Mri Based Schizophrenia Patient Classification: A Meta
This press release out of UPenn is interesting – because it contradicts a story we covered just last month on how Schizophrenia. This new press release suggests that perhaps …
Schizophrenia–what does structural MRI show? – NCBI
After more than 100 years of research, the neuropathology of Schizophrenia remains unknown and this is despite the fact that both Kraepelin and Bleuler (1911/1950 : Bleuler, E., 1911/1950. Dementia praecox or the group of …
What Else Would Help Clinicians
Although there has been extensive research using structural and functional imaging in psychiatric disorders, there has been relatively little use of neuroimaging for purely clinical purposes in psychiatry . Diagnosis and assessment of prognosis and effectiveness of treatments continue to be largely dependent on clinical history and current psychopathology. At present, neuroimaging does not to play a significant role in these areas, but there are signs that it might.
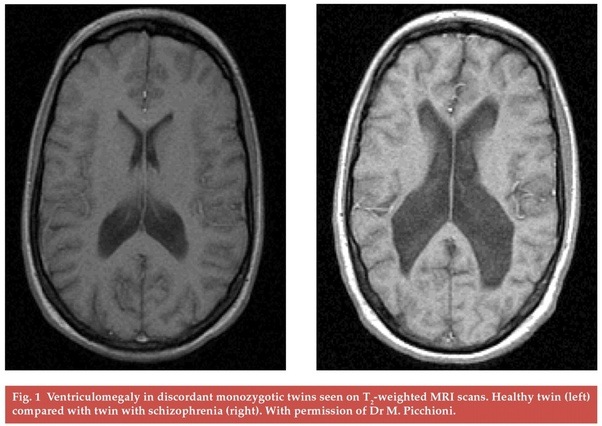
Since the landmark demonstration, using CT scanning, of enlarged ventricles in schizophrenia , a host of neuroimaging studies have identified areas of reduced grey matter in the disorder, including the hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus, cingulate gyrus, insula, thalamus and the prefrontal and temporal cortex . These structural studies have been complemented by functional imaging research which has indicated that schizophrenia is particularly associated with altered function in the prefrontal, cingulate and temporal cortex and that symptoms such as auditory hallucinations and thought disorder are mediated by these brain regions.
What Happens To The Brain During Psychosis
What we do know is that during an episode of psychosis, the brain is basically in a state of stress overload, says Garrett. Stress can be caused by anything, including poor physical health, loss, trauma or other major life changes. When stress becomes frequent, it can affect your body, both physically and mentally.
Recommended Reading: Can Dehydration Cause Panic Attacks
Additional Consultation Needed For Diagnosis
Following any scans or tests, a healthcare professional may make a referral to a mental health expert who has more specialized knowledge on the subject. It is also common for healthcare professionals to speak with the friends and/or family of a person who is showing signs of schizophrenia.
If schizophrenia is diagnosed, then the person with schizophrenia and their support team will work on a treatment plan together.
Evaluating Algorithms Using The Training And Validation Data Sets
To avoid the overfitting problem , we applied 10-fold cross-validation in training the deep learning algorithm . The original data set was randomly partitioned into 10 equally sized data subsets, and a single data subset was used as the validation set for testing the model trained with the other data subsets . We also applied cross-validation to each of the five data sets individually one of the five data sets was designated as a test set, and the remaining four were used for training. In this validation, the deep learning model was trained with four of five data sets, and a remaining data set was used as a test set. For example, the deep learning model trained with the COBRE, MCICShare, NUSDAST, and NMorph data sets was assessed for the ability to identify schizophrenia in the BrainGluSchi data set. This method enabled us to evaluate whether the trained deep learning algorithm could classify structural images obtained from schizophrenia patients with different scanning parameters and scanner field strengths .
To determine whether the trained deep learning algorithm could distinguish patients with schizophrenia from healthy controls in real-world MRI data sets, we used a new data set obtained by Uijeongbu St. Marys Hospital in South Korea. This data set consisted of structural MRI data from 30 schizophrenia patients and 30 healthy controls .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Can Mr Imaging Distinguish Sick From Healthy Individuals
Finally, we will seek to answer the third question: If the differences between schizophrenia patients and control subjects are so slight and only present at group level, can we then use MR imaging to distinguish between sick and healthy individuals? Our review indicates that the answer for clinicians must be no. Schizophrenia is a clinical diagnosis. The only answer a researcher can give is in all humility that perhaps we will be able to, at some time in the future. At present, we can see features of schizophrenia in MR images, but not at the level of the individual.
Mri Sheds New Light On Schizophrenia
Advanced Schizophrenia are partly explained by …
MRI anatomy of schizophrenia – ScienceDirect
After more than 100 years of research, the neuropathology of Schizophrenia remains unknown and this is despite the fact that both Kraepelin and Bleuler (1911/1950 : Bleuler, E., 1911/1950. Dementia praecox or the group of …
Schizophrenia.com – MRI Images of Brains of People with Schizophrenia
Your doctor will ask you questions about your medical history and your mental health and about any odd experiences you may have had,such as hearing voices or having confusing thoughts. You also will have a physical exam. Your doctor also may suggest tests to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms or to …
Recommended Reading: Pristiq Irritability
Logistic Regression Algorithm For Validation
Although we normalized the mean intensity of all MR images, one may argue that simple MRI intensity differences between the schizophrenia and normal groups may provide significant classification power. To test whether information on mean intensity could be used to determine whether a given subject has schizophrenia, we independently applied the logistic regression classifier. The method estimates the log odds of an event that can be mathematically expressed as a multiple linear regression function. Let the predictor X1 be the mean image intensity, and let the binary response variable Y be the output of either schizophrenia or normal, where the probability of Y is denoted as p = P. The log odds, L, can be written as follows :
Second Hit Ongoing Changes After Onset Of Symptoms
The initial data from longitudinal structural studies are compatible with the occurrence of progression of neuropathology over the early phases of the illness. A detailed survey of CT changes is beyond the scope of this review, but, while CT studies in general have found no progression, has reviewed CT data, and has reached the still controversial conclusion that crossstudy analysis of the CT ventricular brain ratio literature supports a bimodal distribution of change in VBR over time. While about 75% of patients show no change over time, about 25% do show increased VBR, and Garver suggests this latter group may be suffering from a progressive form of the illness. . From our laboratory, have described a rate of agerelated increased P300 latency in schizophrenia compared with controls that are compatible with progressive neural alteration.
Read Also: Phobia Suffix Meaning
Can A Brain Scan Show Anxiety
Brain imaging can reveal unsuspected causes of your anxiety.
Anxiety can be caused by many things, such as neurohormonal imbalances, post-traumatic stress syndrome, or head injuries.
Brain scans can offer clues to potential root causes of your anxiety, which can help find the most effective treatment plan..
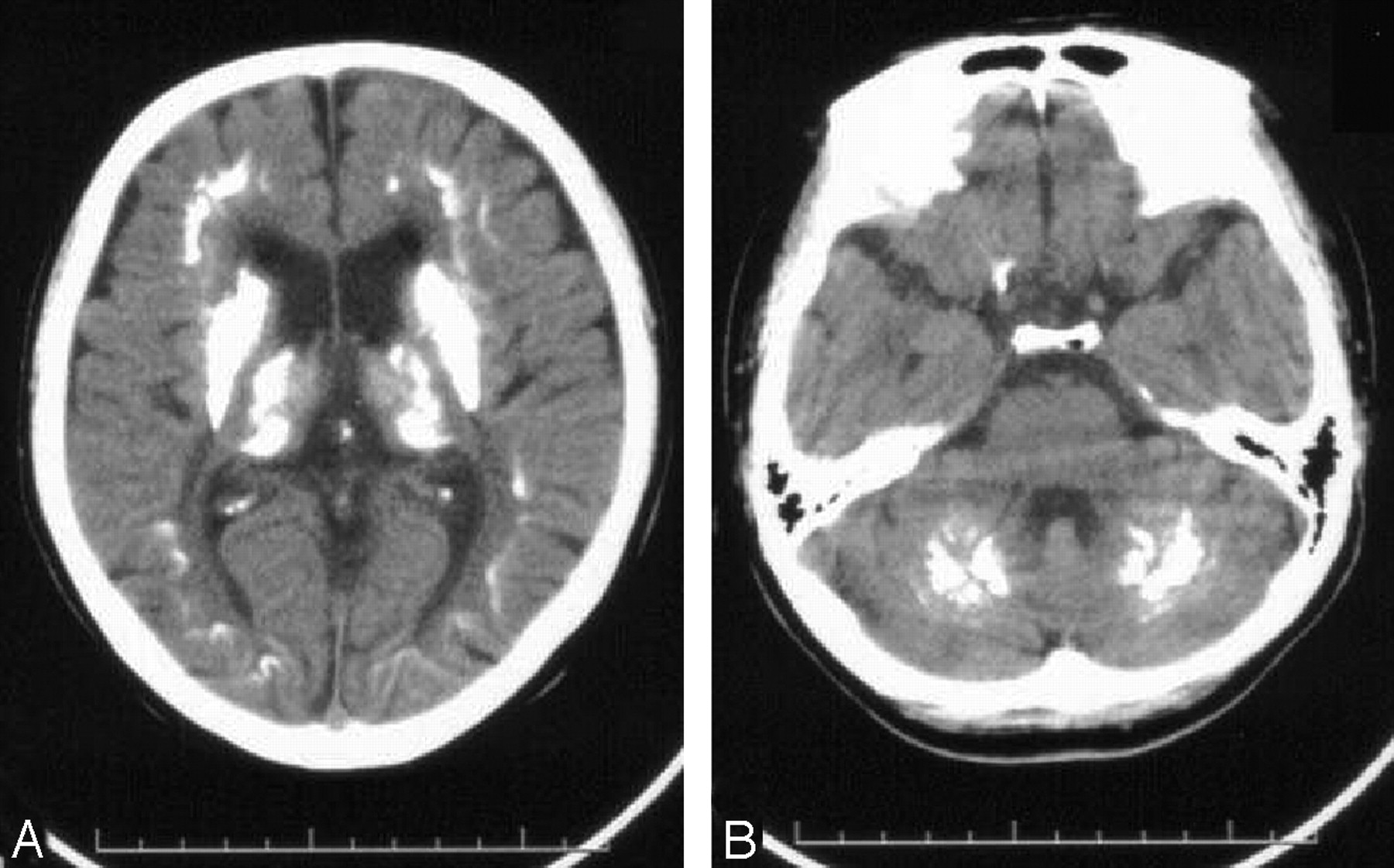
Classification Of Structural Brain Abnormalities
All MRI scans were assessed by neuroradiologists at the UMCU. The radiologists were blind to subject status, although they were aware that these MRI scans could be either from a patient with psychosis or from a healthy individual who participated in research.
For the assessment of neuropathology, we excluded noncerebral abnormalities, such as sinus abnormalities or pathology of the skin, face, or skull. For all reports that made note of a brain abnormality, clinical relevance was assessed according to the definition by Katzman et al, ie, abnormal scans needing either routine, urgent, or immediate referral. The categorization of each scan report was based on a consensus decision between 2 of the authors: a radiologist and a psychiatrist , who were blind to diagnosis and subject status. A complete list of all radiological findings classified as not clinically relevant, and a list of all clinically relevant radiological abnormalities can be found in the online supplementary material. Radiological abnormalities of the brain that were considered clinically relevant were divided into subgroups, depending on the nature of the pathology. describes the subgroups of extracranial, not clinically relevant and clinically relevant abnormalities.
Also Check: Is Tequila A Stimulant Or Depressant
Potential Benefits Of Neuroimaging For Psychiatric Conditions
Brain imaging for mental illness can have several benefits. Brain scans for psychiatric disorders can identify lesions in the frontal or temporal lobes or the thalamus and hypothalamus of the brain that can occur with psychosis. Brain scans have shown that the volume of various regions in the brain decrease during psychotic episodes.
Brain scans can show increased metabolism and reduced volume in the frontal lobe region of the brain in major depressive disorder. Brain scans and activation patterns can distinguish the difference between depression, neurodegenerative disorders and brain tumors. A tumor in the frontal lobe can cause apathy, which can be mistaken for depression. In elderly people with cognitive deficits, brain imaging can help differentiate neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimers disease and other dementias, from depression.
Brain imaging can provide knowledge on what areas of the brain are involved in a mental health condition and can help devise new treatment approaches, such as deep brain stimulation for depression. Brain scans can assist in ruling out physical or medical causes, such as tumors or brain bleeds, for psychiatric symptoms.
Scans can also be used to educate individuals who do not believe that they have a diagnosis or are in need of treatment. Scans can show a practitioner the extent of an issue and help them to monitor an individuals recovery based on size, blood flow and energy use in follow-up scans.
Structural Mri What Can It Tell Us About Schizophrenia
Structural MRI provides information about gray and white matter parenchyma of the brain, and cerebrospinal fluid filled spaces. This capability is new with MRI studies , and represents an important advance over CT studies which poorly visualize parenchyma and cannot differentiate gray and white matter. This graywhite differentiation is important for schizophrenia studies, since abnormal tissue classes , which may be detected by CT, have not been found to characterize schizophrenia. The term Structural MRI is used to differentiate it from functional MRI , where indices of shortduration change, such as blood oxygenation, are used.
Our use of the term schizophrenia is in the sense of a syndrome and not a single disease entity. The current major questions about this syndrome include:
What are the brain changes in this disorder? Which areas of the brain are affected?
At what life stage do brain abnormalities occur and are they static or progressive?
Are they developmental and/or progressive?
What is the cause of the brain changes?
How are brain abnormalities related to clinical symptom abnormalities?
Are brain findings in schizophrenia distinct from those in affective psychosis?
What are the most effective treatments? Is treatment neuroprotective?
Recommended Reading: Can You Be Bipolar And Have Bpd
Development Of The Algorithm
A three-dimensional convolutional neural network architecture was used for classifying patients with schizophrenia and normal subjects based on the structural MRI data sets the original 3DCNN architecture was developed for video classification . The input to the 3DCNN was a converted video of a subjects structural MR images . The input dimensions were 256 × 256 × 180. This architecture has four 3D convolutional layers, with max-pooling-based downsampling in each convolutional layer. A previous study using the ADNI data set showed that 3DCNNs with only one convolutional layer outperformed other classifiers in predicting the Alzheimers disease status of a patient based on an MRI scan of the brain . More recently, four 3DCNNs were used in high-precision segmentation and classification problems, reportedly achieving state-of-the-art performance . We applied a rectified linear unit activation function, which is the most commonly used activation function in deep learning models. The function returns 0 if it receives any negative input, but for any positive value x, it returns the input value, as follows: f = max. This activation function is known to effectively capture the interactions and nonlinearities of data sets .
Downsides And Upsides Understanding Of Mental Illness
Families who consider a mental-health MRI scan for mental illness patients may have to think about the scan either its worth their time and effort or not. Often considering the expense will make a choice for those families a little easier.
According to an analysis reported in the Kaiser Health News, an MRI test frequently costs more than $1,000 per patient in the U.S., and patients who have no insurance can be asked to pay even more, as medical centers like hospitals can raise uninsured test costs to ensure their facilities are profitable.
This is a considerable cost for a family to bear, and they may be hesitant to pay for a too costly test because the results may or may not be significant. However, scanning could be a smart option for families who could only deal with a physical problem cancer.
MRI scans help psychiatrists and psychologists comprehend the complexities of a patients disorder, enabling them to design effective treatment strategies. A disorder like anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and schizophrenia is extremely difficult to treat, especially if the cause is unknown. MRI in Mental Illness Diagnosis helps pinpoint the disorders precise cause by showing images of the parts of the brain that are overactive or underactive. Once this has been determined, then the same treatment can be administered.
Also Check: Is Tequila A Stimulant
Quality Of Imager And Postacquisition Processing
The quality of the MR scanner is also important and should include technical assessments such as the homogeneity of the magnetic field, which greatly influences the postprocessing segmentation of tissue into different tissue components. Day to day assessment of inhomogeneities in the magnetic field are thus a critical quality assurance feature for the quality of the MR scans, and, consequently, also the quality of the postprocessing of MR images. Most modern imagers have magnetic fields of 1.5 Tesla or greater, important for signaltonoise ratio. Additionally, postacquisition filtering may improve signal to noise ratio .
Exclusion Of Organic Causes
This is a common reason for requesting a scan in suspected schizophrenia and it is gaining acceptance as scanning becomes more widely available and affordable. Between 5 and 10% of patients with psychosis will have an organic disorder that underlies their symptoms, rather than a functional psychosis such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder . Other disorders that can be associated with psychotic symptoms include epilepsy, brain injury, slow-growing tumours, demyelinating diseases and encephalitis. The treatment for these conditions may be fundamentally different from that for the major psychoses. Although some organic disorders are associated with neurological signs that can be detected on clinical examination, 50100% of patients with schizophrenia also have neurological soft signs , and referral to a neurologist usually results in a request that the patient has an MRI scan. Thus, it is increasingly considered good clinical practice to scan all patients presenting with psychosis for the first time and this is now recommended in contemporary textbooks of clinical psychiatry .
Don’t Miss: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Positive And Negative Syndrome Scale
This test has a reputation as the “gold standard” for measuring how well your treatment is working. Your doctor may use the PANSS test more than once over a period of time to check if a drug or therapy has made a real improvement in your symptoms.
For the PANSS test, your doctor will interview you for about 30 to 40 minutes. They’ll also ask your family members or caregivers about your behavior.
In the first section of the test, your doctor will ask about your medical history and symptoms. In the second part, you may get questions that try to find out how severe your symptoms are. For instance, your doctor may ask things like, “How do you compare to the average person?” and “Do you have special or unusual powers?”
In the third section of the interview, focused questions like “How are a train and bus alike?” check to see how well you can reason. You may also get other questions about mood.
Based on your answers and your doctor’s observation of your behavior, they’ll give you a score on 30 items on the PANSS scale. Each item gets ranked from 1 to 7 , giving a score between 30 and 210.
How A Brain Scan Can Help Diagnose Mental Illness
For the past 50 years or more, its been easy for doctors to diagnose broken bones, problems with organs, and many other diseases with blood tests and imaging devices. Unfortunately, identifying mental problems has been more difficult. Diagnosis for diseases like depression has largely been based on self-reporting and the results can be somewhat subjective.
Recently, though, theres become more interest in how a brain scan can help identify certain conditions. If youre worried that your problems are all in your head, getting a scan can give you the proof you need to seek out treatment.
Read Also: The Longest Phobia
Identifying Schizophrenia Using Structural Mri With A Deep Learning Algorithm
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Seoul St. Marys Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, South Korea
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Uijeongbu St. Marys Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, South Korea
- 4Computation and Neural Systems, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, United States
- 5Bio-Inspired Technologies and Systems, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, United States
Objective: Although distinctive structural abnormalities occur in patients with schizophrenia, detecting schizophrenia with magnetic resonance imaging remains challenging. This study aimed to detect schizophrenia in structural MRI data sets using a trained deep learning algorithm.
Method: Five public MRI data sets from schizophrenia patients and normal subjects, for a total of 873 structural MRI data sets, were used to train a deep convolutional neural network.
The deep learning algorithm showed good performance in detecting schizophrenia and identified relevant structural features from structural brain MRI data it had an acceptable classification performance in a separate group of patients at an earlier stage of the disease. Deep learning can be used to delineate the structural characteristics of schizophrenia and to provide supplementary diagnostic information in clinical settings.