First Episode Of Psychosis
The first episode of psychosis refers to when you first show signs of being unable to distinguish whats real from what isnt. It typically involves hallucinations and delusions, which can seem very real to the person experiencing them.
Experts say the average age at which people first experience psychosis is 24 years old. The oldest age of onset was 63 years and the youngest age was 3 years.
Acting quickly to connect yourself or your loved one with the right treatment during early psychosis can help dramatically. If you are a family member or friend, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional on behalf of the person you care about.
What Type Of Schizophrenia Has The Most Favorable Diagnosis
The prognosis of schizophrenia is more dependent on the factors relating to the individual themselves, rather than the sub-type of schizophrenia they are diagnosed with. Research suggests multiple factors are associated with a more favorable prognosis: being female, rapid onset of symptoms, older age of first episode, and the presence of predominantly positive symptoms are all examples of such factors.
Criteria For Schizophrenia Diagnosis In Dsm
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition is the authority on mental illness. Created and published by the American Psychiatric Association, this comprehensive manual describes all known mental disorders, among them schizophrenia.
Mental health professionals use the DSM-5 when determining what someone is experiencing. Doctors use the information and analyze:
- diagnostic features and symptoms
- duration of symptoms
- other conditions that share symptoms
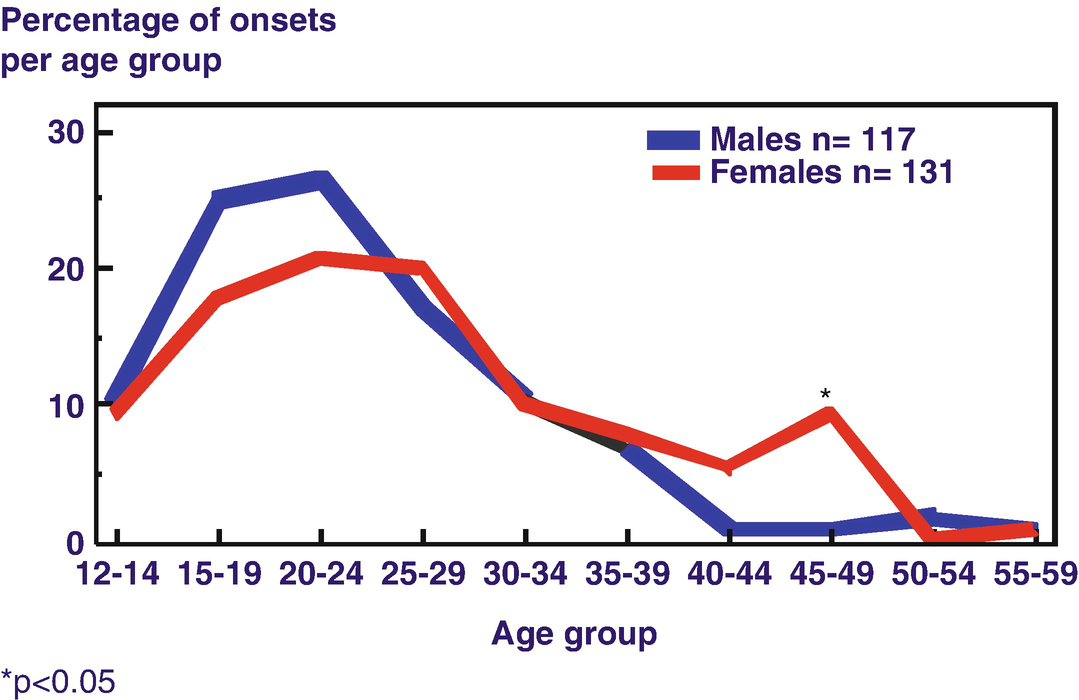
They also look at age. While its not part of the diagnostic criteria, they do consider someones age. The typical age of schizophrenia diagnosis is between late adolescence and the mid-30s. This varies, though, with peak ages ranging from the early- to mid-20s for males and late-20s for females . Further, while its rare, schizophrenia can be diagnosed as early as childhood and as late as the 40s .
Age provides a general idea of the likelihood that someone has schizophrenia. Schizophrenia wont be the first consideration for a man in his 40s, for example. Beyond this, age isnt a diagnostic criterion. Just what are the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia?
Recommended Reading: How Long For Bipolar Meds To Work
The Public Health Challenge
A recent, report by Bartcls and colleagues examined the annual health care costs for adults with schizophrenia, depression, dementia, or physical illnesses in one small US state . In general, except, for dementia, costs of care increased with the age of patients, with those over 85 incurring the greatest per-capita expense. Among people aged 65 or over, annual per-person care for those with schizophrenia, $40 000 or more, was the most, costly: . The patients with schizophrenia incurred higher annual costs in all age-groups compared with depression or medical conditions. The cost-by-age data were different for patients with dementia, where younger patients incurred higher costs. However, among patients over age 65, the cost of care was higher for the patients with schizophrenia compared with those with dementia.
What Are Positive Negative And Cognitive Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
During the acute phase of schizophrenia, children may show symptoms called positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms.
Positive symptoms are psychotic behaviors. During psychosis, a person is not connected with reality. Positive symptoms may include:
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- Movement disorders
- Thought disorders
Negative symptoms of childhood schizophrenia disrupt normal behaviors or emotions. Negative symptoms may include:
- Speaking infrequently or not at all
- Limited or no display of emotions
- Feeling no pleasure in everyday life
- Problems with starting or finishing activities
- Isolation
Cognitive symptoms of childhood schizophrenia reflect changes in thinking or memory. These symptoms may include:
- Being unable to understand information and make decisions
- Poor attention span
- Trouble focusing on a task
You May Like: Can Anxiety Attacks Happen For No Reason
Treating Women With Schizophrenia
Though treatment for mental illness is not typically separated by gender, clinicians serve women best by considering their unique experience of schizophrenia as well as the unique challenges they face. Because women have later onset of the illness and are less likely to experience affective symptoms, clinicians must be careful to rule out other mental illnesses, such as schizoaffective disorder or bipolar disorder, when giving a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Treatment for women with schizophrenia should include psychoeducation and support for the needs of mothers with children. Antipsychotic medication can affect the ability to breast feed and the amount of energy a mother has to parent her children.7 Treatment plans tailored for women should include education about physical health as well. Women with schizophrenia are less likely to care for their physical health. This leaves them at risk for untreated breast cancer, osteoporosis, and thyroid conditions. Mental health professionals should also consider creating safety plans for women with schizophrenia who are at increased risk for committing suicide.
Can Someone With Schizophrenia Live A Normal Life
While schizophrenia cannot be cured, with the right treatment plan many people with schizophrenia can live relatively normal lives outside of a healthcare setting. The treatment must be ongoing for the person with schizophrenia to continue to live a productive, fulfilling life, including maintaining a job or socializing with friends and family.
Also Check: How To Handle Eating Disorders
What Is Childhood Schizophrenia
Childhood schizophrenia is a severe mental health disorder in children younger than age 13 that affects the way they deal with reality. They might have unusual thoughts, feelings, or behaviors. Itâs also called childhood-onset or very early onset schizophrenia.
The disorder is rare — less than 1% of children are diagnosed with it — and may be hard to spot. Thereâs no cure, but treatment can help.
Early Signs Of Psychosis And Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is classified as a lifelong psychiatric disorder that alters how individuals feels, thinks, and behaves. Usually, early warning signs, such as hallucinations and delusions not otherwise seen in healthy people, begin to develop before the first severe episode. These severe episodes are also known as psychosis.
Although both men and women are equally likely to suffer from this condition, men tend to develop symptoms slightly earlier. On average, men are diagnosed between their late teens and early twenties. For women, it tends to be in their late twenties or early thirties. It is rare for someone to develop schizophrenia before the age of 12 or after the age of 40. A persons age at the time of the onset of schizophrenia may influence the symptoms that person experiences. Early warning signs are experienced during the prodromal stage. Schizophrenia may develop over several months or years, and its first signs vary according to the age at which it begins.
You May Like: What Is The Prevalence Of Bipolar Disorder
Childhood Schizophrenia Signs And Symptoms
Some children who develop schizophrenia first go through a period called the prodrome or the prodromal phase. They might withdraw from daily life, with more anxiety and less interest in school or friends. Not all children who show these signs will have a psychotic disorder, so itâs important to talk to your doctor if you notice any issues.
Early childhood schizophrenia symptoms
A baby or toddler may have signs of schizophrenia that are different from those in older children, teens, and adults.
The disorder affects how your child develops. You may notice things like:
- Long periods in which theyâre sluggish or not active
- Floppy arms or legs
- Delays in crawling, walking, or talking
- Odd movements such as rocking or flapping their arms
- A limp or slumped posture
Some of these symptoms show up in children with other problems besides schizophrenia. And some happen in kids without any mental health conditions. Only your child’s doctor can figure out what’s really going on.
Later childhood schizophrenia symptoms
In older kids, you might notice the behavior changes of schizophrenia over time or suddenly, as if out of nowhere. Your child may act withdrawn and clingy, or they may talk about strange and disturbed ideas and fears.
Tell your doctor as soon as you see symptoms of schizophrenia. It’s important to get a diagnosis and start treatment before your youngster shows signs of a break from reality, called psychosis.
Symptoms in older children include:
What Causes Schizophrenia To Get Worse
There are many reasons why schizophrenia may appear to worsen over time. The symptoms of schizophrenia can make it difficult for people with the illness to follow their treatment plan, and this can cause a worsening of the illness over time.
People with schizophrenia need to take medication regularly in order for their symptoms to be controlled. When people with schizophrenia stop taking their medication it is likely that their symptoms will become worse. When people with schizophrenia start taking their medication again it is likely that they will be less symptomatic over time.
For some people, the symptoms of schizophrenia will become so severe that they engage in erratic or violent behavior. When this happens, they may face additional societal challenges which can further damage their chances of improving and living a normal life. Some people who have schizophrenia develop symptoms severe enough that they cannot work any longer.
People with schizophrenia may also find that they need more support as they get older, because adult responsibilities like work and family can become difficult to manage while coping with the illness. This can make it appear as though their illness is worsening, when in fact it is their inability to manage life circumstances that creates problems in older persons with schizophrenia.
You May Like: Can A Person With Ptsd Work
The Complications Of Schizophrenia
When left untreated, Schizophrenia symptoms can quickly degenerate into more complex issues that can affect every area of life. Suicide, suicide attempts, or thoughts of committing suicide are some of the complications of untreated Schizophrenia.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder and some other anxiety-related disorders may also be complications from Schizophrenia. Similarly, abuse of alcohol, nicotine, and other drugs may also arise from the condition.
Inability to concentrate at work or school may be a complication. In some cases, Schizophrenia may lead to a financial crisis, which may lead to homelessness. Social isolation from friends and family may occur, and so are other secondary medical conditions.
Though aggressive behavior may be a complication of Schizophrenia, it is pretty uncommon. In many cases, a schizophrenia patient becomes victimized.
Schizophrenia Diagnosis: Rule Out Other Conditions
A diagnosis involves what someone is experiencing as well as what he is not. Some disorders have some features or symptoms that are shared with schizophrenia therefore, doctors check to see if something else fits better than schizophrenia. Some of the conditions that, according to criteria in the DSM-5, have some similarities with schizophrenia are
- Mood disorders with psychotic features
- Schizophreniform
Also Check: Is Insomnia A Symptom Of Depression
Causes And Symptoms Of Schizophrenia In The Elderly
As with many mental disorders, there is no exact pinpointed cause of schizophrenia but several factors come into play. Genes, chemical imbalances in the brain, family relationships, environments and the use of drugs are all factors that can contribute to the onset of schizophrenia.
Symptoms of schizophrenia include:
- Disorganized and abnormal motor behavior
- Negative symptoms lack of ability to function normally, lack of emotion, lack of expression, etc.
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
Read Also: How Many People Suffer From Depression In The Us
Positive And Negative Symptoms
What psychiatrists call the positive symptoms of schizophrenia are more obvious:
- Abnormal thinking and inappropriate emotions.
- Hallucinations, delusions and odd communication.
What they call the negative symptoms are more subtle and can last longer:
- Not talking much.
- Blunted feelings/little facial expression.
- Staying in bed to avoid people.
Whether their symptoms are positive or negative, people with schizophrenia dont seem to interact with the world in a healthy way, says Dr. Bowers.
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia can be hard to diagnose for a few reasons. One is that people with the disorder often don’t realize they’re ill, so they’re unlikely to go to a doctor for help.Another issue is that many of the changes leading up to schizophrenia, called the prodrome, can mirror other normal life changes. For example, a teen who’s developing the illness might drop their group of friends and take up with new ones. They may also have trouble sleeping or suddenly start coming home with poor grades.
Some research suggests that if a doctor strongly thinks someone is getting the disorder while still in this early phase, low doses of antipsychotic medication might delay it. More studies need to be done to know whether these drugs work for young people at risk for the disease. Cognitive behavioral therapy, family therapy, and social skills training appear to have clearer benefits for them, at least in the short term, when used early on. Learn more about the prodrome phase of schizophrenia.
Read Also: What Age Are Eating Disorders Most Common
What Does Schizophrenia Look Like When It Gets Worse
As the symptoms of schizophrenia get worse people with this illness often become more isolated and they find it difficult to maintain relationships. They may not be able to work or go to school any longer due to their symptoms, and they may spend most of their time alone in their homes.
People with schizophrenia who continue to experience hallucinations and delusions over many years may become increasingly confused about what is real and what is not. They may stop bathing and grooming, and their living conditions will likely decline in quality as they have a harder time maintaining a clean home or paying bills on time.
People with schizophrenia who experience depression, anxiety, or mood swings over many years may become increasingly frustrated due to their illness. They may have difficulty coping with their emotions, and they may feel hopeless about life.
The Following Are Some Signs Of Worsening Schizophrenia:
- Disorganized speech: If the person with schizophrenia is speaking in a jumbled or incoherent manner, this could indicate that their medication needs to be adjusted or that they are experiencing a relapse of their illness.
- Reduced or increased social contact: If the person with schizophrenia becomes less social or more isolated this may be a sign that they are slipping back into old patterns of behavior. On the other hand, if they become too attached to a specific individual it could mean that they are developing a new delusion and need to speak to their doctor about adjusting their medication.
- Changes in appetite or weight: If the person with schizophrenia starts overeating and putting on weight, it could be a sign that they are experiencing negative symptoms related to their illness . On the other hand, if they start losing interest in food and begin losing weight, they may be experiencing hallucinations related to food.
- Changes in sleeping patterns: If the person stops sleeping for long periods of time every day, it could be due to their schizophrenia medication interfering with the quality of their sleep. An increase in nightmares or difficulty falling asleep are also common signs of schizophrenia worsening.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Depression Screening
Articles On What Is Schizophrenia Prodrome
If you have schizophrenia or know someone who does, you’re probably familiar with symptoms like hallucinations and delusions. But you may not realize that warning signs can show up before a full-blown episode. When that happens, it’s called a prodrome or prodromal period.
About 75% of people with schizophrenia go through a prodrome phase. It may last a few weeks, but for some people, these signs slowly worsen over several years.
Its Easy To Live In Denial
Even though your loved one isnt functioning well, isnt meeting their own expectations in life, and is using alcohol or drugs to cope, they may not see theres a problem.
Because of the natural urge to protect those you love, families can stay in denial, as well.
Its often the college that sends a young adult to the hospital for the first time because of erratic behavior or an overdose. The parents get involved only because the college requests their child be evaluated by a psychiatrist.
Families often dont seek help on their own, says Dr. Bowers.
They may continue to struggle try to understand their loved ones symptoms. Or ignore those symptoms until they escalate, sometimes into violent behavior.
But early, continuous treatment is critical, she stresses. Without help, a young adults problems will continue especially if they use drugs or alcohol.
If you find them up all hours of the night, or painting their room black, or too irritable without their meds, or scaring their little sister, call the doctor, she says. And encourage them to keep their appointments.
Read Also: Can You Have Bipolar Disorder And Schizophrenia
What Do I Need To Know About Schizophrenia
There is a lot of fear and stigma surrounding schizophrenia, but ultimately, it is simply a mental health condition like depression or anxiety. With that said, schizophrenia does sometimes present with symptoms that can be alarming if youre not sure whats causing them. Some of the most common schizophrenia symptoms include:
- Hallucinations
- Disorganized thinking, which can lead to trouble communicating
- Stiff, repeated movements or periods of being unable to move, called catatonia
- Negative symptoms: These include dull, monotonous speech, trouble maintaining relationships, and some depression symptoms
Schizophrenia is an uncommon condition, but certainly not rare in fact, estimates put schizophrenia prevalence rates at between 0.25% to 0.64% of the United States population. And while it generally develops in younger adults, there is some variance in when it can present.
There are certainly exceptions to the rule, but men tend to present with schizophrenia symptoms earlier than women. Men usually develop schizophrenia symptoms between their late teens and early twenties, whereas symptoms usually appear in women in their late twenties to early thirties. Across all genders, though, schizophrenia symptoms rarely occur before the age of 13 or after the age of 40.