Structural And Functional Brain Abnormalities In Schizophreni
- Schizophrenia is associated with changes in the structure and functioning of a number of key brain systems, including prefrontal and medial temporal lobe regions involved in working memory and declarative memory, respectively
- Some researchers believe that problems with brain development may be partly responsible for schizophrenia. Others believe that inflammation in the brain may damage cells that are used for thinking..
- Another area of the brain associated with schizophrenia is the prefrontal cortex. Located directly behind the forehead, the prefrontal cortex oversees many aspects of our cognition, behavior, and personality. Everything from our social interactions to our ability to make decisions relies on the proper functioning of this part of the brain
- Andreasen’s team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously..
- What Part Of the Brain Does Schizophrenia Affect? Schizophrenia affects genders equally in the U.S. When it comes to answering the question of, What part of the brain does schizophrenia affect, the disorder involves multiple regions of the brain. These areas include the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and limbic system
Identification Of Brain Regions Included In The Meta
To avoid bias in selecting brain regions for the meta-analysis, we recorded all cortical gray matter regions investigated by the studies included in the database. For some regions, a few studies reported left and right measurements separately, but others reported the total combined volume. In this meta-analysis, the left, right and total measurements were treated as separate measures. To ensure that the analyses were sufficiently powered, we analyzed only those cortical regions for which at least three studies were available.
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Each person may feel symptoms differently. These are the most common symptoms:
-
False beliefs not based on reality
-
Seeing, hearing, smelling, or feeling things that are not real
-
Disorganized speech and behavior
-
Feeling like someone or something is out to get them
-
Withdrawal from others
-
Inflated self worth
These symptoms can make it very hard to function in the world and take care of yourself. People with this illness are usually not violent.
The symptoms of schizophrenia may look like other problems or mental health conditions. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Read Also: What Is The Phobia Of Puke Called
Schizophrenia Brain: Impact Of Schizophrenia On The Brain
- Some effects of schizophrenia, such as unusual behavior, are easy to see. What may be less obvious is how the illness affects the ability to think and reason. These are called cognitive symptoms. If you have a loved one with schizophrenia, you can help them by better understanding how they think and view the world
- d, the cultural context it occurs in can have a serious impact on how it manifests. Cultures in which the family is more important will have delusions.
- Advances in brain imaging are helping to picture how neural changes in these crucial years can lead to chronic debilitating mental illness. Neuroscience is no longer just about neurons. We can also now talk in terms of hubs, networks and connectomes. Restless, disordered, uncertain, impulsive, emotional – the teenage brain can be a confused.
- e and glutamate play a role in schizophrenia. Additionally, structures in the brain, such as the ventricles, look different in those who have schizophrenia
- Memory Loss – Schizophrenia – MedHelp. The controlled seizure that is triggered by the ECT is thought to provoke a major neurochemical release in the brain. Side effects may include short-term Schizophrenia, which usually resolves rapidly. The doctor must clearly explain the pros and cons of ECT to the patient and their guardian or family.
- In a brain with schizophrenia, function within the membranes of nerve cells–and so disturbances of the membrane structure could readily affect how neurons transmit messages across nerve.
Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Because early treatment is thought to be most effective for schizophrenia, researchers are continually looking for ways to detect it before symptoms fully develop.
Hallucinations and delusions are the hallmark symptoms of psychosis and must be present for a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Although psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions are the most common aspects that present in schizophrenia, there are several symptoms involved. People with schizophrenia experience:
- Positive symptoms: The appearance of things that should not be there, like hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder .
- Negative symptoms: The absence of things that should be there, like loss of motivation, disinterest or lack of enjoyment in daily activities, social withdrawal, difficulty showing emotions, and difficulty functioning normally.
- Cognitive symptoms: Problems with attention, concentration, and memory.
Assessment of these symptoms is typically how schizophrenia is diagnosed, but the discovery of brain differences in people with schizophrenia could potentially mean an earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
While schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in the late teens to early thirties, subtle changes in cognition and social relationships may be noticeable before the actual diagnosis, even during adolescence. Often these early symptoms are apparent years before a person is diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Some of these early symptoms include:
Recommended Reading: Depression Topography
Neurodevelopment Medial Prefrontal Cortex And Errors In Source Monitoring
Brain dysconnectivity in schizophrenia is thought to derive primarily from deficits in dendritic spines that arise during development , though axonal pathology may also play a role . Such deficits are likely to be present at least in part in some cases from birth, resulting from an interplay of genetic factors and obstetric complications , but may progress beyond a threshold critical for expression of psychotic symptoms as a function of normal neuromaturational events during adolescence . In other cases, dysconnectivity may emerge during late adolescence and early adulthood as a consequence of overly aggressive synaptic pruning and/or other aberrant processes, such as elevated cortisol leading to dendritic atrophy . The contributions of early and later brain developmental processes to psychosis risk are not mutually exclusive, and both sets of processes may be operative in some cases .
Developmental trajectories of cortical synaptic connectivity, including a number of trajectories in which connectivity is reduced below a hypothetical threshold sufficient for expression of psychotic symptoms.
Cortical surface maps showing regions in which converters to psychosis had significantly greater progressive loss of gray matter thickness compared with non-converters and controls Cortical surface maps showing regions in which higher levels of unusual thought content at baseline predicted a steeper rate of gray matter thinning among converters .
How Does Schizophrenia Affect The Body
Schizophrenia is primarily a disease of the mind. Most of its effects are mental or emotional in nature. However, the disease can affect the body in some key ways. Brain modifications cause the disorder to occur, although what causes the brain modifications is unknown. In addition, schizophrenia may cause sufferers to do harm to their physical bodies, as alcohol abuse, violence, and self-destructive behavior are all complications of the disorder.
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Also Check: What Does Phobia Mean
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
To diagnose this disease, your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. You may also have a physical exam. You may also have lab tests to rule out other conditions.
Mental health care professionals diagnose and treat this illness. They often interview family members. This helps the healthcare team get a complete picture of the symptoms.
Does My Child Have Schizophrenia
Early signs of schizophrenia can be hard to detect because they often overlap with common adolescent behavior. Moreover, these symptoms in people of any age group do not necessarily mean that a person will develop schizophrenia.
These symptoms can be disruptive though, and they may indicate something worrisome is going on, even if it isn’t schizophrenia. If you or your child are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should make an appointment with a healthcare provider.
Read Also: 3 Phases Of Schizophrenia
Frequently Asked Questions About Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality. Although schizophrenia is not as common as other mental disorders, the symptoms can be very disabling.
Schizophrenia is a severe and debilitating brain and behavior disorder affecting how one thinks, feels and acts. People with schizophrenia can have trouble distinguishing reality from fantasy, expressing and managing normal emotions and making decisions. Thought processes may also be disorganized and the motivation to engage in lifes activities may be blunted. Those with the condition may hear imaginary voices and believe others are reading their minds, controlling their thoughts or plotting to harm them.
While schizophrenia is a chronic disorder, it can be treated with medication, psychological and social treatments, substantially improving the lives of people with the condition.
A moving presentation by Dr. Kafui Dzirasa on Schizophrenia
View Webinar on Identifying Risk Factors and Protective Pathways for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia affects men and women equally. It occurs at similar rates in all ethnic groups around the world. Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30.
Learn more about childhood-onset schizophrenia from this expert researcher:
Find answers to more questions about Schizophrenia in our Ask the Expert section.
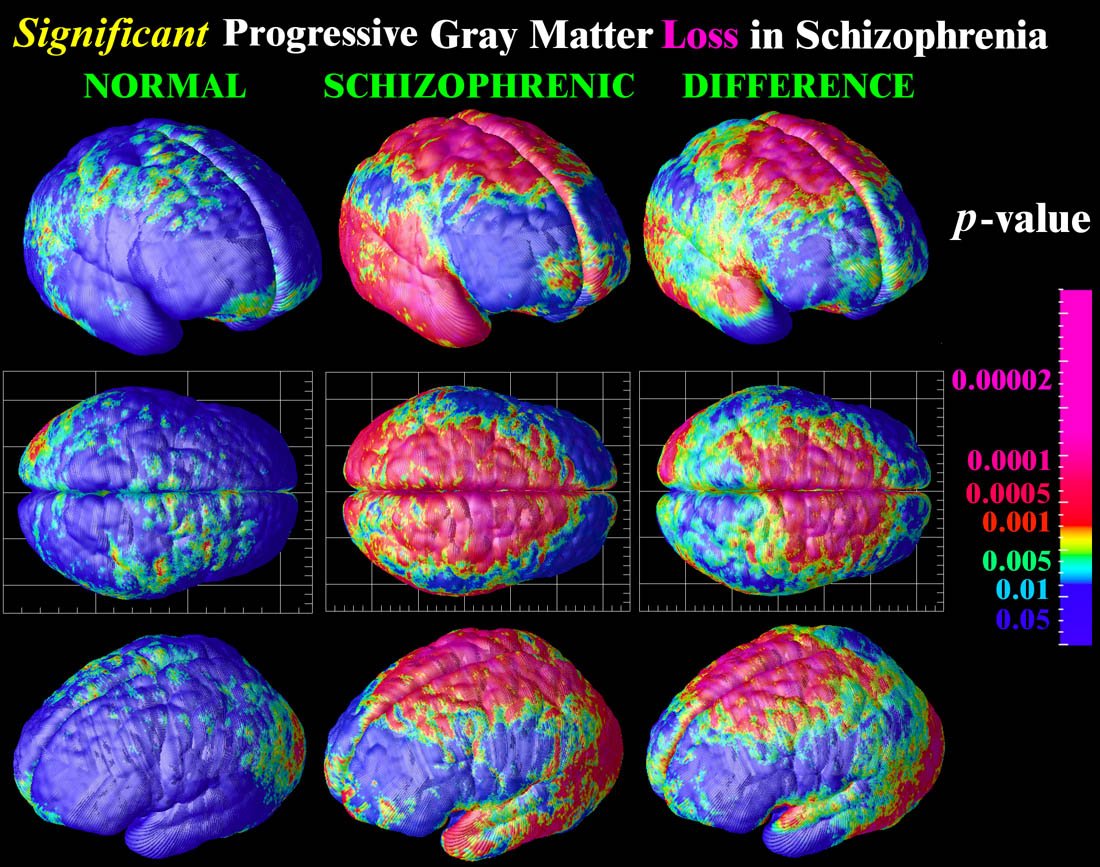
Lack Of Brain Tissue Found In Schizophrenic Patients
Scans from the patients first episode revealed that they had less brain tissue, compared with healthy individuals without the disorder.
The researchers say this finding suggests that something is affecting the brains of those with schizophrenia before they demonstrate obvious symptoms of the conditions.
Prof. Andreasen explains:
There are several studies, mine included, that show people with schizophrenia have smaller-than-average cranial size.
Since cranial development is completed within the first few years of life, there may be some aspect of earliest development perhaps things such as pregnancy complications or exposure to viruses that on average, affected people with schizophrenia.
The brain scans also showed that those who suffer from schizophrenia demonstrated the highest tissue loss in the first 2 years after their first episode, after which point it slowed down significantly.
Prof. Andreasen says that this finding may help doctors to identify the most effective time periods to prevent tissue loss in schizophrenic patients, as well as other effects caused by the disorder.
Also Check: Aphobic Definition
Schizophrenia Is A Very Serious Mental Disorder
May 30, 2016Schizophrenias RealitySchizophrenia is a very serious mental disorder. This disorder affects many people across the world as it does not matter an individuals age, race, and their economic levels. An individuals personality is distorted and they can lose their sense of reality where the individual has an unclear thought process, false beliefs, or even hearing voices. There have been mental disorders that add on to schizophrenia where the individual develops substance abuse
What Happens After You Get The Results From A Schizophrenia Brain Scan

If brain scans are ordered for a person who is showing schizophrenia symptoms, it is usually to rule out or confirm other conditions that could be causing the symptoms.
Whether the scan shows a different condition or plays a part in confirming a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the healthcare provider will discuss treatment options.
You May Like: Phobia Definition
Adolescence Is A Dangerous Time For The Onset Of Mental Health Problems Advances In Brain Imaging Are Helping To Picture How Neural Changes In These Crucial Years Can Lead To Chronic Debilitating Mental Illness
Neuroscience is no longer just about neurons. We can also now talk in terms of hubs, networks and connectomes.
Ed Bullmore
Restless, disordered, uncertain, impulsive, emotional the teenage brain can be a confused fury of neural firings and misfirings.
For most 14- to 24-year-olds the risky age as Professor Ed Bullmore describes it the maelstrom eventually subsides. For some, episodes of depression, low self-esteem, self-harm or paranoia may intensify and become more frequent. For around 1 in 100, the change in mental state is so marked that it will become difficult for them to distinguish their delusions and hallucinations from reality one of the hallmarks of schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia is a particularly feared diagnosis, says Bullmore. People tend to think it means a chronic lifelong dependency on medication and therapy. It can mean this, but it can also last only a few years. The main thing that patients and their families want to know is what does the future hold am I likely to be able to resume my life, get a job, and so on?
Bullmore is co-chair of Cambridge Neuroscience, an initiative to enhance multidisciplinary research across the University, and leads the Department of Psychiatry, where he and colleagues have been developing imaging techniques that are revealing where and over what timescale abnormalities in the brain develop in people with mental health problems.
Data Recorded In The Database
The following data were extracted from the chosen studies: number of subjects and percentage of males in the study sample age of the patient at first MRI measurement duration of illness at the time of the first MRI interval between the two MRI scans type of antipsychotic medications taken during the MRI scan interval Tesla value of the MRI scanner MRI slice thickness year of publication of the study percentage change in brain tissue volume /volume at baseline) × 100) in patients with schizophrenia and in healthy comparison group or volume of a given cerebral structure analyzed at baseline and at follow-up scans in patients with schizophrenia and controls. The percent change in volume was selected to estimate the ES. If this measure was not reported, the percent change in volume over time in each study was calculated by the authors using the following formula: /volume at baseline) × 100.
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Cause Burning Skin
Treating The Whole Patient Not Just The Symptoms
We want people to understand that approaching schizophrenia from a more holistic, integrated model of care is undoubtedly the best way forward, he says. Mental illness has a major impact on every aspect of a persons lifetheir physical health, behavior and relationships. Patients will require several types of interventions, not just medication.
At Janssen, one area of investigation is the vital role caregivers playand the challenges they facein the treatment and management of those with schizophrenia. Currently, patient recruitment is underway for a year-long Family Intervention in Recent Onset Schizophrenia Treatment clinical trial. Researchers plan to evaluate the overall effect caregivers can have on those under their care when they participate in a study-provided caregiver psycho-education and skills training program. The hope is that this type of program can help reduce the number of treatment failures, such as psychiatric hospitalization and suicide or suicide attempts.
The companys deep commitment to improving patients lives is also reflected in its collaborative initiatives with academia, the government and the biotech industry. This illness is so complex that we have to work together to advance research, Dr. Manji says.
Additional Consultation Needed For Diagnosis
Following any scans or tests, a healthcare professional may make a referral to a mental health expert who has more specialized knowledge on the subject. It is also common for healthcare professionals to speak with the friends and/or family of a person who is showing signs of schizophrenia.
If schizophrenia is diagnosed, then the person with schizophrenia and their support team will work on a treatment plan together.
Also Check: Faratrophobia
Opening The Black Box
The arrival of two state-of-the-art MRI machines in Cambridge, thanks to funding from the Medical Research Council , will revolutionise the study of the brain.
A brain scan is much more than an image, contends Ed Bullmore. Its really a very large collection of numbers. With the best scanners and some high-performance computing, you can start to think not only about disease mechanisms but also about identifying early risk factors and preventative action.
Two of the newest scanners in the UK will arrive at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in 2016, and a new high-speed secure link will be created through to the recently opened £20 million West Cambridge Data Centre, which will analyse the data.
One scanner, a new 7-Tesla ultrahigh-field MRI machine, will help researchers see how the human brain works as a whole, yet also with the precision of a grain of sand a fraction of a millimetre across. It will further the study of dementia, brain injury, obesity, addiction, mental health disorders, pain and stroke.
Joining the 7T scanner will be a positron emission tomography MRI machine, which shows changes in the brain down to the level of individual molecules. Until now only two PETMRI scanners existed in the UK, but MRC Dementias Platform UK has invested in five more nationally, creating what is thought to be the first nationally coordinated MRIPET network anywhere in the world.
Schizophrenia And The Brain
- Schizophrenia is a disease that affects the brain. It alters brain chemistry and brain form to produce the different behavior in those afflicted with the problem. It appears that these alterations change the inherent I-function in each individual
- The scans of patients with schizophrenia revealed various abnormalities in portions of the corpus callosum, a bundle of fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain and is considered critical to neural communication
- Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It can cause hallucinations, delusions, and other mental problems that make it seem like a person has lost touch with reality. It affects about 1 in 100 people. Several factors likely contribute to the risk of developing schizophrenia
- e and regulates coordinated movement, motivation and the reward pathway. This complex pathway reinforces patterns of behavior that make a person feel good
- The brain scans also showed that those who suffer from schizophrenia demonstrated the highest tissue loss in the first 2 years after their first episode, after which point it slowed down..
- Brain scans and microscopic tissue studies indicate a number of abnormalities common to the schizophrenic brain. The most common structural abnormality involves the lateral brain ventricles. These fluid-filled sacs surround the brain and appear enlarged in images of the brains of those with schizophrenia
Read Also: What Is Apiphobia