that led to symptoms first described as social withdrawal, apathy, an inability to carry out the activities of daily living, and psychotic events such as hallucinations. Despite Bleulers observations though, schizophrenia was believed to be a psychotic reaction to neglectful parenting, especially from cold, uncaring, perfectionist, and domineering mothers, rather than a disease rooted in brain pathology.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Treating Women With Schizophrenia
Though treatment for mental illness is not typically separated by gender, clinicians serve women best by considering their unique experience of schizophrenia as well as the unique challenges they face. Because women have later onset of the illness and are less likely to experience affective symptoms, clinicians must be careful to rule out other mental illnesses, such as schizoaffective disorder or bipolar disorder, when giving a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Treatment for women with schizophrenia should include psychoeducation and support for the needs of mothers with children. Antipsychotic medication can affect the ability to breast feed and the amount of energy a mother has to parent her children.7 Treatment plans tailored for women should include education about physical health as well. Women with schizophrenia are less likely to care for their physical health. This leaves them at risk for untreated breast cancer, osteoporosis, and thyroid conditions. Mental health professionals should also consider creating safety plans for women with schizophrenia who are at increased risk for committing suicide.
The Incidence Of Schizophrenia Has Changed Over Time
Narrative reviews based on historical texts have speculated that the incidence of schizophrenia has fluctuated over the centuries. In fact, recent empirical studies provide support for this notion. Studies in southeast London between 1965 and 1997 show that the incidence of schizophrenia at this site doubled during the intervening decades. In contrast, a systematic review of the incidence of schizophrenia establishes that more recent studies have found significantly lower incidence rates compared to earlier studies. Such fluctuation would be expected in light of the dynamic shifts in population structure and exposure to various risk factors . Fluctuations in the incidence of schizophrenia across time would also be congruent with the evidence that so-called schizophrenia birth rates shows secular change and intradecadal fluctuations.
You May Like: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Suicide Rates And Seeking Help
Mental health problems are increasingly being recognised in men of all ages, with the highest incidence of mental ill health and suicide reported in elderly men. The highest suicide rate for Australian males in 2015 was in men aged 85-plus years, with 68 deaths reported overall in this age group.
This rate was considerably higher than the age-specific suicide rate in all other age groups. The suicide rate for men between the ages of 40 and 55 was around 31 per 100,000 people. For women, suicide rates didnt differ too much across age groups in 2015 rates were around 8-10 per 100,000 people.
Read more:Elderly men have the highest suicide rate and ageism stops us from doing something about it
One reason women have lower rates of suicide is that they are more likely than men to seek help. Around 18% of women compared with 11% of men sought help for anxiety in 2007. And 7.1% of women compared with 5.3% of men sought help for mood disorders. Only a small percentage of adolescent boys and men seek help for mental ill health.
Women are also more likely than men to use services for mental health problems. This may reflect greater female psychological knowledge and acceptance of mental illness. Mental illnesses in men are frequently masked by risky behaviours such as alcohol and drug abuse, anger and aggression, speeding on roads and drink driving.
The Past And Racial Disparities In Mental Health
According to the American Psychiatric Association, differences in rates of diagnosis can be explained by a confluence of factors in the Black community including lack of access to high-quality mental health care services, cultural stigma surrounding mental health care, discrimination, and an overall lack of awareness about mental health.5Mental Health America, a national non-profit organization dedicated to mental health, says these factors translate into Black and African American people being more likely to experience chronic and persistent , rather than episodic , mental health conditions.
Of course, disparities exist across an eagles wingspan of mental illness. But the relationship between schizophrenia and Black Americans has a particularly nefarious past.
In The Protest Psychosis: How Schizophrenia Became A Black Disease, psychiatrist Jonathan Metzl wrote of the unseemly link between the mental condition and racism. Schizophrenia, he claims, was once seen as a rather benign mental disorder impacting middle-class White women. Much later, in the 1960s and 1970s, schizophrenia developed a reputation as a violent disease, falsely linked with male Black activists during the Civil Rights movement. In 1968, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders listed dangerousness as a symptom of schizophrenia perhaps a way to justify the psychiatric treatment of Black people protesting again injustice.6,7
You May Like: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Sex Differences In Age At Onset
While men and women have similar prevalence of Schizophrenia, most of studies demonstrated that female onset is typically 3â5 years later than males. It is now accepted that men has a single peak age for onset which is between 21 and 25 years old and women have two peaks age of onset, one between 25 and 30 years old and another one is after 45 years old as shown in . It is also observed that women with schizophrenia are more associated with seasonality of first admissions as compared to schizophrenic men. The delayed two peaks of onset ages in women have been consistent with other studies which reported that women make up 66%â87% of patients with onset after the age of 40â50 years.
Sex differences in onset age of schizophrenia
Note: Men have a notable peak of incidence in late adolescence and a subsequent sharp decline into middle age. The peak age of incidence rates in women appears in adolescence as well as after 45 years old.
The Prevalence Of Schizophrenia Varies Widely
While not the main focus of this article, it should be noted that the prevalence of schizophrenia also has prominent variations between sites. Regardless of the type of prevalence estimate , these distributions have prominent variation . This same systematic review found that the prevalence of schizophrenia in migrants was higher compared to that in native-born individuals and that developed countries had significantly higher prevalence estimates compared to developing nations.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Five Years Before Diagnosis Of Ssd
Most women and men had been hospitalized for another psychiatric disorder before the first hospitalization for SSD. 47.8% of women had been hospitalized for another psychotic disorder, and this resulted into a median of 56 hospital days , while the median number of hospital days for any psychiatric diagnosis was 81 . In men, the median number of hospital days for another psychotic disorder before SSD was 53 for 48.5% of men , with corresponding median of hospital days due to any psychiatric diagnosis of 65 .
Significant differences occurred in type of diagnoses in the trajectory before SSD, with more frequent mood disorders , anxiety disorders, eating disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder, dissociative disorder, personality disorder, suicide attempts, and self-harm in women . Men had more often substance disorder and more autism spectrum disorders. The largest gender differences were found for eating disorder and substance abuse, for which women had less than half the risk as men .
Table 1 The prevalence of psychiatric diagnoses before and after a schizophrenia-spectrum diagnosis was made, for men and women .
Schizophrenia In Men And Women: Whats The Difference
Schizophrenia in men and women has the same diagnostic criteria , but differences are known between the genders. Schizophrenia in men tends to develop between the ages of 15-20 whereas for women, schizophrenia tends to develop between 20-25 years of age. Moreover, not only does schizophrenia in men occur earlier, men are often hit harder by the disease. Estrogen, a hormone found in greater amounts in women, may be protective against some of the effects of schizophrenia.1
Recommended Reading: Dehydration And Panic Attacks
Other Concerns For Men With Schizophrenia
Men with schizophrenia may tend to have lower social functioning and other conditions like substance abuse that complicate their treatment plan and recovery. Dr. Estakhri specializes in both general and addiction psychiatry, so if you have schizophrenia but are also dealing with drug or alcohol abuse, you get the most comprehensive treatment at Allied Psychiatry & Mental Health right here in Orange County, California.
Schizophrenia can be debilitating. Let us help you manage your symptoms and live a better quality of life. Contact us to make an appointment with Dr. Estakhri today.
You Might Also Enjoy…
Other Causes Of Schizophrenia
Along with genetics, other potential causes of schizophrenia include:
- The environment. Being exposed to viruses or toxins, or experiencing malnutrition before birth, can increase the risk of schizophrenia.
- Brain chemistry. Issues with brain chemicals, such as the neurotransmitters dopamine and glutamate, may contribute to schizophrenia.
- Substance use. Teen and young adult use of mind-altering drugs may increase the risk of schizophrenia.
- Immune system activation. Schizophrenia can also be connected to autoimmune diseases or inflammation.
You May Like: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Differences In Response To Antipsychotic Medications
Clinical trials examining sex differences in the efficacy of atypical antipsychotic medications found greater rates of symptom reduction in women compared to men. However, women are at a greater risk for experiencing weight gain and developing metabolic syndrome as a result of antipsychotic medication use. It is possible, however, that these differences in treatment response may be confounded by sex differences in clinical symptom severity and age at illness onset described above.
Symptoms Of Women With Schizophrenia
The criteria for a diagnosis of schizophrenia is the same for women as it is for men, but the features of schizophrenia differ between the genders. For example, women may exhibit depression or anxiety which may put them at a higher risk for suicide.2
Women with schizophrenia are lesslikely to have symptoms such as:
- Flat affect
- Blunted emotional responses
- Speech reduction
- Social withdrawal
Women with schizophrenia may be more physically active and more hostile than men with the illness. They may also experience more auditory hallucinations as well as paranoid and persecutory delusions. Paranoid delusions consist of thoughts like, my spouse is cheating on me, when he isnt. Persecutory delusions consist of thoughts like, Im being mistreated, when there is no actual mistreatment. Not every woman with schizophrenia will exhibit these features, but these trends have been noted in some large-scale studies.3
Read Also: Is Tequila A Depressant
How Schizophrenia Symptom Differences Affect Quality Of Life
Men and women can experience symptoms of schizophrenia that are quite different from each other. This difference can impact overall quality of life . All symptoms of schizophrenia are very disruptive to everyone who lives with the illness. Schizophrenia isnt easy for men or women. However, because of the differences in symptoms in males and females, the effects on quality of life are different.
Men tend to experience more problems than women. The schizophrenia symptoms in males can cause more maladaptive behavior such as substance abuse with schizophrenia, isolation, and anti-social behavior. They experience more personal troubles like relationship problems, family trouble, unemployment, and homelessness. Perhaps all of these struggles relate to the difficult cognitive problems schizophrenia creates such as lack of motivation and drive, problems with planning, decision-making, and completing tasks.
Women, in contrast, experience a better quality of life despite living with schizophrenia. Women are more likely to marry, have children, and maintain employment. The higher social functioning that women experience allows them to deal with schizophrenia differently.
Schizophrenia In Mens And Womens Brains

Many differences are known between the brains of those with schizophrenia and the general population, but it may also be that there are differences between the brains of men and women with schizophrenia.
Specifically, there is a structure called the inferior parietal lobule that may hold a key. On the left, the IPL is involved in:
- Spatial relations
On the right, the IPL is involved in:
- Perceiving where each body part is in relation to the others
- Reading facial expressions or posture
In healthy volunteers, men have a larger IPL and their left is larger than their right. In women, the reverse is true.
In schizophrenic men though, differences in IPL have been found. Men with schizophrenia have a smaller left IPL and large right. Whats more, the overall size of the IPL in men with schizophrenia is about 16% smaller than that of healthy men. This may partially explain why the IPL functional areas are negatively impacted in schizophrenia.3
Recommended Reading: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words