How Is Borderline Personality Disorder Diagnosed
There isnt a medical test to confirm a borderline personality disorder diagnosis. Your provider may do a physical exam or order a blood test to rule out health conditions that may be causing your symptoms. Healthcare providers diagnose BPD after several interviews with you. Your provider might also talk to your family members or friends.
The interviews will include questions about your symptoms, relationships, behaviors and mental health history. BPD often occurs along with other mental health conditions. Your provider will work with you to get a clear picture of your unique symptoms and overall health.
How Bipolar And Borderline Personality Disorder Are Similar
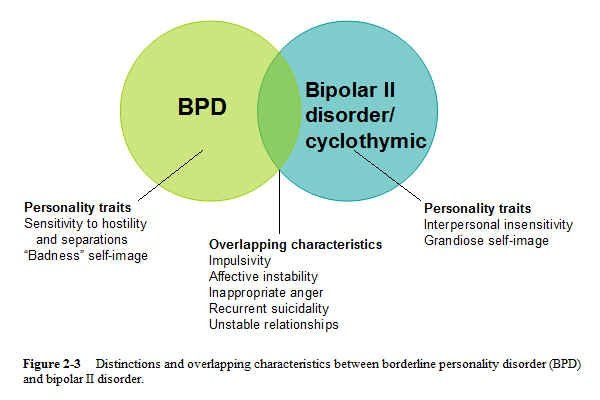
The primary reason that some experts have proposed that BPD and bipolar disorder may be related is that they share the common feature of mood instability.
Bipolar disorder is associated with mood shifts from depression to mania, a mood characterized by elation, a decreased need for sleep and an increase in activity, or hypomania, which is similar to mania but less severe.
BPD is also associated with mood changes, sometimes called emotional dysregulation or affective instability. People with BPD can frequently change from feeling fine to feeling extremely distressed in a matter of minutes.
Impulsive behavior is also frequently experienced both by people with bipolar disorder and by people with BPD.
Can These Conditions Be Prevented
Theres no known way to prevent bipolar disorder or narcissistic personality disorder. However, because childhood trauma is linked to both, it may help to get therapy for issues as soon as possible.
If youre a parent whos concerned about narcissism or NPD in your child, parenting classes or therapy may help you improve your parenting style so it doesnt contribute to narcissistic traits.
Also Check: Fear Of Long Words Name
Whats The Best Way To Support Someone With Bipolar Disorder
Supporting someone with bipolar disorder can be difficult because its hard to know what kind of support they need. According to the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance, some of the best ways to support someone with the disorder are:
- Ask the person what kind of support they need.
- Dont ask the person to snap out of an emotional state they may be experiencing.
- Educate yourself about bipolar disorder to better understand what the person is going through.
- Encourage the person to seek treatment.
- Try to offer as much unconditional love as you can.
Comorbid Bipolar Disorder And Borderline Personality Disorder: Diagnosis Using Machine Learning
Machine learning analysis was able to differentiate comorbid BP and BPD from each condition individually.
-
A distinct set of rules was generated for each analysis, with important items largely differing in distinguishing the comorbid condition from BP and BPD.
-
Classificatory accuracy was superior in distinguishing BP/BPD vs. BP, with lower accuracy when differentiating from BPD.
You May Like: Phobia Medical Definition
Frequency And Ages Affected
Bipolar disorder affects approximately 2.2 percent of people in the United States. Typically, it first appears between the late teen years and early adulthood. Children can also show signs of bipolar disorder.
Schizophrenia isnt as common as bipolar disorder. It affects 1.1 percent of the U.S. population. People usually learn they have it between the ages of 16 and 30. Schizophrenia isnt usually seen in children.
Bipolar Vs Borderline Personality Disorder: Treatment
One of the most significant differences between bipolar and borderline personality disorder is treatment. The most important part of bipolar treatment is medication, followed by psychotherapy. BPD treatment, on the other hand, focuses on psychotherapy, not medication. Sometimes antidepressant drugs and mood stabilizers are prescribed based on specific target symptoms, but medication for BPD is often used as a last resort. The type of psychotherapy used to treat both disorders also varies. Bipolar disorder patients respond best to traditional therapies, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, while BPD patients tend to respond better to Dialectical Behavior Therapy. The Dialectical Behavior Therapy model is rooted in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, but specifically addresses the needs of patients with borderline personality disorder, especially those who tend to self harm or have suicidal ideation. The focus is on building positive relationships, acceptance and emotional control.
In addition to psychotherapy and pharmaceutical medications, some people have successfully eased their bipolar and borderline personality disorder symptoms with holistic treatments, such as yoga, acupuncture, meditation and herbal/natural supplements. These types of treatments help people with either disorder learn how to decompress from stress, relax and feel centered. They promote a sense of mindfulness that can help them better tackle tough times and cope with emotional issues in a healthier way.
Recommended Reading: Claustrophobia Meaning In English
Sleep And Bipolar Disorder
Another important factor worthy of consideration regarding the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder involves the sleep-wake cycle. According to a recent study in the journal Frontiers in Psychiatry, sleep abnormalities often serve as effective indicators that a mood swing is on its way. Additionally, the study reports that 23% to 78% of people with bipolar disorder extend their sleep hours into the day, past nighttime, with episodes of excessive sleepiness during the day.
This sleep issue, along with insomnia that is prevalent in those with bipolar disorder, can affect circadian rhythms in the body. Some postulate that disturbances to circadian rhythms can play a role in bipolar symptoms.
Is Borderline Personality Disorder More Common In Patients With Bipolar Disorder Than Psychiatric Control Groups
Eight studies compared the frequency of BPD in patients with bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder.,,-,,, Four studies found no difference between the two groups,,,, whereas three of the four studies of bipolar II disorder found a higher rate of BPD in the bipolar patients.,,, Another study found no difference in the rate of BPD in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. One study compared the frequency of Axis I disorders in a heterogeneous sample of psychiatric outpatients, and sufficient data was provided to calculate the rate of BPD in patients with different diagnoses. BPD was significantly more frequent in patients with bipolar disorder than in patients with major depressive disorder, as well as more common than in patients with any psychiatric disorder. Another study of psychiatric outpatients with mixed diagnoses found a lower rate of BPD in patients with bipolar disorder. Thus, four of ten studies found a significantly higher rate of BPD in patients with bipolar disorder compared with a psychiatric control group, and three of these four positive studies were comparisons of bipolar II disorder versus major depressive disorder.
Read Also: Is Sex Good For Depression
Borderline Personality Disorder Diagnosis
Because young people with BPD may project symptoms that seem similar to other personality disorders, it is often confused with bipolar, depression, or anxiety disorders. The National Institute of Mental Health offers this description:
Borderline personality disorder is a serious mental disorder marked by a pattern of ongoing instability in moods, behavior, self-image, and functioning. These experiences often result in impulsive actions and unstable relationships. A person with BPD may experience intense episodes of anger, depression, and anxiety that may last from only a few hours to days.
The Core Features Of Bpd
BPD has very specific symptoms, which makes it easy to distinguish from other conditions. It is common not to screen for the core features but to diagnose based on ‘countertransference feeling’. This is particularly the case when people present with self-harming behaviour.
I was trained in DSM 4 which is a more user-friendly diagnostic tool than ICD 10 for BPD as it doesnt subdivide it into two conditions.
The criteria for BPD in DSM 4
In addition to the core features of all personality disorders, the criterion are:
Someone must have five of these nine features to merit the full diagnosis.
Also Check: What’s The Phobia Of Throwing Up
Which Disorder Is More Serious
The American Psychiatric Association classifies and issues standard diagnostic criteria for mental illnesses in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, or DSM. In older versions of the DSM, personality disorders were classified as axis II problems, while mood and thought disorders were classified as axis I disorders. Because they were relational, we used to think that personality disorders were not as serious or disabling as depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia. However, we know from many outcomes studies that untreated personality disorders are quite disabling. Therefore, one of the most important changes in the most recently revised and published edition of the DSM was removing the ordinal hierarchy and classifying personality disorders as equal to mood and thought disorders in terms of impact and disability.
Bipolar Disorder Is A Mood Disorder And Borderline Personality Disorder Is A Personality Disorder

A common feature of bipolar disorder is recurring episodes of depression. Many people with bipolar disorder present a lot like people with unipolar depression, or major depressive disorder: they feel sad, lose interest in activities, feel worthless, have trouble concentrating, etc. To be diagnosed with bipolar disorder, you must also have experienced at least one episode of mania. An episode of mania is characterized by an elevated mood, heightened energy without the need to sleep, racing and/or grandiose thoughts, and impulsive behavior. For most people with a bipolar diagnosis, about 75 percent of the time they are experiencing disability from the illness, they are in depressive episodes. however, having a history of one manic episode ever means that a person has bipolar illness even if the person is currently depressed.
Borderline personality disorder is not a mood disorder. It is classified as a personality disorder. The symptoms of borderline personality disorder can result in mood problems, but the illness is not defined by changes in mood. The symptoms of borderline personality disorder are relational.
However, for individuals with bipolar disorder, for the most part, there is little causal relationship between interactions with other people and the onset of a mood episode. But with borderline personality disorder, interactions with other people or expectations about relationships are what drive the illness and result in mood and anxiety problems.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Def
Diagnosing Borderline Personality Or Bipolar Disorder
Welcome to Priory Bitesize, your monthly e-bulletin in which a mental health expert will discuss dealing with certain conditions to support your patient discussions.
This month, Dr Judith Mohring, Consultant Psychiatrist at Priory Wellbeing Centre Fenchurch Street in London, talks about the challenges in diagnosing borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder.
A common question asked by GPs is whether a patient has BPD or bipolar disorder.
Having worked in a specialist BPD service and having set up a service in Holloway prison for women who self-harm, it was a question I felt reasonably confident to approach.
Despite this, teasing out different symptoms and making a clear diagnosis takes time and is complex. Changes in the understanding and description of bipolar disorder have added to this complexity. A thorough assessment by a specialist in general adult psychiatry can be enormously helpful to patients and GPs in guiding further treatment.
This article focuses on the diagnosis of the two conditions including:
- Controversy over diagnosing BPD
- The benefits of making a distinction between personality and mood disorder
- The core features of BPD
- The core features of bipolar disorder
- Distinguishing between the features of each condition
- A brief overview of treatment options for each condition
Is Borderline Personality Disorder The Most Frequent Personality Disorder In Patients With Bipolar Disorder
Fifteen studies examined the full-range of personality disorders in patients with bipolar disorder.,,,,,,,
In only four of the 15 studies BPD was the most frequent diagnosis.,,, Histrionic personality disorder was the most common diagnosis in four studies ,,, and tied for the most common in another two studies,, and obsessive-compulsive personality disorder was the most common in three studies,, and tied for the most common in another two studies., While this suggests that there is no clear evidence that BPD is the most common personality disorder in patients with bipolar disorder, it is noteworthy that BPD was the most frequent personality disorder diagnosis in the only two studies of bipolar II disorder.,
Read Also: How To Pronounce Cherophobia
There Are Two Classifications Of This Condition:
Bipolar I are diagnoses in which a person is on the extreme end of mania, experiencing highs that impair sleep for days on end and may lead to psychosis and hospitalization.
Those diagnosed with Bipolar II are more apt to suffer serious depression.
One interesting aspect of this mental health condition is that it has been linked to people who are highly creative.
In fact, a number of celebrities with bipolar disorder have been very open about their experiences with the disorder and have discussed how treatment helped them lead healthy lives.
There have also been a number of movies made about bipolar disorder.
Ological Issues In Personality Disorder Assessment
Any review of a topic involving personality disorders needs to consider assessment methodology, because assessment issues can have a significant impact on the findings. In short, there should be some consideration of the who, what, and when of personality disorder assessment.To be sure, these are also issues in the evaluation of Axis I disorders, though they have not been studied as much as they have been studied in the personality disorder field.
Don’t Miss: Fear Conditioning Definition
In English Spanish French
It is clinically important to recognize both bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder in patients seeking treatment for depression, and it is important to distinguish between the two. Research considering whether BPD should be considered part of a bipolar spectrum reaches differing conclusions. We reviewed the most studied question on the relationship between BPD and bipolar disorder: their diagnostic concordance. Across studies, approximately 10% of patients with BPD had bipolar I disorder and another 10% had bipolar II disorder. Likewise, approximately 20% of bipolar II patients were diagnosed with BPD, though only 10% of bipolar I patients were diagnosed with BPD. While the comorbidity rates are substantial, each disorder is nontheless diagnosed in the absence of the other in the vast majority of cases . In studies examining personality disorders broadly, other personality disorders were more commonly diagnosed in bipolar patients than was BPD. Likewise, the converse is also true: other axis I disorders such as major depression, substance abuse, and post-traumatic stress disorder are also more commonly diagnosed in patients with BPD than is bipolar disorder. These findings challenge the notion that BPD is part of the bipolar spectrum.
Keywords: bipolar disorder bipolar spectrum borderline personality disorder.
Symptoms Of Bipolar Induced Depression Can Include:
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness and hopelessness
- Long periods of sadness or crying spells
- Intense worry, fear or anxiety
- Feeling irritable, agitated or angry
- Chronically exhausted
- Cycles of unexplained body aches and pains
- Difficulty concentrating or feeling indifferent about everything
- Inability to find pleasure in activities and people normally enjoyed
- Isolating from friends, family, work, or other social connections
- Thoughts about death and suicide
- Irritability, anger and aggression
- In psychotic episodes, hallucinations and delusions can be present
Obviously, individuals living with Bipolar Disorder I or Bipolar Disorder II will experience symptoms and episodes unique to their own circumstances.
In general however, episodes of depression can last two weeks or longer while manic episodes may last up to a week, sometimes requiring hospitalization.
Don’t Miss: Dehydration Cause Anxiety
A Colleague Approached Me And Said That She Was Referring A Patient To The Partial Hospital Program Who Had Borderpolar Having Not Previously Heard This Term Clarification Was Sought And It Was Explained That The Patient Had Both Borderline Personality Disorder And Bipolar Disorder My Colleague Further Explained That This Term Is Frequently Used In The Psychiatrist Chat Room She Visits As A Shorthand For Patients With Both Disorders Who Are Severely Ill And Have High Levels Of Psychosocial Morbidity A Pubmed Search On The Term Borderpolar Did Not Turn Up Any Citations
Both bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder are significant public health problems. Both disorders are associated with impaired functioning, high utilization of psychiatric services, high rates of substance use disorders, and suicidality. Despite the psychosocial morbidity and risk for premature mortality, both disorders are frequently underdiagnosed. As a result, calls for improved recognition have been voiced for both disorders.1,2
For years there has been debate as to how to conceptualize the relationship between BPD and bipolar disorder. Some experts have suggested that BPD is part of the bipolar spectrum. Review articles have summarized the evidence supporting and opposing the bipolar spectrum hypothesis, with most of the recent reviews concluding that BPD and bipolar disorder are valid and distinct diagnostic entities. And since each disorder suggests different treatment emphases-a focus on pharmacotherapy with possible adjunctive psychotherapy for patients with bipolar disorder versus a focus on psychotherapy with possible adjunctive medication for patients with BPD-making the differential diagnosis is that much more important. Meanwhile, many authors and clinicians have described the diagnostic uncertainty and the challenges in determining if a patient has bipolar disorder or BPD.
The comorbidity: borderpolar
The MIDAS project
Looking forward
Concluding thoughts
How Bipolar And Borderline Personality Disorder Are Different

What is the difference between BPD and bipolar disorder, then? Some major components separate the two.
- Quality: While the disorders are both characterized by mood changes, the quality of the mood changes can be very different. People with bipolar disorder tend to experience mania and depression while people with BPD experience intense emotional pain and feelings of emptiness, desperation, anger, hopelessness, and loneliness.
- Time: In BPD, mood changes are often more short-lived. They may last for only a few hours at a time. In contrast, mood changes in bipolar disorder tend to last for days or even weeks.
- Cause: Mood shifts in BPD are usually in reaction to an environmental stressor, such as an argument with a loved one, whereas mood shifts in bipolar disorder may occur out-of-the-blue.
- Degree: The mood shifts typical of BPD rarely involve elation. Usually, the shift is from feeling upset to feeling OK, not from feeling bad to feeling a high or elevated mood, which is more typical of bipolar disorder.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Pristique