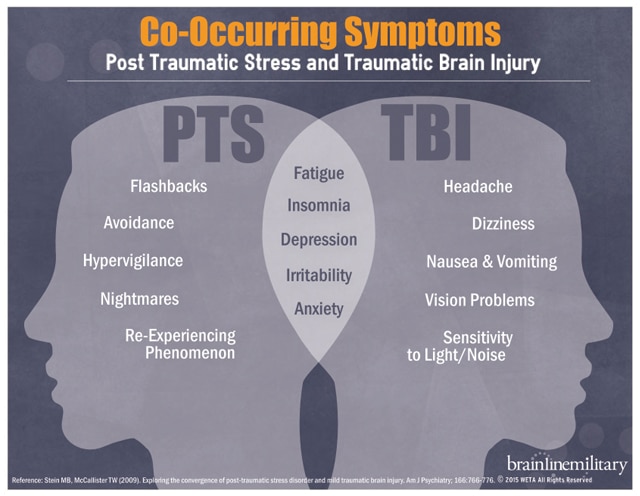
Ptsd Symptoms And Behaviors
Common symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder include reliving a traumatic event through nightmares, flashbacks, or constantly thinking about it. You might avoid situations or people that remind you of the event, have only negative thoughts or emotions, and constantly feel jittery, nervous, or on edge. Although some of these symptoms sound similar to PTS, the difference is the duration and intensity. Symptoms that continue for more than one month, are severe, and interfere with your daily functioning are characteristic of PTSD.
Behaviors that indicate professional intervention is needed may include drinking or smoking more than usual as attempts to reduce anxiety or anger, and aggressive driving. Service members who have experienced combat can be especially nervous driving under overpasses and past litter on the roadside behavior learned in Iraq and Afghanistan where insurgents hide improvised explosive devices in garbage and use overpasses to shoot at vehicles. Other behaviors that indicate that help may be needed can include being wary of crowds, showing reluctance to go to movie theaters, crowded stores, or nightclubs, and avoiding news that addresses overseas combat or getting angry at the reports.
Arousal And Reactivity Symptoms Include:
- Being easily startled
- Feeling tense or on edge
- Having difficulty sleeping
- Having angry outbursts
Arousal symptoms are usually constant, instead of being triggered by things that remind one of the traumatic events. These symptoms can make the person feel stressed and angry. They may make it hard to do daily tasks, such as sleeping, eating, or concentrating.
Free Brochures And Shareable Resources
- Helping Children and Adolescents Cope With Traumatic Events: This fact sheet presents information on how children and adolescents respond to traumatic events, and what family, friends, and trusted adults can do to help. Also available en español.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: This brochure provides information about post-traumatic stress disorder including what it is, who develops PTSD, symptoms, treatment options, and how to find help for yourself or someone else who may have PTSD. Also available en español.
- : Help support PTSD awareness and education in your community. Use these digital resources, including graphics and messages, to spread the word about PTSD.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When Ptsd Triggered
Learn Why Dropping The D From Ptsd Is Significant And How It Can Benefit Those Affected By Post
Post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms have been documented as far back as the Civil War. Though the name has experienced a few changes, from soldiers heart, shell shock, battle fatigue, PTSD and now more recently post-traumatic stress, the definition for the condition remains relatively the same.
If the terms of the condition havent truly changed, why has the name changed? Including D for disorder in the name carries a stigma that often leaves those most vulnerable, such as veterans, unwilling to seek help. Based on this knowledge, notable figures have been pushing to change the name of the condition from PTSD to PTS to encourage more people to seek help.
How Is Pts Different From Ptsd
You may have heard about PTSD . But whats PTS?
PTS is simply post-traumatic stress its not a medical disorder. Most people with PTS never end up developing the disorder .
Unlike post-traumatic stress, the disorder is a lot more severe. It can take a toll on a persons mental and emotional health in the long run. In this blog, well offer more insight into the differences between PTS and PTSD.
You May Like: How To Have An Eating Disorder
How Pts Differs From Ptsd
Like those who experience PTS, people with PTSD may experience similar symptoms. They may feel jittery, jumpy, or nervous all the time. And they may avoid events, situations, or activities that remind them of that life-altering incident. Additionally, their symptoms may include ongoing flashbacks of the event, nightmares, or an inability to stop thinking about what happened.
However, the difference between these two conditions is found in the duration of PTSD symptoms and their intensity. People are likely to have PTSD if these types of symptoms:
- Last for a month or longer
- Are extreme and intense
- Impede their ability to manage their daily routines and function normally
People suffering from PTSD may recognize the need for medical and/or professional help if their behavior begins to include drinking, increased smoking, or any type of action that shows theyre trying to reduce the stress and anxiety they feel. Additionally, they may be afraid to attend social functions in crowded areas, avoid listening to the news about combat situations, or get angry about ongoing reports about war.
Its important for veterans to remember that PTS symptoms are common after theyre deployed but will often diminish soon after. Additionally, most people who experience PTS dont develop PTSD. And its very possible for a veteran to develop PTSD without ever first suffering from PTS.
What Is The Difference Between Pts And Ptsd
Many people can confuse post-traumatic stress and post-traumatic stress disorder . They share a similar name and there are some similarities however, these two disorders are different in symptom presentation, duration, and treatment. Both PTS and PTSD involve feelings of fearfulness, avoidance, nervousness, anxiety, and nightmares. Here are some of the differences.
Post-traumatic StressPTS is a normal response to a traumatic or stressful event. Some people involved in a car accident or who might experience complications from a surgery can exhibit symptoms of PTS. The fight-or-flight response is activated with PTS our bodies tense and we breathe faster. The activation of this response is normal and allows us to deal with the stressor through normal reactions.
Symptoms of PTS include rapid heart rate, sweating, or feeling afraid. Once the stressful event has subsided, there could be some residual effects such as unpleasant dreams or avoiding any situation that resembles the stressful event. These symptoms are usually short-lived and subside after a few days. The stressful event does not cause any prolonged interference with activities of daily living such as working or going to school. One positive outcome of PTS is that it might make someone more aware of how they behaved during the stressful event in order to alter their behavior.
A new life is waiting.
You May Like: How To Use Cbd Oil For Anxiety
Diagnosis Of Complex Ptsd
While the concept of C-PTSD is longstanding, it is not in the fifth edition of the “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders” , and therefore isn’t officially recognized by the American Psychiatric Association .
Although C-PTSD comes with its own set of symptoms, there are some who believe the condition is too similar to PTSD to warrant a separate diagnosis. As a result, the DSM-5 lumps symptoms of C-PTSD together with PTSD.
There are mental health professionals who do recognize C-PTSD as a separate condition because the traditional symptoms of PTSD do not fully capture some of the unique characteristics shown in people who experienced repeat trauma.
In 2018, the World Health Organization made the decision to include C-PTSD as its own separate diagnosis in the 11th revision of the “International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems” .
Because the condition is relatively new and not recognized in the DSM-5, doctors may make a diagnosis of PTSD instead of complex PTSD. Since there is not a specific test to determine the difference between PTSD and C-PTSD, you should keep track of the symptoms you have experienced so that you can describe them to your doctor.
Treatment for the two conditions is similar, but you may want to discuss some of your additional symptoms of complex trauma that your doctor or therapist may also need to address.
What Are Post Traumatic Stress Symptoms
-
feeling afraid or nervous
Interfere with daily ability to function
PTS symptoms:
Last up to 30 days
Reduce in intensity after a few day
Do not interfere with daily living
If you do have PTS and the symptoms don’t seem to let up, you may have developed PTSD and then it would be important to reach out to a therapist for help. Some people suffer in silence and procrastinating caring for trauma symptoms often makes them worse and add to the pain.
Also Check: Do Eating Disorders Cause Infertility
Is It A Ptsd Attack Knowing The Signs And Symptoms
Once relegated to the annals of wartime histories and considered a plague specific to individuals who have seen or fought in the war, Post Traumatic Stress Disorder is an increasingly common problem and one that does not require a history of military service or presence in a war-torn country. Instead, PTSD is being recognized as an issue plaguing adults and children alike, with causes ranging from a traumatic event recognized by almost everyone , to a more covert traumatic event, such as a case of narcissistic abuse. Regardless of the exact trigger or traumatic event at the core of PTSD, Post Traumatic Stress Disorder is a treatable disorder, and individuals who have been diagnosed are not alone in their experiences. If you start to notice any signs of PTSD, it’s important that you seek help in case a treatment plan is necessary.
Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder
Disinhibited social engagement disorder occurs in children who have experienced severe social neglect or deprivation before the age of 2. Similar to reactive attachment disorder, it can occur when children lack the basic emotional needs for comfort, stimulation and affection, or when repeated changes in caregivers prevent them from forming stable attachments.
Disinhibited social engagement disorder involves a child engaging in overly familiar or culturally inappropriate behavior with unfamiliar adults. For example, the child may be willing to go off with an unfamiliar adult with minimal or no hesitation. These behaviors cause problems in the childs ability to relate to adults and peers. Moving the child to a normal caregiving environment improves the symptoms. However, even after placement in a positive environment, some children continue to have symptoms through adolescence. Developmental delays, especially cognitive and language delays, may co-occur along with the disorder.
The prevalence of disinhibited social engagement disorder is unknown, but it is thought to be rare. Most severely neglected children do not develop the disorder. Treatment involves the child and family working with a therapist to strengthen their relationship.
Recommended Reading: How Is Bipolar Depression Different From Other Depression
What Is The Difference Between Post
A lot of people who experienced a traumatic event do not meet the criteria for post-traumatic stress disorder . These people may experience post-traumatic stress . PTSD and PTS have similar symptoms and are easily confused. PTS symptoms are: feeling nervous or afraid, having shaky hands, increased heart rate, sweating, avoiding situations that remind you of the traumatic event, having a bad dream about the event, and being distracted .
The differences between PTSD and PTS/trauma are:
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder symptoms:
- Usually last less than one month.
- Are intense, but subside after a few days.
- Will not interfere with your daily life for a long time.
* For a detailed list of PTSD symptoms, please read: PTSD symptoms.
It can happen that you have PTS and that some symptoms do not disappear. In that case, it is good to seek help and talk about your experience with a counselor. A few sessions is usually enough to restart or kickstart processing the traumatic event. It is better to turn to a trauma therapist than to ignore it, as suffering from these symptoms is simply not worth it.
Ptsd Pts Ptss Cptsd: How To Know The Difference
In 2021, it seems every month is dedicated to some kind of awareness. And the list of what we need to be aware of keeps growing.
Rather than being overwhelmed by the continuous awareness of all topics relating to humanity, we invite you to spend a few minutes scratching the surface of issues that closely hit home with our U.S. Elite family.
Our team’s own internal conversation inspired this topic, and we felt it was information that needed sharing beyond our Zoom room.
Awareness of those around you is like having an awareness of what you eat. The more you know, the better choices you can make. Or in this case, the more empathy you can show toward your fellow brothers and sisters.
First hearing or reading the acronyms PTSD, PTS, PTSS, and CPTSD, might feel like what started as a significant cause now has become a guessing game. However, essential nuances between each acronym exist.
While we can’t promise more of these new nuances won’t crop up over time, we can give you a simplified explanation of how to understand PTSD, PTS, PTSS, and CPTSD in 2021.
Recommended Reading: How Does Trileptal Work For Bipolar
Why Do Some People Develop Ptsd And Other People Do Not
It is important to remember that not everyone who lives through a dangerous event develops PTSD. In fact, most people will not develop the disorder.
Many factors play a part in whether a person will develop PTSD. Some examples are listed below. Risk factors make a person more likely to develop PTSD. Other factors, called resilience factors, can help reduce the risk of the disorder.
Some factors that increase risk for PTSD include:
- Living through dangerous events and traumas
- Getting hurt
- Feeling horror, helplessness, or extreme fear
- Having little or no social support after the event
- Dealing with extra stress after the event, such as loss of a loved one, pain and injury, or loss of a job or home
- Having a history of mental illness or substance abuse
Some factors that may promote recovery after trauma include:
- Seeking out support from other people, such as friends and family
- Finding a support group after a traumatic event
- Learning to feel good about ones own actions in the face of danger
- Having a positive coping strategy, or a way of getting through the bad event and learning from it
- Being able to act and respond effectively despite feeling fear
Researchers are studying the importance of these and other risk and resilience factors, including genetics and neurobiology. With more research, someday it may be possible to predict who is likely to develop PTSD and to prevent it.
Symptoms Of Complex Ptsd
In addition to all of the core symptoms of PTSDre-experiencing, avoidance, and hyperarousalC-PTSD symptoms generally also include:
- Difficulty controlling emotions. It’s common for someone suffering from C-PTSD to lose control over their emotions, which can manifest as explosive anger, persistent sadness, depression, and suicidal thoughts.
- Negative self-view. C-PTSD can cause a person to view themselves in a negative light. They may feel helpless, guilty, or ashamed. They often have a sense of being completely different from other people.
- Difficulty with relationships. Relationships may suffer due to difficulties trusting others and a negative self-view. A person with C-PTSD may avoid relationships or develop unhealthy relationships because that is what they knew in the past.
- Detachment from the trauma. A person may disconnect from themselves and the world around them . Some people might even forget their trauma.
- Loss of a system of meanings. This can include losing one’s core beliefs, values, religious faith, or hope in the world and other people.
All of these symptoms can be life-altering and cause significant impairment in personal, family, social, educational, occupational, or other important areas of life.
You May Like: How Many Different Types Of Phobias
When To Get Medical Advice
It’s normal to experience upsetting and confusing thoughts after a traumatic event, but most people improve naturally over a few weeks.
You should see a GP if you or your child are still having problems about 4 weeks after the traumatic experience, or if the symptoms are particularly troublesome.
If necessary, your GP can refer you to mental health specialists for further assessment and treatment.
Experiences Of Facing Stigma
There are lots of misconceptions about PTSD. For example, people may wrongly assume it means you are ‘dwelling’ on past events. They might even suggest that you should ‘get over it’ or ‘move on’. But having PTSD isn’t a choice or a sign of weakness, and it’s important to remember that you are not alone.
See our page on stigma and misconceptions for lots of ideas on how to deal with stigma.
Also Check: Is Bipolar Type 2 Considered A Disability
Cognition And Mood Symptoms Include:
- Trouble remembering key features of the traumatic event
- Negative thoughts about oneself or the world
- Distorted feelings like guilt or blame
- Loss of interest in enjoyable activities
Cognition and mood symptoms can begin or worsen after the traumatic event, but are not due to injury or substance use. These symptoms can make the person feel alienated or detached from friends or family members.
It is natural to have some of these symptoms for a few weeks after a dangerous event. When the symptoms last more than a month, seriously affect ones ability to function, and are not due to substance use, medical illness, or anything except the event itself, they might be PTSD. Some people with PTSD dont show any symptoms for weeks or months. PTSD is often accompanied by depression, substance abuse, or one or more of the other anxiety disorders.
Symptoms And Treatment Of Pts
Symptoms of PTS may include sweating, shaky hands, a racing heart, and feeling nervous. Sometimes you may have bad dreams about what happened. After the event, you may avoid or be afraid or anything associated with that incident or feel unsettled if youre in a situation that brings it to mind.
However, PTS symptoms usually diminish soon after the event and wont interfere with your daily routine. Because PTS isnt considered a mental disorder, and symptoms usually decrease in about a month, treatment isnt recommended or required.
Recommended Reading: Is Schizophrenia A Dissociative Disorder
How Do Children And Teens React To Trauma
Children and teens can have extreme reactions to trauma, but their symptoms may not be the same as those seen in adults. In young children under the age of 6, symptoms can include:
- Wetting the bed after having learned to use the toilet
- Forgetting how or being unable to talk
- Acting out the scary event during playtime
- Being unusually clingy with a parent or other adult
Older children and teens usually show symptoms more like those seen in adults. They also may develop disruptive, disrespectful, or destructive behaviors. Older children and teens may feel guilty for not preventing injury or deaths. They also may have thoughts of revenge.
For more information, see the National Institute of Mental Health brochure, Helping Children and Adolescents Cope With Disasters and Other Traumatic Events.